Today’s world is constantly evolving, and safeguarding the cybersecurity landscape for critical systems against vulnerabilities is paramount. With the rise of sophisticated threats, organizations must adopt proactive measures to fortify their defenses. Holistic patching emerges as a solution, offering a comprehensive approach to security maintenance for Enterprise Manager environments.
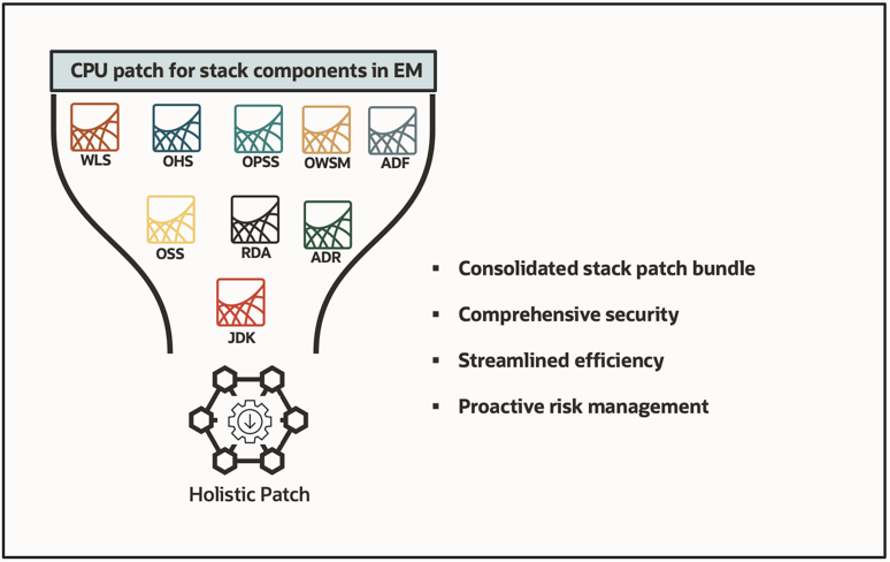
This blog explores the transformative power of holistic patching in bolstering the security posture of Enterprise Manager systems. By addressing vulnerabilities across critical components such as OHS, WLS, OPSS, and JDK, organizations can mitigate the risk of security breaches and enhance overall risk management practices.
Through the consolidation of patches into a single holistic bundle for the quarterly CPU cycle, the patch management process is streamlined, minimizing complexity and downtime. This streamlined approach not only simplifies operations but also optimizes efficiency, enabling organizations to allocate resources more effectively to core business activities.
In this blog post, we review the holistic patching process, explore how it enhances security, minimizes disruption, and empowers organizations to navigate the cybersecurity landscape with confidence.
How Holistic patching manages Enterprise Manager infrastructure security updates
Holistic patching, facilitated by the Stack Patch Bundle (SPB), offers a comprehensive solution for efficiently managing security updates for Enterprise Manager infrastructure. SPB consolidates critical components in Enterprise Manager such as OHS, OPSS, WLS, JDK, etc., streamlining the patching process through the OMSPatcher utility. This approach simplifies the application of CPU patches, as administrator can download a single holistic patch from MOS for Enterprise Manager’s quarterly CPU cycle.
By orchestrating the application of SPB through OMSPatcher, organizations can mitigate security risks effectively. Additionally, SPB ensures that the JDK inside the OMS home is updated to comply with the latest certified version, enhancing system security and stability.
Holistic patching also reduces the maintenance window by consolidating patching activities into a single downtime window. This streamlined approach minimizes disruption to operations and ensures timely release updates. Moreover, system and environment prechecks are performed once, optimizing the overall patching process, and reducing apply time.
Holistic Patching commands
Holistic patching is orchestrated using the OMSPatcher (omspatcher) new parameters that execute the SPB patch. The new parameters introduced to support holistic patching using omspatcher are -spb_patch and -jdk_update. Refer to this document for details on the new parameters.
Get started with Holistic Patching for CPU cycle in 3 steps!
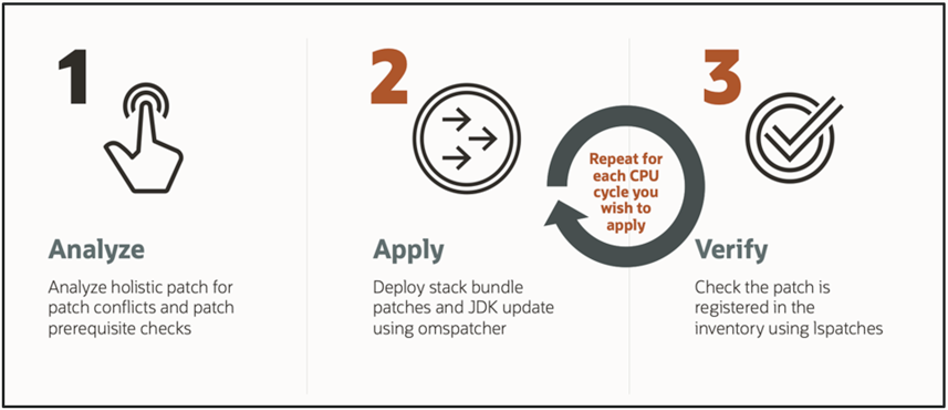
With Holistic Patching for the CPU cycle, EM administrators can fortify their systems against vulnerabilities in just three straightforward steps:
- Analyze
- Apply
- Verify
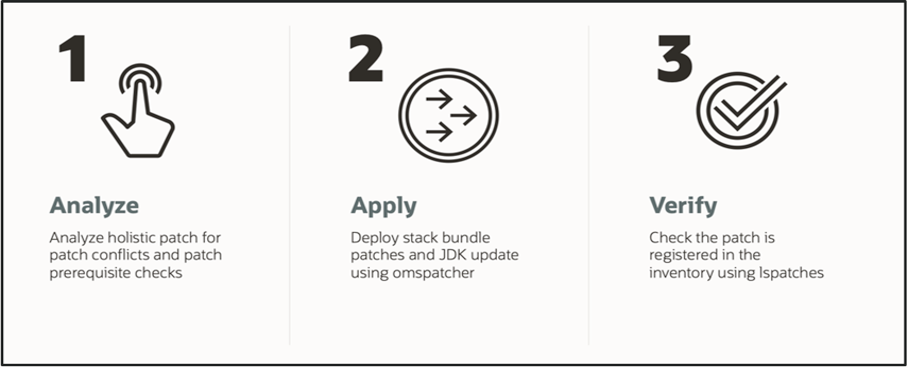
Figure 2: Simplified steps for applying CPU patch through holistic patching
1. Analyze
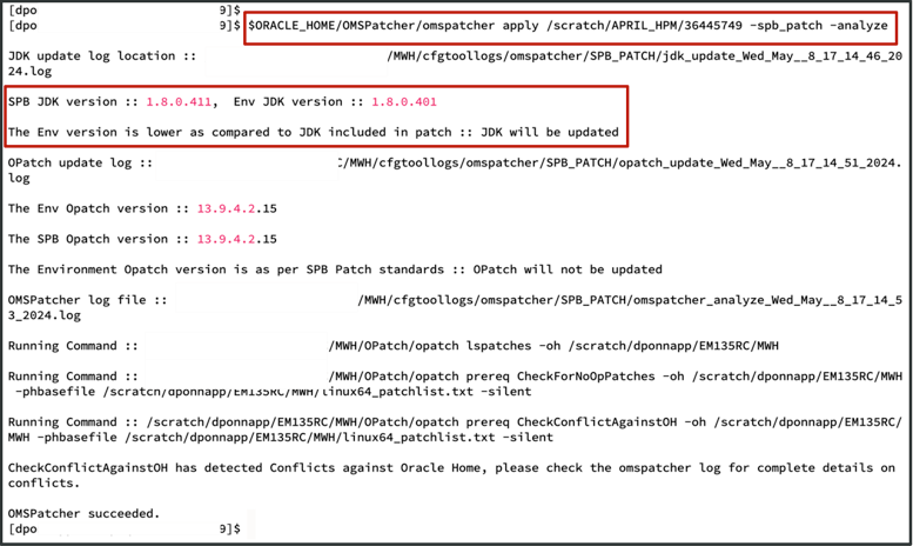
Conduct a thorough analysis of your patching process to identify any potential conflicts and ensure that all prerequisite checks are met before deployment. If there are patch conflicts the command will return with the conflicting patch information. Here is an example of an analysis indicating that the JDK is not the recommended version, therefore it will be updated. In addition, this analysis step found some conflicts and details are available for your review in the log.
2. Apply
Holistic patching application is enhanced with the “-spb_patch” parameter, enabling users to easily identify and designate the application specifically for holistic stack patches.
During the apply flow, omspatcher first validates the JDK update. The JDK update is seamlessly integrated within the holistic patch bundle, eliminating the need for manual JDK updates outside of the patching process. Then, omspatcher compares the JDK update version inside the OMS home with the version included in the holistic patch. If the JDK update version inside the OMS home is outdated, the apply process automatically updates the JDK and proceeds with subsequent steps. During the apply process, the OPatch inside the OMS home is automatically updated to the required version specified by the holistic patch, as it is seamlessly integrated within the bundle. Subsequently, patch prerequisite checks are executed, examining the metadata files and patch location provided to the apply command. Once prerequisites are validated, the OMS is stopped, and the OMSPatcher utility internally invokes the ‘opatch napply‘ command. This command conducts patch conflict checks and system analysis before applying patches.
After conflict analysis, patches are applied to various components such as OHS, OPSS, OSS, WLS, ADR, ADF, etc., within the OMS home. Upon completion of the apply phase, the primary OMS is started. For multi-OMS patching, the additional OMS patching scripts are generated after primary OMS patching is complete. EM administrators are required to copy these scripts to additional OMS nodes and manually execute them to finalize the patching process.
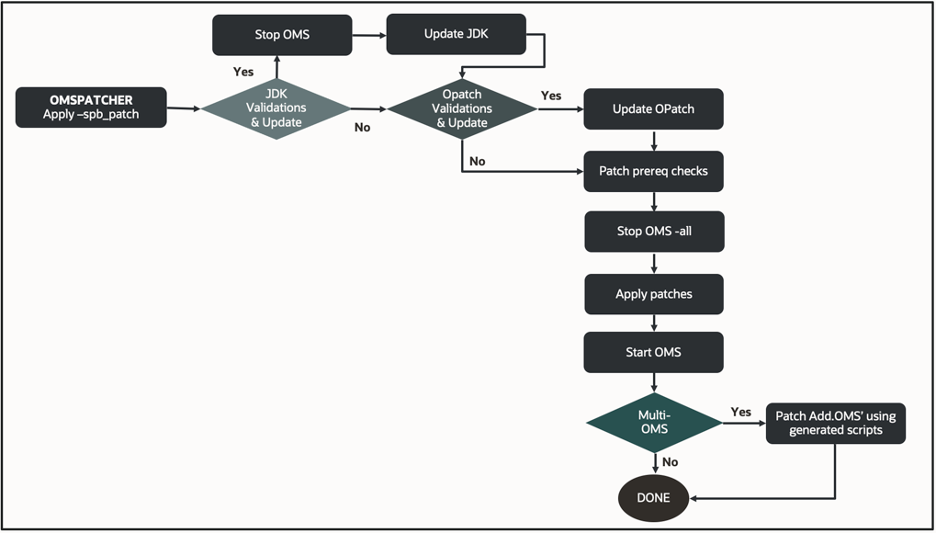
This efficient approach to patch application not only simplifies the process but also ensures that systems are updated to the latest certified versions seamlessly, enhancing overall security and stability. Here is an example of the “apply” output:

3. Verify
The final step in the holistic patching process is to verify the applied patches inside the OMS home by executing the ‘omspatcher lspatches’ command.
Repeat the same steps for each CPU cycle you wish to apply on your Enterprise Manager system.
Holistic patching emerges as a solution, offering a comprehensive approach to security maintenance within enterprise systems. By addressing vulnerabilities across critical components such as OHS, WLS, OPSS, and JDK, holistic patching ensures comprehensive security coverage, significantly reducing the risk of security breaches. Furthermore, the consolidation of patches into a single holistic bundle for the quarterly CPU cycle streamlines the patch management process, reducing complexity and minimizing downtime.
In essence, holistic patching offers a transformative approach to security maintenance, providing comprehensive coverage, better risk management, reduced complexity, minimized downtime, and improved efficiency. By embracing holistic patching, organizations can fortify their systems against threats and ensure resilience in the face of evolving cybersecurity challenges.
