The Power of Parameterization:
Oracle Service Cloud’s Job Scheduler is a powerful tool, allowing tasks to be automated and executed at specific times or intervals. To get the most out of this feature, it’s essential to understand the importance of parameterizing jobs and how to do it effectively.
In Oracle Service Cloud, job parameterization refers to the ability to pass variables or parameters to a job, allowing it to be customized and adapted to different scenarios. This is achieved using query parameters, which can be added to a job to provide additional data or configuration.
Why is Parameterization Needed for Scheduled Jobs?
Query parameters allows scheduled jobs to be adapted to different environments, data sets, or business requirements. By passing variables or parameters to a job, you can change its behaviour without modifying the underlying code.
Parameterized jobs can be reused across multiple scenarios, reducing the need to create duplicate jobs or modify existing ones. This saves time, effort, and resources.
By decoupling job logic from specific data or configuration, parameterization makes it easier to maintain and update jobs over time. Changes can be made to the parameters or variables without affecting the underlying job code.
Now let’s see how to parameterize the php script and use it in Job scheduler.
In the below PHP snippet, we have a parameter named Contact, which is used to fetch contact information using connect PHP.
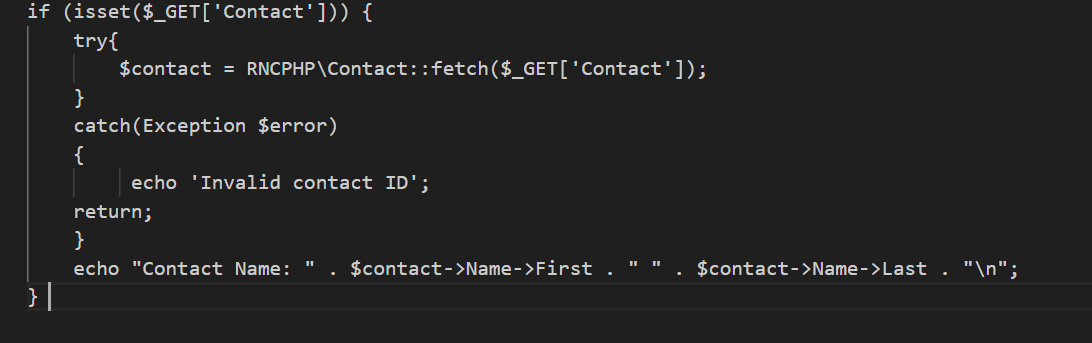
Let’s also see a usage of parameterized script in Job Scheduler.
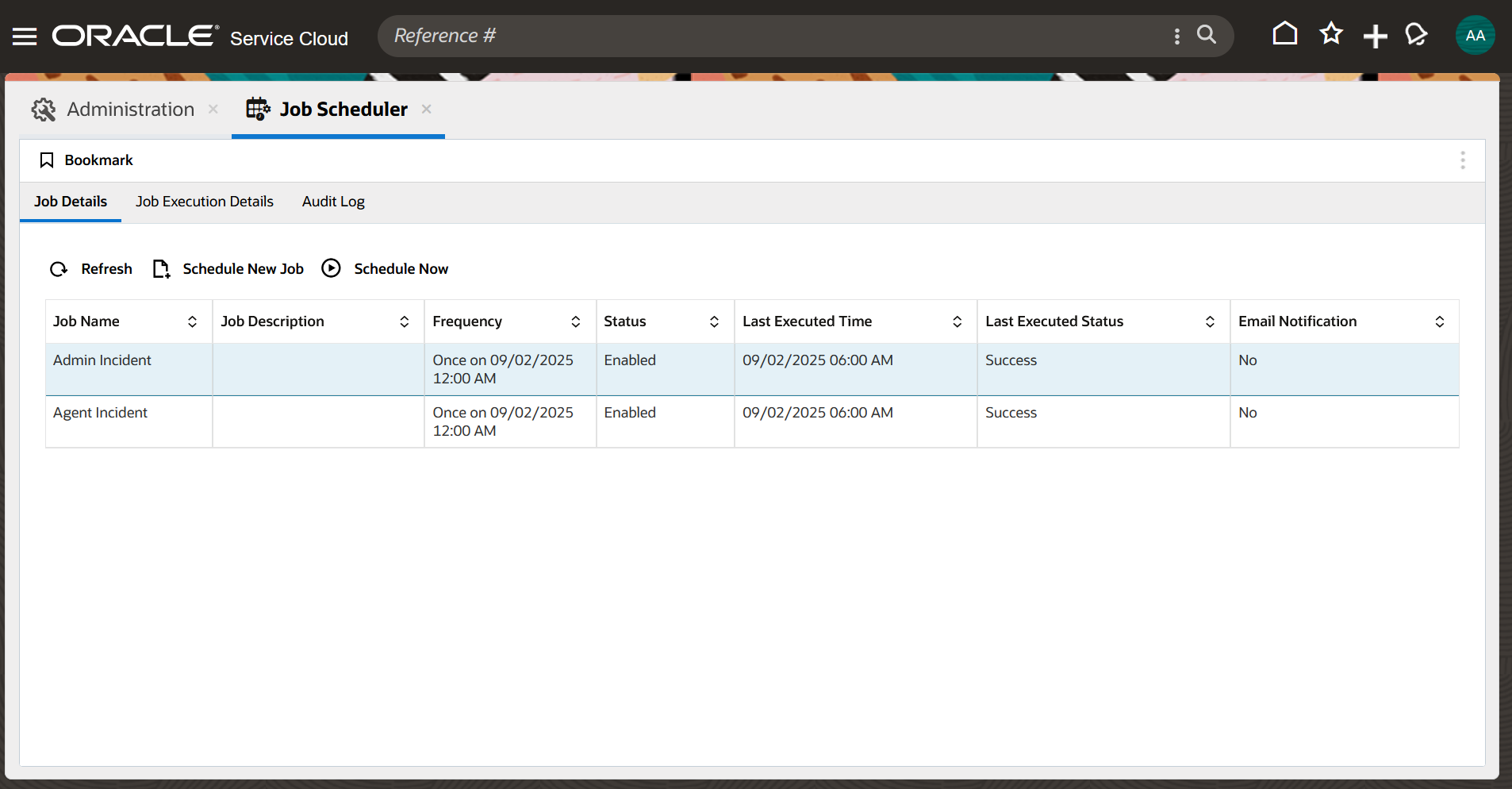
Here we have 2 Jobs named Admin Incident and Agent Incident. Both are using the same script named create_inc_with_params.php; however, the query parameter values differ.
One has Contact query parameter as 2 and Subject query parameter as AdminIncident

The other has Contact query parameter as 132 and Subject query parameter as AgentIncident
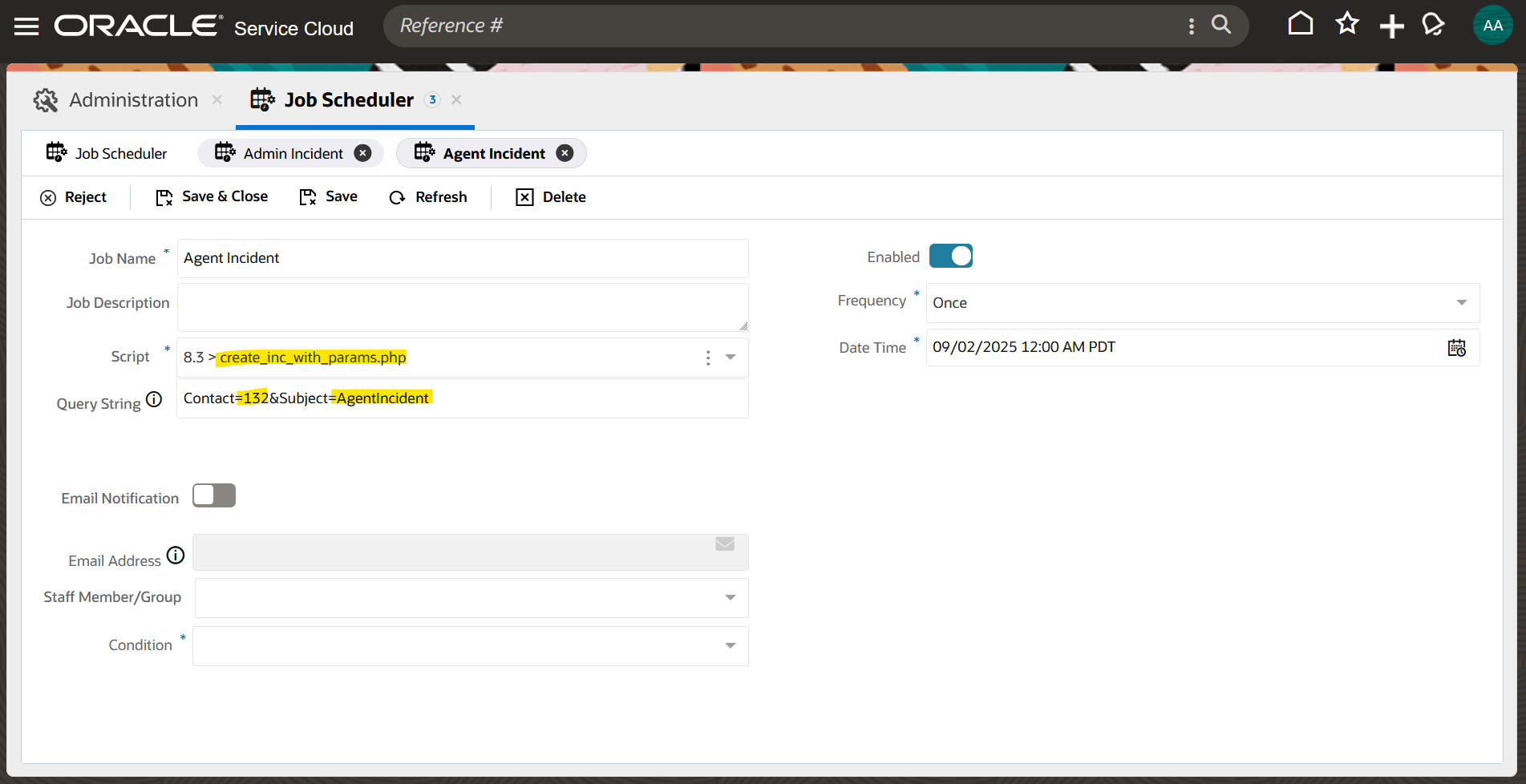
Best Practices for Parameterizing Scheduled Jobs
Use descriptive and meaningful names for parameters to make it clear what they represent.
Validate parameters to ensure they are valid and consistent with the job’s requirements.
Ensure that the query parameter fields total length is within the allowed limit (255 characters).
Validate the query parameter format to prevent errors, such as duplicate parameter names or invalid characters.
In conclusion, parameterization is a powerful technique for making scheduled jobs more flexible, reusable, and maintainable. By leveraging query parameters and following best practices for validation and security, you can unlock the full potential of this feature and take your automation to the next level.