This blog is the second part of our two-part series on setting up and managing on-premises (External) MySQL DB systems in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). In the first part, we covered the prerequisite steps required before registering and managing External MySQL DB systems. In this blog, we will walk you through the registration process, fleet monitoring, key metrics, alarms and events to help you optimize performance and gain operational insights.
Before you begin managing External MySQL DB systems with Database Management in OCI, make sure you’ve completed the prerequisites outlined in the first blog. Additionally, you must be a member of your tenancy’s Administrators group or have the appropriate permissions to register and monitor the systems.
Register External MySQL DB systems
When registering an External MySQL DB system that is deployed on-premises, you will perform the following tasks:
- Create a resource to represent the External MySQL DB system.
- Create connector to connect External MySQL DB system.
- Enable Database Management for the External MySQL DB system.
These tasks can be performed through the Console, CLI, and REST API. Below are the steps for registering the system using the console.
To register an External MySQL DB system:
- Sign in to the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console.
- Open the navigation menu, click Observability & Management. Under Database Management, click Administration.
- On the left pane, click MySQL Databases and select a compartment in the Compartment drop-down list.
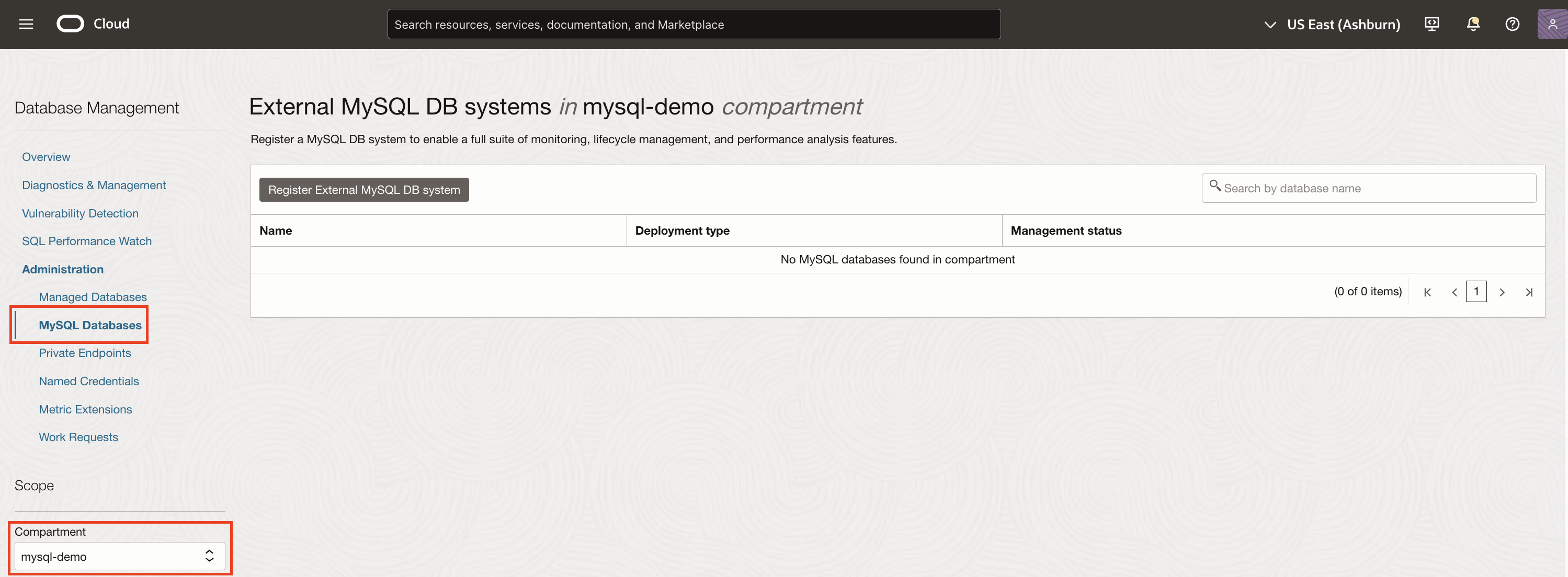
Figure 1: MySQL Databases Administration page - On the External MySQL DB systems page, click Register External MySQL DB system.
- In the Register External MySQL DB system panel:
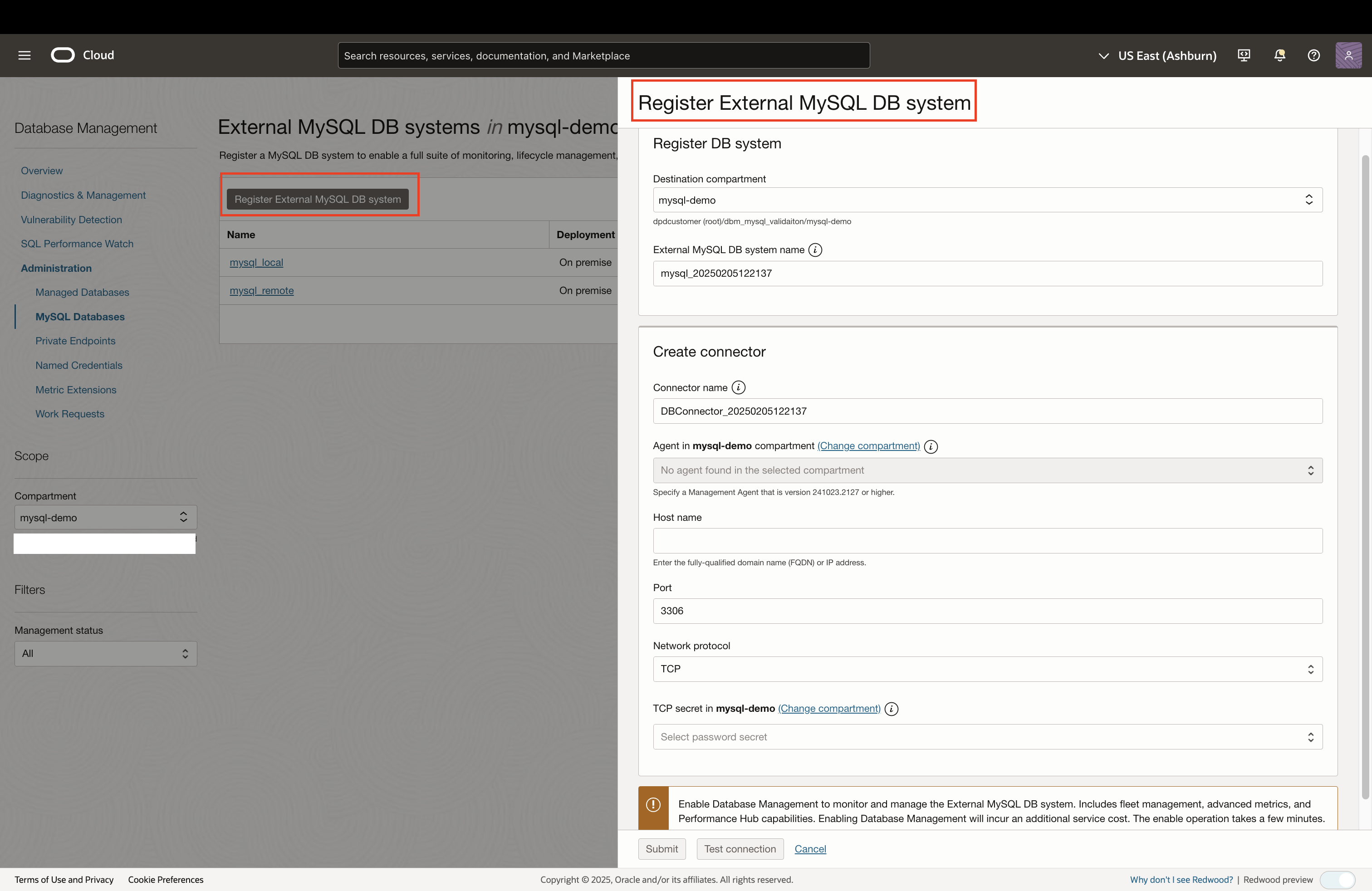
Figure 2: Register External MySQL DB system panel - Specify the following details to register the External MySQL DB system:
- Destination compartment: Select the compartment in which you want the External MySQL DB system resource to reside.
- External MySQL DB system name: Enter a user-friendly name to easily identify the External MySQL DB system resource.
- Specify the following details to create a connector:
- Connector name: Enter a user-friendly name to easily identify the connector resource.
- Agent: Choose a Management Agent from available list to establish a connection to the External MySQL DB system.
- Host name: Enter the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) or IP address of MySQL DB system host.
- Port: Enter the port number being used by the External MySQL DB system for connections.
- Network protocol: Select a network protocol to connect to the MySQL DB system.
- TCP: Transmission Control Protocol, which is a fundamental network protocol used to exchange data.
- TCP with SSL: Transmission Control Protocol with Secure Sockets Layer, which is a more secure option to exchange data as SSL encrypts data before it’s transmitted.
- Sockets: Endpoints used for sending and receiving data across a network.
- Secret: Select the secret containing the network protocol credentials and details. If it hasn’t been created yet, you can choose the ‘Create New Secret’ option to create one directly from this page. For information on creating secrets while registering, refer Create a Network Protocol Secret.
- Optionally, click Test connection to confirm if the provided credentials are correct and connection to the External MySQL DB system is established. Test connection process may take a few minutes to complete and you should not exit or refresh the page.
- Click Submit to register the External MySQL DB system, create a connector, and enable Database Management.
- Specify the following details to register the External MySQL DB system:
The Register External MySQL DB system panel remains open till the entire registration process is complete and automatically closes after Database Management enablement process has started successfully.
Note: In case the window is closed and the registration process fails, you can use the same DB system name provided earlier to retry the registration. Opening the registration window again and providing new details will create a new DB instance, so ensure you use the previously assigned name to avoid duplication.
Monitor HeatWave & External MySQL Fleet
On the Overview page, expand the MySQL Databases tile to view the total number of HeatWave and External MySQL DB systems in the compartment, along with the count of DB systems where Database Management is enabled.
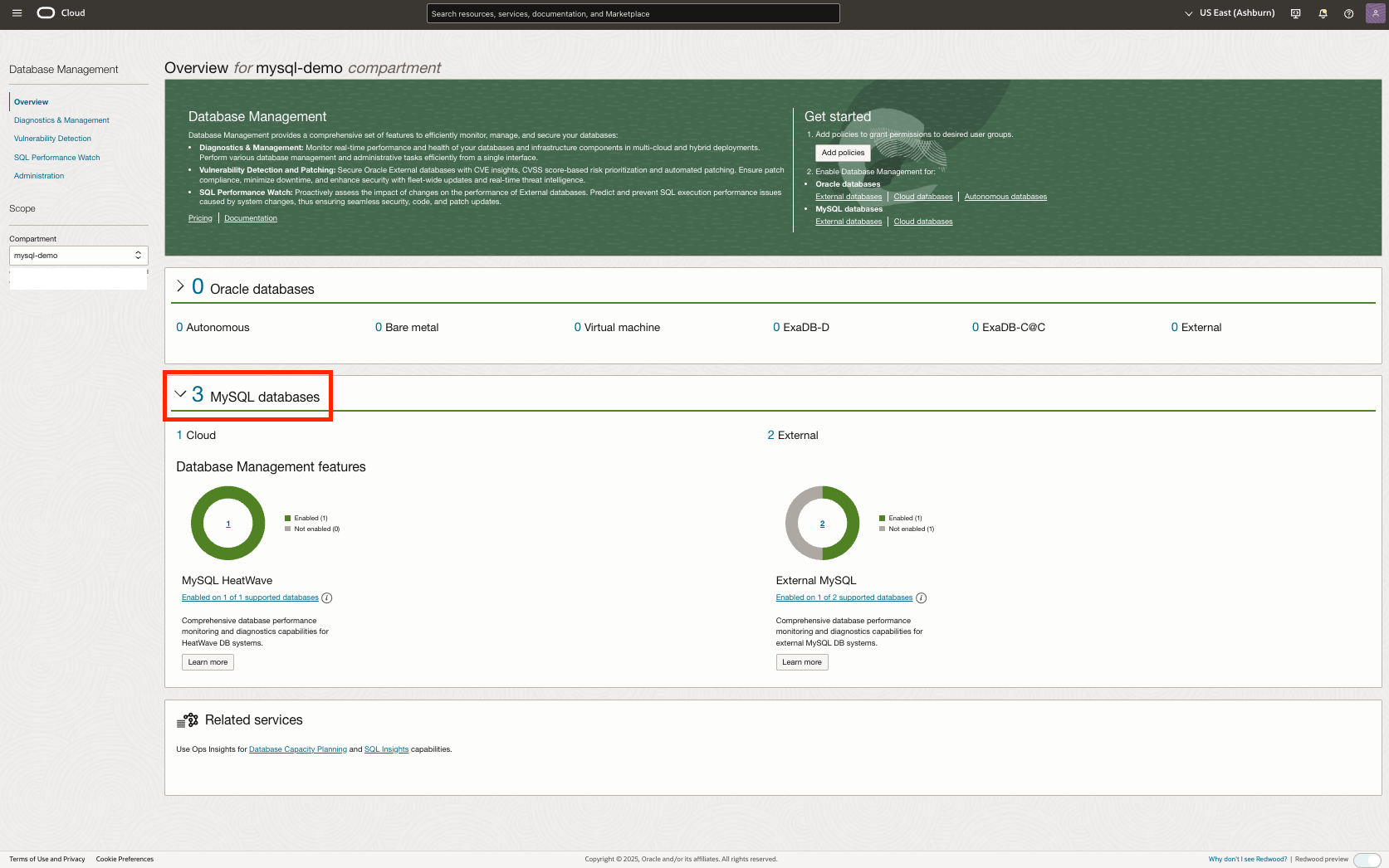
You can monitor the status and performance of your fleet of HeatWave, External MySQL DB systems and HeatWave clusters on the HeatWave & External MySQL fleet summary page.
To access the HeatWave & External MySQL Fleet Summary page:
- Under Database Management, click Diagnostics & Management, followed by HeatWave & MySQL in the left pane.
- In the left pane, select the Compartment containing your HeatWave and External MySQL DB systems.
- Choose a time period from the Time Period drop-down list in the upper-right corner of the page. The available options are Last 60 min (default), Last 24 hours, and Last 7 days.
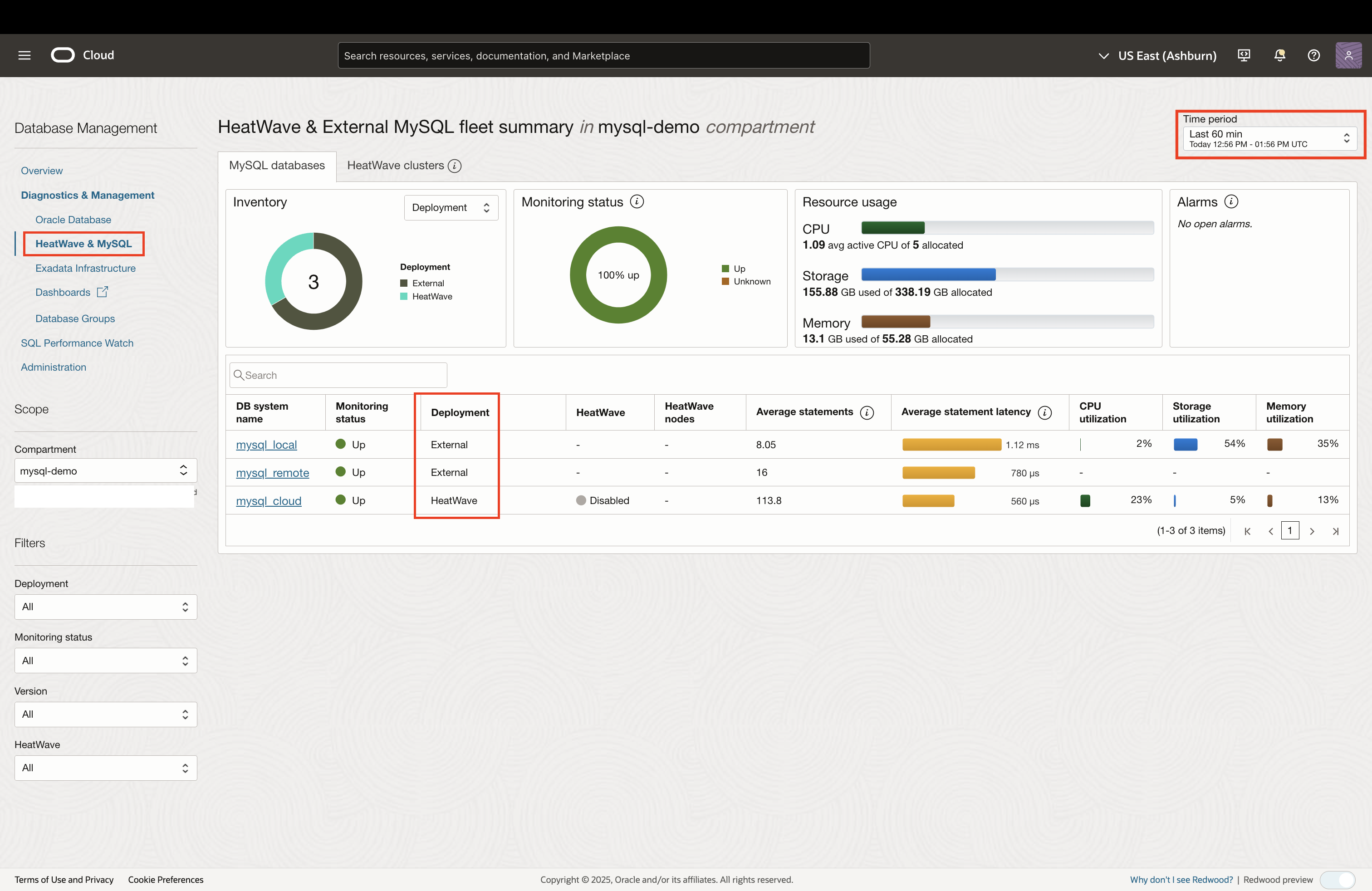
Below the tiles, a list of HeatWave and External MySQL DB systems with Database Management enabled is displayed, showing the DB system name, monitoring status, and deployment type, along with Average Statements, Average Statement Latency, CPU Utilization, Storage Utilization and Memory Utilization.
Monitor Single External MySQL DB system
You can monitor and manage a single External MySQL DB system using Database Management by navigating to corresponding database MySQL database details page.
To go to the MySQL database details page, click the name of the DB system on the HeatWave & External MySQL fleet summary page or from Administration page (both options work).
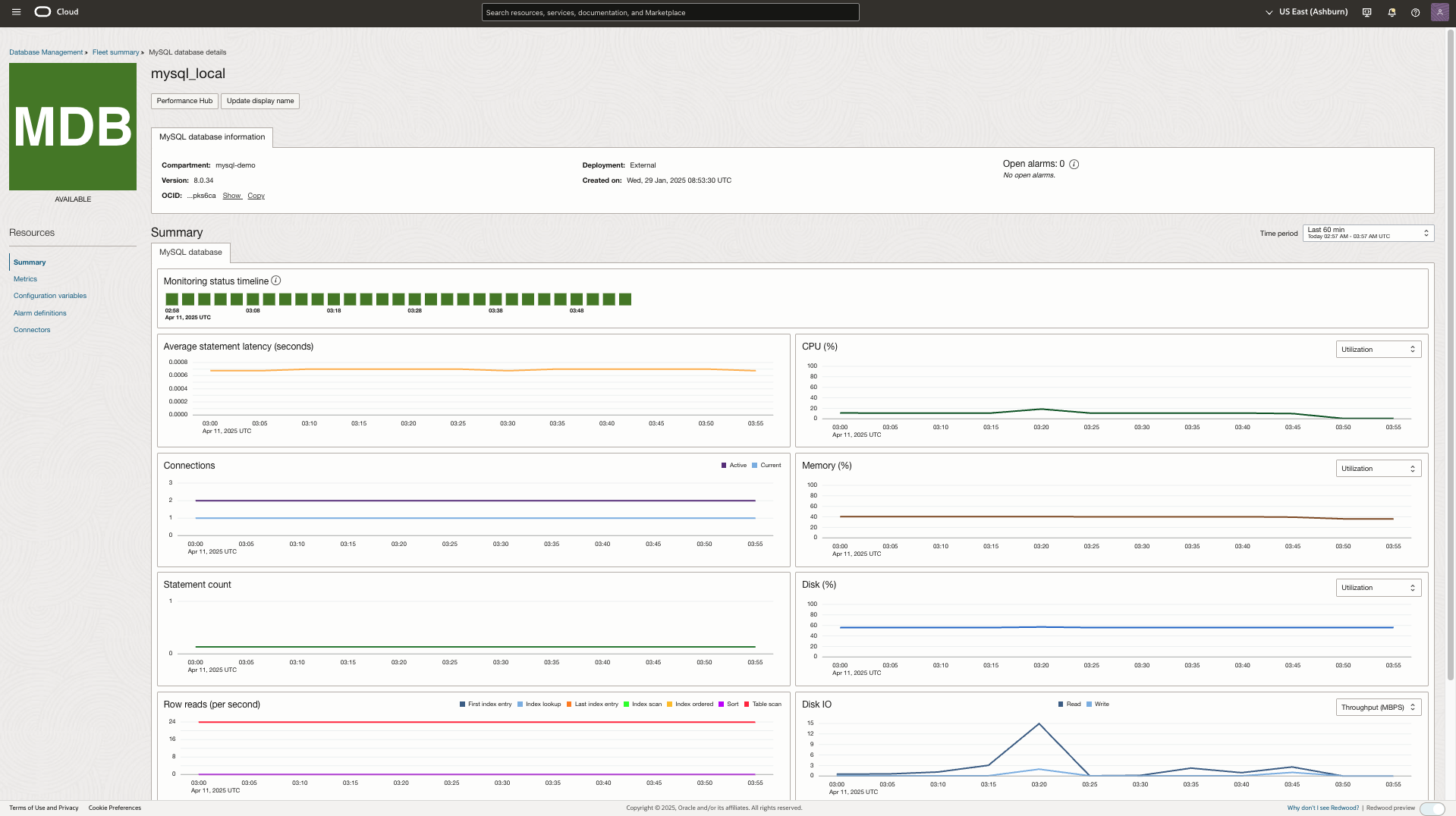
On the MySQL database details page, you can:
- Click Performance Hub to go to Performance Hub to monitor and analyze SQL performance and obtain greater visibility into performance issues.
- View MySQL database information, which includes details such as the compartment, deployment, OCID, Created on, Open Alarms and version of the DB system.
- Monitor DB system status and metrics in the Summary section for the time period selected in the Time period drop-down list. Default time period is Last 60 min.
- Monitoring status timeline: The monitoring status indicates whether Database Management can collect monitoring metrics for the DB system for selected time frame.
- Metric charts : Visual representation of DB system metrics or metric charts in the Summary section enable you to analyze data better by monitoring different parameters such as active connections, new connections and statement count.
The Summary section is displayed by default on the MySQL database details page, however, you can click other options on the left pane under Resources to perform the following tasks:
- Metrics: Monitor key database system metrics to proactively identify and address performance issues.
- Configuration variables: Monitor the configuration variables that are currently used by running instances.
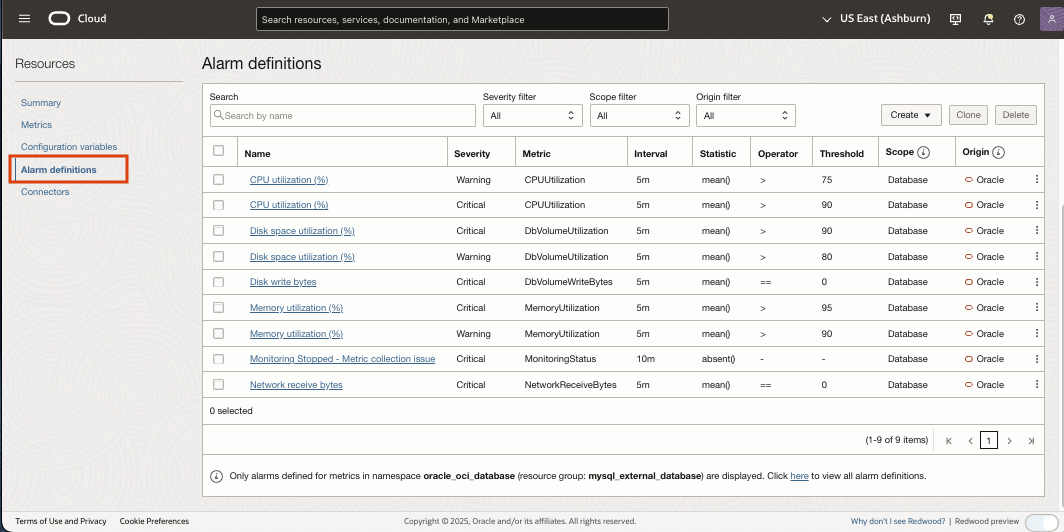
- Alarm Definitions: Use the Alarm Definitions section to implement Oracle-recommended alarms with predefined rules, thresholds, and conditions for effective DB system monitoring.
- Connectors: View or add connectors to integrate with External MySQL DB systems. This feature supports multiple configurations, enabling seamless switching between setups, such as remote and local hosts, while experimenting with different secret types for quick and efficient transitions.
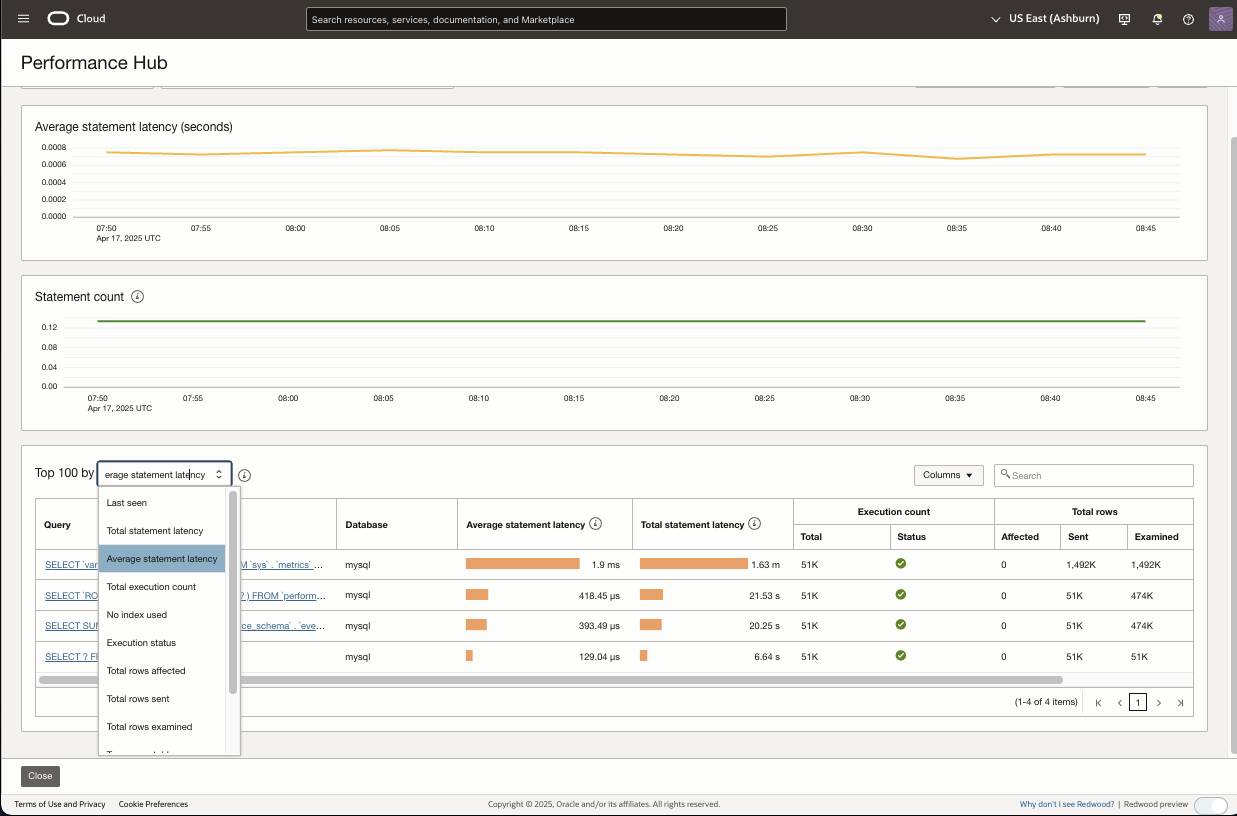
Performance Hub
Performance Hub is a powerful tool for monitoring and analyzing SQL performance which helps identify expensive or inefficient queries, offering deep insights into query activity and execution. With Performance Hub, you can optimize SQL during development and continuously tune production systems for better performance, resulting in faster and more efficient database operations.
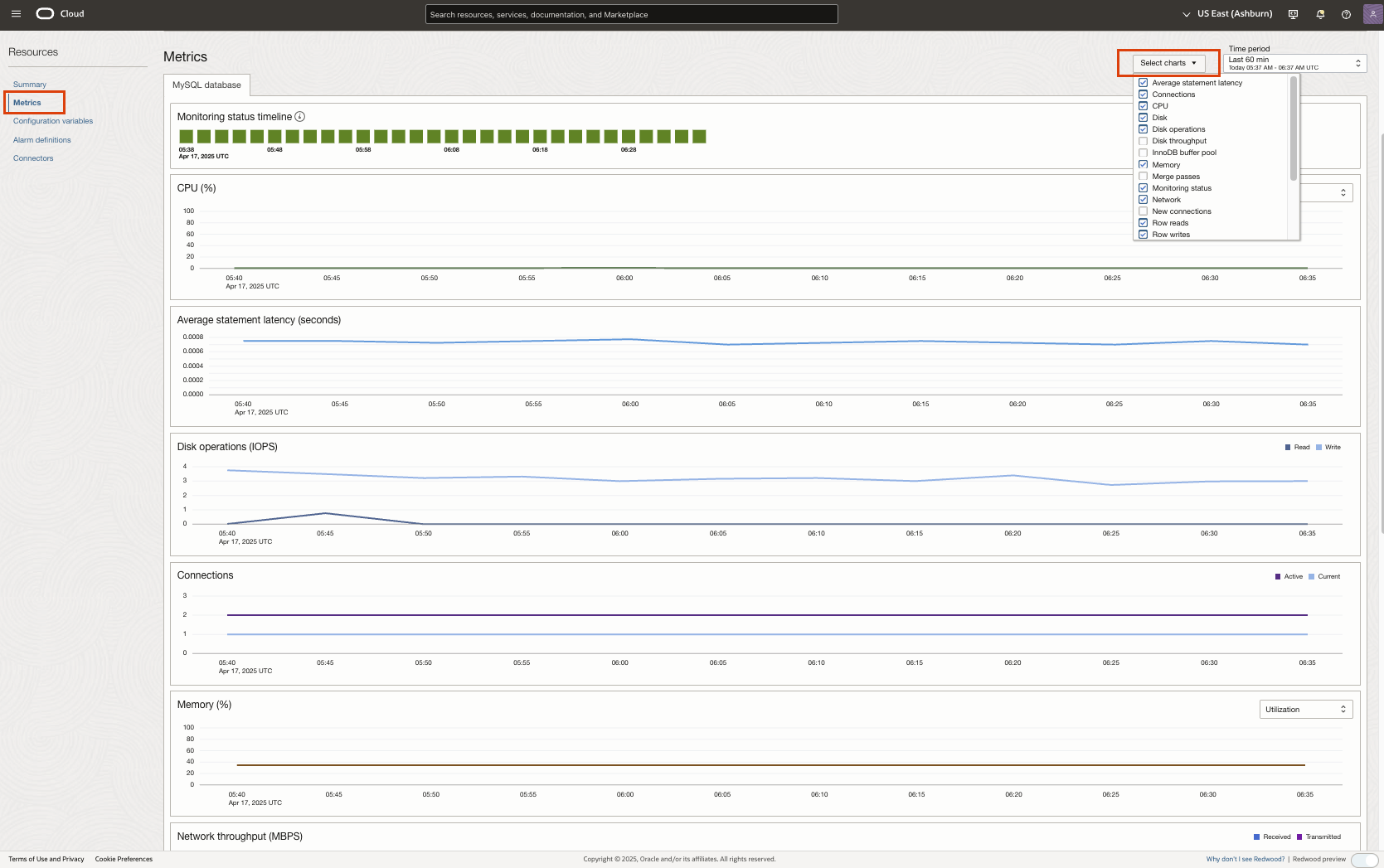
Metrics
In the Metrics section, you can monitor a variety of essential MySQL DB system metrics to help proactively identify and resolve performance issues. This section includes charts from the Summary section and additional metric charts selectable via the Select Charts dropdown, offering detailed insights through various indicators, refer Metric charts for more details.
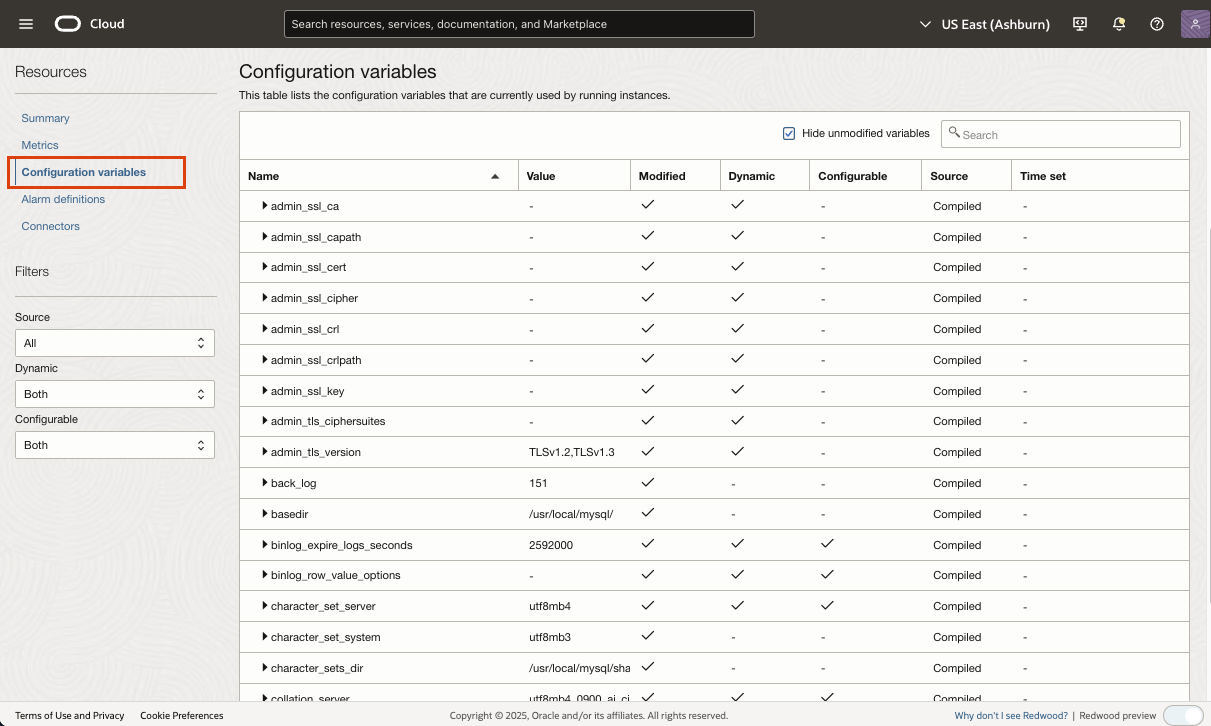
Configuration variables
In Configuration variables section, you can monitor and manage the configuration variables currently used by your MySQL DB system. These variables are the user, system, initialization, or service-specific variables that define the operation of a MySQL DB system. For information on configuration variables, see Configuration variables.
Alarm definitions of MySQL DB system
In the Alarm Definitions section, you can quickly implement Oracle-recommended alarms using predefined rules, thresholds, and conditions. These built-in configurations are designed to help you effectively monitor your DB systems and identify potential issues or deviations from Oracle’s recommended best practices.
Events for External MySQL DB systems
You can use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Events to create rules that trigger an action when the state of an External MySQL DB system or connector resource changes.For example, you can create a rule to be notified when the External MySQL DB system is registered or when the Database Management enablement process begins or ends.
To monitor the key statistics of the MySQL instances in the Database Management-enabled External MySQL DB systems you can use ou can use metrics, alarms, and notifications . Metrics emitted by Database Management in the oracle_oci_database namespace for the mysql_external_database resource groups can be used for alarms and events.
For information on Events service, see Overview of Events .
Get started today!
Take advantage of the OCI Database Management service today to enhance the reliability and efficiency of your on-premises (External) MySQL DB systems. These services supports MySQL 8.x and later versions, ensuring compatibility with the latest features.
Watch this video series to quickly get started onboarding for Database Management and Ops Insights. For more information on how to use, see the documentation for Database Management and Ops Insights.

