We recently announced the availability of MySQL AI which enables predictive and generative AI workflows for on-premise MySQL customers. MySQL AI includes built-in LLMs and embedding models that run on CPUs, a vector store, semantic search functions, automated machine learning and a graphical console called MySQL studio. Since its release there has been considerable interest from customers in various industries in particular finance, manufacturing, telecom, and public sector.
This blog outlines some use cases and how to get started developing predictive and generative AI applications with MySQL AI
The predictive AI applications are enabled using automated machine learning – examples being financial fraud detection, monitoring inventory and forecasting demand, assessing loan default or payment risks, and detection anomalies in streaming data or log entries.
The generative AI capabilities enable content generation, summarization, translation, semantic search of documents, chat and NL2SQL, RAG, or other GenAI use cases. The LLMs and embedding models are run within the database and accessible using simple to use APIs. MySQL can now securely query documents in your local file system, with all processing remaining within the database and your environment—no data ever leaves your infrastructure. The system runs on your existing infrastructure and the LLMs operate on CPUs, so there is no need for integration with a specialized vector database or need for specialized hardware/GPUs.
Use Cases for MySQL AI
Users can develop and run applications accessing content from documents in a local file systems and MySQL database. The goal is to analyze the data, generate useful responses, and perform tasks, such as prediction or generation.
The in-database LLMs help you to
- Generate content in multiple languages for activities such as social media posts, blog articles, and email campaigns.
- Generate concise and correct summaries of documents, reports, and logs while keeping essential information. For example, ecommerce sites with many SKUs—hundreds or thousands or more—have multiple reviews per product. Users can tap into GenAI’s capabilities to quickly summarize, translate, or even analyze sentiment in the reviews.
- Perform retrieval augmented generation aka RAG: Easily search private documents or generate new content for contextual, business-specific applications. Store and search proprietary documents using vector similarity search and augment LLM prompts with relevant business content—easily and securely. These techniques enable enterprises to build chatbots for a variety of needs such as answering questions about company policies, or helping customers choose proper training courses.
In addition to generating or summarizing content, imagine being able to predict for example, whether you should offer a rate to a customer to encourage them to stay and prevent churn. Predictive AI enables this.
With MySQL AI users can combine predictive and generative AI for truly innovative applications. They could leverage log analytics from predictive AI to identify unusual patterns indicating an impending failure. For example, if the number of connections is rising, memory usage is increasing, or disk usage is climbing and nearing capacity, they can receive an early warning. This is an improvement over traditional monitoring systems, which only alert users after an issue, such as a failed disk or a full disk, has already occurred. The benefit is a warning before the failure happens.
The GenAI part takes these ML results and generates useful responses. For instance, if the system detects that a disk is filling up or the number of connections on an instance is increasing rapidly, GenAI can suggest concrete actions based on similar problems encountered and addressed in the past.
Using MySQL AI
MySQL AI is built on the top of MySQL Enterprise Edition and provides ML/Gen AI functionality. All the functionality is exposed via SQL functions/stored procedures and REST interface, and can be used from all existing MySQL clients such as the popular MySQL Shell or Python and Java connectors.
Let’s look at two examples of using the SQL functions and stored procedures. The first outlines the steps and commands for performing RAG on documents. The second shows how to use the predictive analytics capabilities for fraud detection.
Retrieval augmented generation on documents
The RAG process involves three steps: (i) upload documents to a file system location accessible to MySQL, (ii) ingest the documents into the vector store, and (iii) query the documents.
Step 1: copy the files into a suitable location, e.g. the /var/lib/mysql-files folder using a copy command such as
sudo cp /home/john_doe/Olympics_2024.pdf /var/lib/mysql-files
Step 2: ingest the documents into the vector store, i.e. extract segments and store them along with their embeddings and some metadata, using a load command
CALL sys.VECTOR_STORE_LOAD('file:///var/lib/mysql-files/2024_Summer_Olympics_Wikipedia.pdf', JSON_OBJECT("schema_name","mlcorpus","table_name","vector_store_data_1"))""");
The above command loads and stores the embeddings, segments, and metadata in the mlcorpus.vector_store_data_1 table (aka the vector store) for use in subsequent semantic search.
Step 3: use the ML_RAG procedure to query the documents in natural language
CALL sys.ML_RAG("Where were the 2024 Summer Olympics held?", @output, JSON_OBJECT("model_options",JSON_OBJECT("model_id","llama3.2-3b-instruct-v1"),"vector_store", JSON_ARRAY("mlcorpus.vector_store_data_1")));
SELECT JSON_PRETTY(@output);
This outputs the answer
‘The 2024 Summer Olympics were held in France.‘
This RAG operation makes a knowledge base available to the end user.
See this sample notebook on Github for a detailed example.
Credit card fraud detection
Credit card fraud poses a significant threat to financial institutions and individuals alike, resulting in substantial financial losses and eroded trust. Traditional rule-based systems often struggle to keep pace with the evolving tactics of fraudsters, making machine learning-based anomaly detection a vital tool.
The example below is based on a public data set with a sample notebook on Github explaining all the steps in detail.
The example uses the unsupervised anomaly detection feature of the AutoML pipeline and relies on the inherent patterns and structures within the transaction data to identify deviations from the norm.
Step 1: use the ML_TRAIN API to train the model. Given this is unsupervised anomaly detection, we pass the target column name as NULL, and AutoML builds a model learning from the patterns inherent in the data.
SET @model = NULL;
CALL sys.ML_TRAIN('mlcorpus.creditcard_train', NULL, JSON_OBJECT('task', 'anomaly_detection', 'exclude_column_list', JSON_ARRAY('Class')), @model);
The model handle generated at the end of training is stored in the model variable. We will use this handle to refer to the model in future interactions.
Step 2: invoke the ML_PREDICT_TABLE API to generate prediction for the above model on test data. The output table contains an extra column with the prediction.
CALL sys.ML_PREDICT_TABLE('mlcorpus.creditcard_test', '{model}', 'mlcorpus.creditcard_test_predictions', NULL);
SELECT Time, Amount, ml_results FROM creditcard_test_predictions;
Time Amount ml_results
74165.0 1.98 "predictions": {"is_anomaly": 0}, "probabilit...
94428.0 0.75 "predictions": {"is_anomaly": 0}, "probabilit...
63603.0 77.50 "predictions": {"is_anomaly": 0}, "probabilit...
131607.0 1.00 "predictions": {"is_anomaly": 0}, "probabilit...
Developing applications
MySQL AI introduces new tools for developers to build rich AI/ML applications and deploy the applications on-premises or cloud.
The first is an MCP (Model Context Protocol) server supporting agentic AI. The second is MySQL Studio, a new graphical interface that provides an intuitive, integrated environment for database management and application development. The third is a Python SDK.
Support for agentic frameworks such as Model Context Protocol
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard enabling seamless integration between applications powered by large language models and external data sources or tools. The MySQL MCP Server provides a collection of specialized tools that help you leverage the full capabilities of both MySQL HeatWave and MySQL AI.
User applications such chatbots and IDEs execute MCP clients, which connect directly with the MCP servers. The LLMs inside the clients acts as the orchestrator or decision maker. The clients talk with the MCP server(s) via a standard MCP interface and access raw data as well as processed information (like responses from RAG) from various MCP tools, This is then fed back to the client for context, which analyses it and decides on next course of action, with an intent of solving a business problem
The MCP client server model simplifies integration of MySQL AI in applications. It enables agentic data-driven application development, analytic workflows and infrastructure management, thus facilitating AI driven data management.
MySQL AI also provides a set of built-in tools for database connection management and query, predictive and generative AI tasks, and vector store ingestion and usage. Developers can augment these or add new ones for their applications. Some of these tools are listed below:
| Category | Tool | Description |
| Database Connection Management | Load connection configs from JSON/env vars | Import database configs from JSON files or environment variables |
| List all configured database connections | Display all available/pre-configured database connections | |
| Validate connectivity and resolve provider mode | Test database connections and identify DB provider mode | |
| Database Operations | Execute SQL queries | Run SQL statements against the connected database |
| GenAI Operations | Text generation with HeatWave GenAI | Use GenAI to generate or augment text |
| Create/populate vector columns for embeddings | Generate and save vector representations in DB columns | |
| Retrieval-augmented generation from vector stores | Use vector store for improved GenAI results | |
| Vector Store Ingestion | Load documents from Object Storage into vector store | Ingest files/objects from Object Storage to populate vector DB |
MySQL Studio
MySQL Studio is a new, unified graphical interface designed to make database management and AI integration simple and efficient, whether you’re a data professional or just starting out.
It includes a SQL workshop, a chat interface for querying documents stored in the vector store and data in MySQL, and an interactive notebook for developing machine learning and generative AI applications. The notebooks are compatible with Jupyter, allowing developers to import existing notebooks for use with MySQL AI and MySQL HeatWave or share and collaborate on ML and GenAI projects.
With SQL Workshop, you can write, test, and run SQL statements in an intuitive editor, streamlining your workflow. The AI Chat feature provides a conversational way to harness advanced AI capabilities built-in to MySQL AI, helping you harness advanced AI capabilities directly from within MySQL Studio. And, with integrated Python notebooks, you can explore data, build custom applications and unlock powerful interactive features using Python and widgets—all within a single, seamless environment.
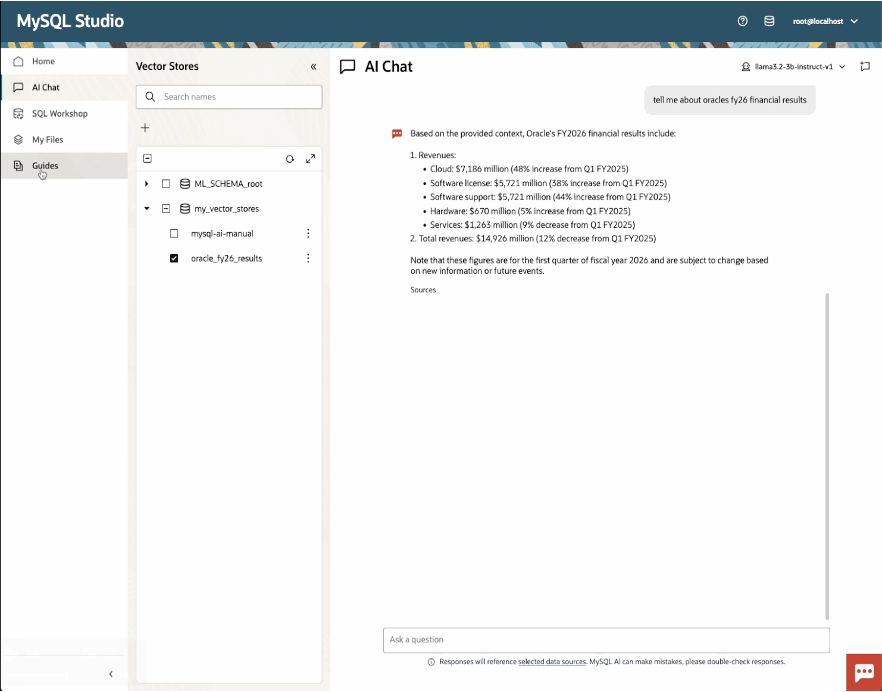
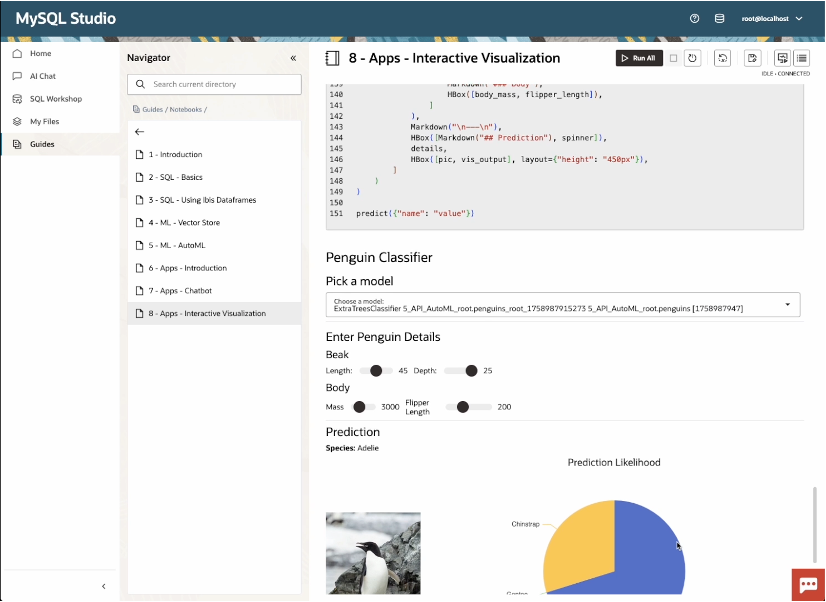
The Python SDK
The Python SDK bridges integration gaps for MySQL AI or HeatWave by streamlining data ingestion, automating table lifecycle management, and offering components that interoperate with leading GenAI and machine learning libraries.
For generative AI, the SDK delivers three MySQL AI-backed LangChain components:
MyLLM(generative model)MyEmbeddings(embedding model)MyVectorStore(vector/document store)
These can be integrated into existing LangChain pipelines or used to build new ones.
For predictive AI, the SDK introduces MyModel, which provides direct access to MySQL AI’s AutoML via Scikit-Learn-compatible components:
MyClassifierMyAnomalyDetectorMyRegressorMyGenericTransformer
This flexibility allows developers to easily integrate MySQL AI into machine learning workflows.
Core use cases include:
- Dedicated ML pipelines (e.g., fraud detection) using familiar Python and Scikit-Learn paradigms
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
- LLM applications with tool-calling
With clear, composable APIs, the SDK speeds up development and enables advanced use of MySQL HeatWave in both new and existing applications.
Key Benefits:
- Seamless integration of MySQL HeatWave GenAI and ML features into Python projects
- Automated handling of data transformations, ingestion, and table lifecycle tasks to minimize manual work
- Full interoperability with LangChain and Scikit-Learn ecosystems
Natural Language to SQL
MySQL AI lets users query their database using natural language, making it easy for anyone—technical or non-technical—to extract information and gain insights. This boosts productivity and helps uncover valuable information from your data.
When you ask a question in natural language, the system automatically collects only the relevant parts of your database structure, such as table and column names and their relationships. This targeted information is included with your question and sent to the AI model, allowing it to better understand your intent and generate accurate SQL queries tailored to your data.
Before running any query, the system checks the generated SQL for accuracy and consistency, using automated validation to reduce errors. Only validated queries are executed, so you receive reliable results that answer your original question.
With this streamlined, multi-step process, data exploration becomes simple, intuitive, and trustworthy for all users—no SQL expertise required.
Summary
MySQL AI provides integrated, automated, and secure machine learning (ML) and generative AI capabilities. AutoML simplifies ML processes, helping you build, train, and explain ML models without data movement or added costs. In-database LLMs, a built-in vector store, and embedding models enable GenAI, semantic search, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) at reduced infrastructure costs and without data movement.
Fully compatible functionality and APIs provide the option of prototyping on-premises and migrating to the cloud for the benefits of a fully managed service, higher scalability, and better price-performance. Customers in various industries are building and deploying applications with MySQL AI and we encourage you to try building an application yourself.
Get a trial download from Oracle E-Delivery today.
Learn More
Python SDK blog (the SDK is the same for MySQL AI and MySQL HeatWave)
