Oracle Container Engine for Kubernetes (OKE) provides a robust managed environment for deploying, managing, and scaling your containerized applications using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). While OKE makes container orchestration easier, developers need to account for traffic management, observability, and security of their microservices.
Here, Istio comes to rescue. Istio allows developers to transparently add capabilities like observability, traffic management, and security. This blog explains on how Istio can use the powerful features of OCI’s flexible load balancer.
Oracle Container Engine basics
Container Engine for Kubernetes uses versions of Kubernetes certified as conforming to the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF).
OKE is managed and aligned with the tenets of the cloud. OKE also provides many OCI shapes to cater to the workload needs. We recommend using the same shapes within a node pool. For OKE scalability features, see Cluster Node Autoscaling with OCI Container Engine for Kubernetes and for the security best practices, see Kubernetes security: Nine features to secure your workloads.
Load balancer and ingress service mesh
Typically, the communication between services can stay internal to the Kubernetes cluster and doesn’t need to be exposed to the external world. For some parts of the applications such as frontends, you can expose services to outside of cluster. Native options with default Kubernetes implementation include cluster IP node port, load balancer and external name
Kubernetes also offers ingress that exposes HTTP and HTTPS traffic from outside the cluster to services within the cluster. Ingress objects offer limited customization. When you need extensive customization, flexibility, monitoring, and route rules, Istio’s Igress Gateway comes to your rescue. In any case, the external access is provided by the load balancing service of the cloud provider. OCI offers load balancer as service (LBaaS).
OCI Load Balancing service’s bandwidth is determined by the shape: A template that determines the load balancer’s total preprovisioned maximum capacity (bandwidth) for ingress and egress traffic. Available shapes include 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 400 Mbps, and 8,000 Mbps. OCI also offers the capability to specify flexible bandwidth to cater to the spikes and scale—one of the true hallmarks of the cloud. Flexible shapes allow you to specify minimum and maximum values to create an upper and lower size range for the load balancer’s bandwidth shape. Possible sizes range 10–8,000 Mbps.
Installing istioctl
The details of creating the OKE cluster are outside the scope of this blog. Let’s validate the cluster is created.
[root@bastion opc]# kubectl get nodes -A -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
10.1.2.18 Ready node 5d8h v1.21.5 10.1.2.18 Oracle Linux Server 7.9 5.4.17-2136.302.7.2.1.el7uek.x86_64 cri-o://1.21.2
10.1.2.199 Ready node 5d8h v1.21.5 10.1.2.199 Oracle Linux Server 7.9 5.4.17-2136.302.7.2.1.el7uek.x86_64 cri-o://1.21.2
istioctl is the command line configuration utility to configure Istio service mesh. You can install Istioctl from the host or Cloud Shell that has access to the OKE cluster.
curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | sh -
cd istio*
export PATH=$PWD/bin:$PATH
Enabling default Istio
Now that istioctl is installed, we can install Istio on OKE with the following command:
istioctl install --set profile=demo
Considering that OKE supports external OCI load balancers, Istio create a load balancer with the default shape. The default load balancer shape supports a bandwidth of 100M, which might not suit your needs.
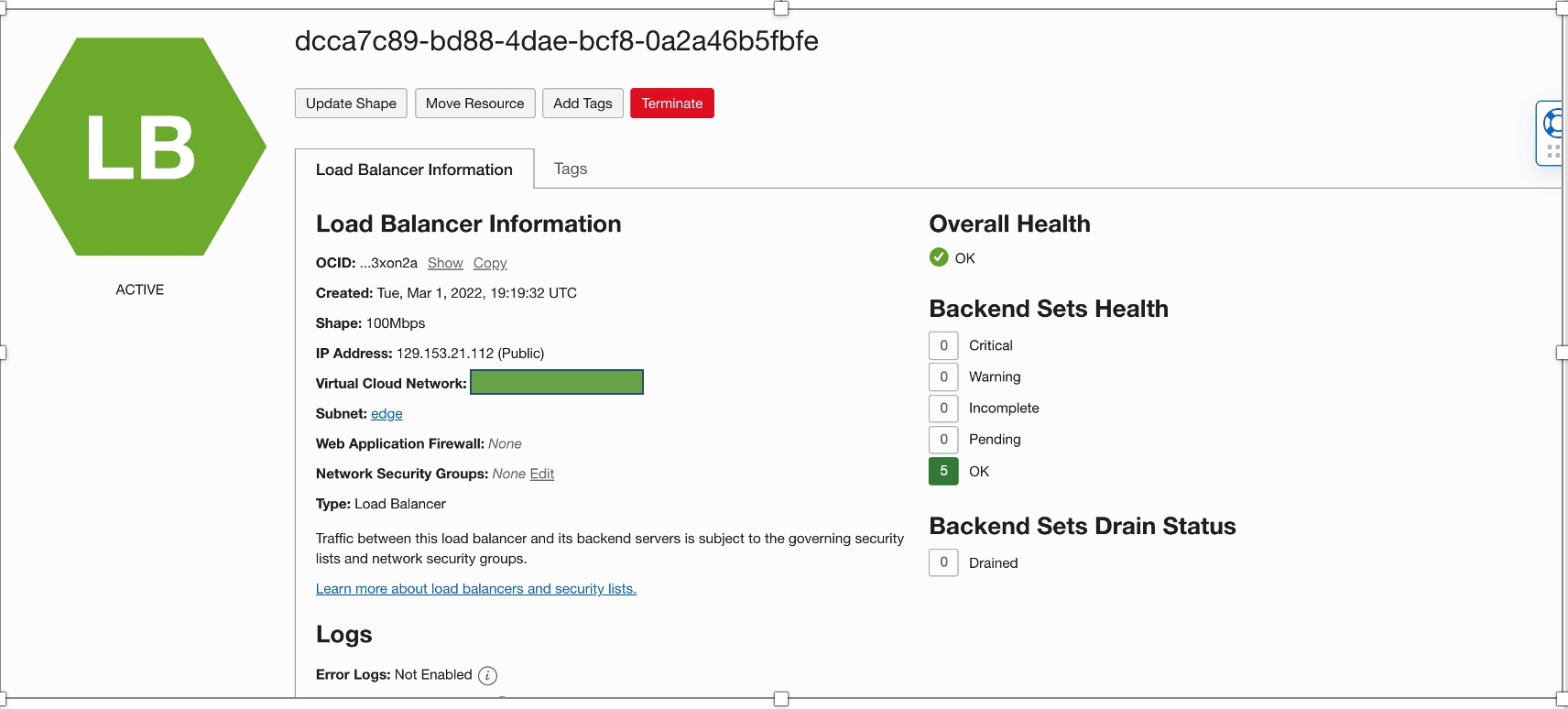
Using the flexible load balancer
If your application has nondefault bandwidth needs, you need to customize the Istio installation. The istioctl install provides a complete API for customizing the configuration. For the purposes of this blog, let’s see how we can customize the flex load balancer by creating an overlay file that provides the appropriate Kubernetes annotations for the flex load balancer.
Use the following commands to create the overlay file for a flex load balancer with minimum bandwidth of 10 MB and maximum bandwidth of 800 MB:
cat <<EOF>>overlay.yaml
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha2
kind: IstioControlPlane
metadata:
namespace: istio-operator
spec:
profile: default
values:
gateways:
istio-ingressgateway:
serviceAnnotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/oci-load-balancer-shape: "flexible"
service.beta.kubernetes.io/oci-load-balancer-shape-flex-min: "10"
service.beta.kubernetes.io/oci-load-balancer-shape-flex-max: "800"
service.beta.kubernetes.io/oci-load-balancer-enable-proxy-protocol: "true"
istioctl install --set profile=demo --skip-confirmation -f overlay.yaml
Now, the load balancer is aligned to the demands of the applications, as shown in the following screenshot:
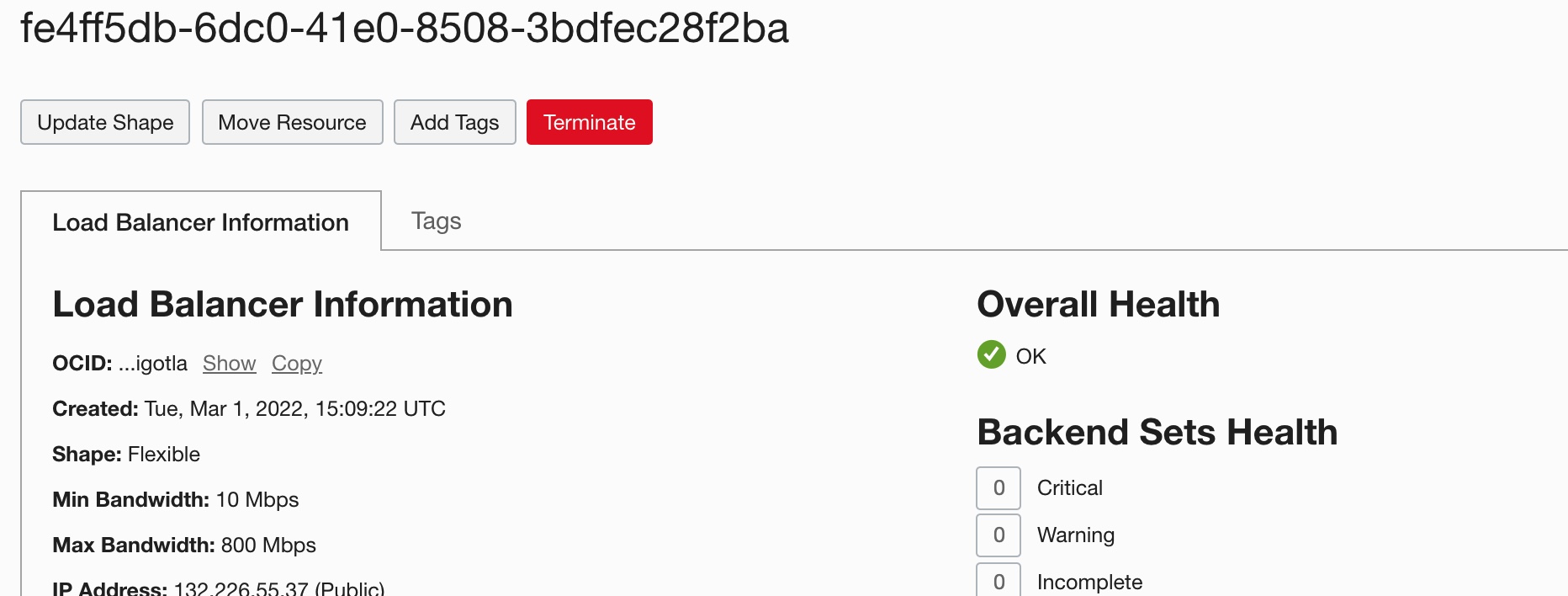
Conclusion
OKE complemented with Istio provides a robust toolkit to develop applications that are not only cloud native, but also scale to your demands, provide nimble traffic management capabilities, and ensure zero trust.
Get started with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure today with our Oracle Cloud Free Tier and get trained and certified on OCI.
