This blog is the first of a two-part series that guides you through setting up and managing on-premises (External) MySQL DB systems in OCI, ensuring optimal performance and operational insights. In this part, we will cover the prerequisite steps before registering and managing External MySQL DB systems. To use Database Management features for External MySQL, you must belong to your tenancy’s Administrators group or have the required permissions.
Overview
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Database Management enables seamless integration of On-premises (External) MySQL DB systems with OCI resources. Database Management supports External MySQL DB systems running version 8.x and later and offers robust features to optimize database management and setting alerts to track performance thresholds with timely notifications. Using Database Management, you can:
- Create an OCI resource representing your External MySQL DB system within your tenancy.
- Establish connectivity using a connector resource, enabling integration with local or remote hosts.
- Monitor performance and operations directly within OCI.
Here are the key features of Database Management for External MySQL DB systems:
- Fleet Monitoring: Keep track of performance and configuration metrics for your entire fleet of External MySQL DB systems.
- System Metrics: Dive deep into monitoring the metrics and configuration variables of individual External MySQL DB systems.
- Performance Hub: Leverage this tool to monitor and troubleshoot SQL performance effectively.
If you’re new to using Database Management, we recommend exploring Database Management for MySQL to get started and for information on its features.
System Setup for External MySQL DB systems
Before you enable and use Database Management for External MySQL DB systems, you must complete the prerequisite tasks listed below:
- Install Management Agent
- Create MySQL User and Grant Privileges
- Permissions for Creating and Using Secrets
Install Management Agent
The Management Agent service is required to establish a connection to an External MySQL DB system deployed on-premises. It is also used by Database Management to collect compute performance data and operational metrics from the database.
To set up the Management Agent:
- Install the Management Agent on a host that has network connectivity to the External MySQL DB system.
- If the host does not have direct internet access, install a Management Gateway, which acts as a communication bridge between the Management Agent (on the External MySQL DB system host) and OCI.
Important: A Management Agent version 241023.2127 or later is required to connect to External MySQL DB systems.
The Management Agent does not need to be installed on the same host as the MySQL DB system. However, in such cases, host-specific metrics will not be available.
- A single Management Agent can monitor multiple MySQL DB systems, as long as they are accessible from the agent’s host.
- If you plan to use Capacity Planning or OCI Operations Insights (OPSI), installing the Management Agent on the same host as the MySQL DB system is required.
For information on how to install Management Agents, see Install Management Agents.
For information on Management Gateway, see Management Gateway.
Create MySQL User and Grant Privileges
To enable Database Management for an External MySQL DB system, you should create a dedicated MySQL user with the necessary privileges or use user having required privileges . This user allows the Management Agent to collect database metrics and performance insights.
Step 1: Create the MySQL User
Run the following command to create a MySQL user. Replace <username> with your desired username and <hostname/IP> with the host where the Management Agent is installed.
CREATE USER '<username>'@'<hostname/IP>' IDENTIFIED BY '<UNIQUEPASSWORD>';
- <hostname/IP> refers to the compute instance where the Management Agent is deployed.
- This ensures the MySQL user can connect from that specific host to fetch database metrics.
Alternatively, you can allow broader access by using a wildcard (%), which permits connections from any host:
CREATE USER '<username>'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '<UNIQUEPASSWORD>';
For better security, avoid using wildcard (%) access unless necessary. Instead, restrict the user to the specific agent host.
Step 2: Grant Required Privileges
GRANT SERVICE_CONNECTION_ADMIN, SYSTEM_USER, SELECT, PROCESS, SHOW VIEW, SHOW DATABASES, REPLICATION CLIENT, REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO '<username>'@'<hostname/IP>';
GRANT SELECT ON performance_schema.* TO '<username>'@'<hostname/IP>';
GRANT SELECT, EXECUTE ON sys.* TO '<username>'@'<hostname/IP>';
Note: If you are monitoring multiple MySQL instances, ensure the Management Agent’s host has access to all required databases.
Permissions for Creating and Using Secrets
You must ensure that you have the required Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Vault service permissions to create and use secrets that contain the network protocol credentials and details required to securely connect to the External MySQL DB system.
You can create secrets from registration page as well but If creating the network protocol credentials secret directly in the Vault service, the following free-form tags must be associated against key DBM_Wallet_Type with the secret to make it available for use when registering the External MySQL DB system:
- Secret for TCP credentials: TCP_SECRET_MYSQL
- Secret for TCP with SSL credentials: TLS_SECRET_MYSQL
- Secret for socket credentials: SOCKET_SECRET_MYSQL
For information on the Vault service, its concepts, and how to create vaults, keys, and secrets, see Vault.
Permissions and Policies for External MySQL DB systems
User must add the following permissions and policies to register and manage External MySQL DB systems:
- Granting User Group Permissions
- Service-Level Permission
- Create Dynamic Group (if not already created)
- Policies for the Dynamic Group
Granting User Group Permissions
You can grant permissions to user groups for accessing Database Management features either through a guided setup or manually. The guided setup streamlines the process and reduces the risk of policy-related errors.
Before accessing the Overview page to automatically generate and add user policies, ensure the following prerequisites:
- You are a member of your tenancy’s Administrators group.
- A user group is created, and users are added to it. For details, see Managing Groups.
To automatically generate and add user policies:
- Sign in to the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console.
- Open the navigation menu, click Observability & Management. Under Database Management, click Overview.
Figure 1: Database Management menu navigation - On the Get started tile, click Add policies.
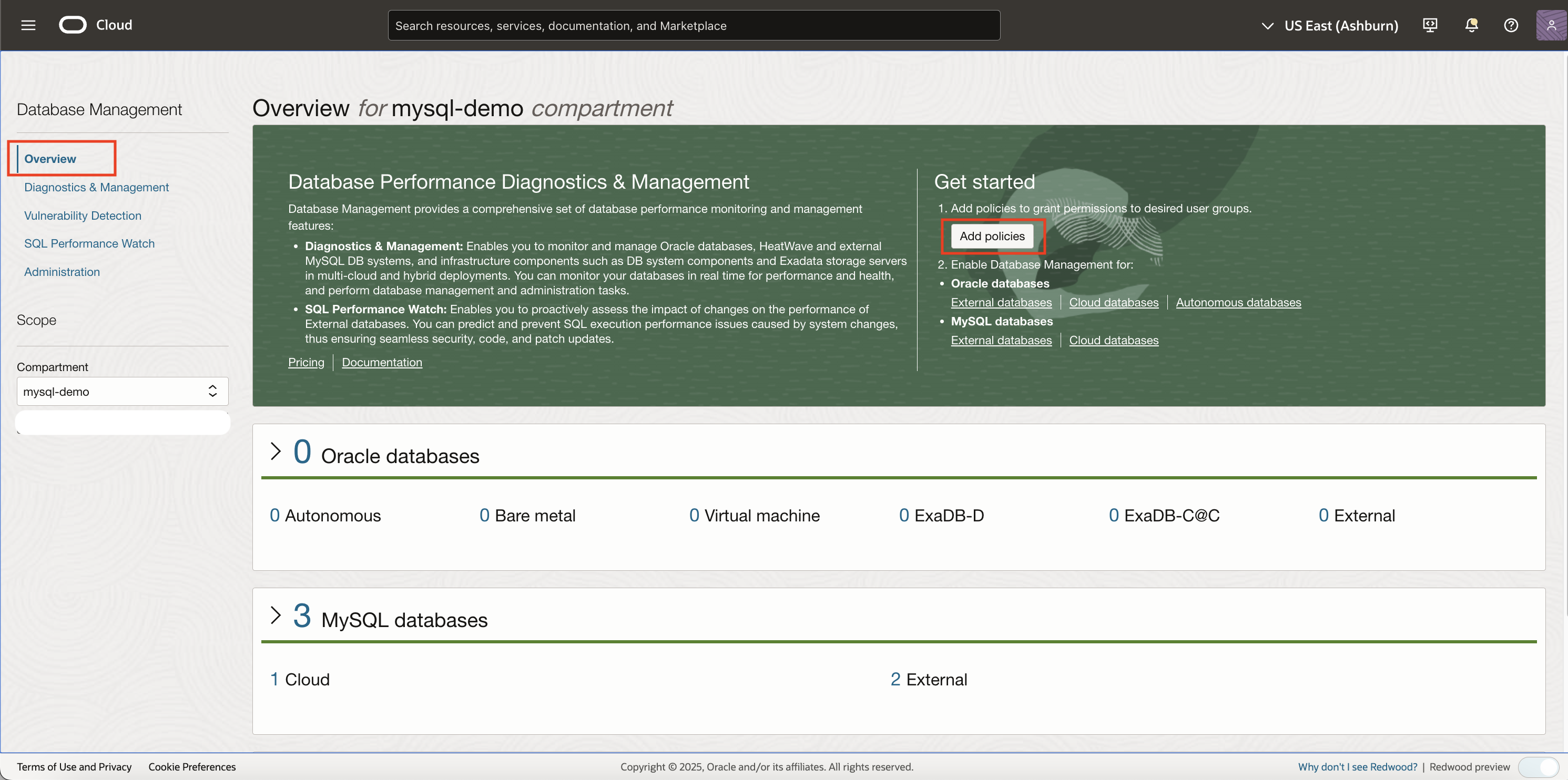
Figure 2: Database Management Overview page - In the Add policies panel, specify the following details:
- Policy compartment: Select the compartment in which the automatically generated Database Management policies will be added.
- User group: Select the user groups to which you want to grant permissions.
- Access: Select the type of access you want to provide to the user groups:
- Read: Grants read-only access.
- Manage: Grants the permission to perform the entire set of tasks in Database Management.
- Database type: Select MySQL databases to generate the list of policies required to enable and use Database Management for HeatWave and External MySQL.
- Database compartment: Select the compartments in which the resource-types reside.
- Click Generate.
- Review the list of recommended policies to use Database Management for HeatWave and External MySQL, and click Add policies.
The IAM service creates the policies and adds them to the DBMgmt_User_Policy collection of policies. For information on how to create, edit, or delete a policy in the IAM service, see Managing Policies.
Service-Level Permission
To allow Database Management (dpd) to deploy necessary plug-ins on the Management Agent in a specific compartment, you need to configure the following service-level policy.
Allow service dpd to manage management-agents in compartment '<compartment-name>'
Create Dynamic Group
When adding user policies using the guided process, the policy to manage the Management Agent is automatically included. Additionally, you must create a dynamic group for all Management Agents used by the External MySQL DB system. This is required to allow the External MySQL DB system to interact with various Oracle Cloud Infrastructure service endpoints. When creating a dynamic group, you can define a rule to add the management agents in a compartment or in the tenancy to the dynamic group. This will ensure that this step is a one-time setup step and any new management agent being installed will automatically belong to the dynamic group.
Create a dynamic group (e.g., agent-dynamic-group) in the default domain using one of the following matching rules:
-
For a specific compartment:
ALL {resource.type='managementagent', resource.compartment.id='<AGENT_COMPARTMENT_OCID>'}
- For all compartments in the tenancy:
ALL {resource.type='managementagent'}
For detailed steps, see Creating a Dynamic Group.
Policies for the Dynamic Group
Assign the following policies to the dynamic group (agent-dynamic-group) to enable it to interact with OCI services:
Allow dynamic-group agent-dynamic-group to manage management-agents in tenancy
Allow dynamic-group agent-dynamic-group to use metrics in tenancy
Allow dynamic-group agent-dynamic-group to manage log-content in tenancy
Allow dynamic-group agent-dynamic-group to use tag-namespaces in tenancy
Note: If necessary, you can limit these policies to a specific compartment instead of applying them at the tenancy level.
For more information on Agent service resource-types and permissions, see Details for Management Agent and for Dynamic groups Managing Dynamic Groups.
Next Steps: Registering and Managing External MySQL DB Systems
In this blog, we’ve walked you through the essential prerequisites for setting up and managing External MySQL DB systems in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) using Database Management. We’ve covered steps such as installing the Management Agent, creating MySQL users with the necessary privileges, and configuring permissions and policies.Once these tasks are completed, you’ll be ready to register and manage your External MySQL DB systems in OCI, enabling you to monitor and optimize performance effectively.
For the actual process of registering and managing your External MySQL DB systems, check out our next blog Manage External MySQL in OCI, where we’ll guide you through the registration process and demonstrate how to leverage Database Management to its full potential.

