Auditing is one of the key concerns with Security & Compliance for many organizations.
This article is written to share a tutorial how to do audit log archiving by reading the audit log. The tutorial is for demo purpose only.
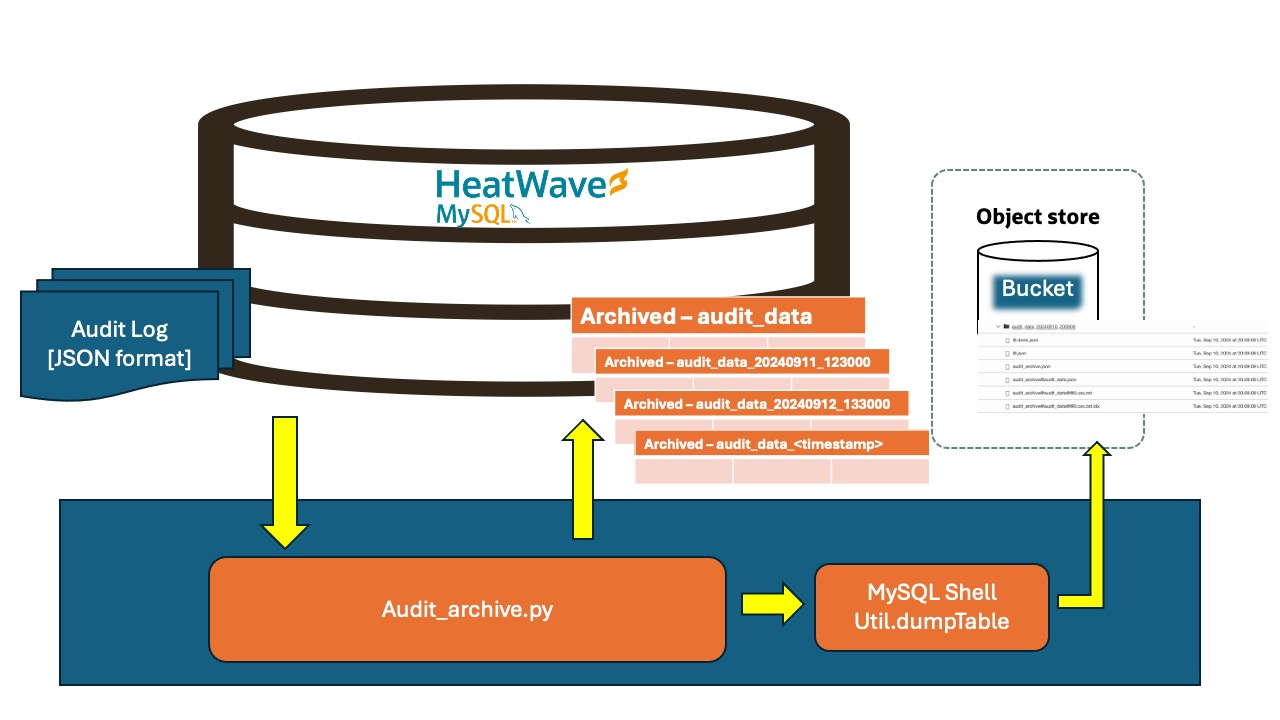
The audit archiving process is to read the audit log using audit_log_read function. The audit record once is archived to Table “audit_archive.audit_data” and the table is renamed to “audit_data_<timestamp>” accordingly. This archived table is dumped to OCI Object Storage bucket using mysql shell utility.
MySQL Audit is the Enterprise feature allowing audit to be implemented. For managed service of “MySQL” on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure – HeatWave Service, Enterprise Audit is installed by default. If running MySQL Enterprise Edition on your compute VM, please refer to the documentation on how to install MySQL Enterprise Audit
Ref : https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.4/en/audit-log-installation.html
The current practice with default AUDIT feature in HeatWave is to generate the AUDIT record in JSON format. Here below is system variables “audit%” example when HeatWave MySQL is provisioned.
mysql> show variables like 'audit%'; +--------------------------------------+---------------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------------------+---------------------+ | audit_log_buffer_size | 10485760 | | audit_log_compression | GZIP | | audit_log_connection_policy | ALL | | audit_log_current_session | OFF | | audit_log_database | mysql_audit | | audit_log_disable | OFF | | audit_log_encryption | NONE | | audit_log_exclude_accounts | | | audit_log_file | /db/audit/audit.log | | audit_log_filter_id | 1 | | audit_log_flush | OFF | | audit_log_flush_interval_seconds | 60 | | audit_log_format | JSON | | audit_log_format_unix_timestamp | ON | | audit_log_include_accounts | | | audit_log_max_size | 5368709120 | | audit_log_password_history_keep_days | 0 | | audit_log_policy | ALL | | audit_log_prune_seconds | 604800 | | audit_log_read_buffer_size | 32768 | | audit_log_rotate_on_size | 52428800 | | audit_log_statement_policy | ALL | | audit_log_strategy | ASYNCHRONOUS | +--------------------------------------+---------------------+ 23 rows in set (0.09 sec)
Audit Log Pruning
Audit Log Pruning is enabled for JSON format on OCI HeatWave Service.
For details about Audit Log Pruning, please refer to documentation : https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.4/en/audit-log-logging-configuration.html#audit-log-pruning
The audit_log_max_size is configured as 5368709120 (~5GB). The audit_log_prune_seconds is configured as 604800 (7 days).
Based on the documentation above,
“Nonzero values of audit_log_max_size take precedence over nonzero values of audit_log_prune_seconds. “
The audit_log_max_size as 5GB takes precedence for pruning action. The “audit_log_rotate_on_size” is about 50MB.
Demo Environment
– Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) HeatWave Service
– Version : 9.0.1
– Compute VM : Oracle Linux 8
– MySQL Shell version : 9.0.1
– oci cli installed and configured
https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/API/SDKDocs/cliinstall.htm#InstallingCLI__oraclelinux8
Creating Table Structure for AUDIT ARCHVE
The archived audit records are stored in DB table(s).
| Table | Description |
| audit_config | To keep track the last record of the timestamp and id for audit log identifier for each server_uuid |
| audit_data_template | The Table Structure template for audit_data |
| audit_data | The Table to store the running archived records. |
| audit_data_<timestamp> | Each time archiving is executed, it retrieves audit records from timestamp registerd in audit_config table until all records are retrieved. Thereafter it renames the table to the audit_data_<timestamp>. |
CREATE TABLE if not exists audit_archive.`audit_data` ( `server_uuid` varchar(45) NOT NULL, `id` int NOT NULL, `ts` timestamp NOT NULL, `class` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, `event` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL, `the_account` json DEFAULT NULL, `login_ip` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL, `login_os` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL, `login_user` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL, `login_proxy` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL, `connection_id` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL, `db` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL, `status` int DEFAULT NULL, `connection_type` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL, `connect_os` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL, `pid` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL, `_client_name` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL, `_client_version` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL, `program_name` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL, `_platform` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL, `command` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL, `sql_command` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL, `command_status` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL, `query` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL, `query_status` int DEFAULT NULL, `start_server_id` varchar(400) DEFAULT NULL, `server_os_version` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, `server_mysqlversion` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, `args` json DEFAULT NULL, `account_host` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL, `mysql_version` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL, `the_os` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL, `the_os_ver` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL, `server_id` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`server_uuid`,`id`,`ts`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci; CREATE TABLE if not exists audit_archive.audit_data_template like audit_archive.audit_data;
Creating Audit archive user
The audit archive user ‘audituser’ is created for the archiving process. This user is restricted to the specified database activities “audit_archive” and the user is granted with privileges to allow reading the audit log and dumping the table to Object Storage.
drop user if exists audituser; create user audituser identified by 'audituser'; grant AUDIT_ADMIN on *.* to audituser; grant all on audit_archive.* to audituser; grant SELECT on mysql.default_roles to audituser; grant REPLICATION CLIENT on *.* to audituser;
Enabling Audit Logging
By default, even the AUDIT Log feature is installed. There is no audit log produced. To enable Audit Logging, filter rule and assignment must be configured.
The following SQL commands are to create a filter rule “log_all” to enable logging and assign the rule “log_all” to all user (“%”). The filter rule “log_nothing” is assigned to audituser to exclude audit archiving activities from being written to the audit log.
SELECT audit_log_filter_set_filter('log_all', '{ "filter": { "log": true } }');
SELECT audit_log_filter_set_user('%', 'log_all');
SELECT audit_log_filter_set_filter('log_nothing', '{ "filter": { "log": false } }');
SELECT audit_log_filter_set_user('audituser@%', 'log_nothing');
Audit Log Archiving
The audit archive python script can be found under github repository
Github Repository : https://github.com/ivanxma/mysql_audit_archive
To execute the audit log archiving, the script is executed via mysqlsh.
Here is example to run the auditarchive_rename.py with parameter “–rename” as true. It reads all audit records since the (timestamp, id) registered in audit_archive.audit_configtable until all records are retrieved. The records are archived to table “audit_data” and finally renamed to “audit_data_<timestamp>” accordingly.
mysqlsh --py --file auditarchive_rename.py --host 127.0.0.1 --port 33060 --rename true
| Parameter | Value |
| host | The IP/host for the HeatWave DB service |
| port | The mysqlx port (e.g. 33060) to the HeatWave DB service |
| user | The user (audituser) to do the audit log archiving |
| password | The password for the audit log archiving |
| rename | true / false : to determine if rename to audit_data_<timestamp> or leave it with audit_data table |
| osbucket | Object Storage Bucket Name |
| osnamespace | Object Storage Namespace |
Here is an example to run audit archive for DB and dump to Object Storage
Note : 33060 port is used where the mysqlx port is connected
mysqlsh --py --file auditarchive_rename.py --host 127.0.0.1 --port 33060 --rename true --osbucket audit_archive --osnamespace xxxxxxx
For more information about how to read audit log, please refer to the documentation : https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.4/en/audit-log-file-reading.html
Note:
- The audit_log_read ([arg]) produces exception when reaching the end of audit log. Here is an example exception message which is normal :
MySQL Error (3200): Session.run_sql: audit_log_read UDF failed; Reader not initialized.
- The audit_log_read( [arg] ) when returns the last chunk of log may contain null value for the last record. The code is written to skip the null timestamp record.
- Each time reading the audit log, there is a read buffer which is 32KB [ The default audit_log_read_buffer_size is 32KB ]. The python script sets the session variable to max value [4194304] – 4MB. For more information, please refer to documentation : https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.4/en/audit-log-reference.html#sysvar_audit_log_read_buffer_size
- The mysqlsh python script leverages util.dumpTable to dump the table in csv dialet to Object Storage using OCI Object Storage Bucket and Namespace Syntax. For more information about dumpTable( … ) command, please refe to documentation : https://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql-shell/8.4/en/mysql-shell-utilities-dump-instance-schema.html
