MySQL Heatwave, a fully managed database service, not only provides customers with one database service for OLTP, OLAP, and ML, but it also supports centralized access management for these databases via integration with OCI IAM. Using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (OCI IAM) customers can protect themselves against security threats, streamline access management, and achieve governance and compliance with industry standards.
In addition to centralized access management, integrating MySQL HeatWave with OCI IAM provides strong multifactor authentication (MFA) options such as:
- Mobile app that offers one-time passcodes or click-to-allow mechanisms
- Support for FIDO2-enabled hardware security keys
- Single Sign-On
- Risk-aware adaptive security
Across OCI, OCI IAM is the source of truth for authentication and authorization. Instead of using local accounts in each database, users can now use credentials managed by OCI IAM to access their database accounts. OCI IAM groups map to database proxy users and associated roles to provide centralized management of user privileges. This integration improves the database administrator and user experience in the following ways:
- Administrators can now centrally manage all OCI database platform users without making changes to each database individually when users join, change roles, or leave an organization.
- Database users can log in using their centrally managed OCI IAM credentials instead of remembering and using a different password for each database.
- Tools or applications that accept OCI IAM tokens can authenticate to the database without having to store or embed a database username and password.
Every OCI MySQL Heatwave database (8.0.33 or higher) can now authenticate and authorize their users with OCI IAM.
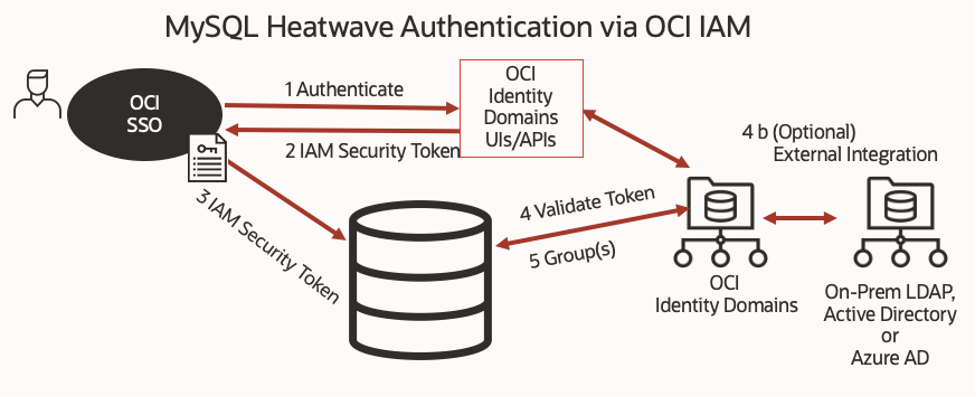
These capabilities can be enabled by following these steps:
Define the policy statement in each tenancy.
- This policy – shown here – tells the identity system to allow MySQL Heatwave access needed to authenticate a user and retrieve group memberships
ALLOW service mysql_dp_auth TO {AUTHENTICATION_INSPECT, GROUP_MEMBERSHIP_INSPECT, DYNAMIC_GROUP_INSPECT} IN TENANCY - Map a local user to an IAM USER or map a MySQL Proxy user to an IAM group.
1. In MySQL a “proxy user” a way to bind together a group of users that share grants and permissions.Thus we map this to and external group.
2. When a user logs and connects to MySQL using OCI IAM
The users IAM Security Token is validated
The users group membership returned to MySQL Heatwave by OCI IAM.
If the user has a 1-1 mapping (not based on a group mapped to a proxy)
The session in MySQL shows that “user” (who authenticated) and “current_user” are the same.
If the user is setup in a group and mapped to a proxy user
The session shows “user” (who authenticated) and the current_user will show as the proxy user name.
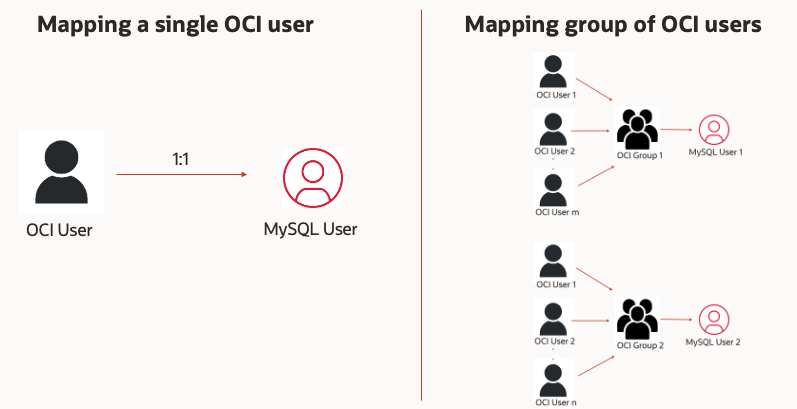
Once enabled users can obtain an OCI IAM Security Token which lasts for 1 hour by running:
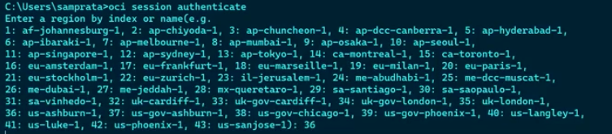
oci session authenticate –profile-name <profile_name> –region <region>
Step 1 – Run the OCI command line and select a region
Step 2 – Your brower will lauch – start the sign in process in your browser
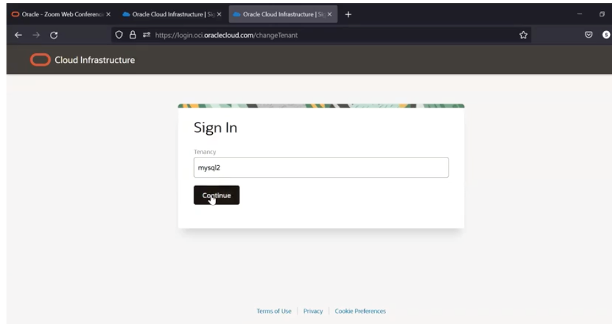
Step 3 – Specify provider
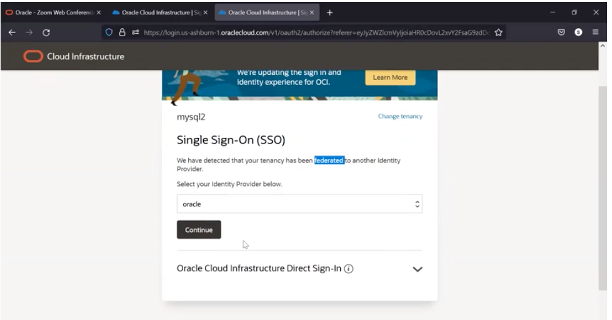
Step 4 – Enter Credentials or other authentication requirements
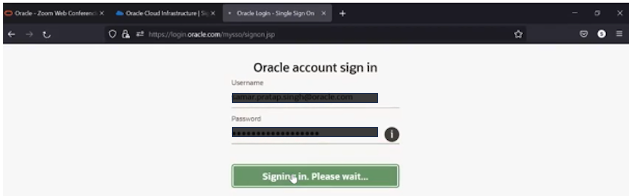
Step 5 – Provide a profile name to the OCI commandline prompt – here we use the name IAM_SECURITY_TOKEN
Now I can connect to many MySQL Heatwave databases where access has been provisioned using the token.
When using the mysql command line for example – only change the IP/Hostname –
Same token different database
It is typical for MySQL users and applications to require access sometimes up to thousands of databases. Centralized management where access is managed via group memberships is a obvious significant security posture improvement.
Additionally, all MySQL Connectors – version 8.0.33 and higher support OCI IAM authentication as well, thus providing custom application support for OCI IAM authentication.
This approach also provides benefits in scenarios such as:
- In break glass situations where access should be granted temporarily, adding a group membership is a quick way to enable access that can be revoked just as quickly.
- Security audits and monitoring becomes much easier. Each connection to an instance clearly identifies the individual user within monitoring tools. This is true for both the MySQL instance and the IAM event logs. And database level grants that are applied to groups are easier to evaluate by viewing the group memberships in the identity system.
- In distributed environments, OCI IAM spans multiple data centers, realms, and clouds. Managing access across a heterogenous environment with a single source for authentication and group memberships dramatically reduces effort.
Managing access across large, distributed database environments can be complex and time consuming. Integrating MySQL Heatwave with OCI IAM enables centralized access management. This simplifies administration, improves the user experience, and improves security.
To learn more:
- Technical Blog – MySQL Heatwave: Authenticate using OCI IAM Security Token
- MySQL Heatwave website
- MySQL Heatwave documentation
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (OCI IAM) website
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (OCI IAM) documentation
- Explore OCI IAM with an Oracle Cloud Free Trial or contact the Oracle sales team today for a demo.
