Marketing automation terminology is changing as fast as the industry is. In an era where marketers oversee multiple platforms to help them automate basic tasks—from email campaigns to loyalty program management—the language of marketing automation has become part of our lexicon.
But with each new platform comes plenty of variations on these terms. Some terminology, however, is universal to all marketing automation systems.
To that end, here is a list of key terms you’ll want to know.
Marketing automation terms A-G
A/B testing compares two versions of an asset or offer (for instance, a piece of marketing collateral like email templates and web pages) to measure performance stats and qualities of both versions.
ABM (account-based marketing) identifies accounts (or groups of accounts) that have the most growth potential. Once the accounts are segmented, marketers can create personalized campaigns targeted at those high-growth accounts.
An anonymous visitor is a visitor to your site who does not have an email associated with their computer IP address.
Attribution (first touch, last touch) identifies the specific marketing interaction responsible for converting a prospect into a sales lead or sales opportunity. In other words, the new lead or opportunity can be attributed to the marketing touch. First touch attribution means customers converted after their very first interaction with your brand, such as downloading a whitepaper. Last touch attribution means the prospect did not convert until they interacted multiple times. For example, they clicked an ad, visited your site, and opened an email but did not convert until they responded to an event invitation. Marketing attribution allows you to connect a conversion to the relevant channels that drove it.
Contacts are all unique entries in your marketing automation database, often organized by name or by a piece of contact information such as an email address or a phone number.
Behavior-based marketing automation is a system that triggers communications (like email) based on online and offline customer activity. Some example activities are filling out online forms, watching a video, or clicking on an advertisement.
Conversion is a term that broadly refers to a customer engagement that completes a marketing goal, whether that represents downloading a file, clicking a link, or making a purchase.
Cost per lead (CPL) is a pricing structure in which payment is based on the number of leads rather than sales. In essence, an advertiser can pay an agreed-upon price for each lead that is generated from a particular campaign.
A customer relationship management (CRM) solution is a software platform that stores customer contact information, in addition to logging and managing interactions with existing customers and potential prospects.
Cross-platform marketing automation is the ability for your digital communications to be viewed as easily on mobile devices as they are on desktop devices.
CTA or “call to action,” is the element of a marketing message aimed at getting a direct response. A CTA could be an encouragement to make a purchase, click on a link, or take advantage of a promotional offer, among other activities.
Drip marketing is a type of lead nurture in which an automated program sends a series of emails at specific intervals to engage leads with the goal of moving them through the sales funnel.
Gated content/offers are usually long-form pieces of content like research reports that require a visitor to enter personal information in exchange for access. For example, premium content on a site can be downloaded after a user enters their email information.
Marketing automation terms I-O
Inbound marketing is a strategy built around providing content to your audience to attract new business and organically create more interest in a product or service. This strategy is often associated with search engine optimization and generating organic (free) visitor traffic. Blogs, websites, and campaign landing pages are types of inbound marketing touchpoints designed to generate inbound leads or new business opportunities derived from inbound marketing.
Interruption-based marketing interrupts audiences with a sudden message to buy a product or service designed to capture immediate conversions. Pop-up ads are an example.
A known visitor is a user record that contains an email address that has been associated with their computer IP address due to filling out a form or interacting with an email sent by a marketing automation platform.
Leads/prospects are potential customers who have exchanged their information with you.
Lead/demand generation uses targeted marketing programs to raise awareness and build interest in a brand and its products and services. Demand generation is focused on gathering contact information of new prospects or progressing existing leads and opportunities toward closed deals and revenue.
Lead score/scoring rates the overall status of a contact’s readiness to buy based on activity, demographic, and firmographic data. Marketers establish a scoring system that awards points for every qualifying characteristic (like company size) and marketing interaction (e.g. opening an email). Leads that accumulate a certain number of points are then moved on to other marketing programs or directly to sales.
Loyalty programs are promotions offered to active customers as a reward for their loyalty to your brand for example, being a long-time subscriber, a repeat customer, a social advocate or participating in other activities that help your brand.
Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL) is a lead that has demonstrated enough engagement with your content—from site visits to opened emails—that they’re ready to be handed off to sales.
Multichannel marketing automation ensures that the customer experience across all channels and platforms is consistent and relevant.
Nurture campaigns (sometimes called lead nurture) are designed to engage prospects over time through email content and exclusive engagements that help move them through the sales funnel.
Outbound marketing is a proactive marketing method in which a company pushes its message to target audiences and initiates a sales conversation. Outbound marketing is often contrasted with inbound marketing. Outbound marketing requires high levels of personalization and customer analysis to be effective.
Marketing automation terms P-W
A persona is a fictional character that is an amalgamation of primary customer characteristics. Examples of this include job role and title, presumed wants and needs, and business goals.
Progressive profiling collects data via dynamic web forms that progressively ask users to enter more pieces of information. For example, the first time a prospect encounters a form, they may only need to provide name and email address. The next time to the same prospect encounters a from, they may be asked to enter their company name and industry. This process may increase form completions and helps you develop a complete customer profile.
A sales funnel is a marketing model or visual representation of the stages of the buyer journey. For example, the top of the funnel reflects the early stages of customer interest. Middle of funnel represents those customers in the stage between awareness and making a decision. Bottom of funnel content aims to make a final persuasive pitch to customers, taking them over the line to a purchase.
Permission-based marketing are programs or communications a customer has explicitly agreed to receive (email opt-ins, subscribing to a blog, etc.)
Personalization uses customer data including purchase history, demographics, firmographics, etc. to customize content, campaign offers, and purchase recommendations.
Sales enablement refers to marketing activities and materials that empower the sales team. Enablement may consist of content offers salespeople send to prospects to encourage further engagement. Sales enablement also often refers to internal programs and training content that prepare sales reps to be successful.
Segmentation divides your database into categories based on various factors, including demographics, online activity, job role, and income. These factors inform audience targeting and personalization.
Smart lists are dynamic and constantly updated based on new information such as engagement by region, age, or other demographics.
Static lists are lists of contacts that do not change or update automatically. They’re typically used to organize contacts related to a specific “point-in-time” marketing activity, such as respondents to a past campaign or a conference attendee list.
A workflow/automated program refers to a series of activities or steps programmed to execute within a marketing automation system. For example, it can refer to triggered emails when leads engage with one or more pieces of content.
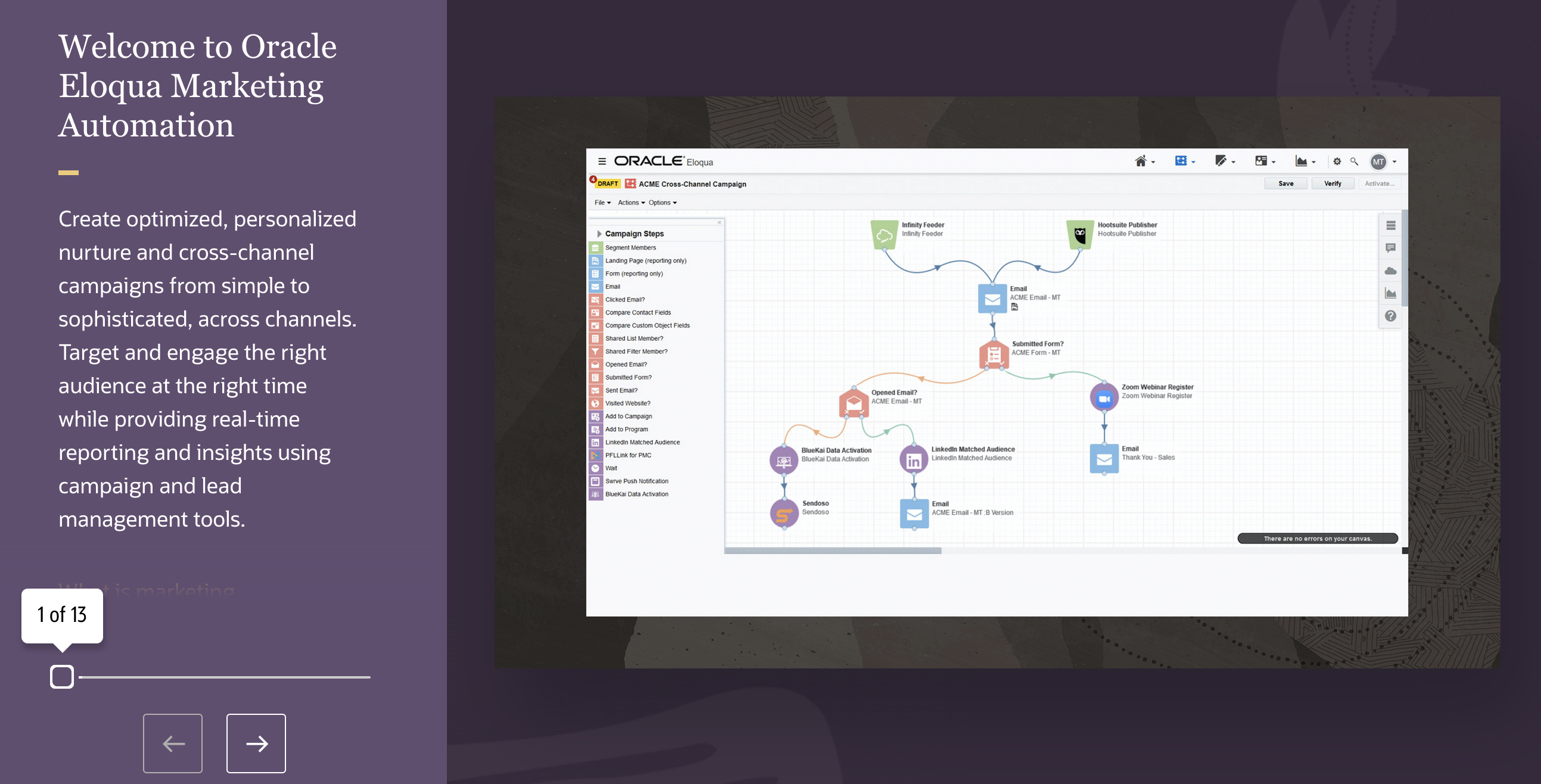
Want to learn more about marketing automation software? Check out the following resources and take the brief self-guided tour of Oracle Eloqua Marketing Automation below:
- Essential Strategies for Marketing Automation
- Marketing Automation Best Practices
- Oracle Eloqua Marketing Automation
- Oracle Responsys Campaign Management