Many IT organizations use Oracle Enterprise Manager (EM) to monitor and manage their fleet of Oracle databases. These databases can be deployed in on-premises data centers, in Oracle’s Cloud, or in other clouds such as Amazon Web Services (AWS).
EM can be deployed in a customer’s on-premises data center or on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). As more organizations adopt a multi-cloud strategy, it becomes crucial to establish secure and reliable connections between the clouds in order to manage these environments.
This blog explains the general steps involved in setting up, discovering, and monitoring Oracle databases in Amazon AWS using Enterprise Manager.
Overview of monitoring Relational Database Service (RDS) for Oracle
There are two ways to use RDS for Oracle Database in AWS:
- RDS for Oracle: In this option, AWS provisions and manages the Oracle database and provides a way to optionally configure the EM Agent. This option does not allow access to the underlying host.
- RDS Custom for Oracle: In this option, AWS provisions the Oracle database using the database installation files you provide. This option provides access to the underlying host. To monitor the database with EM, you will have to install and configure an EM Agent.
Before discovering RDS Oracle databases in EM, it’s essential to establish connectivity between EM and AWS RDS. The specific networking configuration depends on whether you intend to monitor from an on-premises-hosted EM or an EM hosted on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). We describe these networking configurations in greater detail later.
Once the network connectivity is in place, the next step involves installing the EM Agent through which the database will be monitored. With RDS for Oracle, direct database host access is not available. The EM Agent is both installed and managed by AWS. In contrast, RDS Custom for Oracle provides database host access and the autonomy to install and manage the EM Agent.
Next, we can discover the RDS Oracle databases.
In the subsequent sections, we review the steps required for setting up networking, EM Agent installation, and the discovery of RDS Oracle Databases in EM.
- Setting up connectivity between EM and AWS RDS
- EM on-premises
- EM on OCI
- Installing and configuring the EM Agent
- RDS for Oracle
- RDS Custom for Oracle
- Discovering AWS RDS for Oracle in EM
Setting up connectivity between Enterprise Manager and AWS
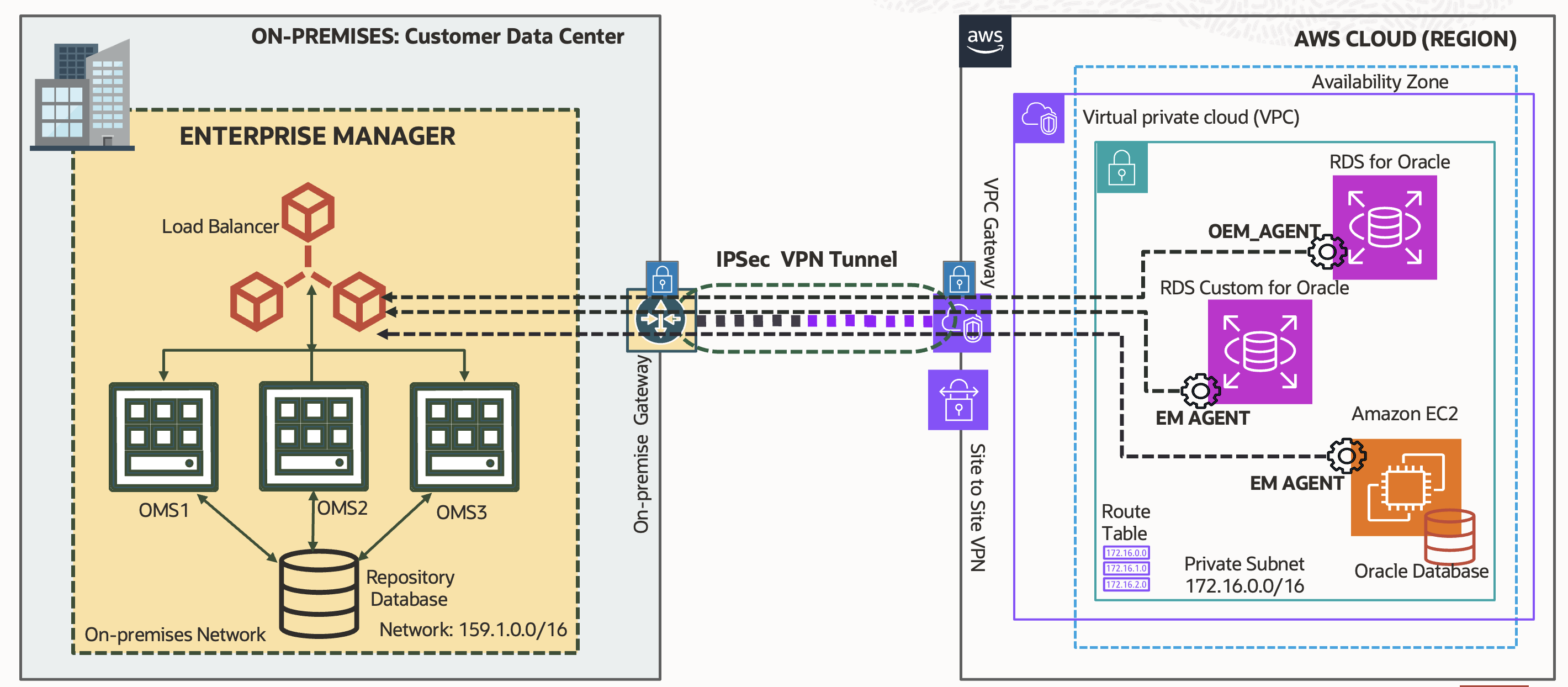
To discover and monitor Oracle databases in AWS using EM, establish connectivity between EM and AWS first. EM could be running in an on-premises data center, in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), in AWS, or any other cloud.
EM on-premises
When EM is running in an on-premises data center, set up an IPSec VPN tunnel between the on-premises network and AWS. The configuration depends on the gateway device deployed in the on-premises network. Follow the AWS documentation customer gateway device for the configuration options.
EM on OCI
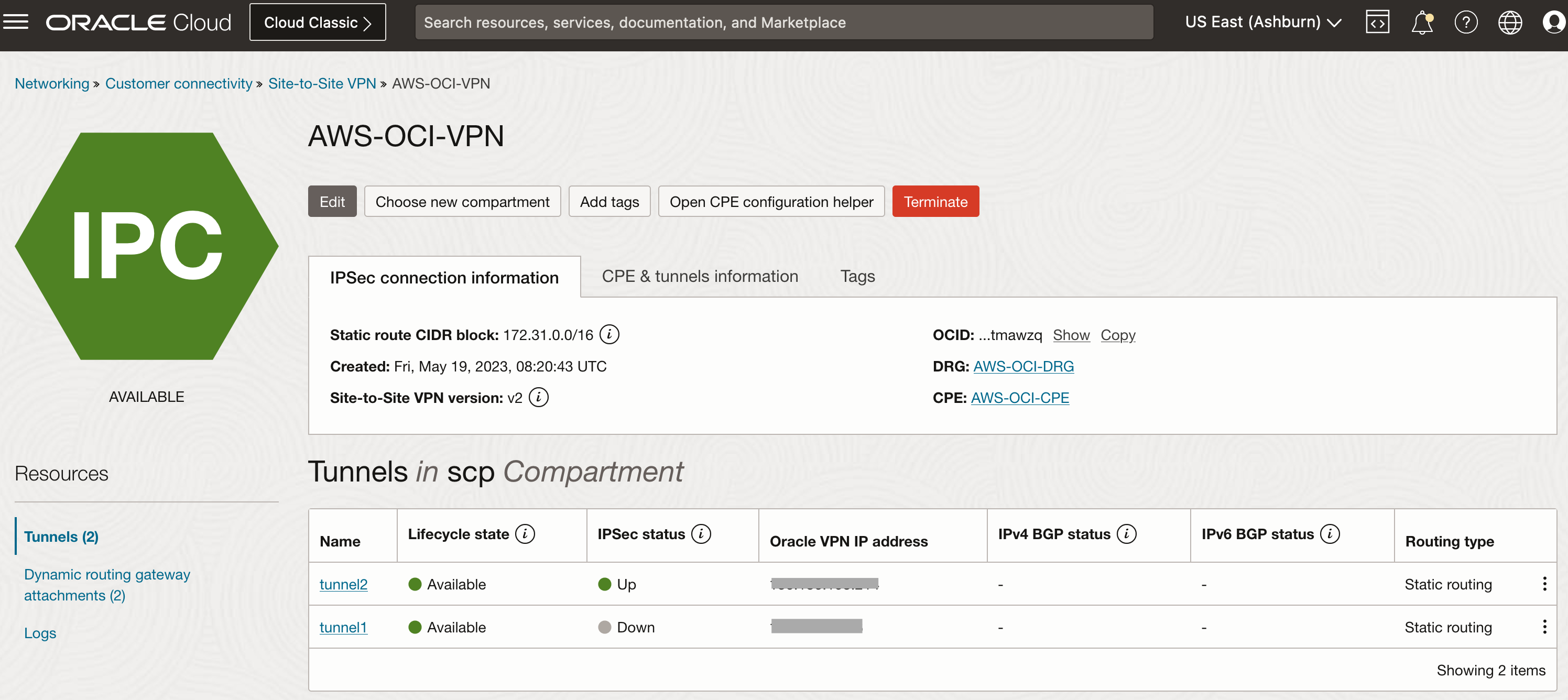
When EM is running in an OCI tenancy, follow the OCI documentation VPN Connection to AWS for configuration of IPSec VPN tunnel between OCI and AWS.
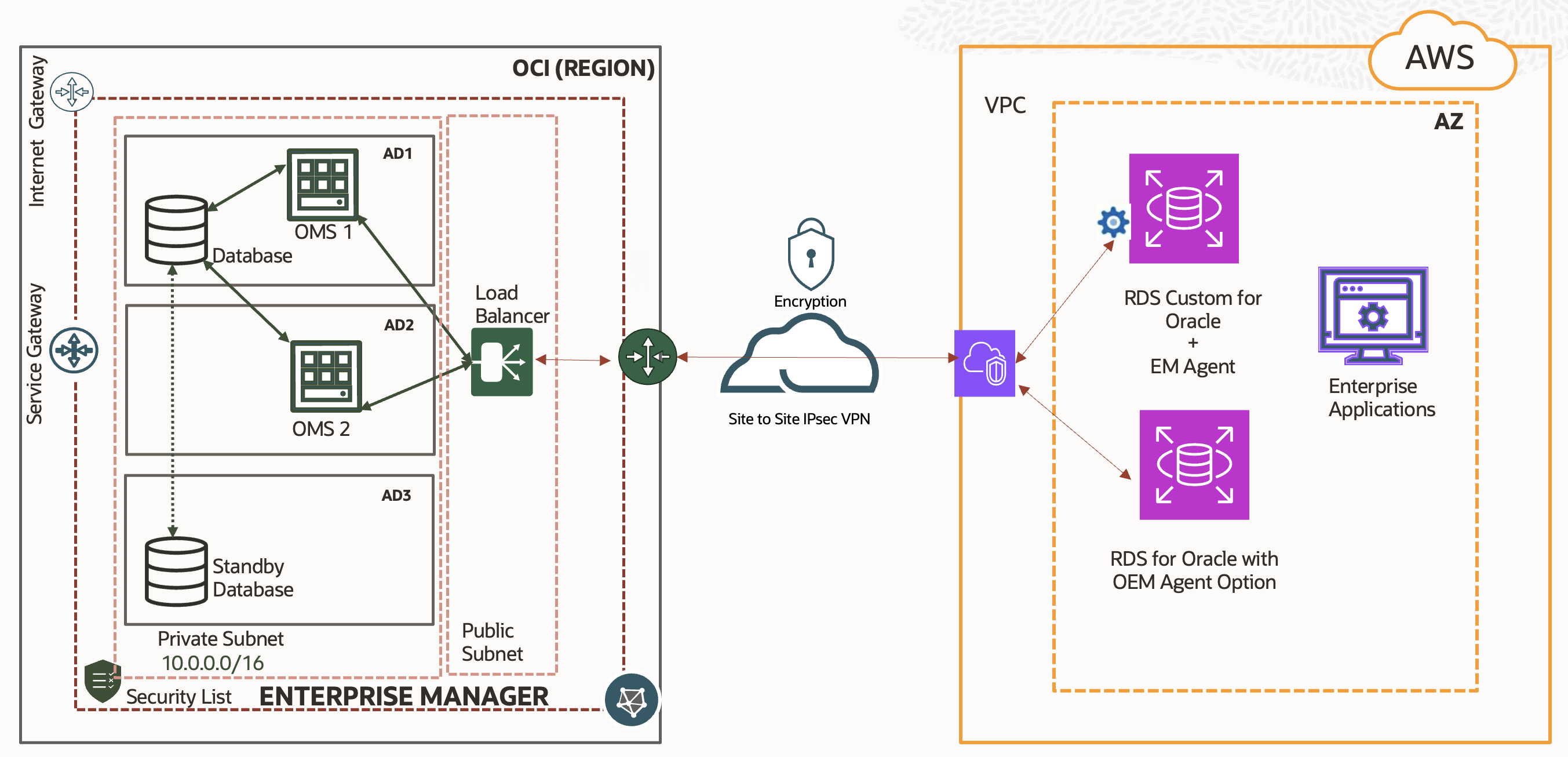
Once the connectivity is set up, OCI resources can connect to AWS resources via a private network.
Installing and configuring the EM Agent
RDS for Oracle
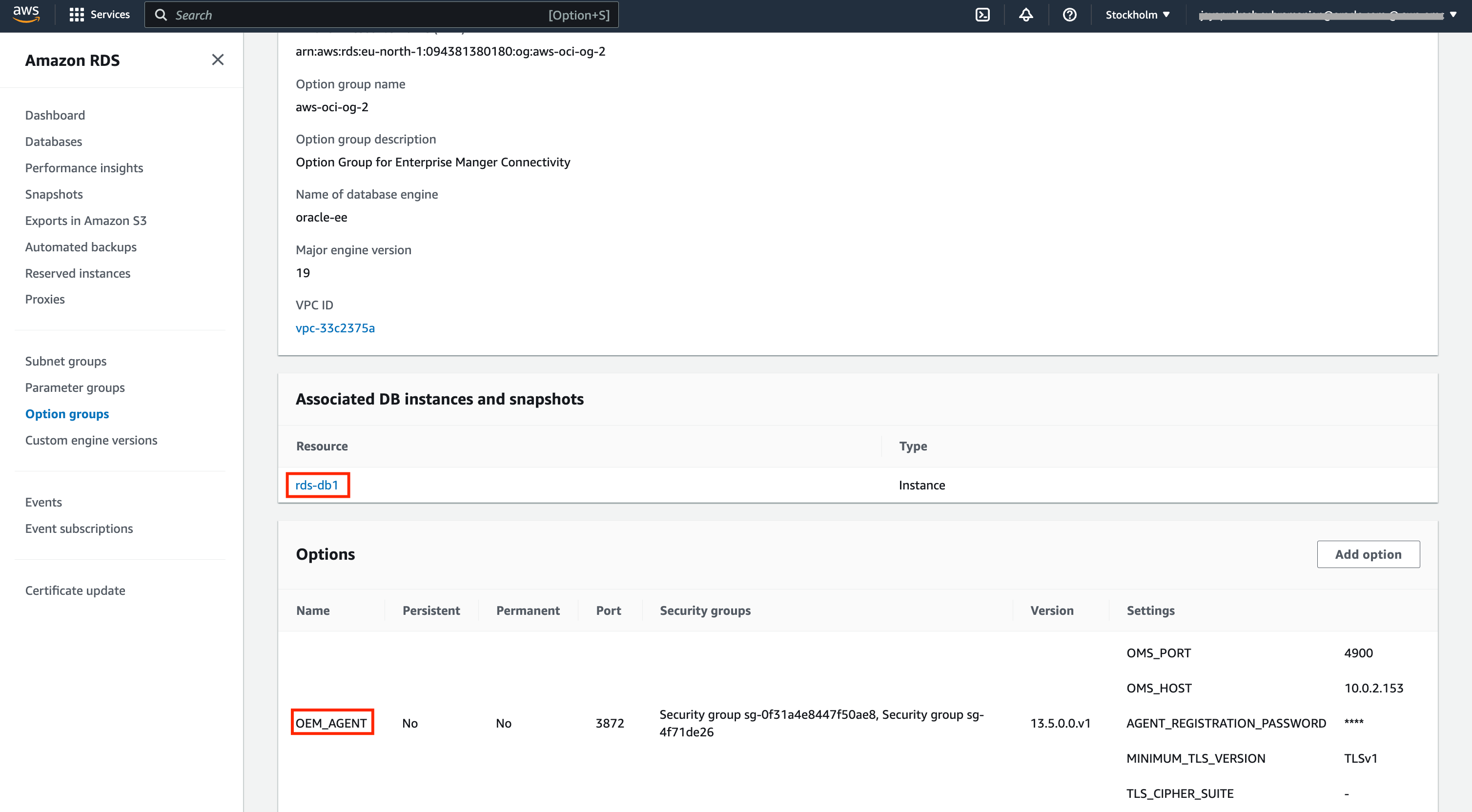
In this type of RDS configuration, the EM Agent is installed using the AWS option “OEM_Agent” by providing OMS Host, Port, Agent Registration Password, optional parameters minimum TLS version, and TLS Cipher Suite. If you do not have these details, run emctl status OMS -details to get this information.
Once the installation is completed, you will see the agent configuration in AWS “Option groups” first and then in EM.
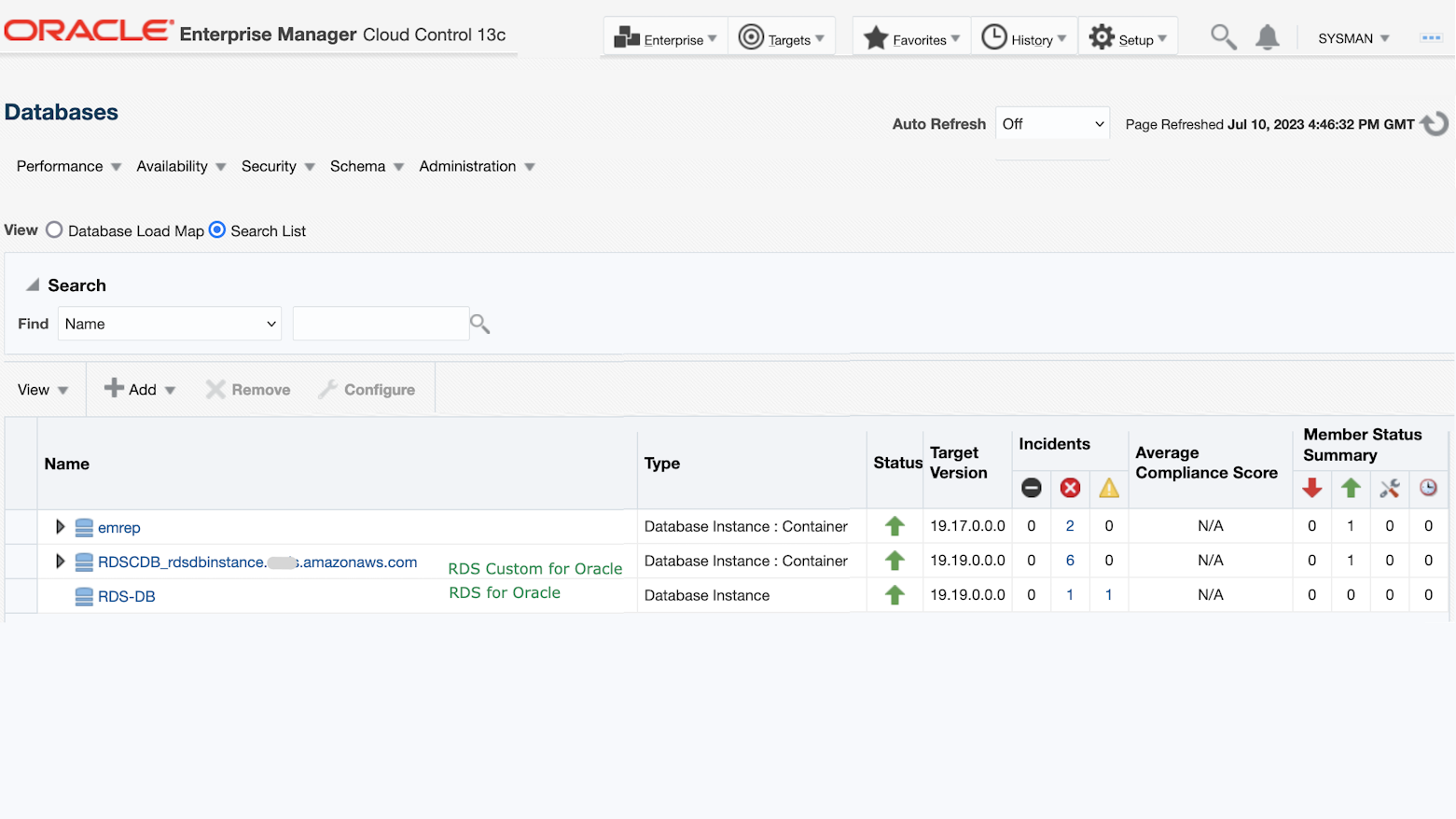
Note that there are documented limitations using the RDS “OEM_AGENT” option. These include not having support for administration tasks such as jobs and database patches, i.e., operations that require host access. Also, there is no support for alert log monitoring. RDS for Oracle limitations – Amazon Relational Database Service documents these restrictions.
Use Enterprise Manager to deploy the EM Agent to the EC2 instance.
Pre-requisites for EM Agent deployment
- Add the OMS and EC2 instance details on the /etc/hosts on the OMS host and EC2 host respectively.
- Make sure the OMS and EM Agent ports are opened on the security lists of OCI VCN and AWS VPC.
- Open the required ports on the host’s firewall.
- Use rdsdb database user to install the EM Agent.
After the prerequisites are completed, push the EM Agent using the EM console.
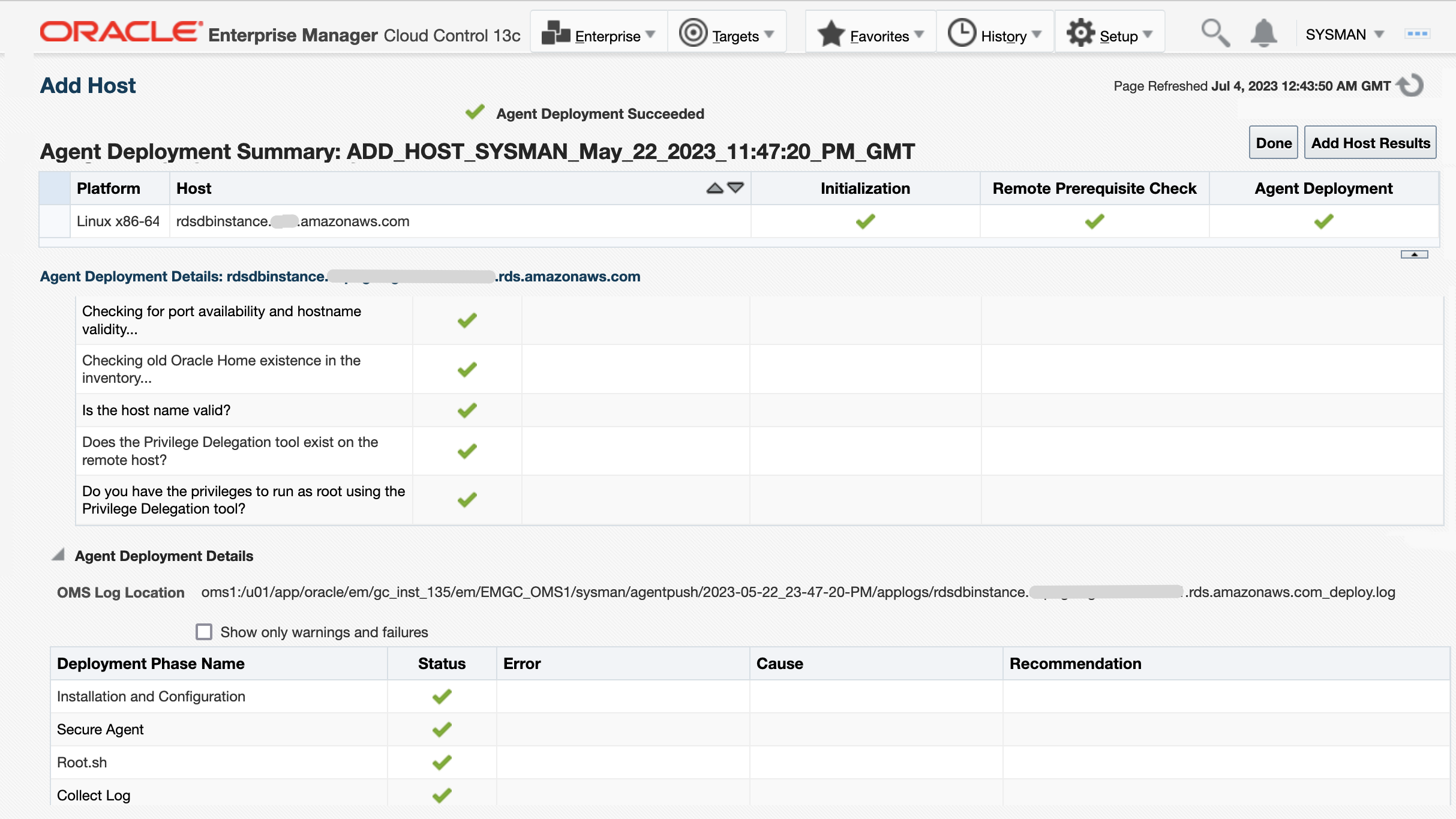
Once the agent has been deployed, you can now proceed with the database discovery.
Discover and monitor databases in Enterprise Manager
RDS for Oracle Database
Once the agent has been set up, the Oracle database in the EM Console is discovered using the option to ‘Add Targets Manually”.
After discovery, you can use many EM monitoring features on the database. These include monitoring and alerting for most metrics (except alert log), metric extensions, administration groups and monitoring templates, incident management and event correlation, notifications and ticketing, dynamic runbooks, blackouts, access to database performance, and other database admin operations based on the privileges of the AWS-provisioned database user.
RDS Custom for Oracle Database
Discover RDS Custom for Oracle using any of the supported discovery options: Auto-discovery, Guided discovery, or Manual discovery.
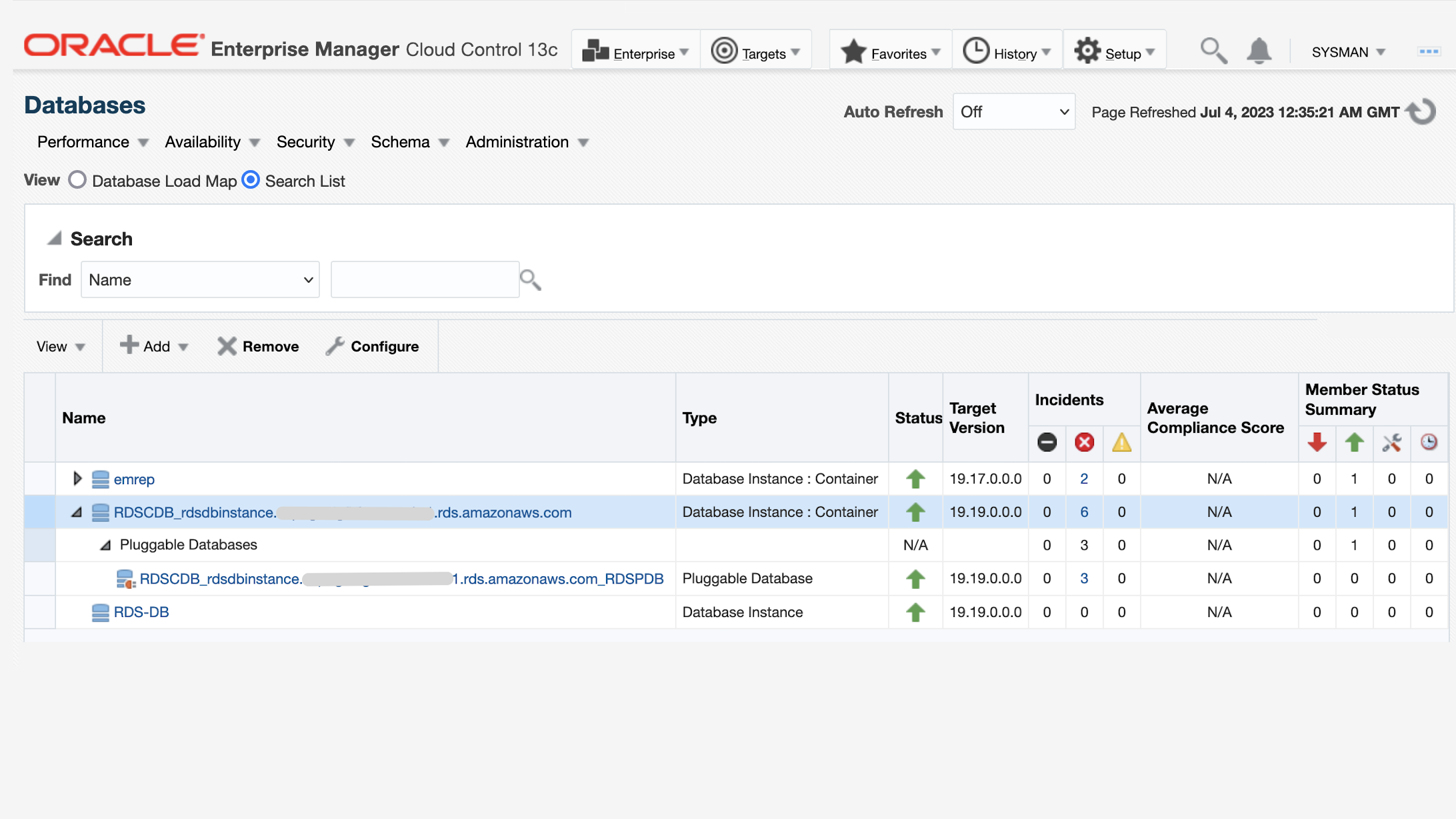
Once discovery has completed all of EM’s monitoring features on the Oracle database can be used. These include features that are not supported in RDS for Oracle: jobs and corrective actions, OS-based features (e.g., alert log monitoring, OS Command, SQL Script job), and host monitoring.
Enterprise Manager for multi-cloud environments
In summary, Enterprise Manager can be used for multi-cloud environments such as AWS. For Amazon RDS specifically, follow the option-specific instructions for the discovery of the Oracle database in EM. Once discovered, you’ll be able to monitor the Oracle database using many Enterprise Manager monitoring features. Hence, the existing EM monitoring setup should work seamlessly with your Oracle databases in AWS. This enables you to continue to use EM as a single monitoring and management tool for your multi-cloud Oracle estate. Refer to the table below for the options on how to monitor Oracle Databases in AWS and manage your environments
| S.No | Options | What it Means | Level of Monitoring | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RDS for Oracle |
|
|
|
| 2 | RDS Custom for Oracle |
|
|
|
| 3 | AWS-EC2 |
|
|
|
Resources
Connection from AWS to Oracle
Connection from on-premises to AWS
AWS RDS
AWS RDS Custom
RDS Custom Engine Version
Enterprise Manager Documentation
Database Management with Enterprise Manager
Enterprise Manager on OCI Marketplace

