Introduction
TimesTen XE supports both client/server and direct linked database connections.
TimesTen XE client/server connections can be over TCP or TCP/TLS.
Direct linked connections can only occur when the TimesTen XE client and server are on the same machine. Direct linked connections are significantly faster than client/server connections.
TimesTen clients on Windows, MacOS, Linux, Solaris and AIX can connect to TimesTen XE servers on Linux without requiring local config files.
Once the relevant TimesTen Client is installed, client/server connectivity is the same on Linux, Windows, macOS, AIX and Solaris.
A separate blog will cover client/server with client config files.
Components not requiring client config files

When no client config files are used, the following SQL APIs are supported:
OCI based SQL APIs require client config files

The above OCI based APIs require client config files. See this blog for using TimesTen client config files.
TimesTen XE Server
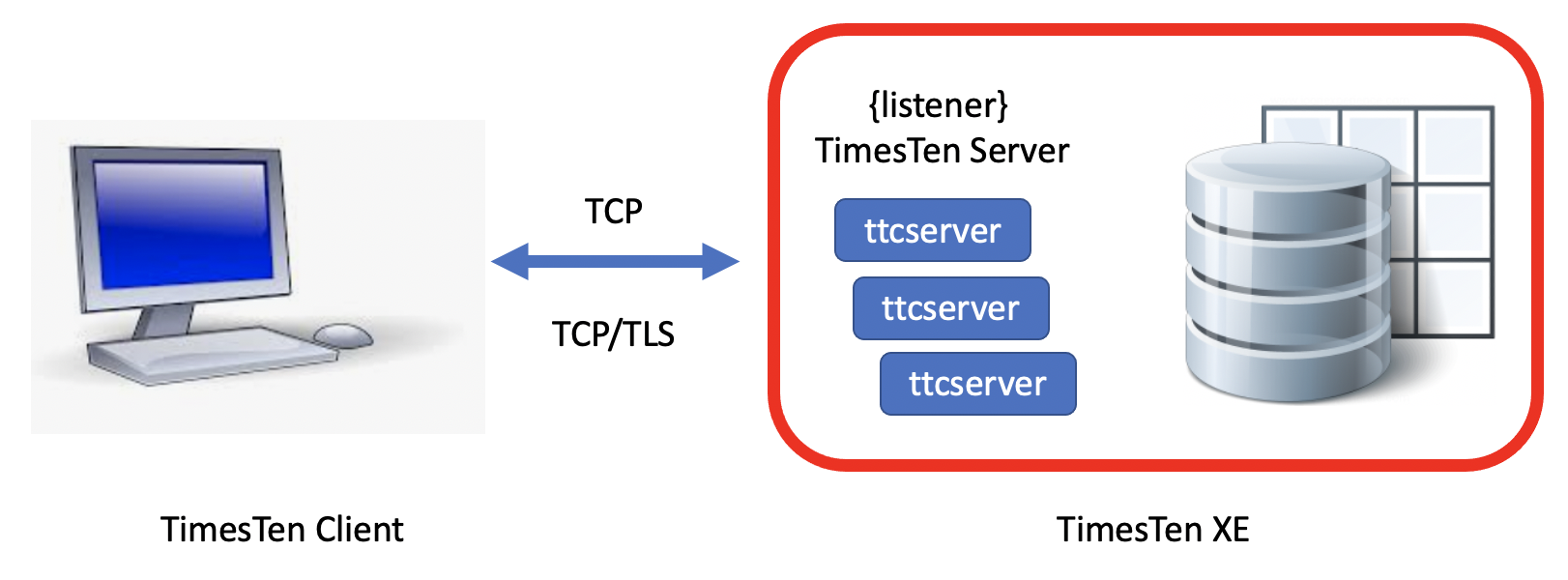
The TimesTen XE client/server listener is called the TimesTen Server. The TimesTen Server is a database listener similar to the Oracle Net tnslsnr.
The TimesTen Server has a set of processes called ttcserver which listen for TimesTen client requests. The ttcserver processes can be single-threaded or multi-threaded.
By default, the TimesTen XE Server listens on TCP port 6625.
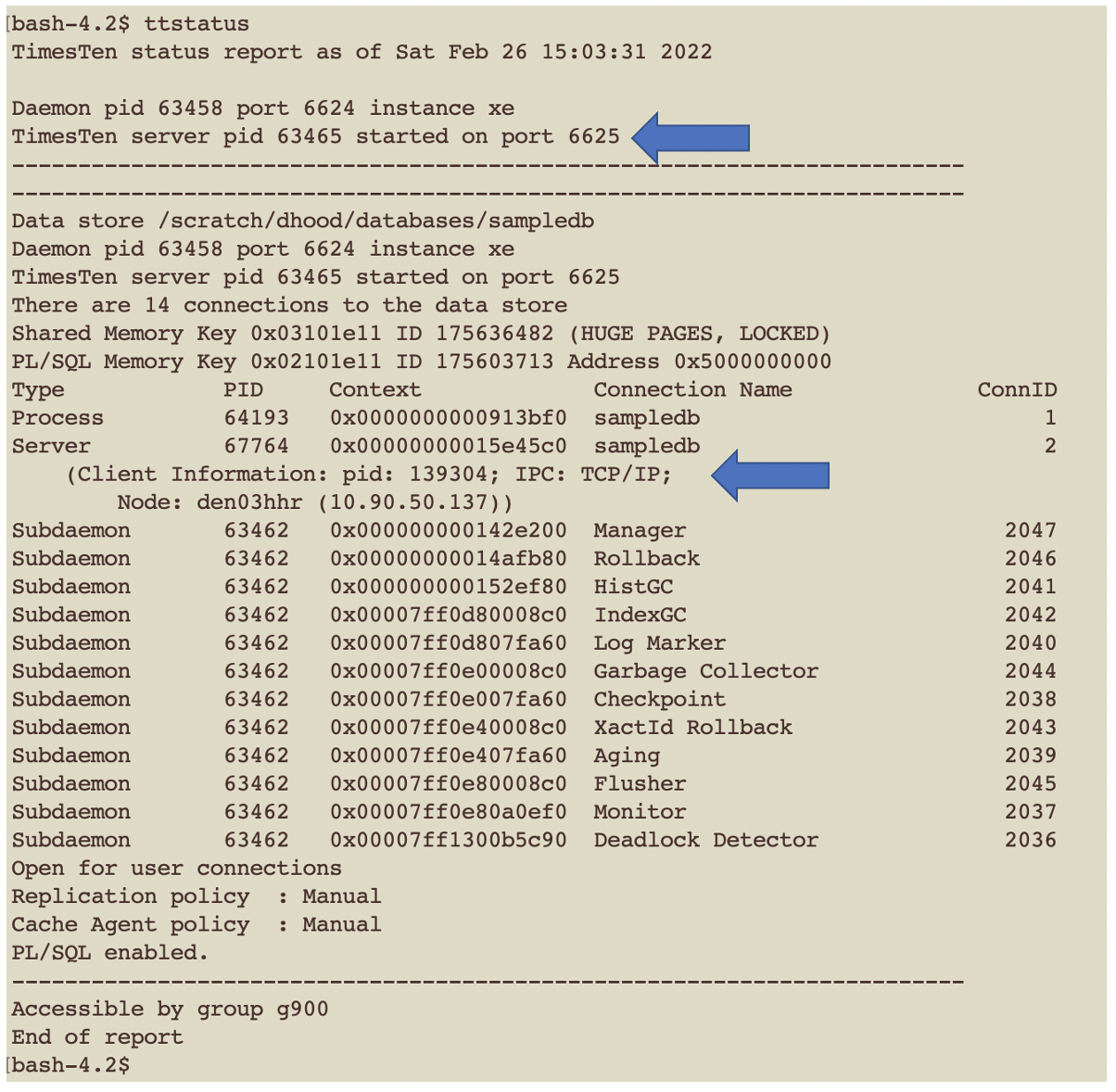
In the above example, the TimesTen Server is listening on TCP port 6625 and had two connections to the sampledb database:
- A direct linked connection of type process
- A client/server TCP/IP connection from a machine called den03hhr
- The connection is of type server as it is a ttcserver process
The TimeTen XE Server listens by default when the TimesTen XE daemon is started.
Configuraing and tuning the TimesTen XE Server will be covered in another blog.
Connection Metadata
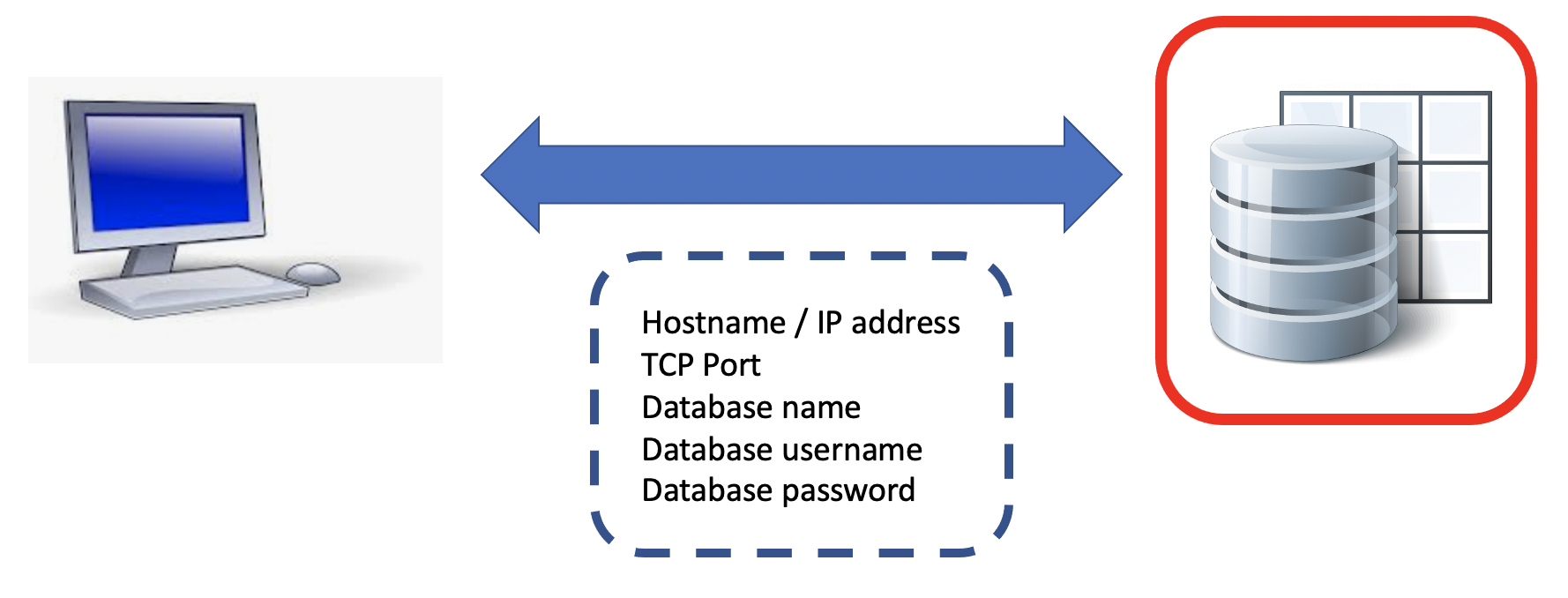
Conceptually, all database clients need the same metadata to connect to a remote database server.
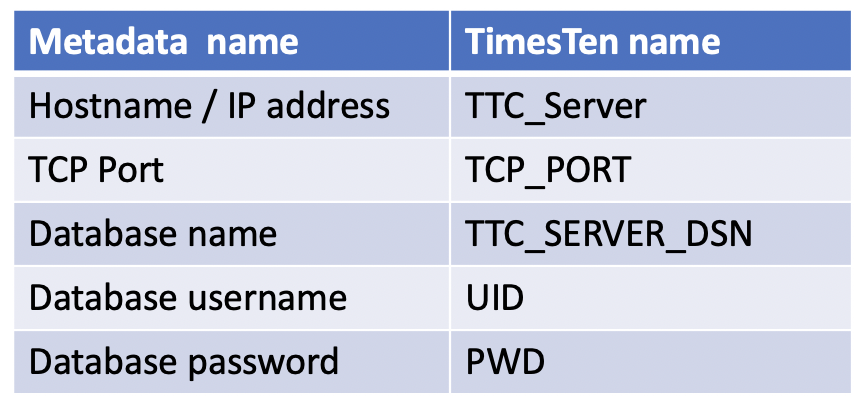
A connect string for TimesTen XE has the following form:
- “UID=yourUserName;PWD=yourPassword;TTC_SERVER=hostname_or_IP_address;TCP_PORT=tcp_port;TTC_SERVER_DSN=yourDatabase”
An example connection string is:
- “UID=doug;PWD=hood;TTC_SERVER=slc11wrj;TCP_PORT=6625;TTC_SERVER_DSN=sampledb“
The order of the attributes in the connect string does not matter.
The database hostname and TCP port can be combined in the TTC_SERVER using a /. eg:
“UID=doug;PWD=hood;TTC_SERVER=slc11wrj/6625;TTC_SERVER_DSN=sampledb”
Linux Client
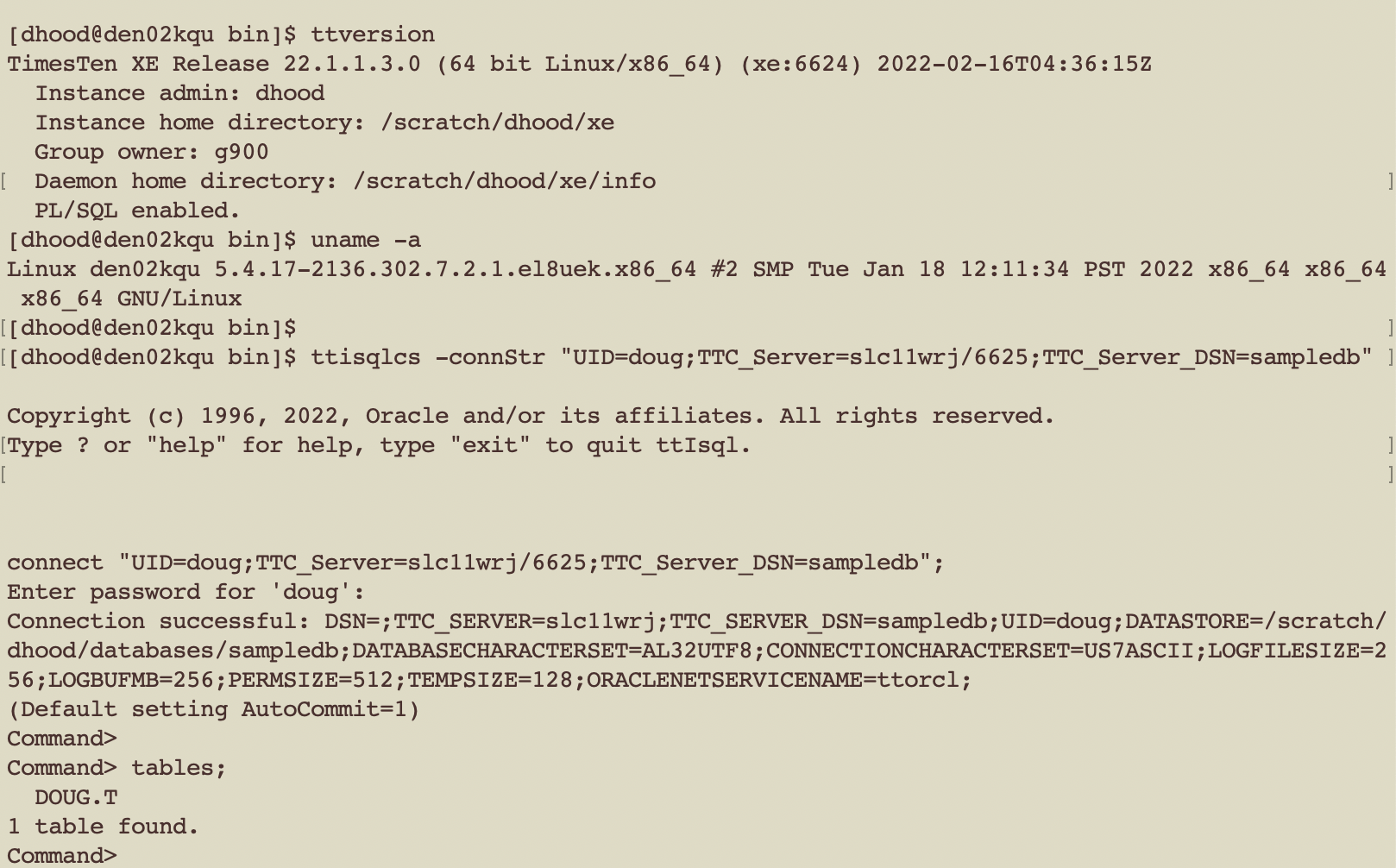
In the above example, a TimesTen XE client is using ttIsqlCS to connect to a TimesTen XE server on a Linux host called slc11wrj on port 6625 with user doug to database sampledb. The pasword was not included so it was prompted.
ttisqlcs -connstr “TTC_SERVER=slc11wrj/6625;TTC_SERVER_DSN=sampledb;uid=doug”
Windows Client
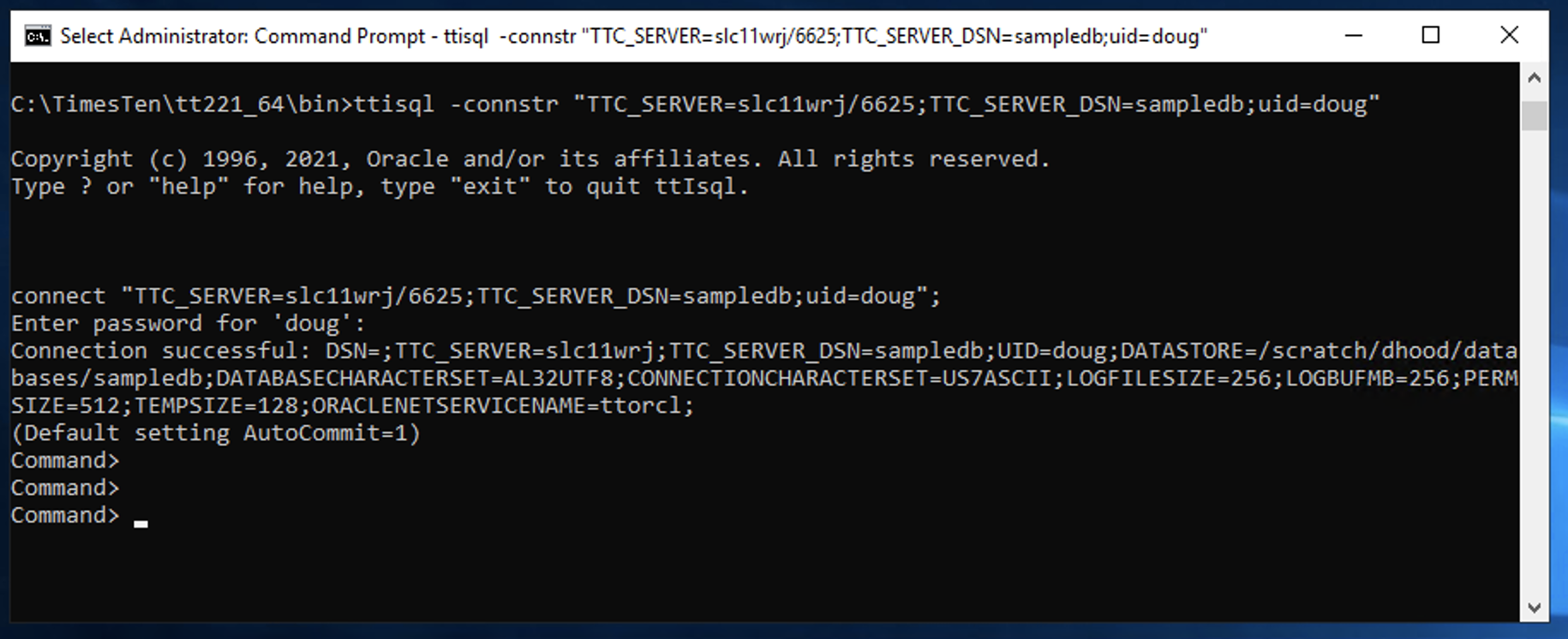
In the above example, a TimesTen 22.1 Windows client is using ttIsql to connect to TimesTen XE on a Linux host called slc11wrj on port 6625 with user doug to database sampledb. The password was not included so it was prompted.
The same generic ttIsqlCS connect string is used to connect to the TimesTen XE server from a Windows machine.
ttisql -connstr “TTC_SERVER=slc11wrj/6625;TTC_SERVER_DSN=sampledb;uid=doug”
Note
On Windows, the client serveer utility is called ttisql.exe, not ttisqlcs.
MacOS Client
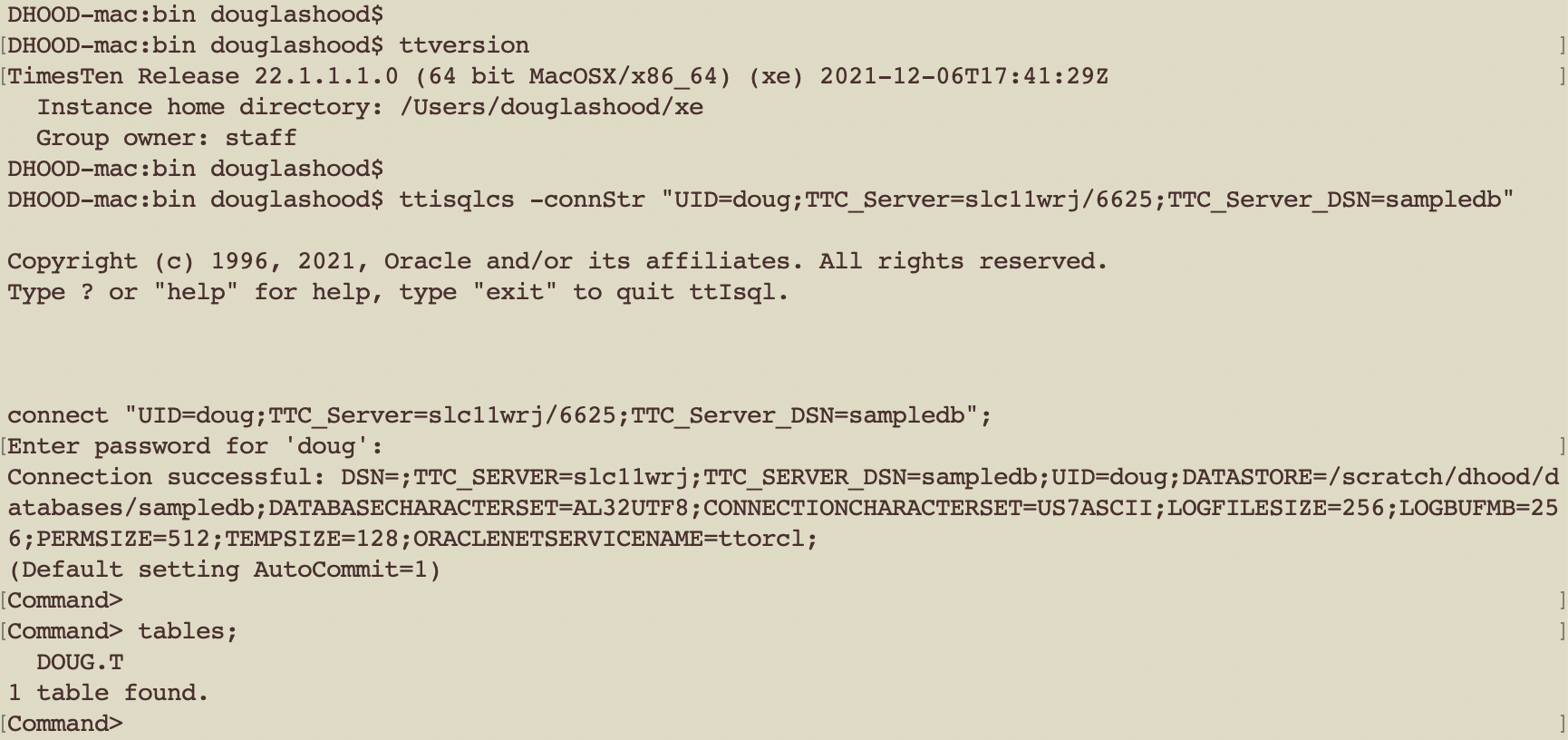
The same generic ttIsqlCS connect string is used to connect to the TimesTen XE server from a macOS machine.
ttisqlcs -connstr “TTC_SERVER=slc11wrj/6625;TTC_SERVER_DSN=sampledb;uid=doug”
IBM AIX Client
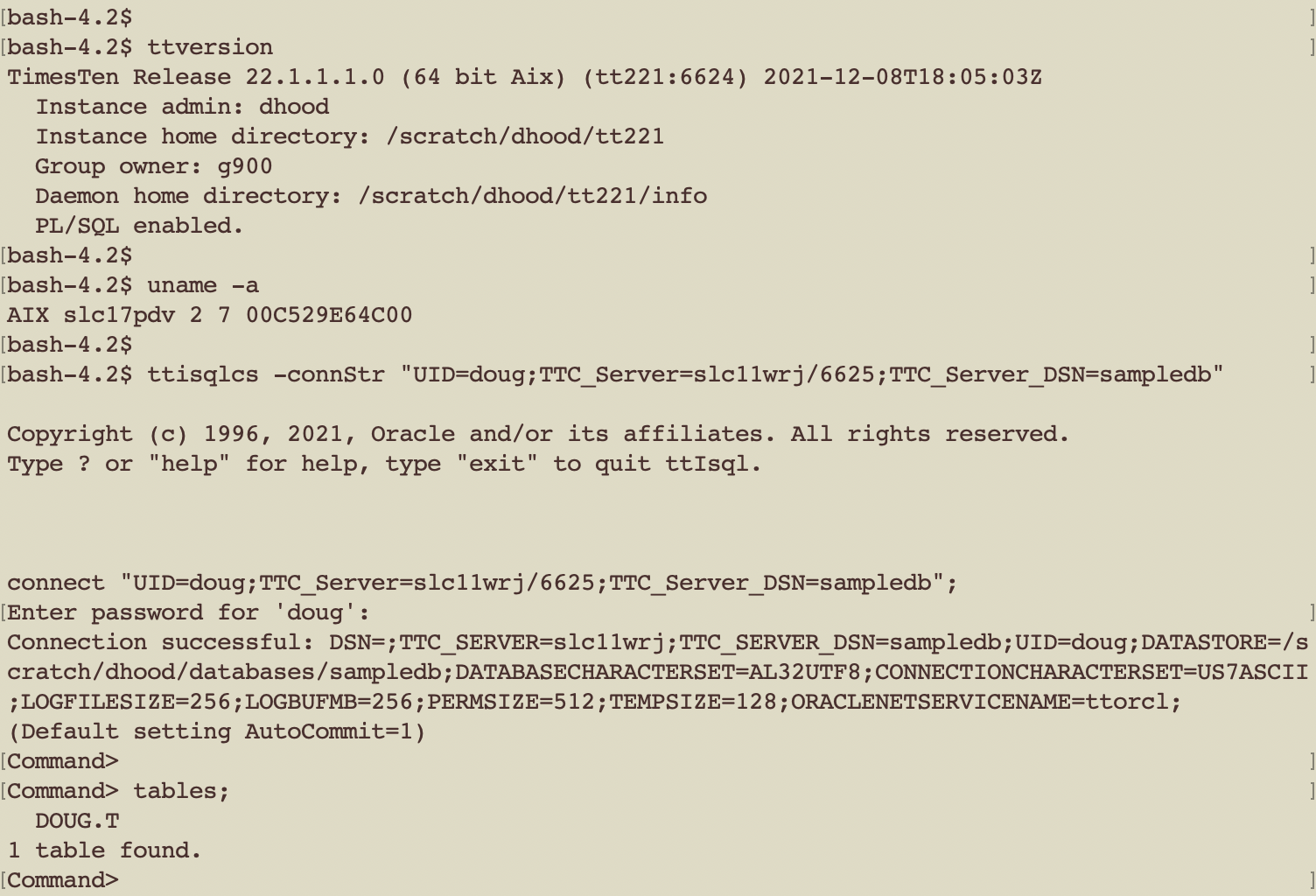
The same generic ttIsqlCS connect string is used to connect to the TimesTen XE server from an AIX machine.
ttisqlcs -connstr “TTC_SERVER=slc11wrj/6625;TTC_SERVER_DSN=sampledb;uid=doug”
Solaris SPARC Client
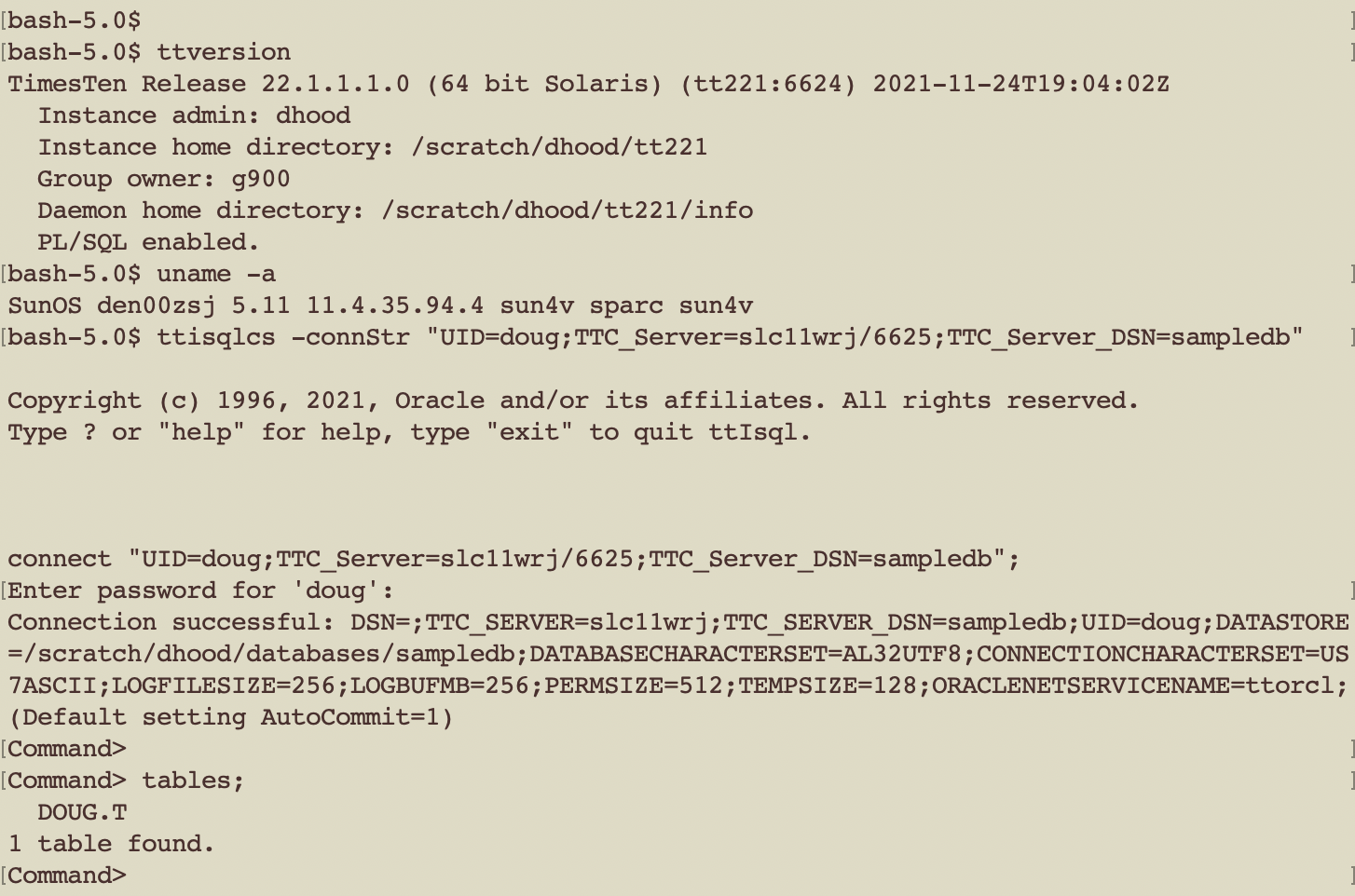
The same generic ttIsqlCS connect string is used to connect to the TimesTen XE server from a Solais/SPARC machine.
ttisqlcs -connstr “TTC_SERVER=slc11wrj/6625;TTC_SERVER_DSN=sampledb;uid=doug”
Solaris x86 Client
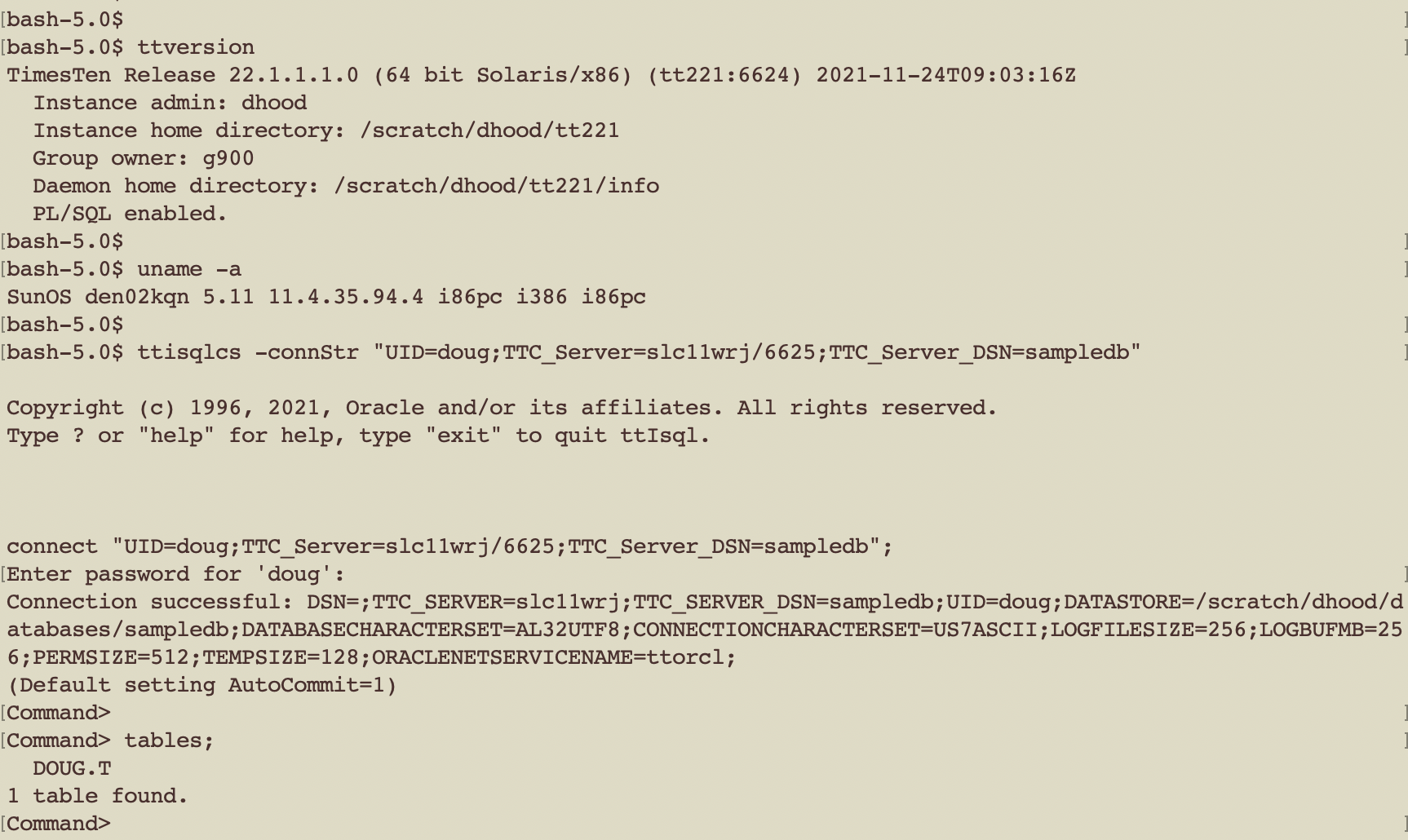
The same generic ttIsqlCS connect string is used to connect to the TimesTen XE server from a Solaris/x8664 machine.
ttisqlcs -connstr “TTC_SERVER=slc11wrj/6625;TTC_SERVER_DSN=sampledb;uid=doug”
Learn more about TimesTen XE:
- Oracle TimesTen XE Home Page
- Oracle TimesTen XE Download
- Oracle TimesTen XE Docker Container
- Oracle TimesTen Classic Home Page
- Oracle TimesTen Scaleout Home Page
- Oracle TimesTen VM with Hands On Labs
- Oracle TimesTen Documentation
More TimesTen XE Blogs
- An introduction to TimesTen XE
- How fast is TimesTen XE
- How to install TimesTen XE
- How to create a database on TimesTen XE
- TimesTen XE SQL
- Using TimesTen XE on WSL
- Using client/server with config files on TimesTen XE
Summary
- TimesTen XE uses TPC/IP for client/server database connections
- The TimesTen XE connection metadata is similar to any other database
- The connection string metadata is the same for Windows, macOS, Linux, Solaris and AIX
- TimesTen Client/server can be used without client config files, but it does not work wit OCI based APIs
- Direct linked connections do not use TCP/IP and are significantly faster
Disclaimer: These are my personal thoughts and do not represent Oracle’s official viewpoint in any way, shape, or form.
