PCI DSS 4.0 Compliance and MySQL
The financial services industry and its customers are increasingly embracing digital banking, leading to a surge in digital payment transactions. This rapid growth, coupled with the constantly evolving threat landscape, significantly increases the risk of data breaches. Protecting customer data is paramount in this environment.
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a crucial framework for organizations that handle cardholder data. Developed to enhance payment card security globally, PCI DSS outlines security requirements and testing procedures to safeguard sensitive information.
While primarily focused on payment card data, the principles of PCI DSS can be applied to enhance the overall security posture of organizations within the broader payment and technology ecosystems.
| Goals |
Requirements |
| Build and Maintain a Secure Network and Systems |
|
| Protect Account Data |
|
| Maintain a Vulnerability Management Program |
|
| Implement Strong Access Control Measures |
|
| Regularly Monitor and Test Networks |
|
| Maintain an Information Security Policy |
|
Over time, threats and technology evolve. To address this, the PCI Security Standards Council (SSC) released version 4.0 of the Data Security Standard (DSS).
PCI DSS 4.0 is designed to enhance cardholder data security by:
- Promoting a holistic security approach: Organizations are encouraged to take a broader view of their security posture.
- Addressing emerging threats: The standard adapts to the evolving threat landscape posed by advances in technology.
Key drivers for the improvements in PCI DSS 4.0 include:
- Evolving industry needs: Ensuring the standard remains relevant to the evolving security needs of the payments industry.
- Continuous security: Promoting a continuous and proactive approach to security.
- Enhanced testing: Improving testing and validation methods for more effective security assessments.
- Increased flexibility: Offering organizations greater flexibility in their implementation approaches while maintaining strong security outcomes.
PCI DSS 4.0 shifts the focus from prescriptive methods to achieving strong security outcomes.
The six core areas of PCI DSS 4.0 are:
- Flexibility: Provides organizations with the flexibility to choose between custom or standardized implementation approaches, focusing on achieving security outcomes.
- Security: Enhances security through stronger standards that promote continuous and governed security throughout the data lifecycle (processing, storage, and transmission).
- Authentication: Emphasizes the use of stronger, NIST-aligned authentication methods for accessing payment systems and authorizing transactions.
- Encryption: Promotes broader adoption of cryptographic best practices to protect network transmissions across all environments, including cloud, mobile, and IoT.
- Monitoring: Enables the use of risk-based solutions for continuous monitoring, allowing for faster deployment of security controls.
- Testing: Requires a higher level of critical control validation, including increased testing requirements.
Timing of PCI DSS 4.0:
- March 2022 – PCI DSS version 4.0 published.
- March 2024 – PCI DSS v3.2.1 is replaced with 4.0.
- March 2025 – PCI DSS 4.0 goes into full effect.
Impact
While PCI DSS 4.0 impacts the entire payment card supply chain, how the controls are implemented and by whom varies based on the environment.
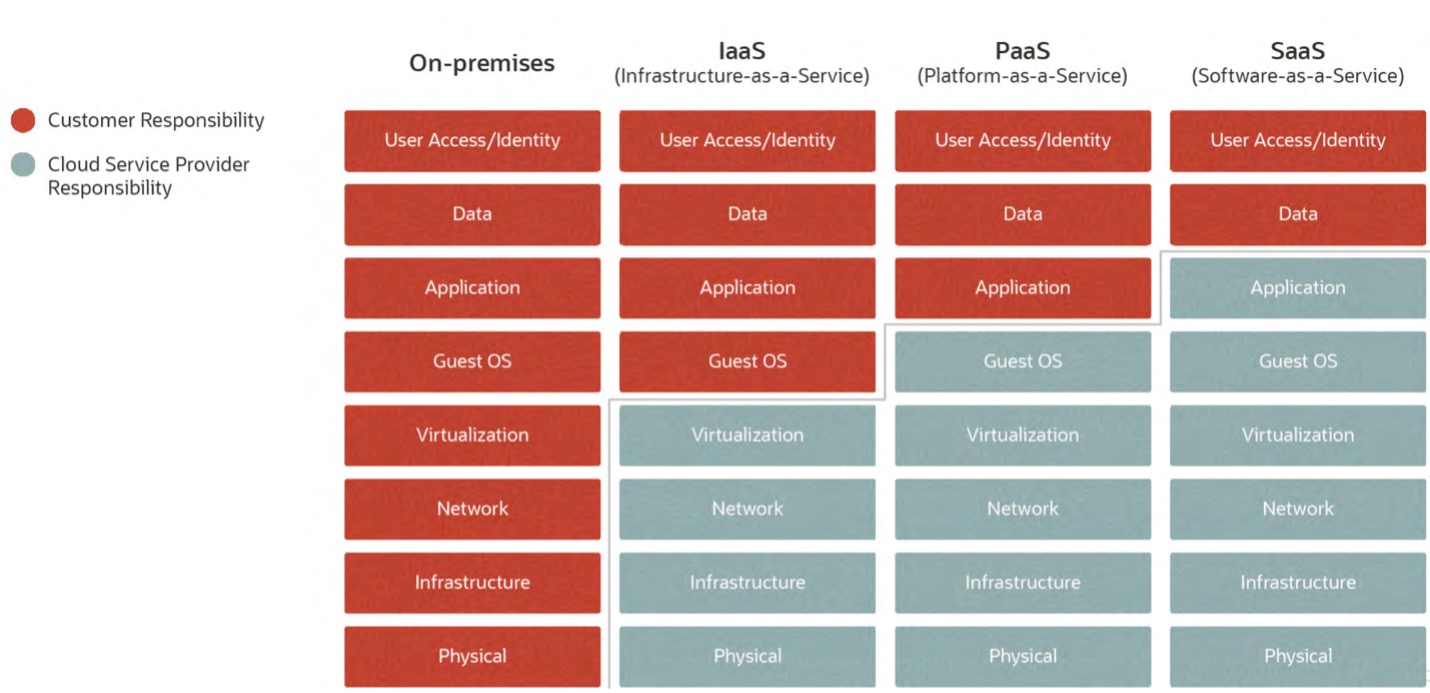
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Security
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) offers a robust security posture with a defense-in-depth model. OCI’s comprehensive security services integrate seamlessly across all layers, providing automated protection based on Oracle’s decades of security expertise. This simplifies security management for organizations, allowing them to focus on core business initiatives while OCI handles the heavy lifting.
PCI DSS 4.0 Compliance with OCI
OCI is independently assessed by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) against the latest PCI DSS 4.0 requirements. To access these documents from the OCI Console navigate to Identity and Security and select Compliance.
OCI HeatWave MySQL and PCI DSS
HeatWave MySQL is included in these assessments, ensuring its compliance with PCI DSS 4.0 and other relevant regulations and included in OCI Compliance.
Customer Responsibilities with HeatWave MySQL
It’s important to note that while OCI takes care of the underlying infrastructure security, customers remain responsible for:
- Their applications
- User access and identity management
- Data security within a HeatWave DB System (including grant and revoke controls)
Meeting User Access/Identity Requirements with OCI Identity
OCI Identity integration with HeatWave MySQL helps organizations meet PCI DSS 4.0 user access and identity requirements. OCI Identity provides advanced user authentication and management capabilities required by PCI DSS 4.0.
Preparing MySQL Enterprise for PCI DSS 4.0
Organizations using MySQL Enterprise on-premises databases need to adapt to the new requirements and testing procedures introduced in PCI DSS 4.0.
MySQL Enterprise Security Features
Fortunately, MySQL Enterprise offers a robust set of security features that can help organizations meet these compliance requirements. These features include:
- Advanced Authentication: Supports various authentication methods, including Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) which is strongly recommended by PCI DSS 4.0.
- Encryption: Provides encryption for data at rest, in transit, and during authentication using industry-standard protocols like SSL/TLS.
- Access Controls: Granular access controls allow organizations to restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles and permissions.
- Audit Logging: Comprehensive audit logging helps organizations track user activity and identify potential security breaches.
- Security Management Tools: Integrates with security management tools like Oracle Enterprise Manager for MySQL and OpenTelemetry for centralized monitoring and logging.
Addressing PCI DSS 4.0 Pillars with MySQL Enterprise
Let’s consider how MySQL Enterprise addresses the six core areas of PCI DSS 4.0:
- Flexibility: MySQL Enterprise offers a wide range of security options, allowing organizations to choose a configuration that meets their specific compliance needs and security posture.
- Security: The built-in security features and integrations with security ecosystems (LDAP, Kerberos, OpenID Connect, OpenTelemetry, etc.) provide a strong foundation for a secure database environment.
- Authentication: Supports strong authentication methods like MFA to enhance access control.
- Encryption: Provides encryption capabilities for data at all stages.
- Monitoring: Integrates with various monitoring tools for continuous security oversight.
- Testing: While MySQL itself undergoes rigorous security testing, proper configuration and secure coding practices remain crucial to mitigate user-introduced risks.
Importance of Best Practices
Even with robust security features, following best practices for setup, configuration, and ongoing management of MySQL Enterprise is essential to maintain a secure environment. MySQL offers validated guidelines from CIS (Center for Internet Security) and DISA (Defense Information Systems Agency) to assist with security risk assessments and secure configuration.
Conclusion
The evolving digital banking landscape necessitates robust data security measures to protect sensitive customer information. The PCI DSS 4.0 standard provides a comprehensive framework for organizations handling cardholder data. It emphasizes a holistic security approach, continuous monitoring, and flexibility in implementation, while addressing emerging threats.
This blog explored PCI DSS 4.0 requirements and how MySQL Enterprise and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) can help organizations achieve compliance. Remember, staying current with best practices is crucial for maintaining a secure environment.
For further information, refer to the following resources:
CIS Benchmark for MySQL Enterprise
- Reviewed by both CIS Engineers as well as members of the CIS Community
- CIS provide mappings to other controls/regulations including PCI DSS
-
DISA STIG
- Security Technical Implementation Guides (STIGs) are configuration standards developed by the Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA).
Additional Resources
- PCI DSS 4.0 Resource Hub
- PCI DSS Documents Library
- Oracle Trust Center
- MySQL HeatWave
- MySQL Enterprise
As always, thank you for using MySQL!
