[May 28, 2014 Update: Clarified support implications of custom partitions]
[Nov 13, 2009 Update: Removed outdated reference to alterations to preseeded partitioned objects.]
[May 27, 2008 Update: Added link to latest official documentation for DB partitioning for Apps 11i]A frequently-asked question is, “Can I use the database partitioning feature in my E-Business Suite environment?” The answer to this question is yes: you may introduce custom partitioning with the E-Business Suite. In addition, several Apps modules take advantage of partitioning right out of the box.
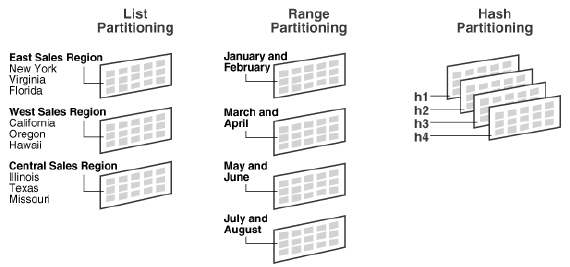
What’s Custom Partitioning?
Custom partitioning applies when:
- A customer partitions an existing standard Apps product table is not partitioned using various methods, including the range, list, hash, or composite partitioning methods; or,
- A customer modifies the partition scheme and/or partitioning method of an existing standard product table which is already partitioned by Oracle.
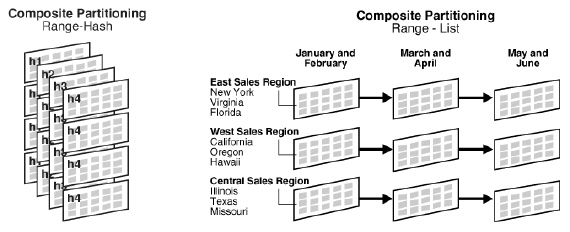
Examples of Custom Partitioning
If you choose to partition the table OE_ORDER_LINES_ALL which is currently not partitioned in the standard product, then this is an example of custom partitioning.
What are the support implications of partitioning?
If
Oracle-provided partitioning causes a particular E-Business Suite flow
or transaction to fail and the failure is caused by standard Apps
product code, it is considered a product defect, as Oracle Applications
is committed to being transparent to its seeded partitions. Oracle
Development will issue patches or workarounds for all reported issues
with standard Apps product code.
Standard Apps Partitioning “Out of the Box”
Oracle Applications utilizes partitioning in the standard product including the following modules:
- Advanced Planning and Scheduling
- Payables (Trial Balances)
- Projects Resources
- Workflow
- Directory Services
- Daily Business Intelligence
- HR (Employee Directory)
- Engineering
- and other products…
Partitioning Based on Functional Implementation
Many E-Business Suite tables do not have a natural partitioning key which would apply to all customers, simply because the data distribution and access path is highly dependent on each customer’s functional implementation. However, you are free to partition the tables in a logical manner based on your own requirements.
For example, many of our Oracle Financials customers partition the table GL_BALANCES by either period_name or set_of_books_id, depending on their implementation:
- Some customers have a large number of books for which partitioning by set_of_books_id makes sense
- Other customers use a single or a few set of books for which period_name makes sense.
Using Partitioning to Boost Performance
The use of custom partitioning can improve the performance and manageability of your E-Business Suite environment, and many customers are already seeing the numerous benefits of custom partitioning. Choosing the optimal partitioning method and partition key requires careful and thorough analysis of your system including the access paths of the relevant tables. For examples and guidelines, refer to the presentation and forma ldocumentation:
- Partitioning and Purging Best Practices for Oracle E-Business Suite
(PPT, 493K, by Ahmed Alomari, OpenWorld 2005)
- Database Partitioning for Oracle E-Business Suite (Metalink Note 554539.1)
Testing & Licencing
It is important that you thoroughly test the affected Apps modules after implementing custom partitioning, to ensure that your objectives of employing custom partitioning — including performance and manageability — have been achieved.
Just one final thing: if you implement custom partitioning, you must license the database partitioning
option. Your Oracle account representative is always your best source for
licensing details.
References
- Database Partitioning for Oracle E-Business Suite (Metalink Note 554539.1)
- E-Business Suite High Scalability & Availability, Performance & Benchmarks (OTN)
- Oracle Partitioning (OTN)
- Partitioning and Purging Best Practices for Oracle E-Business Suite
