In this part of the blog series, we will review how to deploy a search definition/category to Elasticsearch and schedule the search index build process. We will use the Search Administration pages available in PeopleTools Search Framework.
Navigation: PeopleTools > Search Framework > Search Administration
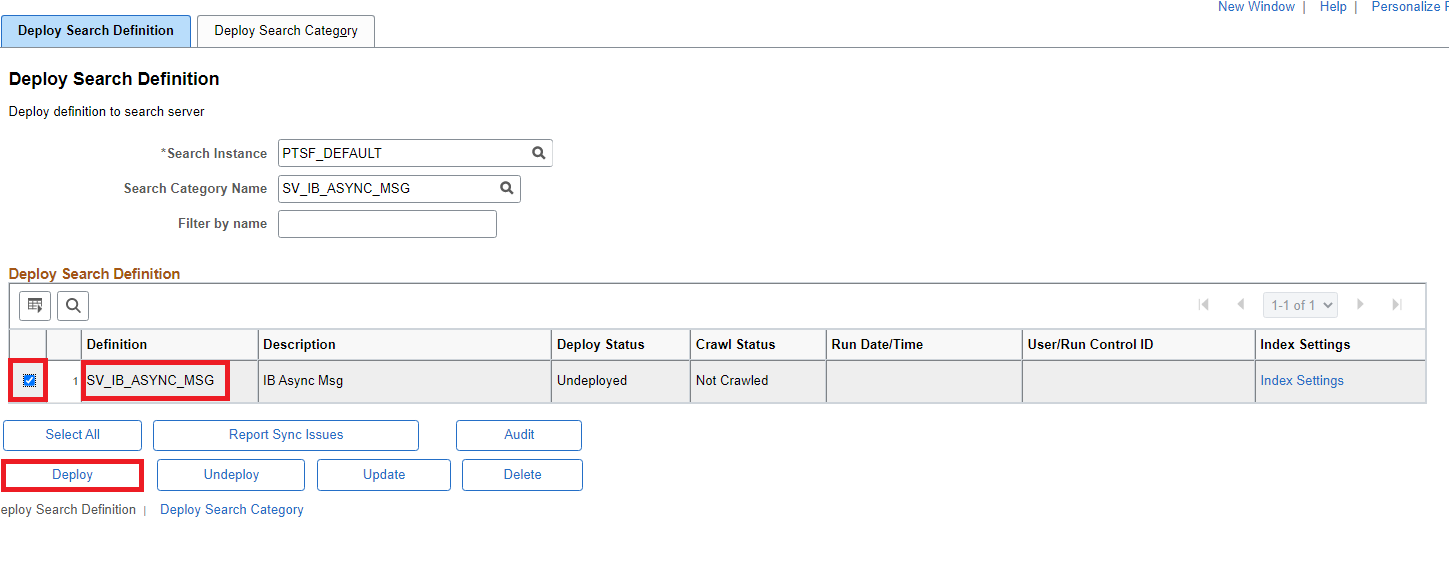
Deploy Search Objects
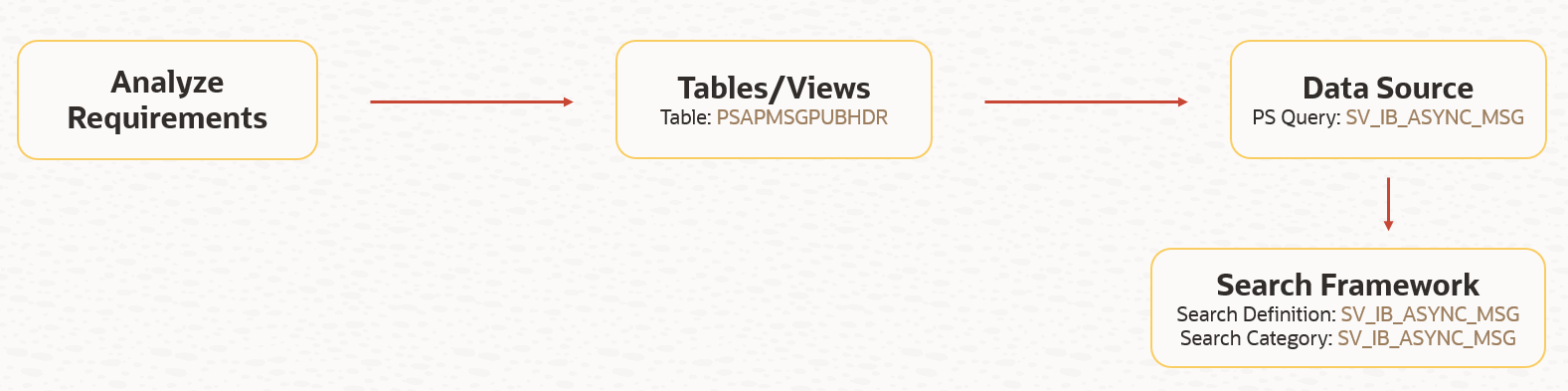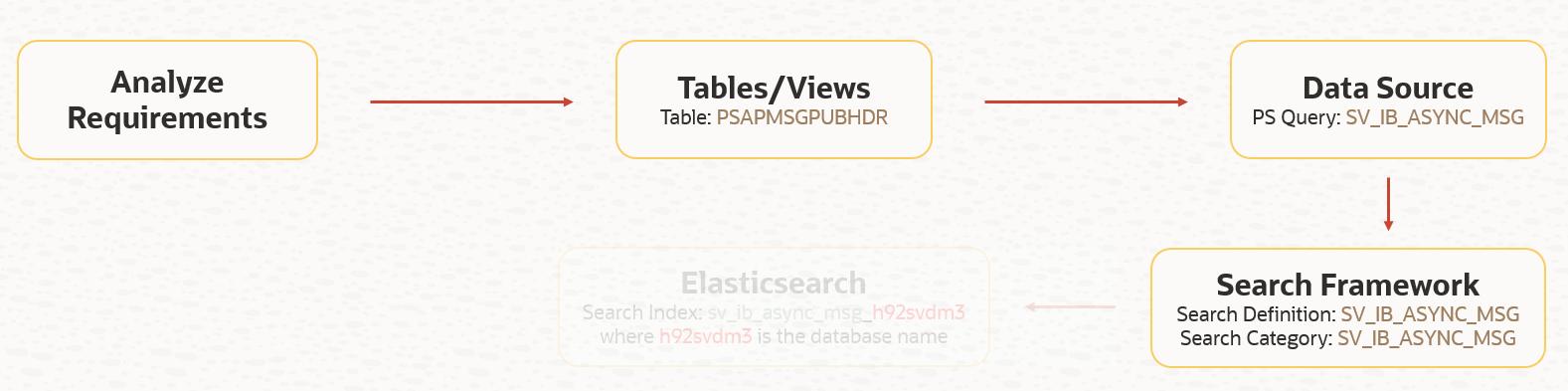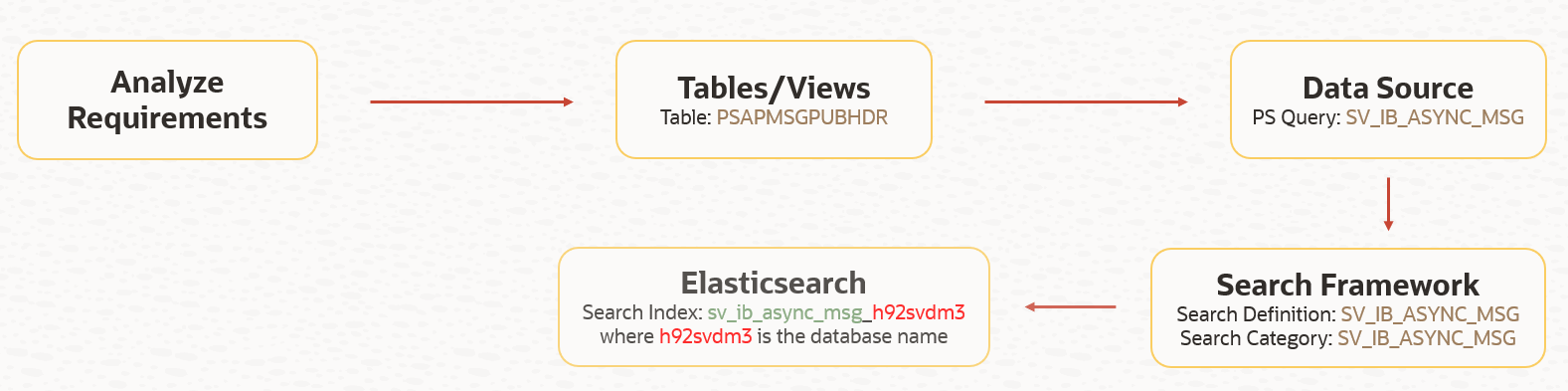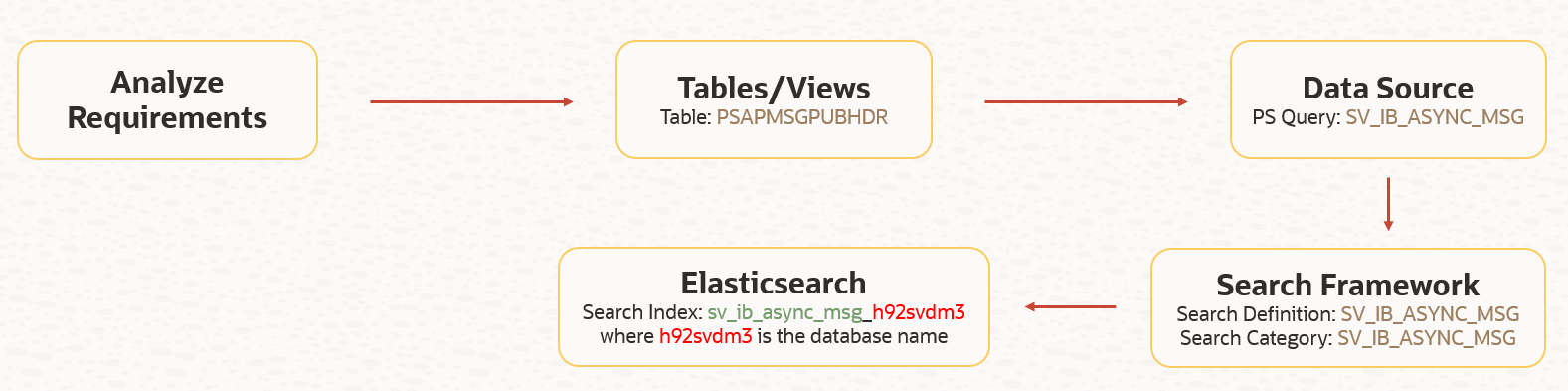
The first step is to deploy the search objects or metadata (search definition/category) created within the PeopleTools Search Framework. When we say deploy, we are referring to the deployment of the search definition/category to Elasticsearch. The deployment step will create the structure of the search index (within Elasticsearch) based on the search definition.
Once the deployment is complete, the page will update the Deployment Status as shown below.
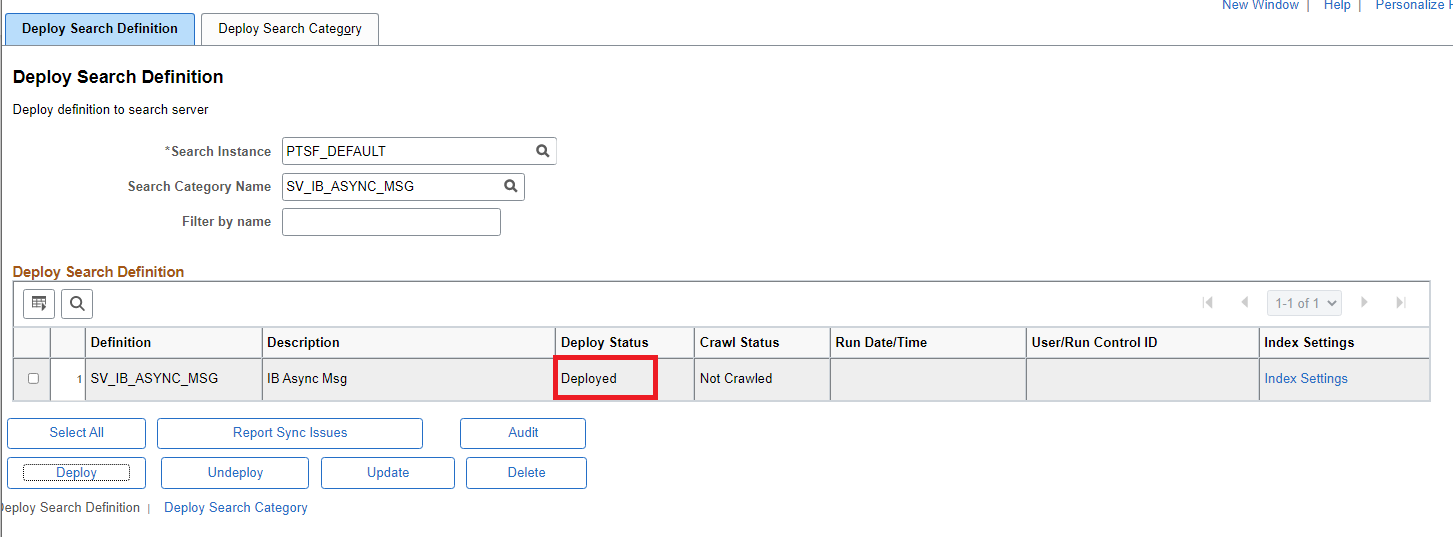
Verify Deployment
While we know the deploy status changed to ‘Deployed’, what if we want to explore some more? What if we want to see the search index properties, mappings, etc. in Elasticsearch? We can use a very useful troubleshooting page called ‘ElasticSearch Interact’ which is available on the ‘Define Search Instances’ page.
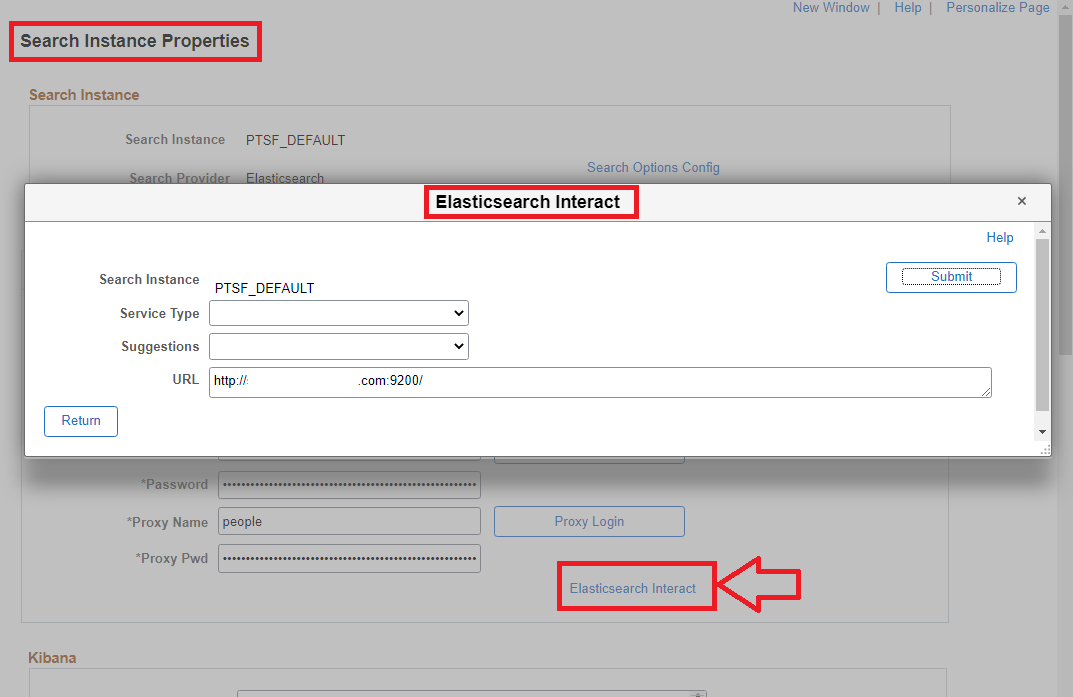
What can we do with Elasticsearch Interact? We can review the search index corresponding to a search definition using the mapping option as shown below. We will notice that the search index naming format is as follows: <search_definition>_<dbname> . It is important to recognize this naming format as it will play a part ( index pattern) when we build visualizations and dashboards in Kibana.
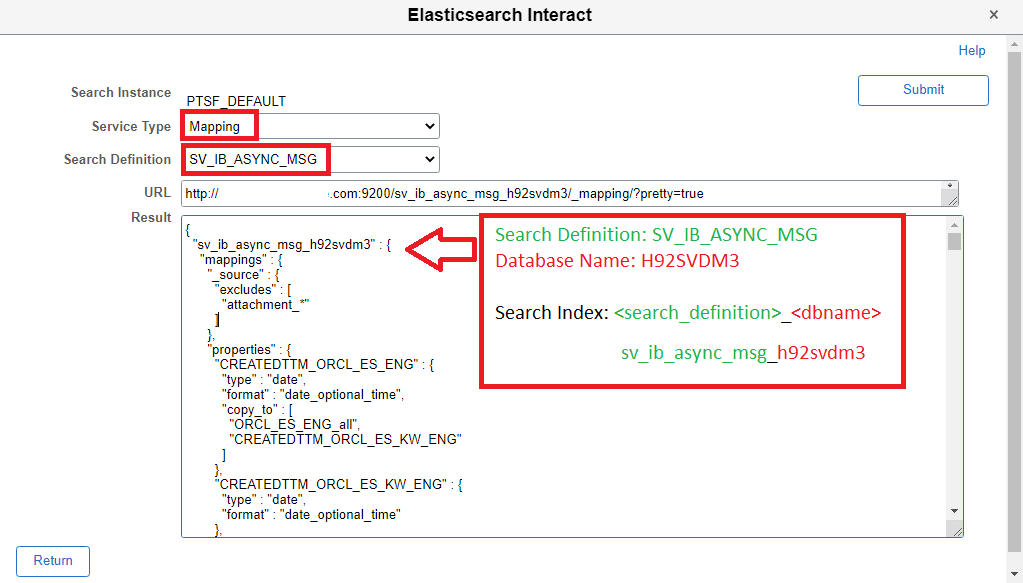
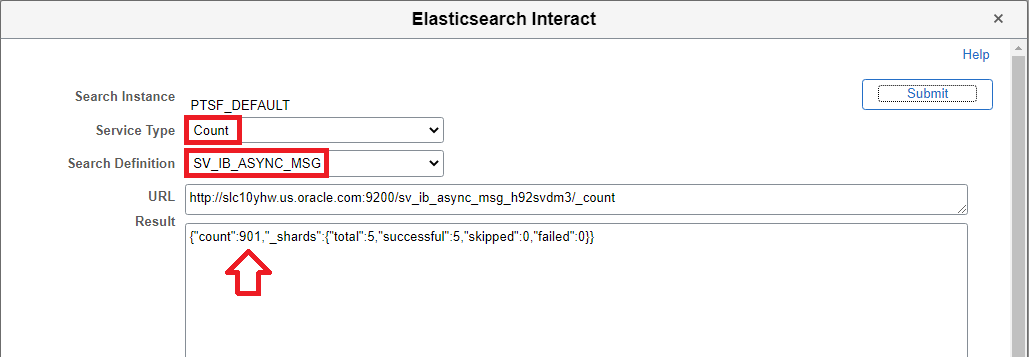
Using Elasticsearch Interact, we can also check the number of documents that are available for the search index in Elasticsearch using the count option. What is a document in the context of a search index in Elasticsearch? Basically, every row in the data source (PS Query/Connected Query) associated with the search definition is indexed (or stored) as a JSON document in Elasticsearch for the corresponding search index.
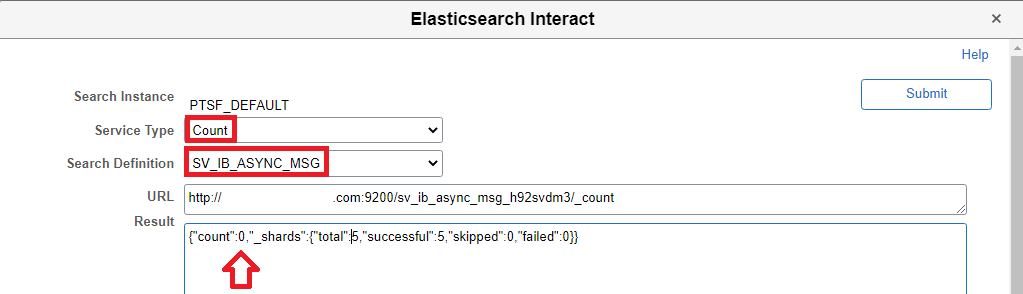
As we can see, the count of documents for the search definition used in the example is 0. This is because we have only deployed the search definition. This has created the search index and the associated mappings, properties, etc. But we are yet to index the data in Elasticsearch.
Search Index Build Process
After deploying the search definition, we can use the ‘Build Search Index’ page to index the transactional data.
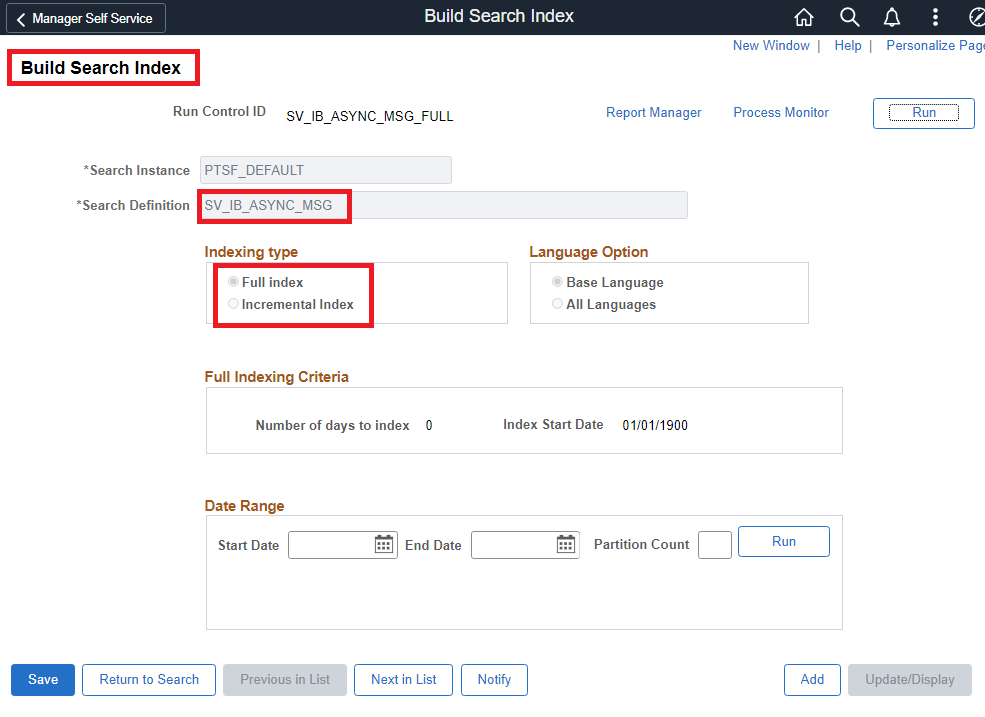
We have two indexing options – full and incremental. We can use the full indexing option the first time an index is built. Subsequently, we can schedule periodic incremental indexing to catch up the data that has been added or updated since the last index build.
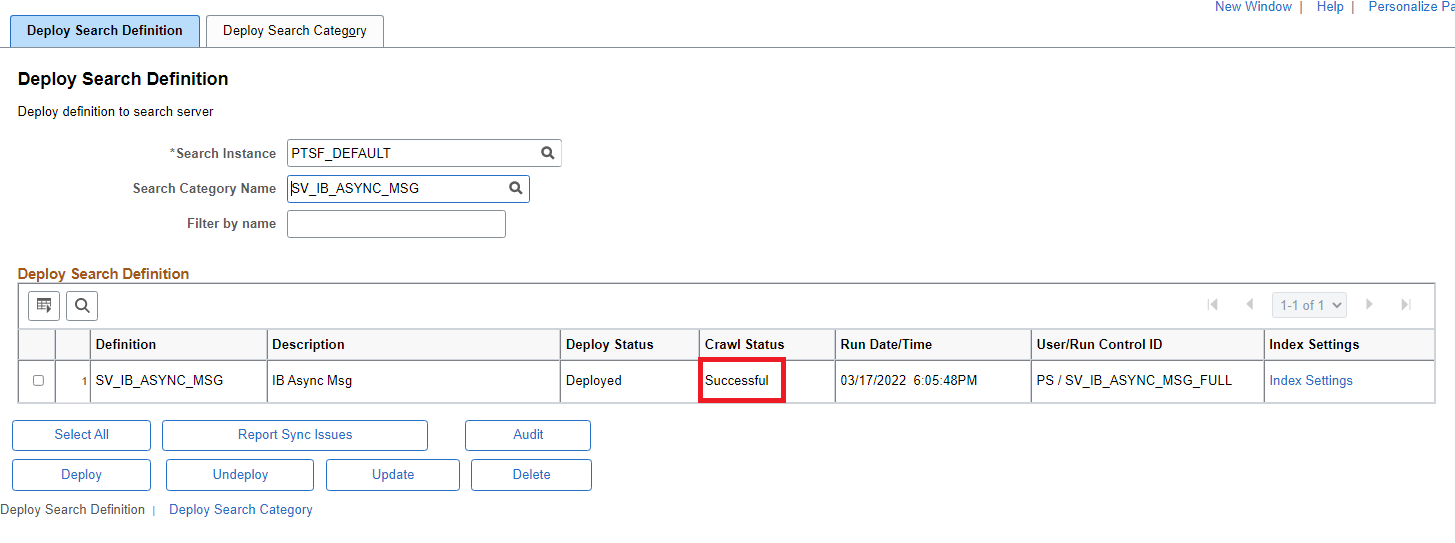
Once the indexing is completed, the crawl status on deploy search definition page will change from ‘Not Crawled’ to ‘Successful’.
Verify Search Index Build
We can use the Elasticsearch Interact – count option once again to verify the number of documents indexed in Elasticsearch for the corresponding search index.
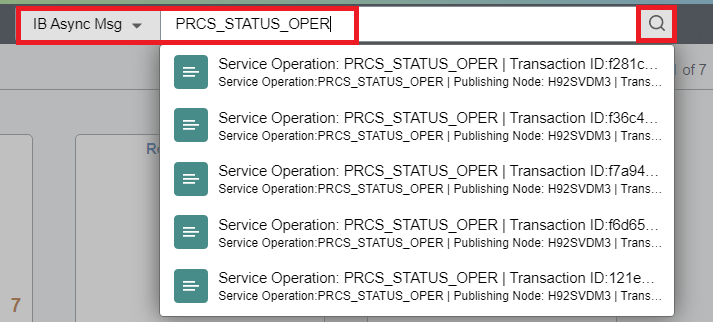
Testing Search
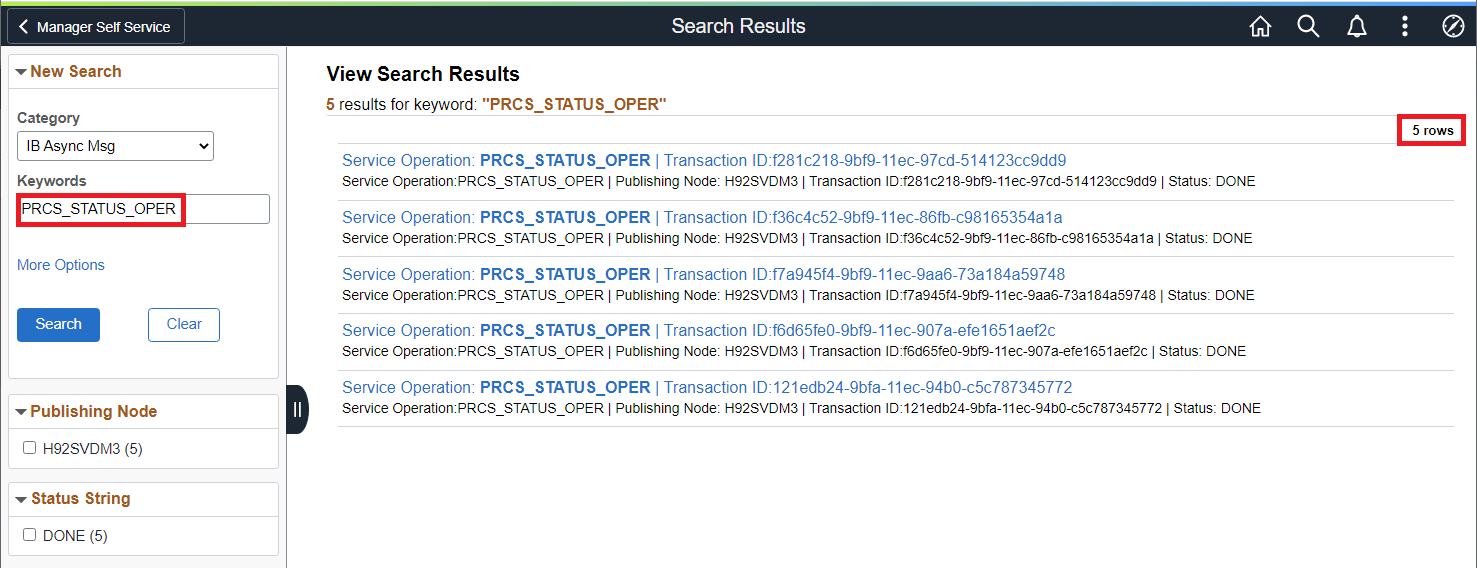
If the search category is defined in the Global Search context, then we can simply use Global Search to test if search is working as expected.
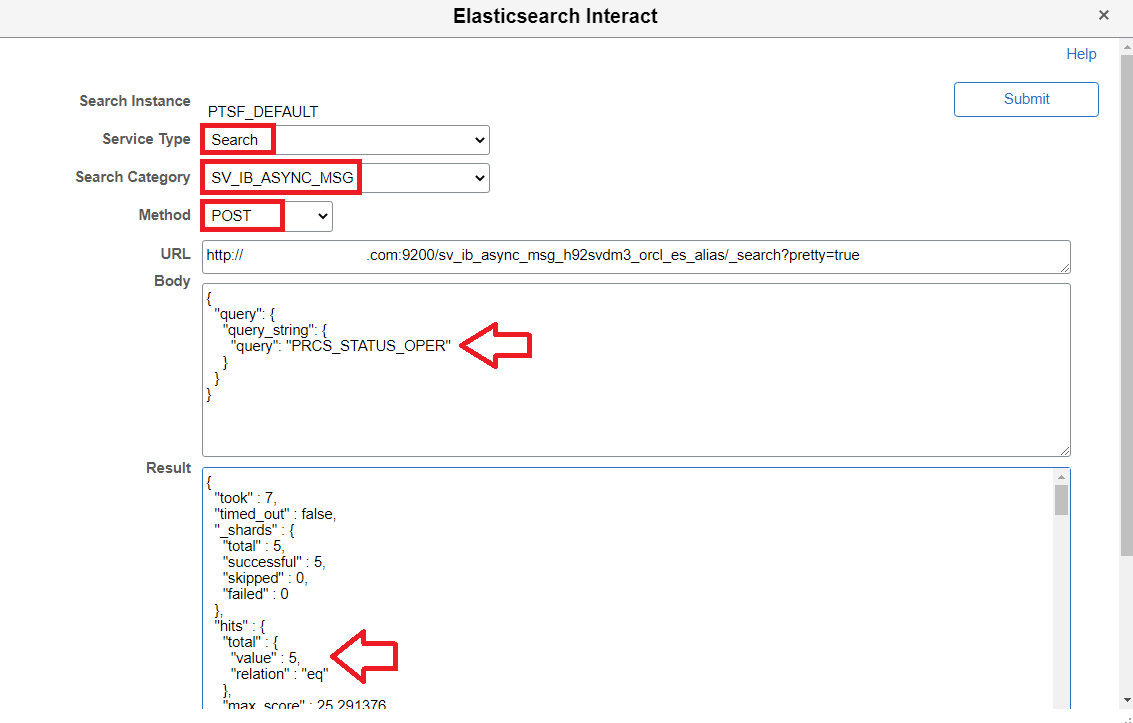
Next, we can also use the Elasticsearch Interact page search option to troubleshoot using the search query as shown below.
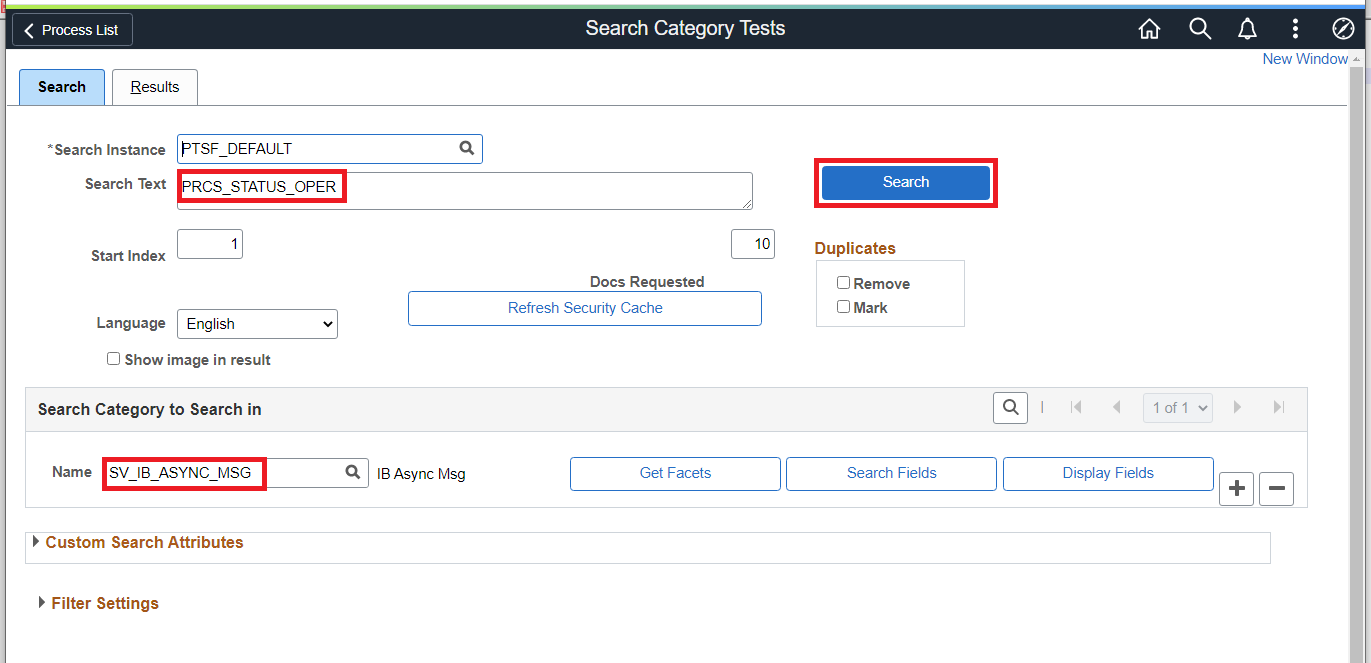
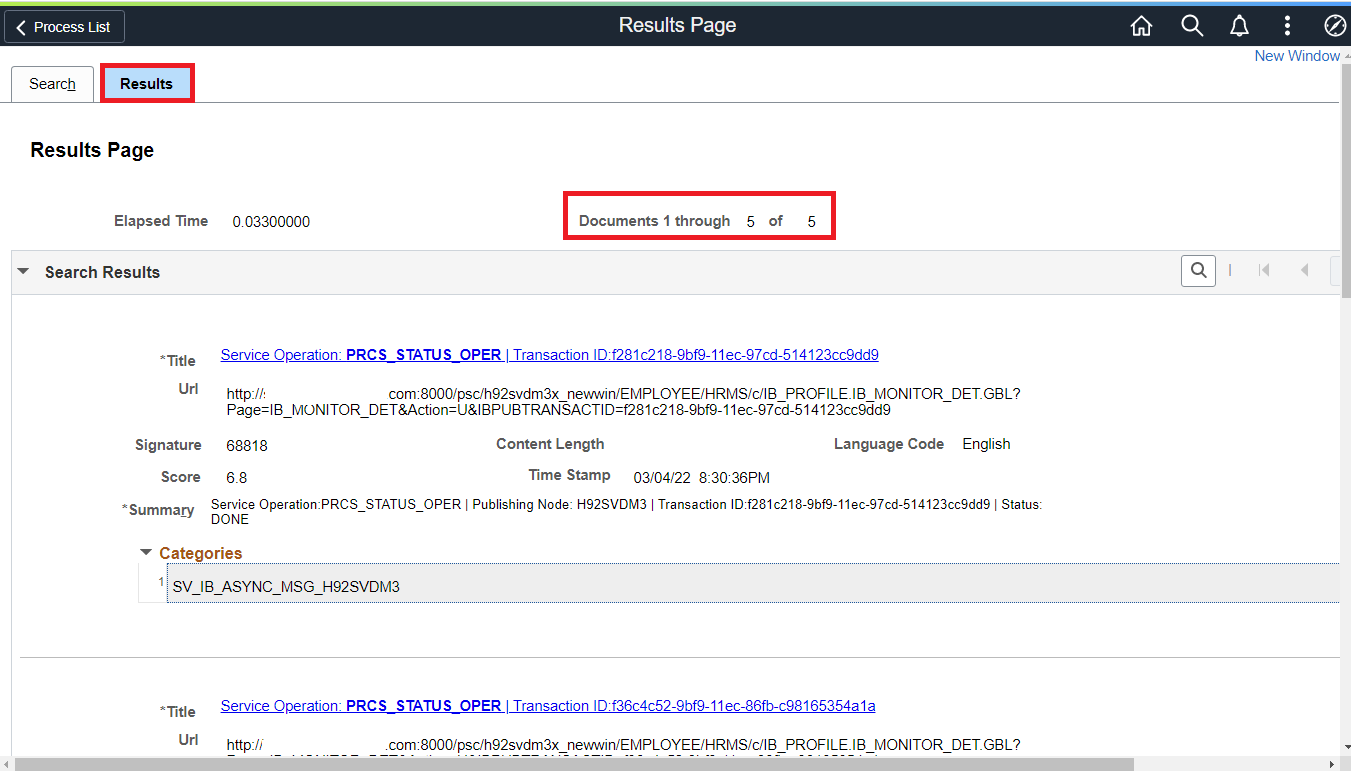
Finally, we can also use the search category test page.
This completes the deployment of the search definition/category and the indexing of the transactional data in Elasticsearch.