We have been working very hard to make it easy for you to migrate your applications to newer, faster SPARC hardware and Oracle Solaris 11. This post provides an overview of the process and the tools that automate the migration.
Migration helps you modernize IT assets, lower infrastructure costs through consolidation, and improve performance. Oracle SPARC T8 servers, SPARC M8 servers, and Oracle SuperCluster M8 Engineered Systems serve as perfect consolidation platforms for migrating legacy workloads running on old systems. Applications migrated to faster hardware and Oracle Solaris 11 will automatically deliver better performance without requiring any architecture or code changes.
You can migrate your operating environment and applications using both physical-to-virtual (P2V) and virtual-to-virtual (V2V) tools. The target environment can either be configured with Oracle VM for SPARC (LDoms) or Oracle Solaris Zones on the new hardware. You can also migrate to the Dedicated Compute Classic – SPARC Model 300 in Oracle Compute Cloud and benefit from Cloud capabilities.
Migration Options
In general there are two options for migration.
1) Lift and Shift of Applications to Oracle Solaris 11
The application on the source system is re-hosted on new SPARC hardware running Oracle Solaris 11. If your application is running on Oracle Solaris 10 on the source system, lift and shift of the application is preferred where possible because a full Oracle Solaris 11 stack will perform better and is easier to manage. With the Oracle Solaris Binary Application Guarantee, you will get the full benefits of OS modernization while still preserving your application investment.
2) Lift and Shift of the Whole System
The operating environment and application running on the system are lifted as-is and re-hosted in an LDom or Oracle Solaris Zone on target hardware running Oracle Solaris 11 in the control domain or global zone. If you are running Oracle Solaris 10 on the source system and your application has dependencies on Solaris 10 services, you can either migrate to an Oracle Solaris 10 Branded Zone or an Oracle Solaris 10 guest domain on the target. Oracle Solaris 10 Branded Zones help you maintain a Oracle Solaris 10 environment for the application while taking advantage of Oracle Solaris 11 technologies in the global zone on the new SPARC hardware.
Migration Phases
There are 3 key phases in migration planning and execution.
1) Discovery
This includes discovery and assessment of existing physical and virtual machines, their current utilization levels, and dependencies between systems hosting multi-tier applications or running highly available (HA) Oracle Solaris Cluster type configurations. This phase helps you identify the candidate systems for migration and the dependency order for performing the migrations.
2) Size the Target Environment
This requires capacity planning of the target environment to accommodate the incoming virtual machines. This takes into account the resource utilization levels on the source machine, performance characteristics of the modern target hardware running Oracle Solaris 11, and the cost savings that result from higher performance.
3) Execute the Migration
Migration can be accomplished using P2V and V2V tools for LDoms and Oracle Solaris Zones.
We are continually enhancing migration tools and publishing supporting documentation. As a first step in this exercise, we are releasing LDom V2V tools that help users migrate Oracle Solaris 10 or Oracle Solaris 11 guest domains that are running on old SPARC systems to modern hardware running Oracle Solaris 11 in the control domain. One of the migration scenarios is illustrated here.
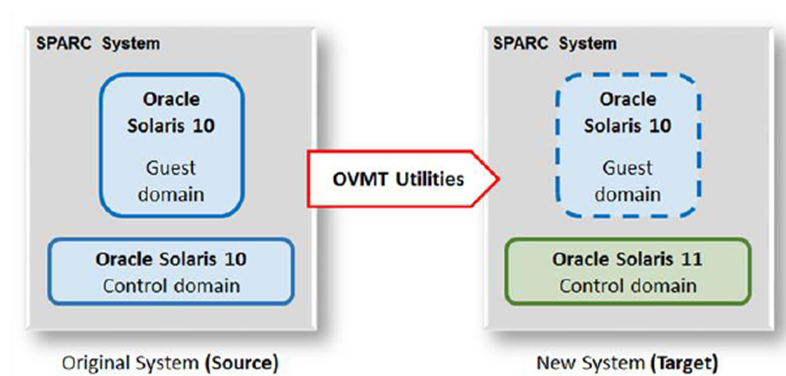
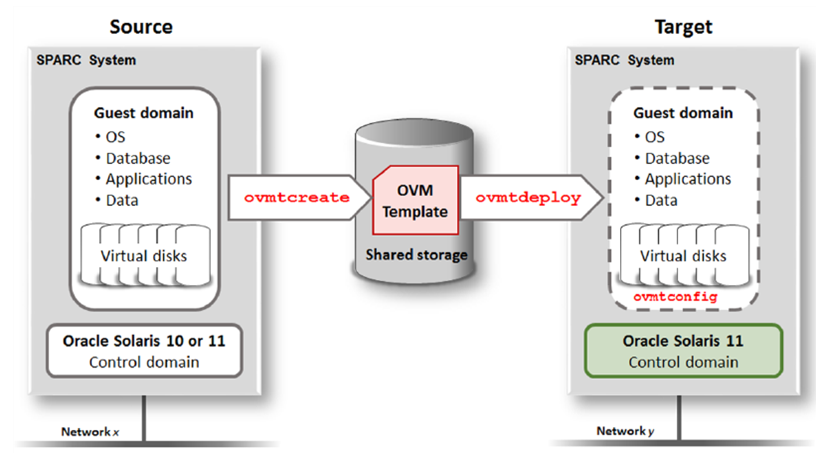
Three commands are used to perform the LDom V2V migration.
1) ovmtcreate runs on the source machine to create an Open Virtualization Appliance (OVA) file, called an OVM Template.
2) ovmtdeploy runs on the target machine to deploy the guest domain.
3) ovmtconfig runs on the target machine to configure the guest domain.
In the documented example use case, validation is performed using an Oracle Database workload. Database service health is monitored using Oracle Enterprise Manager (EM) Database Express.
Migration Resources
We have a Lift and Shift Guide that documents the end-to-end migration use case and a White Paper that provides an overview of the process. Both documents are available at:
Lift and Shift Documentation Library
Stay tuned for more updates on the tools and documentation for LDom and Oracle Solaris Zone migrations for both on-premise deployments and to SPARC Model 300 in Oracle Compute Cloud.
Oracle Advanced Customer Services (ACS) offers SPARC Solaris Migration services, and they can assist you with migration planning and execution using the tools developed by Solaris Engineering.