MySQL allows the grouping of grants and privileges using database ROLEs. A ROLE is a named collection of database privileges.
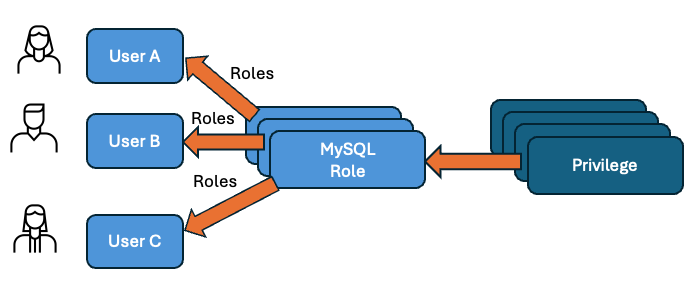
Diagram 1: Users in MySQL can be GRANTED one or more ROLEs, ROLEs can be granted one or more Privilege
A MySQL DBA can
A MySQL application developer can
- Decide which ROLEs are active during a user’s database connection’s session
DBAs should create job-related task-based ROLEs and assign them to users versus maintaining permissions for server users with the same privileges on a per user.
ROLEs allow DBAs to
- Simplify security permissions management
- Avoid mistakes in user privilege assignment
- Define permissions by grouping privileges
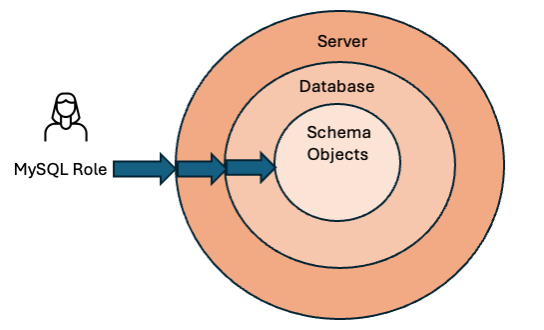
Diagram 2: GRANTS in MySQL define Server, Database (Schema), or Object Level rights
ROLEs can be set as “DEFAULT” using one of the following commands
Default ROLEs define the active privileges of a user when the user first connects to the MySQL server. A user can have additional ROLEs that are not included as DEFAULT. The permissions for these are not applied when initially connected. Once connected, the ROLE(s) that are in effect can be changed to one of more of the ROLEs that were granted to a particular user using:
- SET ROLE – changes the active role(s) within the current session.
Using the SET ROLE, it is possible to either increase privileges or decrease privileges during a user session. From a security standpoint this allows further refinement, providing more granular access control to limit to what is needed for the task hand.
SET ROLE can be used to define a “Least Privilege” model for accessing database objects based on a user’s current task.
Permissions should be limited to the least needed for a specific task.
Consider the following scenario
- The ORDER role (for the Order application) contains privileges for the ORDER table
- The INVENTORY role (for the Inventory application) contains privileges for the INVENTORY table
- Several order entry clerks have been granted both the ORDER and INVENTORY roles
In this scenario, an order entry clerk who has been granted both roles, can use the privileges of the ORDER role when running the INVENTORY application to update the INVENTORY table. The problem is that updating the INVENTORY table is not an authorized action when using the INVENTORY application, but only when using the ORDER application.
To avoid this problem, limit privileges by calling the SET ROLE statement.
Within the Order Application – upon connecting to the MySQL database
SET ROLE ORDER;
Within the Inventory application – upon connecting to the MySQL database
SET ROLE INVENTORY;
With the appropriate SET ROLE, “least privilege” is enforced and will limit users to the privilege needed for a specific task.
Demo
Here is a short youtube on how this works in practice.
Alternatively you can run the SQL from the demo yourself.
Setup the demo – as DBA
mysqlsh -u root -p
# Create each database schema
create schema inventory_schema;
create schema order_schema;
# Define tables in each schema
use inventory_schema;
create table inventory_details (id int, name varchar(44));
INSERT INTO `inventory_schema`.`inventory_details` (`id`, `name`) VALUES (1, ‘Tomato’);
INSERT INTO `inventory_schema`.`inventory_details` (`id`, `name`) VALUES (2, ‘Potato’);
INSERT INTO `inventory_schema`.`inventory_details` (`id`, `name`) VALUES (3, ‘Steak’);
use order_schema;
create table order_details (id int, name varchar(44));
INSERT INTO `order_schema`.`order_details` (`id`, `name`) VALUES (1, ‘Meal Deal’);
INSERT INTO `order_schema`.`order_details` (`id`, `name`) VALUES (2, ‘Kids Meal’);
INSERT INTO `order_schema`.`order_details` (`id`, `name`) VALUES (3, ‘Seafood Combo’);
# create roles
create role ORDER_Role;
create role INVENTORY_Role;
#Grant rights to each role
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE ON `inventory_schema`.`inventory_details`
TO ‘INVENTORY_Role’;
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE ON `order_schema`.`order_details`
TO ‘ORDER_Role’;
# Create
CREATE user order_and_inventory IDENTIFIED BY ‘YOUR_PASSWORD’;
CREATE user order_only IDENTIFIED BY ‘YOUR_PASSWORD’;
# Grant the user order_and_inventory – both roles
grant INVENTORY_Role, ORDER_Role to order_and_inventory;
# Grant the user order_only – only the ORDER_Role
grant ORDER_Role to order_only;
# Set the Default roles for each user
set default role INVENTORY_Role, ORDER_Role to order_and_inventory;
set default role ORDER_Role to order_only;
Run as the’order_only’ user – who does not have access to the Inventory Schema
mysqlsh -u order_only -p
# View the user and their role
select user(), current_role();
# This will fail – as the INVENTORY_Role was not assigned
select * from `inventory_schema`.`inventory_details`;
# This will succeed – as the Order_Role was assigned
select * from `order_schema`.`order_details`;
Run as the ‘order_and_inventory’
#Demo – As user who has rights to both tables via roles
mysqlsh -u order_and_inventory -p
# View the user and their role
select user(), current_role();
# This will succeed – as the INVENTORY_Role was assigned
select * from `inventory_schema`.`inventory_details`;
# This will succeed – as the Order_Role was assigned
select * from `order_schema`.`order_details`;
SET ROLE ORDER_Role;
select user(), current_role();
# This will fail now – as the INVENTORY_Role is no longer in place
select * from `inventory_schema`.`inventory_details`;
select * from `order_schema`.`order_details`;
Conclusion
Creating ROLEs and using SET ROLE to limit privileges greatly enhances security by enforcing the principle of least privileges. By minimizing the active privileges using SET ROLE, cyber or other attacks on your applications and MySQL Server are far less likely to succeed.
As always, thank you for using MySQL!
