We are excited to announce the release of Natural Language to SQL (NL2SQL) capability for MySQL (with the AI option) and MySQL HeatWave cloud service. Natural language interface is essential for modern data platforms, allowing users to explore information more quickly. NL2SQL capability converts natural language statements into SQL queries, simplifying data analysis, accelerating insights, and unlocking more value from data.
This new capability in MySQL HeatWave which allows natural language access to structured data complements our existing support in MySQL and MySQL HeatWave for querying documents in natural language – so now you can use natural language to access both structured and unstructured data.
NL2SQL is generally available across all realms in OCI and other clouds where MySQL HeatWave is deployed, and through the MySQL AI release, also available on‑premises.
Read more about MySQL AI functionality in our latest update.
NL2SQL available on-premises and in the cloud
Natural-language interfaces are key to unlocking enterprise data for a broad audience. Customers can deploy this capability wherever it is needed:
- On-premises with MySQL AI, to run the same functionality locally on smaller, self-managed compute.
- In the cloud with MySQL HeatWave, for lower cost, higher performance, better scalability and access to larger LLMs which yield higher quality translation.
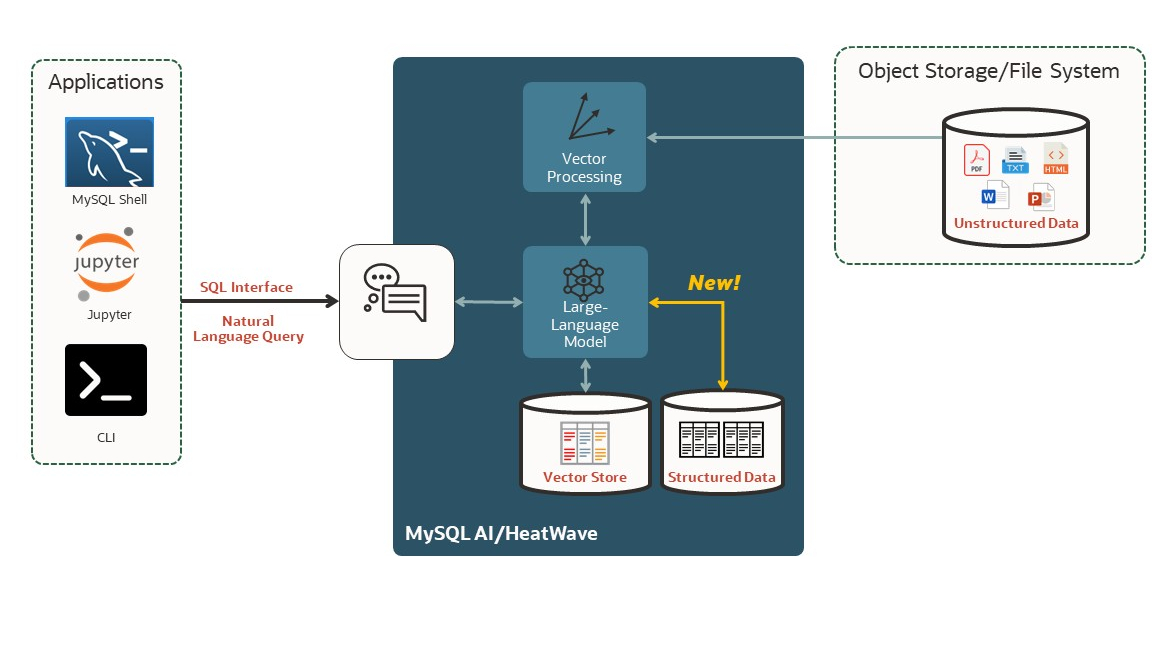
By enabling interaction with MySQL database in natural language, analytical tasks become accessible to business users, data scientists, domain experts and developers alike. Natural‑language interaction with enterprise data is supported across familiar tools and interfaces, including standard MySQL client, MySQL Shell VS code extension, Jupyter Notebooks, MySQL Studio (a new visual interface for MySQL), SQL APIs via a single stored procedure, and the HeatWave REST Service. With this, customers can query and analyze both unstructured text (via RAG with the HeatWave vector store) and structured data (via NL2SQL). The user experience is consistent in MySQL HeatWave (cloud) and MySQL AI (on‑premises), allowing applications to run locally or leverage MySQL HeatWave service for lower cost, better performance and access to larger models.
End-to-end Natural Language to SQL in MySQL
LLMs translate natural-language questions into SQL. To make those results accurate and trustworthy at enterprise scale, MySQL adds a set of in-database steps that enhance, validate, and automatically execute the generated SQL.
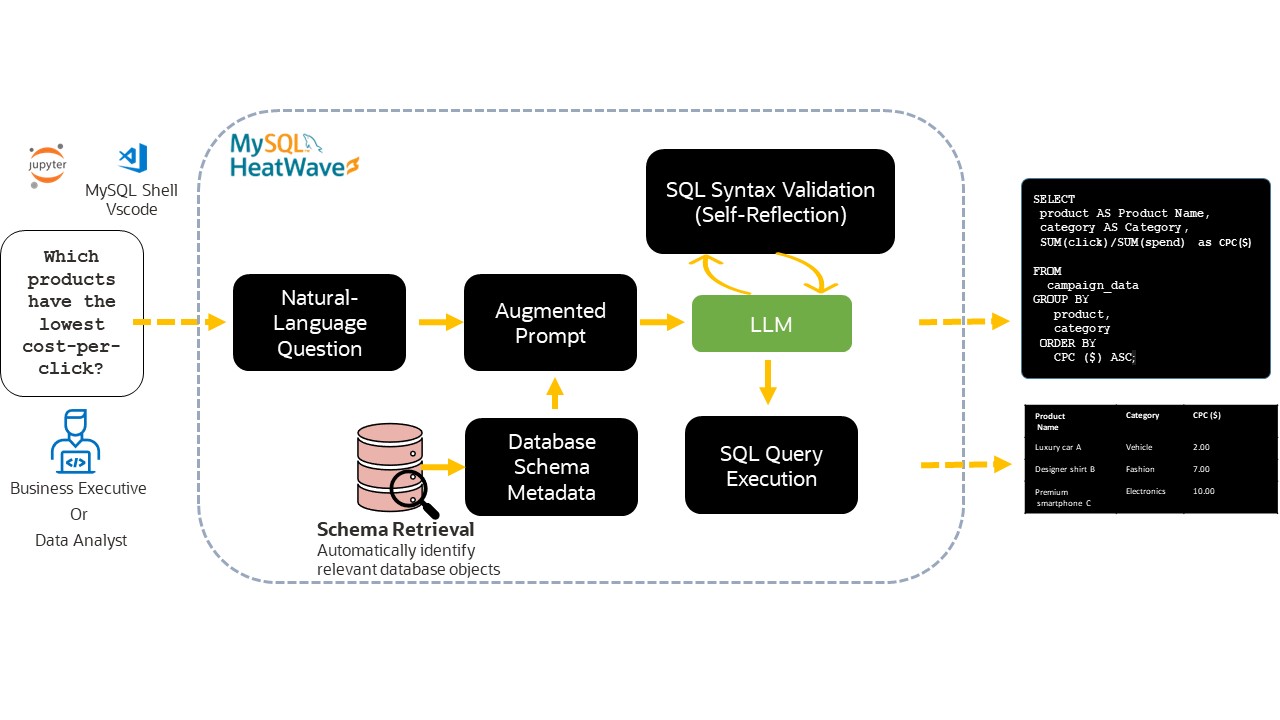
For each natural language query, MySQL does the following:
- Gather relevant metadata: Identify and summarize schema elements (tables, columns, keys, relationships) likely related to the question.
- Select and scope context: Retrieve only the most relevant schema details to avoid prompt bloat and ambiguity.
- Augment the LLM prompt: Package the user question together with the scoped schema context (“augmented prompt”) to guide SQL generation.
- Parse and validate the SQL: Check syntax and validate against the actual schema to catch missing tables/columns and incompatible types early.
- Self-reflect and auto correct: Run an automated review step to detect common issues (e.g., alias mismatches) and revise the SQL when possible.
- Enforce permissions: Respect database privileges so generated SQL only accesses data the requester is authorized to see.
- Execute (optional/automatic): Execute the validated SQL on HeatWave, or return it for review
- Return results with traceability: Provide the final SQL and execution outcome so users can review, reuse, or refine.
Together, these capabilities deliver more precise SQL on complex schemas, fewer manual edits with faster iterations, and a fully integrated, easy-to-use solution.
Access NL2SQL from multiple interfaces
NL2SQL is accessible through multiple interfaces so users can work in their preferred tool:
- SQL APIs for programmatic integration
- MySQL Shell with the VS Code extension
- MySQL Studio
- MySQL HeatWave REST Service
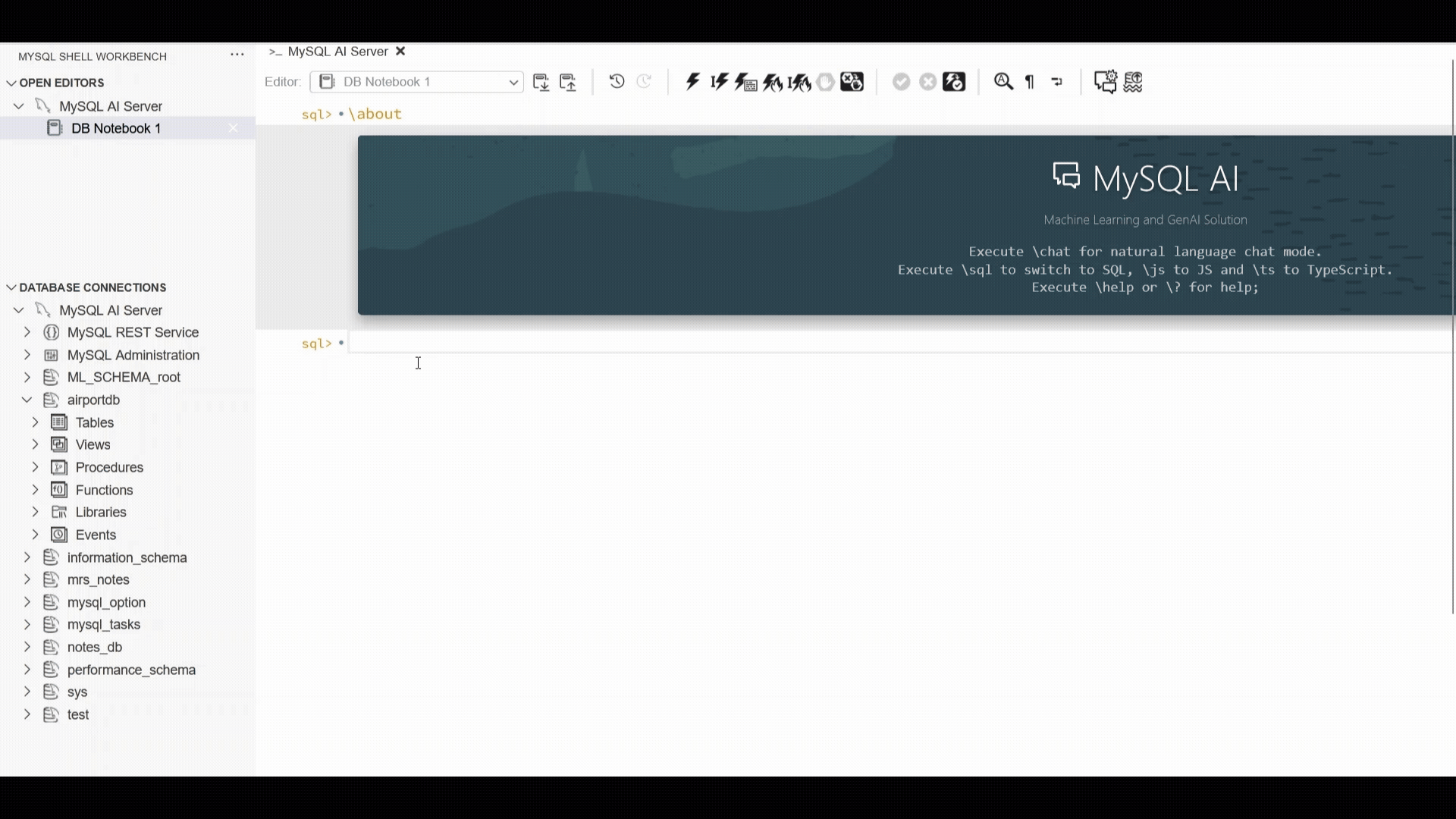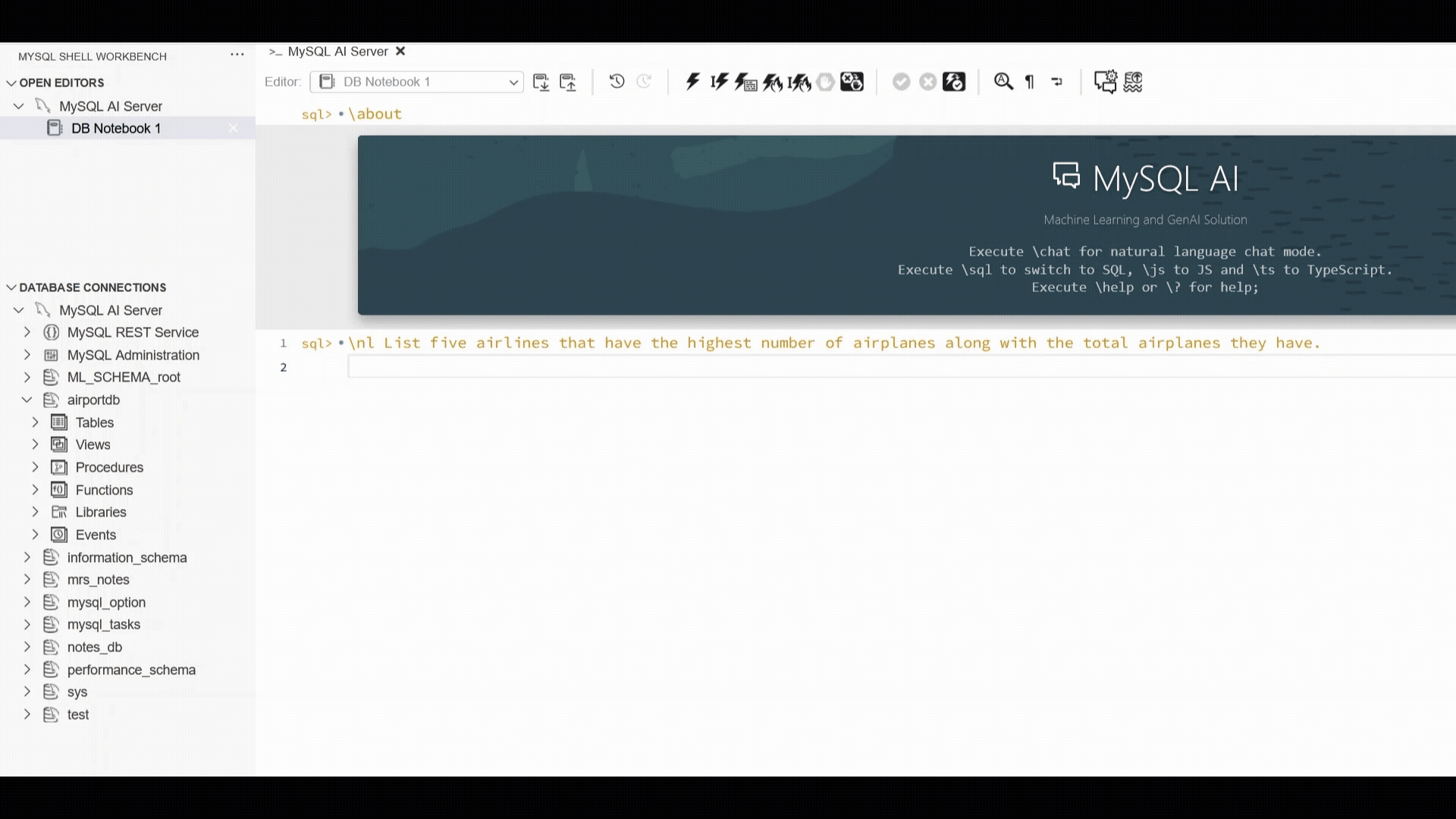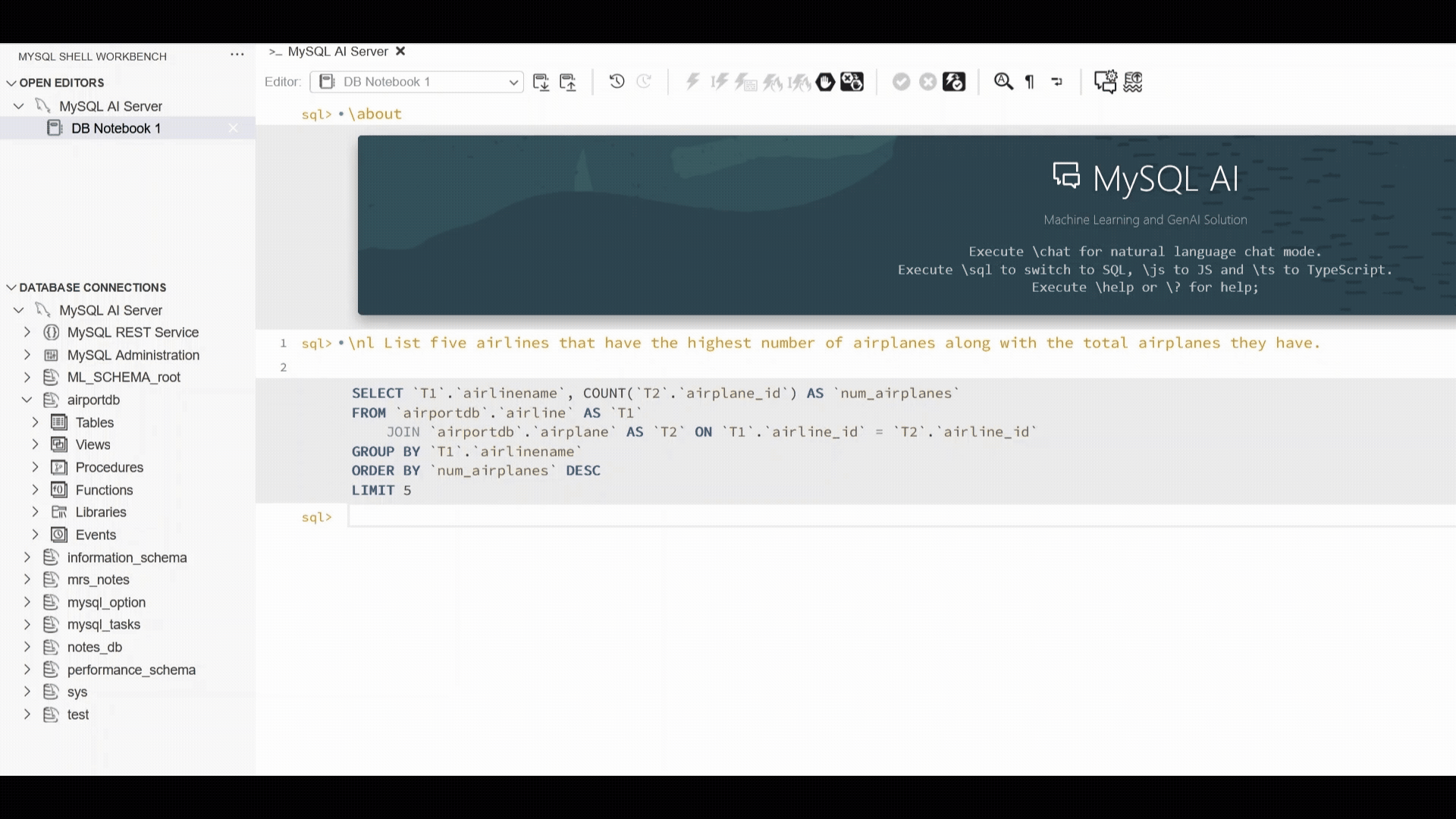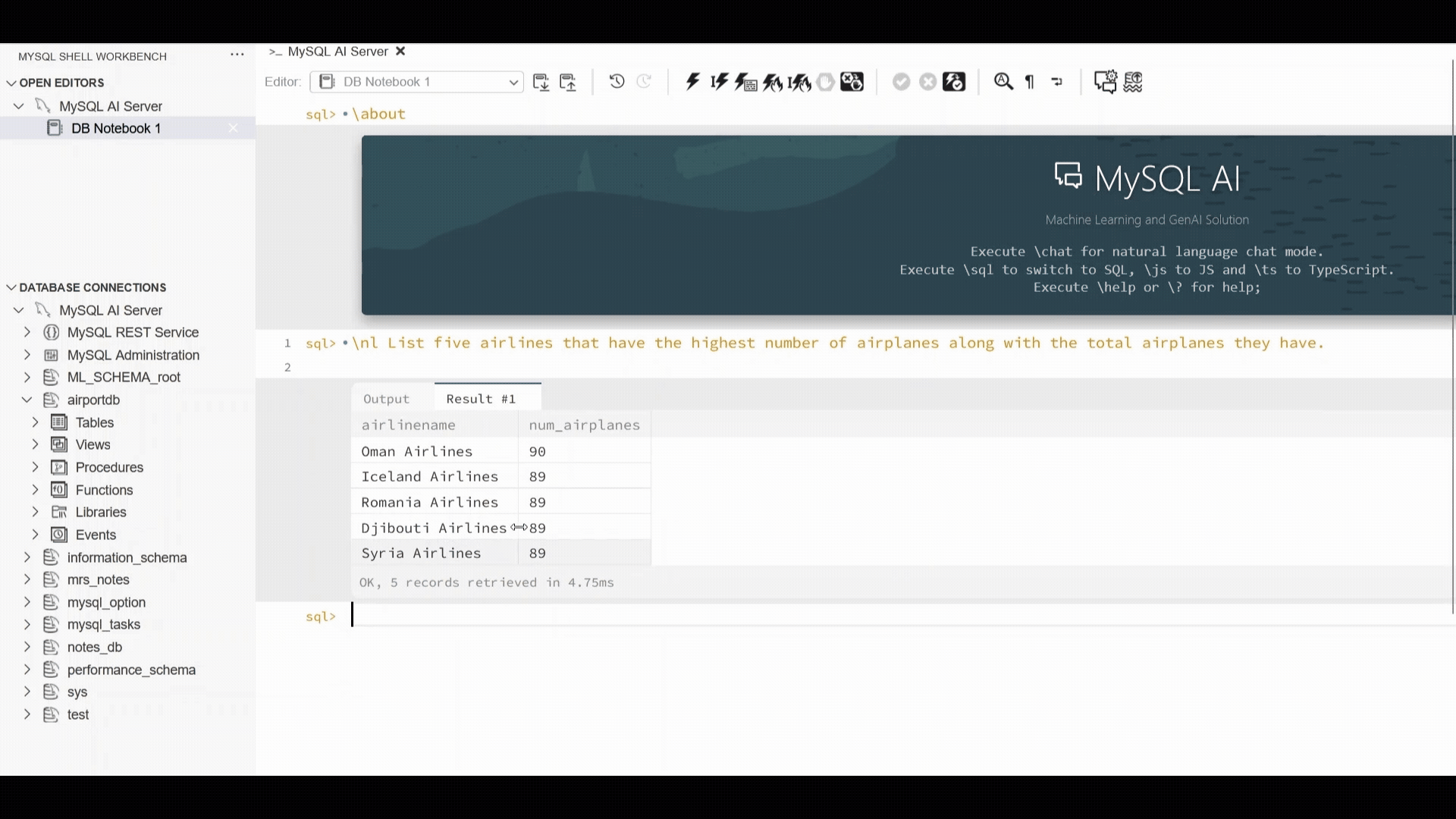
The example below showcases the MySQL Shell plugin for VSCode workflow which has introduced support for “\nl”: enter a plain‑language request, and the extension generates the SQL, executes it, and displays both the SQL and the result set. This provides a fast, consistent way to interact with structured data using natural language, alongside the other supported interfaces.
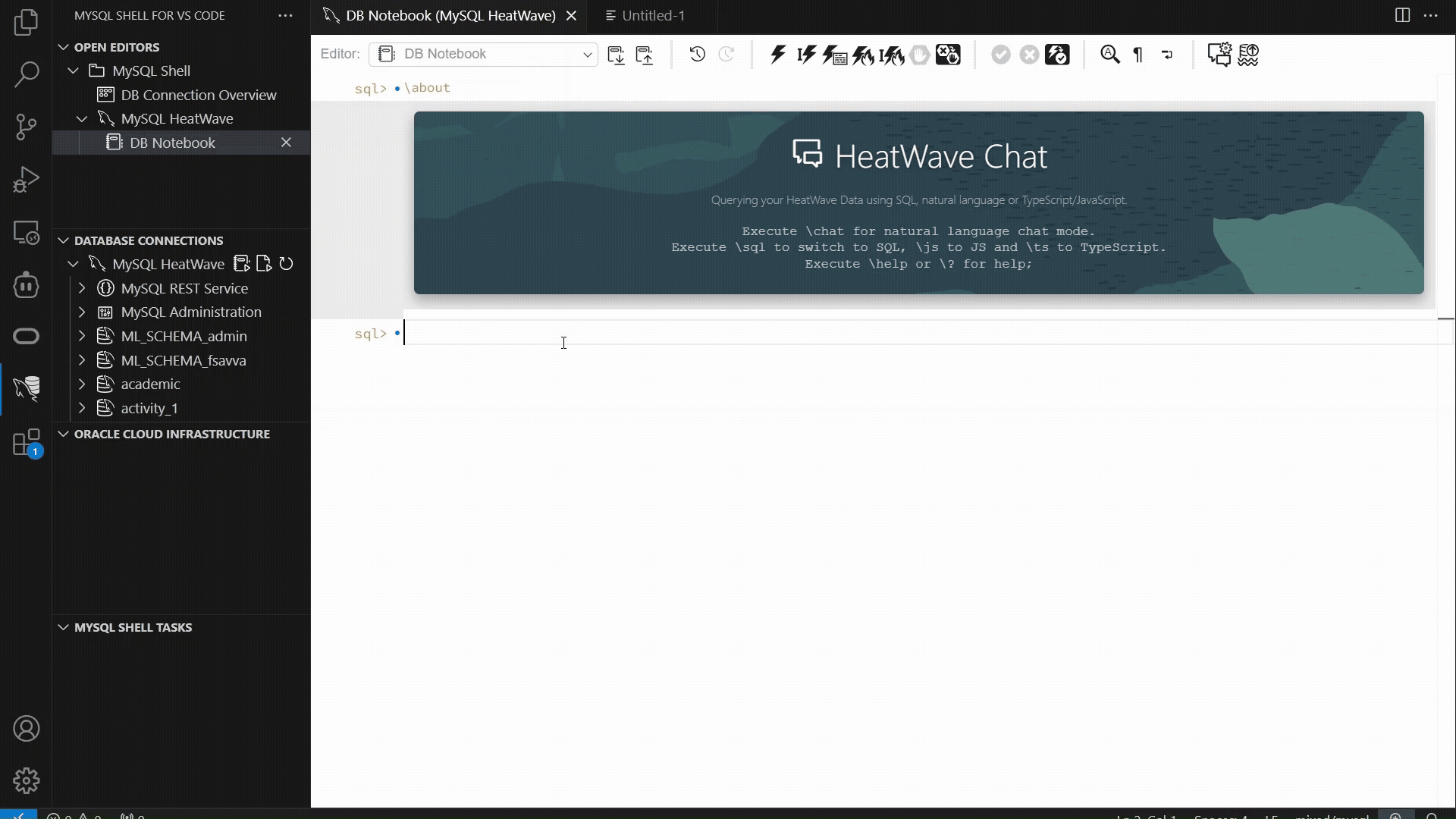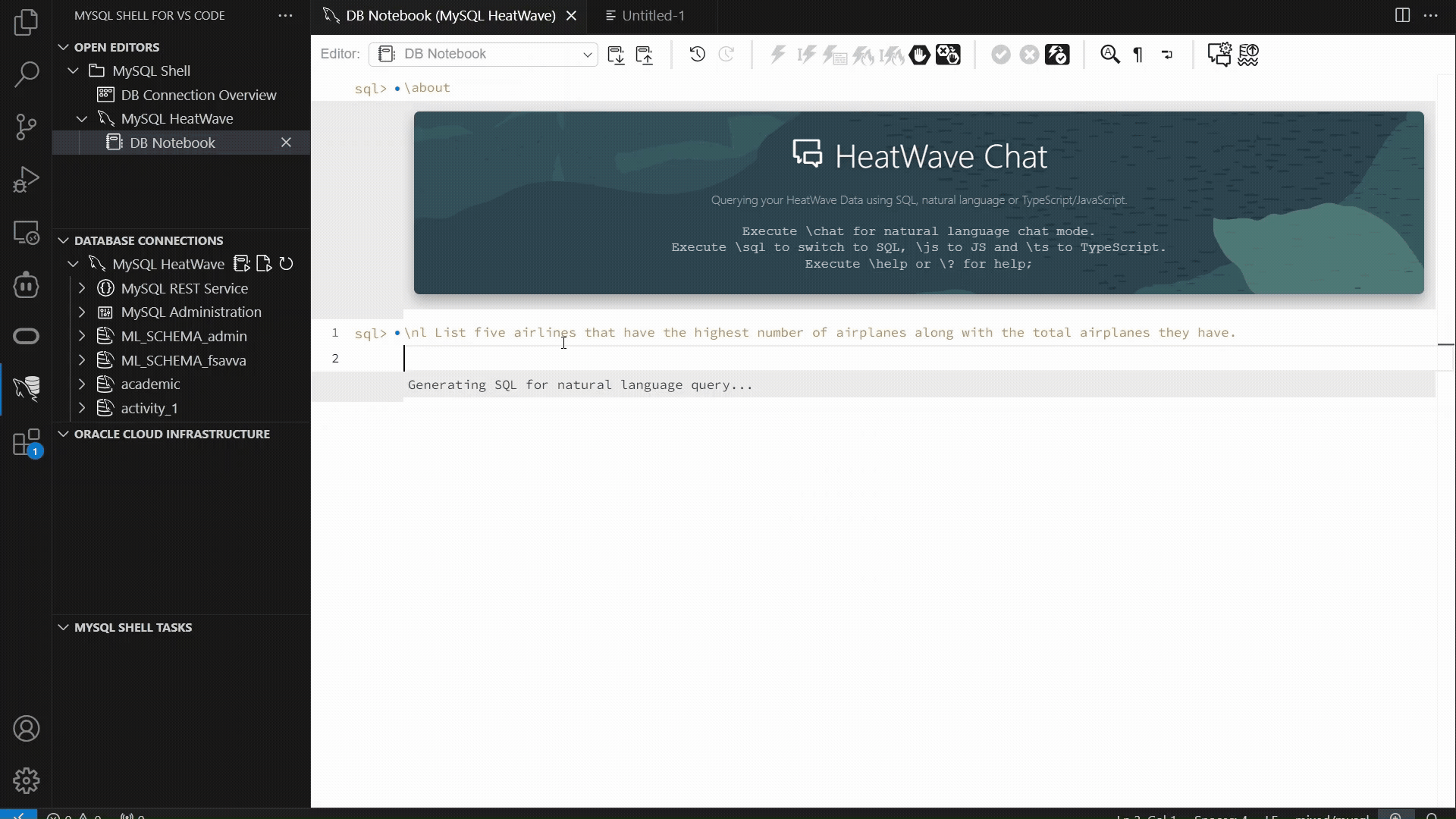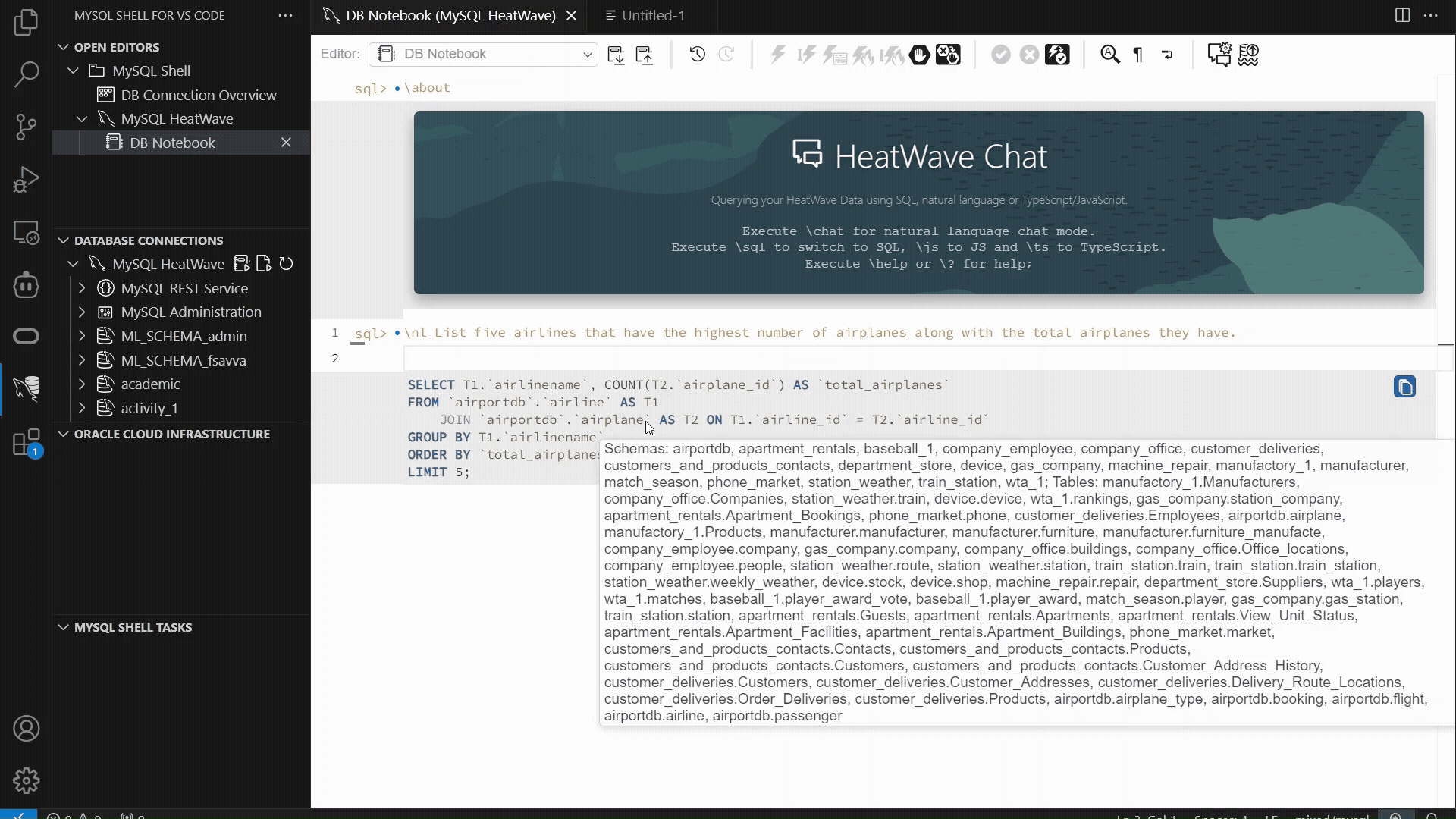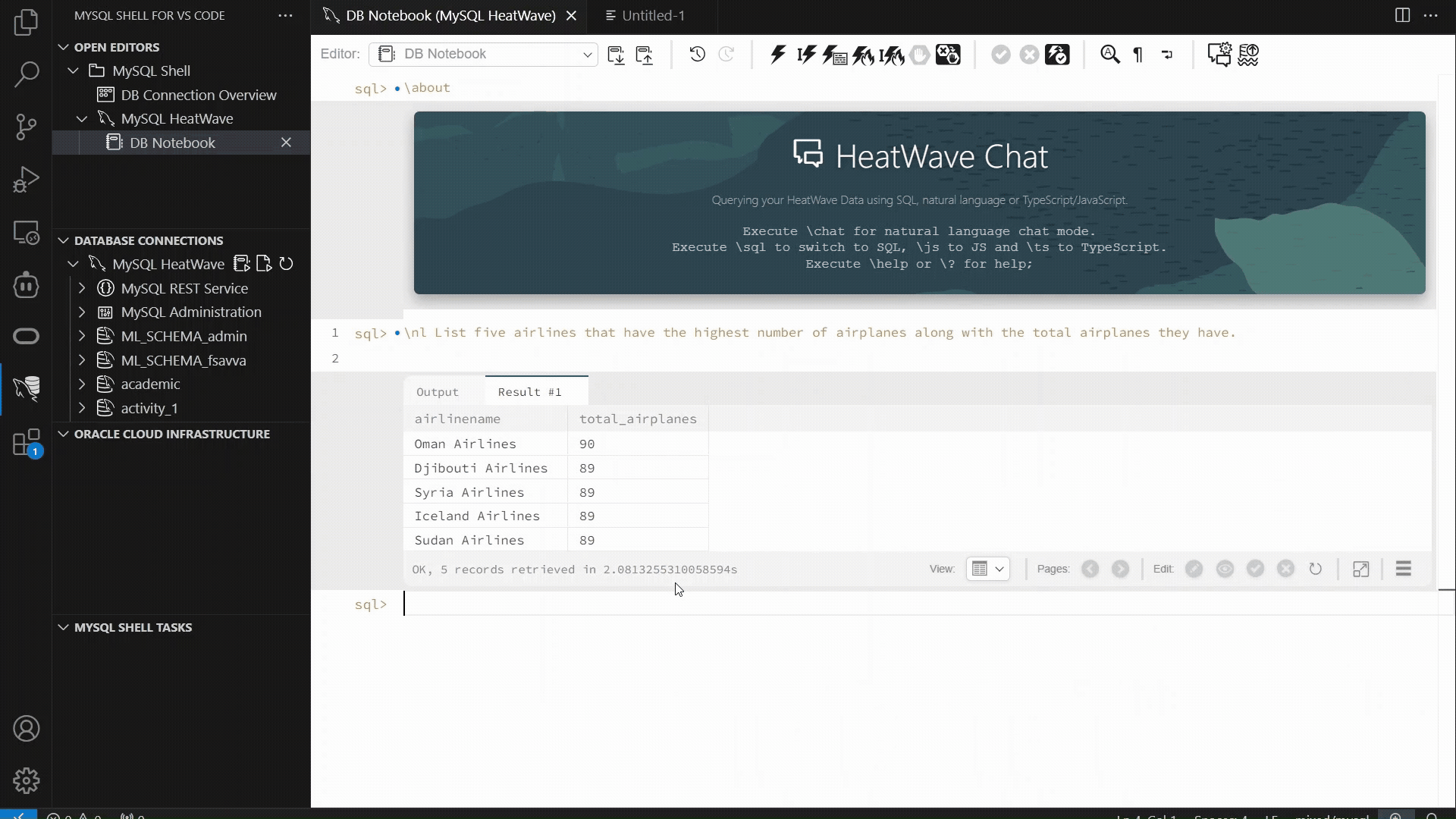 MySQL HeatWave |
 MySQL AI |
The SQL interface is the lowest-level API, giving customers a precise and transparent way to call NL2SQL from any standard SQL tool and reuse the pattern in scripts, automation, and applications. NL2SQL can be invoked via a single stored procedure, enabling clients to submit natural language prompts, receive the generated SQL, and based on options, execute and return results.
CALL sys.NL_SQL(input, @output, options)
Here, input is your natural language question, @output is a user-defined session variable to store results, and options is a JSON object for customizing the query generation. Options allow you to control query execution, restrict schema or table metadata, specify which Large Language Model to use, adjust verbosity, enable retries for syntactically invalid SQL, and include table and column comments. After processing, @output contains valuable details such as the generated SQL, validation results, and metadata context.
We use the well known AirportDB to demonstrate how you can query your data using natural language. A basic call can be issued as follows.
CALL sys.NL_SQL("What is the total number of bookings priced over $200?", @output, NULL);
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Executing generated SQL statement... |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| SELECT COUNT(`booking_id`) FROM `airportdb`.`booking` WHERE `price` > 200 |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
+---------------------+
| COUNT(`booking_id`) |
+---------------------+
| 32699080 |
+---------------------+
This will automatically identify all relevant database objects and execute the generated SQL statement.
Summary
In this blog, we announced the availability of Natural Language to SQL (NL2SQL) support in MySQL – both on premise and in the cloud. The NL2SQL generated by LLMs has been augmented by various techniques in MySQL which improve the quality of the SQL generated. Customers can interact in natural language with both structured data and unstructured text (via RAG). NL2SQL is accessible from multiple interfaces, including a single stored procedure for programmatic use, MySQL Shell, Jupyter Notebooks, the new MySQL Studio Console and MySQL HeatWave REST Service. On‑premises, users can run the same functionality on local compute or migrate to the cloud for lower cost, better performance and leverage larger models. We believe this functionality will improve the productivity of MySQL developers and will make enterprise data analysis richer with MySQL.
