[Updated November 2023] General availability of MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse was announced on July 20, 2023. If you didn’t see the announcement webcast live, you can watch it on-demand.
Read about additional HeatWave Lakehouse enhancements announced at Oracle CloudWorld 2023
MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse has been praised by leading industry analysts as “an unprecedented innovation in cloud data services.” Yet, you may be wondering “why should this matter to me and my organization?”
This blog aims to answer that question. First, we’ll start out with the basics…
What is MySQL HeatWave?
MySQL HeatWave is the only cloud service that combines transaction processing, machine learning, and real-time analytics across data warehouses – and now data lakes – within one MySQL database. MySQL HeatWave eliminates the need for separate analytics databases, lakehouse, and ML cloud services, and for complex, time-consuming ETL processes between those disparate information silos. Customers avoid the latency and security risks of data movement between data stores while reducing costs. MySQL HeatWave also includes MySQL Autopilot, providing workload-aware, machine learning-powered automation of various aspects of the database system lifecycle. MySQL HeatWave uses the standard MySQL APIs and syntax. If you have existing MySQL applications, you can migrate them to MySQL HeatWave without changes.
97% of data isn’t used
To remain competitive in today’s business environment, it’s critical for organizations to perform analysis across a wide variety of data from various sources. Different data types often have different formats, and are stored in different locations.
For example, organizations need to query mission-critical data used for daily operations, such as financial transaction systems, online reservation bookings, or inventory control and production scheduling—which is stored in databases. Yet, a large amount of data is not stored within databases, and is instead stored in files, such as IoT data, web content, log files, etc. Data lakes on object stores have become a popular method for the cost-effective storage and management of large-scale file data. Hence it has become increasingly important to analyze data across both databases and object storage to gain business insights.
So, why does 97% of data still remain unused?
The challenge: analysis across different data types
Many of the applications that generate file data are designed to work with file system abstraction; it takes far more tedious labor and time to store it within a database. A couple of examples: If you want to move a file that has a simple structure—for example a CSV file—into a database to run analytics queries, you have to transform that data, as well as format it and write it into persistent storage to query it via the database. This can mean writing your own scripts to process this data, or installing an ETL tool to perform these mappings and transformations. In general, this file data will change rapidly. This means that when users have indexed this data in the database, they have to constantly rebuild those indexes and update the associated statistics every time a change occurs to avoid performance degradation. It’s hard to justify the complexity, time, and expense of transforming file data into OLTP data structures that traditional databases are designed to use.
The solution: HeatWave Lakehouse simplifies data management
For those looking to simplify their data management, the addition of lakehouse capabilities to MySQL HeatWave is a game changer. It enables you to combine transactional data in the database with object store data in a single query, using standard MySQL syntax. Users can query up to half a petabyte of data from object storage in a variety of file formats like CSV, Parquet, and even exports from other databases like Aurora and Redshift with MySQL HeatWave, and optionally combine it with data from MySQL’s InnoDB storage engine in a single SQL query. As opposed to traditional lakehouse offerings, MySQL HeatWave makes this process very easy – you can complete it in 3 simple steps.
What does this mean for you?
You no longer need to use multiple services, pay for storing multiple copies of your data, nor perform complex ETL processes to gain lakehouse capabilities. With MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse, object store files are queried directly by HeatWave without copying the data into the MySQL database. Data lakehouse capabilities just became more accessible!
5 Reasons to consider adopting HeatWave Lakehouse
1. Ease of use
It can be complex to query data in object storage. Many organizations lack the skills, budget, or both to perform the complex integration needed. With MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse, there’s no transformation into the persistent storage representation of MySQL. In other words, this means that data is not copied from the object store to the MySQL database. Instead, data from files in the object store is converted into the HeatWave in-memory optimized format and loaded into the HeatWave in-memory cluster for processing.
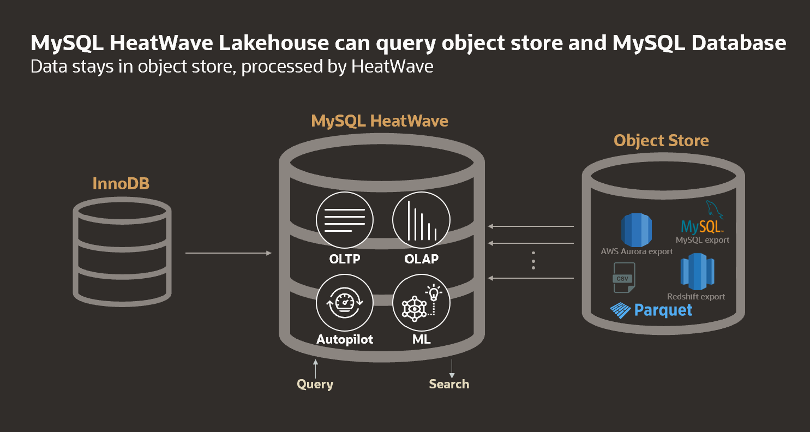
Moreover, you use standard MySQL syntax to query data in the object store together with your data in the database. DDLs are automatically generated by MySQL Autopilot for you, which you can then execute to query data across both files and tables.

In addition to the elimination of ETL, here are some more complexities alleviated by MySQL Autopilot:
• Difficulty estimating accurate cluster size—You want a cluster big enough to process your workload, but don’t want to waste money over-provisioning…nor time to determine the proper size via trial and error. MySQL Autopilot automatically determines the optimal cluster size for you using machine learning.
• Lack of visibility into the schema of file data—MySQL Autopilot automatically infers the mapping of file data to the corresponding schema definition for all supported file types, including for files without metadata like CSV. Even for a file format like Parquet that contains metadata, MySQL Autopilot provides recommendations on column precisions. As a result, you don’t need to manually define and update the schema mapping of files, saving time and effort.
“As an ex-IT executive, I have felt the pain associated with data integration. Different types of .CSV files with different schema mappings can cause hours of headache in trying to perform this very tedious function. Hours that could otherwise be spent focusing on more proactive tasks. With MySQL Autopilot, MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse automatically generates corresponding schema without requiring the user to specify anything about the .CSV file. MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse can simplify the life of data management professionals and should improve the customer experience.”—Matt Kimball, Vice President, Principal Analyst, Moor Insights & Strategy
• Lack of visibility into time needed for data loading prevents planning (“Will loading this data take 4 hours or 24 hours?”) MySQL Autopilot estimates data load time for you based on the suggested cluster size.
For in-depth technical specifics about all HeatWave Lakehouse capabilities that enable greater ease-of-use check out this blog.
2. Faster speeds enable faster time to market
Perhaps you’re thinking: “I want to leave my data in the object store because I have other applications using it, BUT…traditionally, it’s faster to run complex queries in the database than across flat files in object storage.” No longer is this an “either/or” decision with MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse.
• Query data across database and object store with identical performance—Lauded by analysts as an “industry first,” querying the data in object storage is as fast as querying the database. This is particularly noteworthy because it dramatically reduces the time between wanting to know the answer to a complex business problem and obtaining it.
As stated by leading industry analyst Holger Mueller of Constellation Research, “With query performance parity, HeatWave allows CxOs to stop worrying where to put data and how to query it.”
• Eliminate the long provisioning, query, and data load times that prevent real-time insights/analysis—MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse is dramatically faster than alternative solutions. Regardless of the size of your organization, you’ll benefit from time saved, and won’t have to worry about latency as your data volumes grow. For example:
- Provisioning: 512 nodes can be provisioned in under 16 minutes
- Query Time: In the record-setting 500 TB TPCH benchmarks HeatWave Lakehouse is 9X faster than Amazon Redshift, 17X faster than Snowflake, 17X faster than Databricks, 36X faster than Google BigQuery
- Data Load Time: 500 TB TPCH Benchmarks show that HeatWave Lakehouse is 2X faster than Snowflake, 6X faster than Databricks, 9X faster than Amazon Redshift, 8X faster than Google BigQuery.
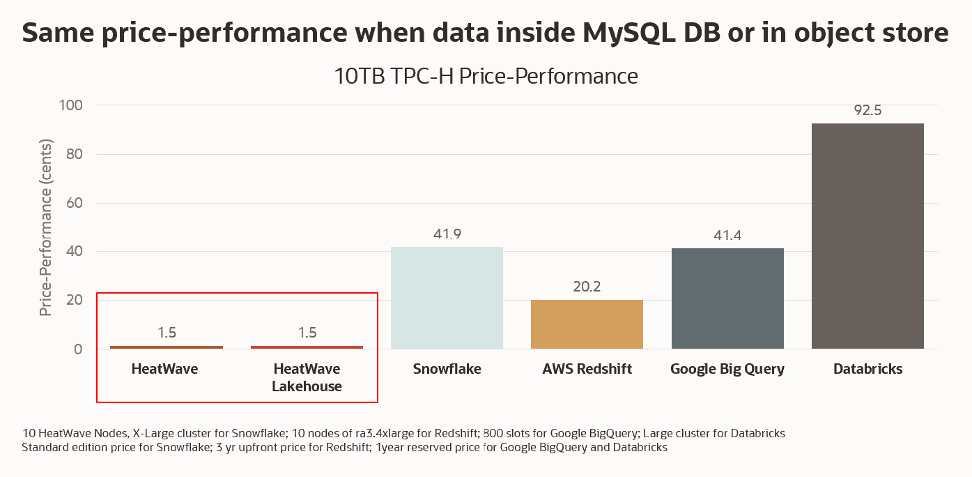
3. Industry’s best price-performance for data lakehouse
You may be wondering “Won’t it be expensive to achieve HeatWave Lakehouse’s performance levels?”
The answer is no 😊.
MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse offers both the best performance and price-performance for query processing and data loading, as demonstrated by the latest 500 TB TPC-H benchmarks. This means faster time to insights with less impact on your wallet. This is the icing on the cake.
“The close integration of an OLTP database, an in-memory query accelerator, and in-database machine learning with object storage is designed to ensure that organizations don’t need to pay for multiple services and multiple copies of data stored on multiple object stores. Organizations looking for the best value in the cloud data lakehouse landscape must seriously consider MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse.”—Carl Olofson, Research Vice President, Data Management Software, IDC
4. Machine learning on data in object storage made easy
Machine learning with HeatWave Lakehouse was announced at Oracle CloudWorld 2023. This means that customers can now use MySQL HeatWave’s AutoML – a collection of in-database, automated machine learning capabilities known for ease-of-use among developers, data scientists, and data analysts alike – to perform machine learning operations on data loaded from object storage on OCI and AWS.
Automated machine learning is an important addition to HeatWave’s data lakehouse offering because it makes it dramatically easier for you to perform ML tasks on data in object storage – a traditionally onerous endeavor. To underscore the most notable benefit, you don’t need to move data to a separate machine learning service. You can run predictions and explanations on machine learning models to perform regression, classification, prediction, and anomaly detection tasks, generate personalized recommendations (recommender system), conduct time-series forecasting, and more…using data stored inside your MySQL database and in object storage.
In brief, data scientists (and others performing ML) save time, and reduce complexity and tedium thanks to machine learning with HeatWave Lakehouse. Organizations benefit from an increased speed of innovation and time-to-market, as well as reduced costs; because these advanced machine learning capabilities are built-in directly to HeatWave Lakehouse there’s no need to purchase separate services. With AWS on the other hand, you’re charged separately for Redshift ML and SageMaker, not to mention AWS S3 storage.
5. MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse on AWS
If you haven’t already heard about the announcement of MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse on AWS (Limited Availability), read this technical blog to learn how you can replace five AWS services with one and gain the best price-performance in the industry for analytics. In addition to an incredibly user-friendly console, you can continue to run applications on AWS with no changes and without high AWS data egress fees.
How can I try MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse? How can I learn more?
Here are some recommended next steps if you’re interested in learning more about MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse, or trying it out for yourself:
1. Request a MySQL HeatWave workshop for your team
2. Watch this Oracle CloudWorld Keynote replay: The Future of Scale-out Data Processing with HeatWave Lakehouse
3. Get familiar with HeatWave Lakehouse by taking a hands-on-lab
4. Inside MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse on OCI—Read the blog or watch the video for a behind-the-scenes look at the architecture that powers MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse
5. Dive into technical details for MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse
Visit Oracle.com/mysql and follow us on Twitter @MySQL and LinkedIn.
