We saw in part 6 how to use OCI’s GenAI Service. GenAI Service uses GPUs for the LLMs, but did you know it’s also possible to use GenAI directly in MySQL HeatWave? And by default, those LLMs will run on CPU. The cost will then be reduced.
This means that when you are connected to your MySQL HeatWave database, you can call some HeatWave AI procedures directly from your application.
Connecting in Python to your DB System
I will demonstrate this using Python on the Webserver. We already saw in part 5 how to install mysql-connector-python.
Before being able to use the HeatWave GenAI procedures, we need to grant an extra privilege to our user:
SQL > grant execute on sys.* to starterkit_user;Now, let’s modify our previous Python script to use HeatWave GenAI:
import mysql.connector
cnx = mysql.connector.connect(user='starterkit_user',
password='St4rt3rK4t[[',
host='10.0.1.19',
database='starterkit')
query = "select version(), @@version_comment"
cursor = cnx.cursor()
cursor.execute(query)
for (ver, ver_comm) in cursor:
print("{} {}".format(ver_comm, ver))
cursor.execute("call sys.HEATWAVE_CHAT(\"What is MySQL HeatWave?\")")
rows = cursor.fetchall()
for row in rows:
print(row)
cursor.close()
cnx.close()And we can execute it:
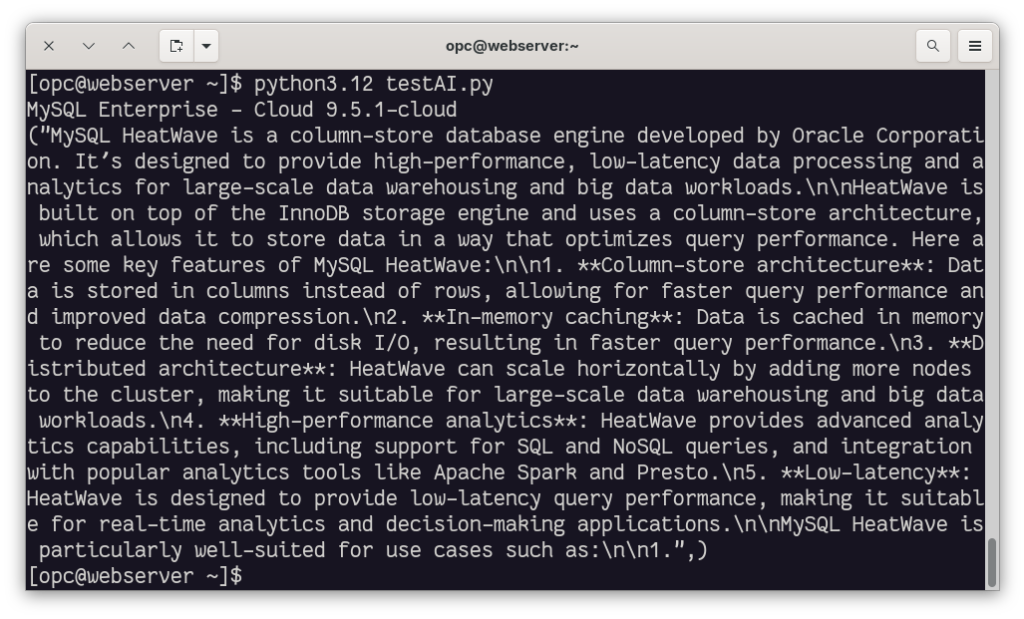
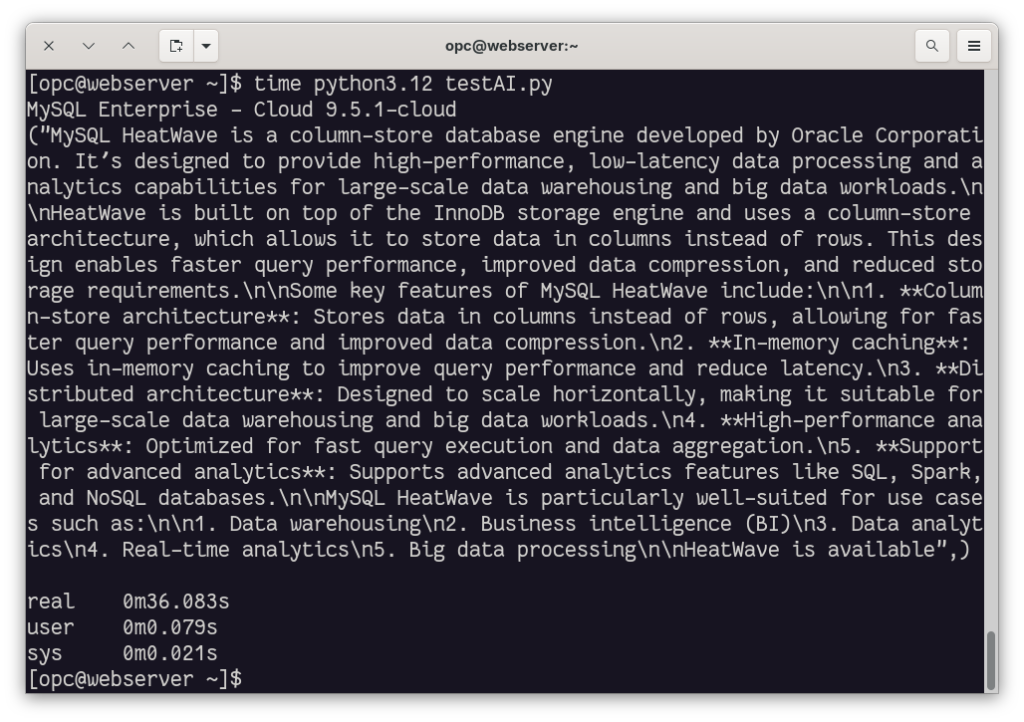
The first time, it takes some time, but after that, the execution time becomes faster:
Supported Models
You can also list the supported models in HeatWave:
SQL > SELECT * FROM sys.ML_SUPPORTED_LLMS\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
provider: HeatWave
model_id: llama3.2-1b-instruct-v1
availability_date: 2025-05-20
capabilities: ["GENERATION"]
default_model: 0
*************************** 2. row ***************************
provider: HeatWave
model_id: llama3.2-3b-instruct-v1
availability_date: 2025-05-20
capabilities: ["GENERATION"]
default_model: 1
*************************** 3. row ***************************
provider: HeatWave
model_id: all_minilm_l12_v2
availability_date: 2024-07-01
capabilities: ["TEXT_EMBEDDINGS"]
default_model: 0
*************************** 4. row ***************************
provider: HeatWave
model_id: multilingual-e5-small
availability_date: 2024-07-24
capabilities: ["TEXT_EMBEDDINGS"]
default_model: 1
4 rows in set, 1 warning (1.4607 sec)OCI GenAI Service in HeatWave
You can also use the OCI Generative AI Service (with GPUs) directly in HeatWave.
This provides access to more LLMs:
SQL > SELECT provider, model_id FROM sys.ML_SUPPORTED_LLMS;
+---------------------------+--------------------------------+
| provider | model_id |
+---------------------------+--------------------------------+
| HeatWave | llama2-7b-v1 |
| HeatWave | llama3-8b-instruct-v1 |
| HeatWave | llama3.1-8b-instruct-v1 |
| HeatWave | llama3.2-1b-instruct-v1 |
| HeatWave | llama3.2-3b-instruct-v1 |
| HeatWave | mistral-7b-instruct-v1 |
| HeatWave | mistral-7b-instruct-v3 |
| HeatWave | all_minilm_l12_v2 |
| HeatWave | multilingual-e5-small |
| OCI Generative AI Service | cohere.command-latest |
| OCI Generative AI Service | cohere.command-plus-latest |
| OCI Generative AI Service | cohere.command-a-03-2025 |
| OCI Generative AI Service | meta.llama-3.3-70b-instruct |
| OCI Generative AI Service | cohere.command-r-08-2024 |
| OCI Generative AI Service | cohere.command-r-plus-08-2024 |
| OCI Generative AI Service | cohere.embed-english-v3.0 |
| OCI Generative AI Service | cohere.embed-multilingual-v3.0 |
+---------------------------+--------------------------------+
17 rows in set (1.8044 sec)However, you need to give access to these services to your DB System. Accessing OCI GenAI Service from HeatWave is not part of the always-free tier.
To grant such access, check whether your DB System is in your tenancy or in a dedicated compartment (such as a sandbox).
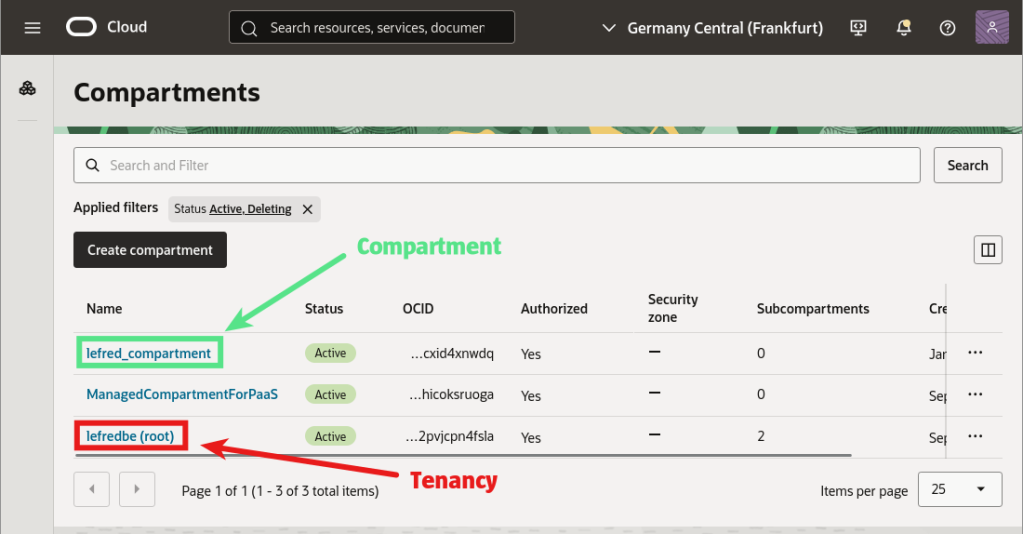
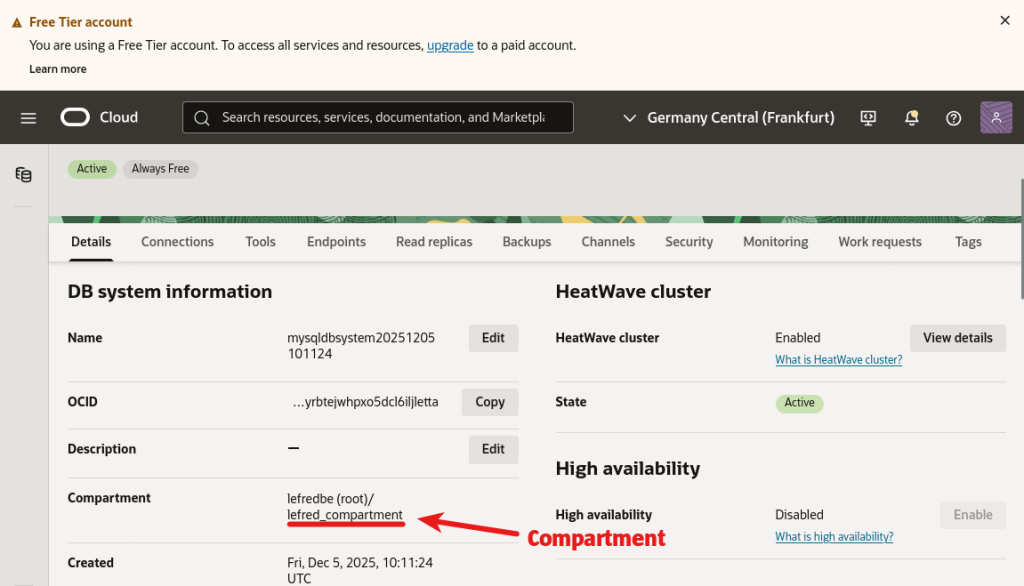
In our case, the DB System is in a compartment.
Dynamic Group
We now need to create a dynamic group to which we will provide access to the GenAI Service:
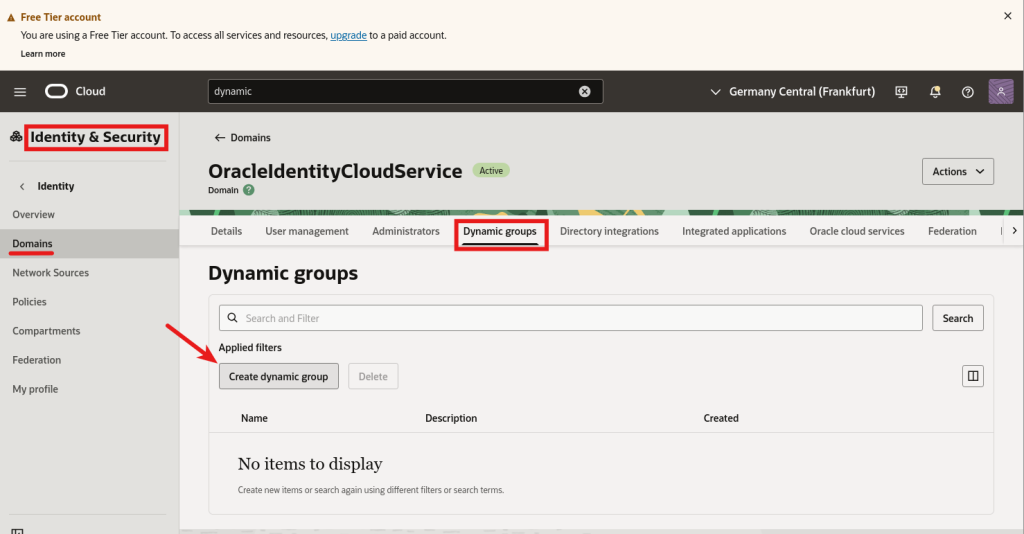
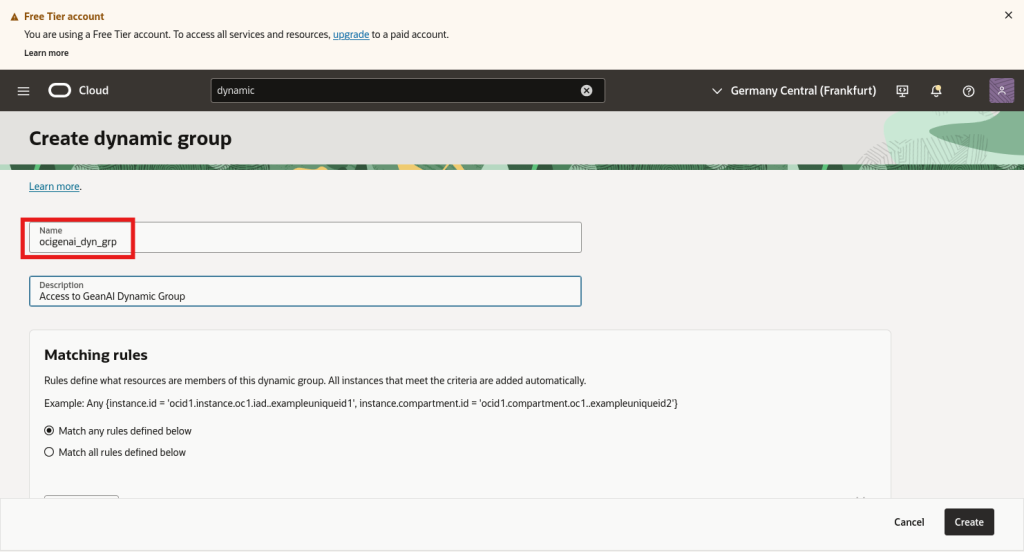
The group’s name is essential as we will use it later when creating the policies.
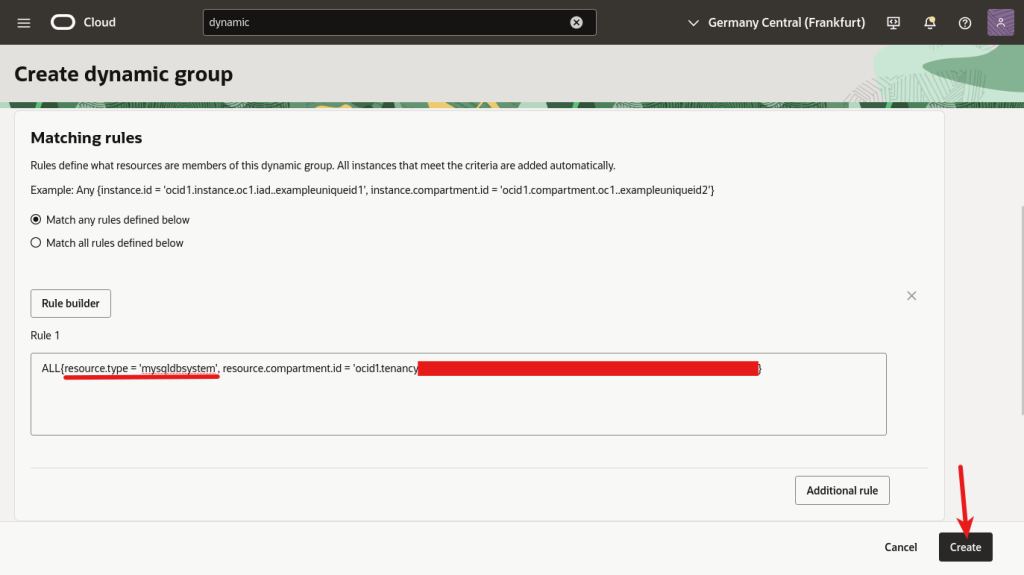

If the DB System was not part of a specific compartment but directly deployed in the tenancy, we could remove the “,resource.compartment.id= ‘ocid1.tenancy….” part.
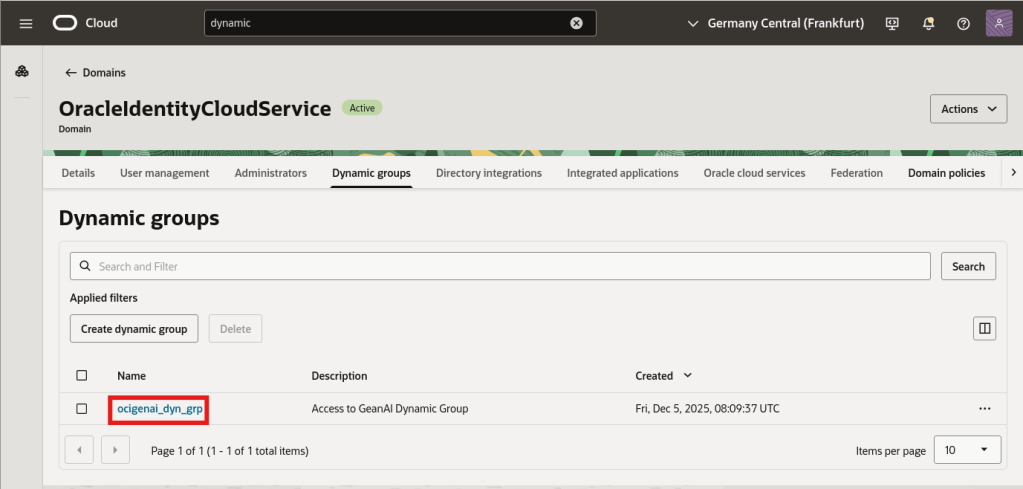
When created, the group should be visible:
Policy
Finally, we can create the policy:
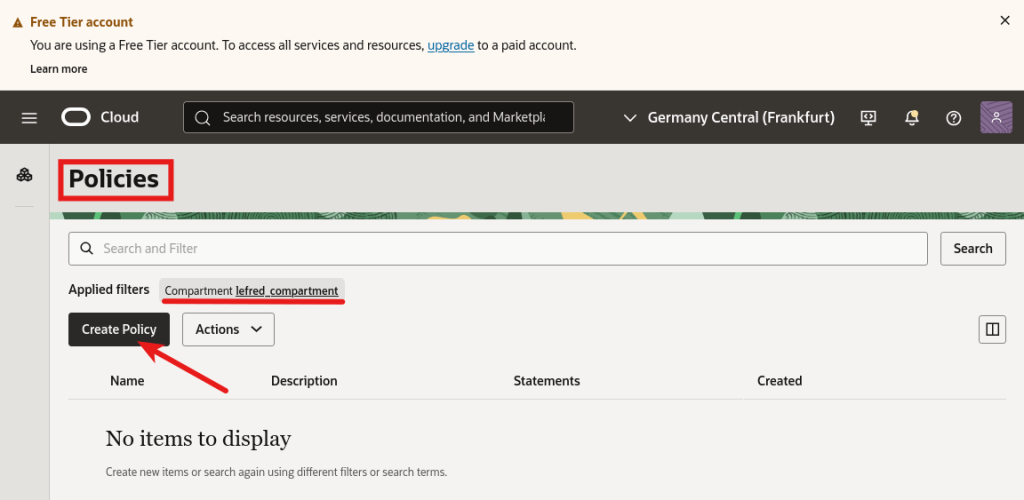
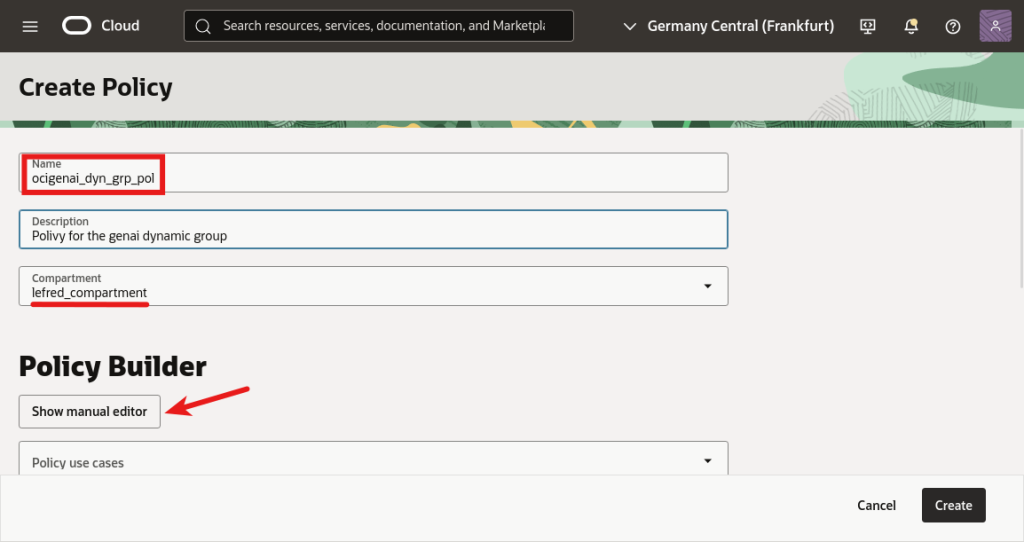
And we need to add three essential rules:
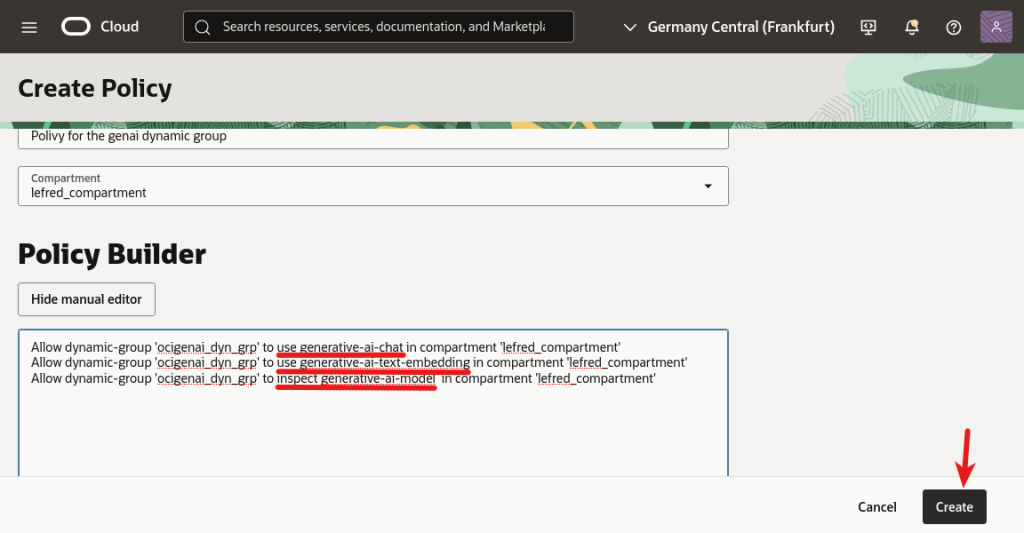
The three required rules are:
- use generative-ai-chat
- use generative-ai-text-embedding
- inspect generative-ai-model
We need to allow these rules for the dynamic group we created.
And if we have our DB System running in a compartment, the three policies are in compartment ‘name of it’. Otherwise, if the DB System was running in the root compartment of the tenancy, the rules should have been in tenancy.
Using OCI GenAI with HeatWave
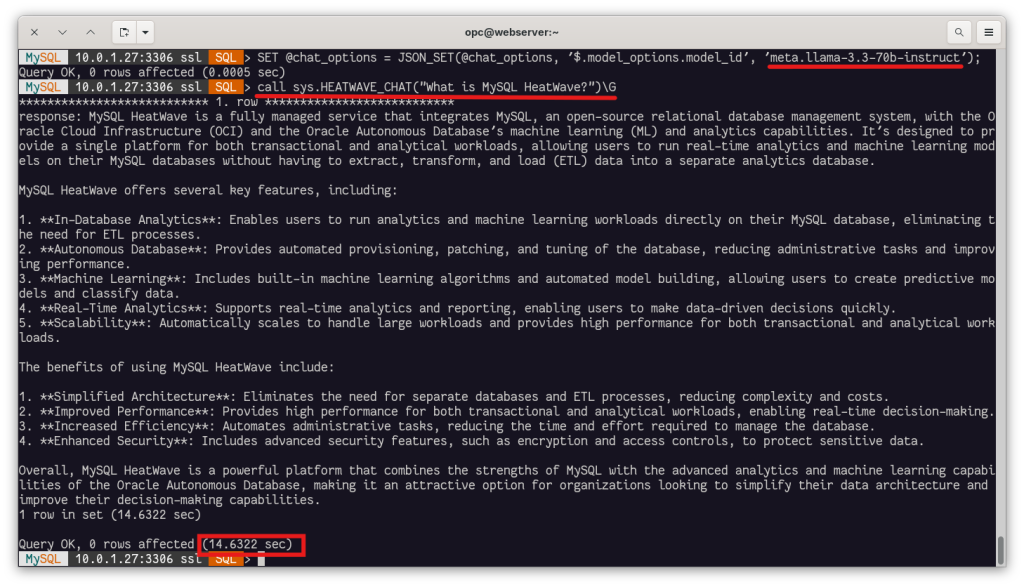
Now we can specify a model from the OCI Generative AI Service and call the procedure sys.HEATWAVE_CHAT() directly from our database connection:
Let’s discover how to use HeatWave GenAI in video:
Conclusion
With just a few additional steps, we’ve been able to extend our MySQL HeatWave setup to support GenAI capabilities directly from our MySQL connection —and even leverage the power of OCI Generative AI Service when needed. Whether you are working with the built-in HeatWave LLMs or accessing more advanced models running on GPUs, integration remains seamless and fully managed within the database layer.
This approach not only simplifies development but also unlocks new possibilities for AI-powered applications—everything from natural language chat interfaces to embedding-based search—without orchestrating external services or data pipelines. As HeatWave continues to expand its supported models and capabilities, it’s becoming a compelling solution for bringing generative AI directly to your data.
