Healthcare organizations face the dual challenge of accelerating AI driven innovation while meeting strict privacy, security and regulatory requirements. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) offers a comprehensive set of services: compute, networking, storage, data science and managed generative AI designed to host sensitive healthcare workloads at scale. This blog examines how OCI can be used to build secure, compliant and performant healthcare AI systems. We present reference architecture patterns, best practices for compliance and governance, operational considerations for MLOps and security controls that map to HIPAA, SOC and other common frameworks. Where applicable, we cite OCI documentation and Oracle guidance to ground architectural recommendations.
Why healthcare?
Healthcare organizations are rapidly adopting AI for clinical decision support, population health analytics, operational automation and patient engagement. However, the sensitivity of protected health information (PHI) and strict regulatory regimes (e.g., HIPAA in the U.S., GDPR in the EU) require cloud platforms to provide both technical controls and clear compliance guidance. OCI provides a portfolio of services: Data LakeHouse patterns, OCI Data Science and a managed Generative AI service paired with security first infrastructure and compliance attestations intended to address these needs.
Background: OCI’s Positioning for Healthcare Workloads
Oracle positions OCI as an enterprise-grade cloud for regulated industries, offering:
- Dedicated tenancy and bare-metal options for isolation and performance.
- Well-Architected guidance covering security, reliability, performance, cost and operational efficiency, useful for healthcare architecture reviews Telemedicine and virtual care enablement.
- Managed AI and ML services including OCI Data Science (notebooks, MLOps) and a managed Generative AI service for LLMs, enabling model development, hosting and inference workflows.
- Compliance documentation and region/service level attestations, including HIPAA-assessed regions and service lists, which inform where PHI can be processed and which services are in scope.
These foundations make OCI suitable for healthcare AI when architectures and operational controls are designed with shared responsibility and privacy by design principles.
Reference Architecture Patterns for Healthcare AI on OCI
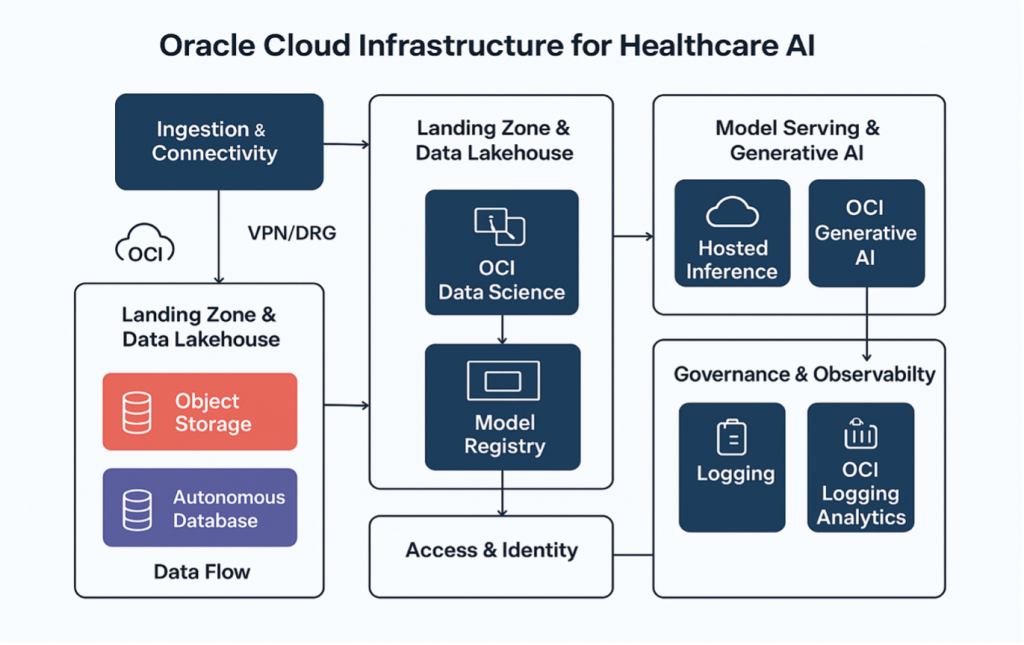
- High-level components
Ingestion & Connectivity: Secure APIs, VPN/DRG (Dynamic Routing Gateway), FastConnect for high-throughput private links to on-premises EHRs or partner systems.
- Landing zone & Data LakeHouse:
Object Storage (encrypted) + Autonomous Database / ADW or Data Flow for ETL, forming a governed data LakeHouse for EHR, imaging, device telemetry and genomics.
- Feature Store & ML Platform:
OCI Data Science + model registry, feature store (custom or via database), training on GPU clusters/bare metal and artifact storage.
- Model Serving & Generative AI:
Hosted inference on managed AI endpoints or OCI Generative AI for LLM-based summarization, triage assistants and clinical note generation.
- Governance & Observability:
Logging, OCI Logging Analytics, Audit, and Application Performance Monitoring for model drift detection and operational metrics.
- Access & Identity:
IAM, compartmentalization, least privilege, and integration with enterprise identity providers (SAML, OIDC).
AI Use Cases and OCI Services Mapped to Healthcare Needs
- Clinical decision support & diagnostics: Use structured EHR data + imaging pipelines in the LakeHouse; train multimodal models on GPU clusters or bare-metal compute; deploy with OCI Data Science MLOps for CI/CD and canary rollout.
- Clinical documentation and summarization (LLM use): Use OCI Generative AI to summarize patient histories, synthesize visit notes and draft discharge instructions while ensuring LLMs do not leak PHI and are deployed within HIPAA-assessed services/regions. Apply retrieval augmented generation (RAG) with private vector stores in OCI Object Storage/Autonomous Database.
- Population health and analytics: Aggregate claims, EHR and SDOH data into a governed Lakehouse; use Oracle Analytics + ML to identify at risk cohorts and generate intervention workflows.
- Operational automation: Prior authorization automation, billing reconciliation, and supply chain forecasting using scheduled MLOps pipelines and event-driven functions. OCI Functions and Streaming enable serverless eventing and decoupled pipelines.
Compliance, Privacy, and Regulatory Controls
- HIPAA & regional compliance:
Oracle publishes HIPAA-assessed regions and services and provides guidance on shared responsibility; organizations must review the in-scope service list and sign appropriate Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) as needed. Deploy PHI-only workloads in HIPAA assessed regions and use in scope services for processing PHI.
- Data residency & sovereignty:
OCI supports region selection and realm configuration (dedicated or local deployment) to meet residency requirements; consider dedicated tenancy or on-prem/edge solutions for strict sovereignty constraints.
- Technical controls:
Encryption: At rest encryption (customer managed keys via OCI Vault) and TLS for transit.
Access controls: Fine-grained IAM policies, compartments and vault backed key management.
- Monitoring & audit:
Retain audit logs, use OCI Audit and Logging Analytics to meet evidentiary requirements for audits and incident response.
- Model governance:
Data lineage & provenance: Track datasets used for training and preprocessing steps.
Explainability: Integrate explainability tooling (SHAP, LIME) into model pipelines for clinical validation and regulatory scrutiny.
- Access controls for models:
Restrict model access, enforce logging of inference requests and mask PHI where possible.
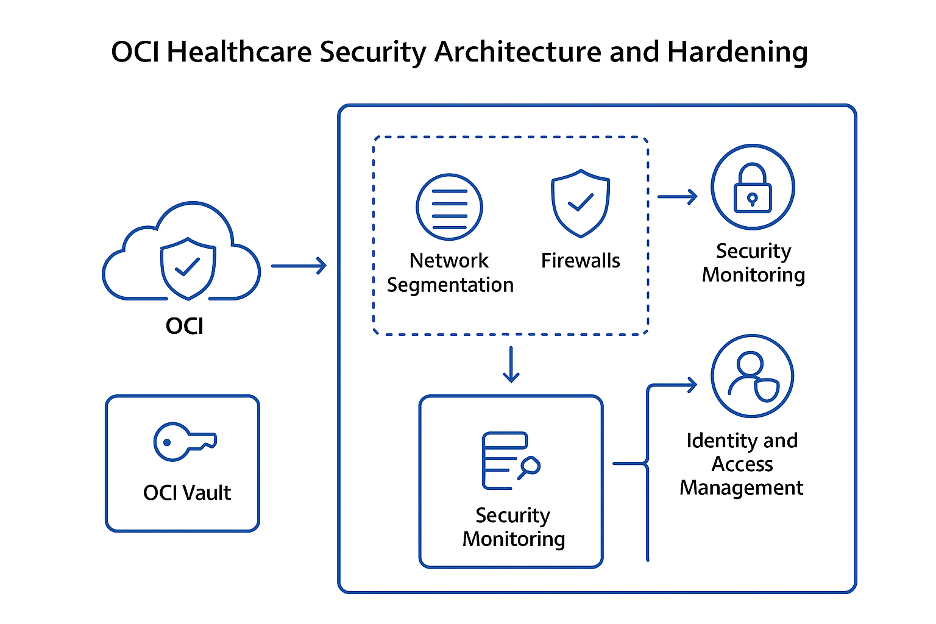
Security Architecture and Hardening
OCI’s security-first architecture provides primitives that healthcare teams must adopt and extend:
- Network isolation with Virtual Cloud Networks (VCNs) and private endpoints.
- Host/Platform hardening: Use OCI’s recommendations for secure configuration of compute, databases, and container platforms; apply immutable infrastructure and vulnerability scanning.
- Secrets & key lifecycle: OCI Vault for keys/secrets and HSM backed key protection for especially sensitive cryptographic operations.
- Secure ML lifecycle: Scan model artefacts and containers (image scanning), sign artifacts and store provenance metadata to mitigate supply chain attacks.
A defense in depth posture combining network, host, data, identity and application controls aligns with OCI’s Well-Architected security pillar.
Case Studies & Industry Signals
Oracle publishes healthcare customer stories where OCI has enabled EHR modernization and analytics capabilities. These examples typically highlight lowered TCO, faster time to insight and improved scalability for clinical workloads. Oracle’s ongoing investments in AI infrastructure and ecosystem deals (model partnerships) indicate a strategic push to make OCI more attractive for enterprise AI workloads, including healthcare workloads that demand high compliance and isolation.
Risks, Limitations, and Ethical Considerations
- Data leakage & model hallucination: LLMs can generate plausible but incorrect outputs and may inadvertently expose sensitive information if trained on PHI without safeguards. Mitigate with strict data handling, prompt-filtering and human in the loop review for clinical outputs.
- Regulatory ambiguity: AI in clinical decision making may require new certifications or approvals (e.g., FDA in the U.S.) depending on intended use, engage legal and regulatory teams early.
- Operational dependency: Heavy reliance on managed AI offerings may create vendor lock in or contractual complexity, adopt portability and clear SLAs where possible.
Conclusion
OCI provides a robust platform for healthcare organizations aiming to harness AI while meeting compliance obligations. By combining OCI’s security first infrastructure, managed AI services and well-architected guidance with strong governance, MLOps and regulatory planning, healthcare providers can accelerate AI innovation safely and responsibly. The path to production grade clinical AI requires technical rigor, regulatory alignment and an organizational commitment to monitoring and continuous.
For more information, see the following resources:
