The OS Management service (OSMS) can help you maintain a secure and optimized Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) compute environment for running your applications. It also auto-discovers and monitors a set of curated application types running on Oracle Linux instances in OCI. The latest update enables auto-discovery and basic monitoring of MySQL databases running on OCI compute instances.
Auto-discovery of MySQL on OCI compute instances
Resource Discovery and Monitoring of OSMS periodically checks for running processes on Oracle Linux instances and automatically identifies the type of application to which it belongs. Supported application types include Oracle Database, Oracle Database Listener, WebLogic Server, Oracle HTTP Server, Apache Server, and Tomcat. In this release, MySQL Databases are now supported. This means a MySQL database is automatically discovered after a user has installed the MySQL database on an Oracle Linux compute instance. Once discovered, OSMS automatically starts monitoring its state, overall CPU utilization, and memory utilization.
Basic monitoring of MySQL databases with OS Management
From the OCI compute homepage, you can go to the Monitored Resources tab under the OS Management option to monitor the MySQL database’s current state, CPU utilization, and memory utilization. Time controls can be adjusted on the page to monitor different time periods. Use the percentage change values to get insights into how CPU and memory values compare with the same time last week, where a higher percentage change could mean higher workloads on the MySQL database.
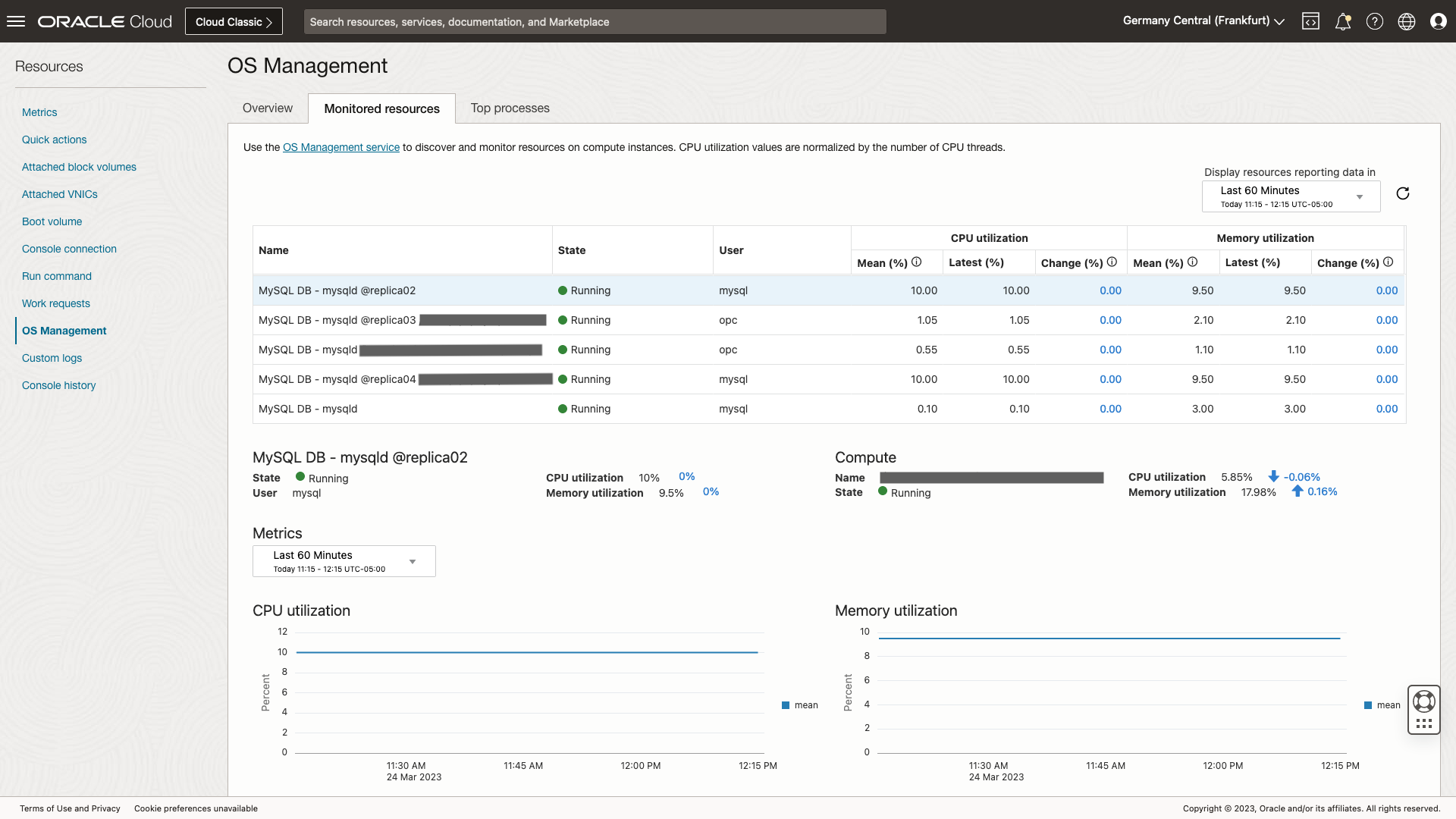
Monitoring across many MySQL databases
The Monitored Resources page has a compartment-level view to monitor visibility across all MySQL databases running in different compute instances within the compartment. Using this page, you don’t need to go to individual compute instances to monitor each MySQL database. You can sort the table of resources by Name to see all MySQL databases together and holistically check their status and resource usage. This view allows easy identification of MySQL databases that are not running or have unusually high CPU or memory utilization.
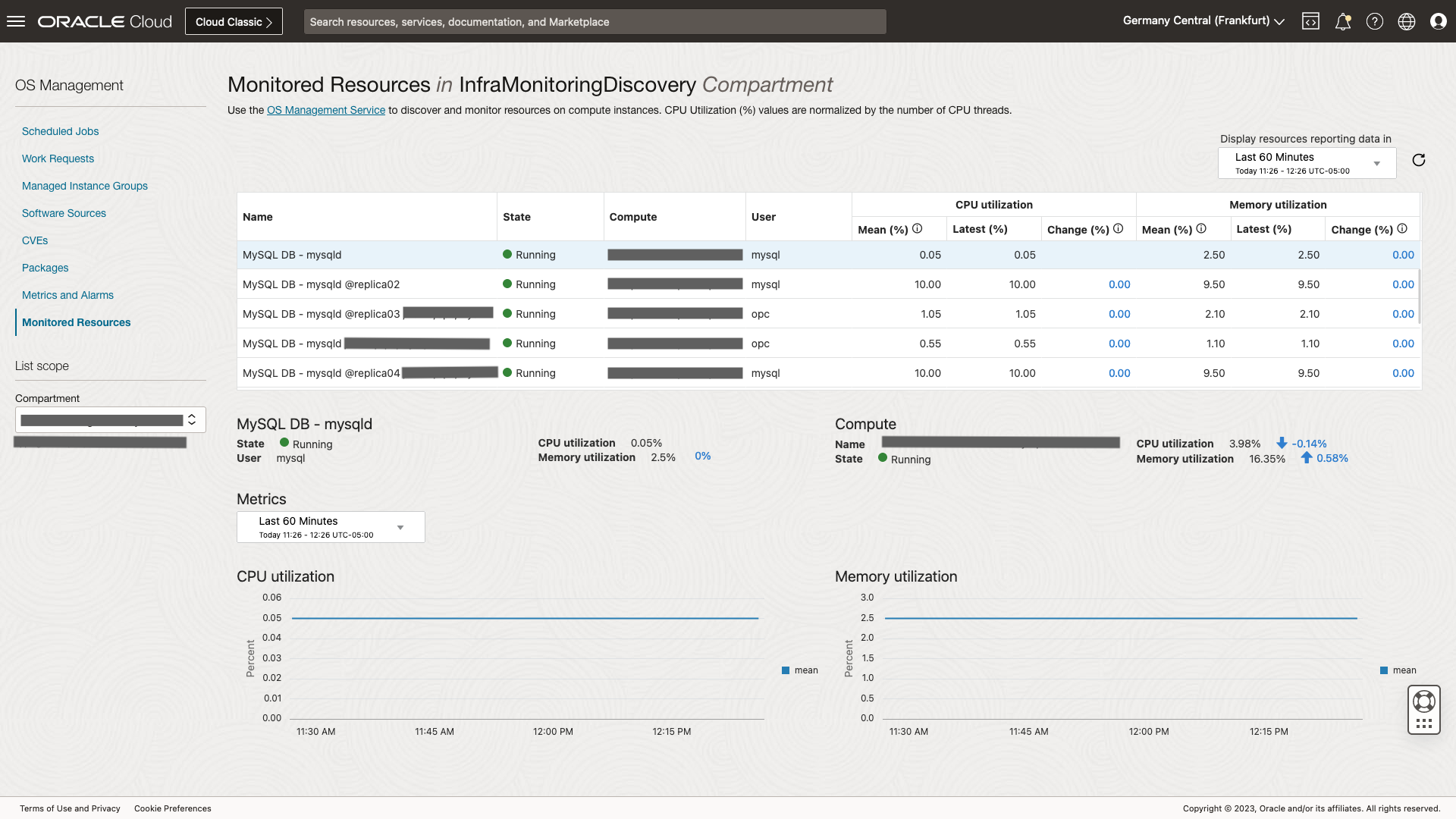
OCI Monitoring service Alarm when resource usage is high
All state, CPU and memory metric data for MySQL databases is stored with the OCI Monitoring service. This enables the creation of alarm rules to generate alarms and send notifications if the MySQL database is not running or if the MySQL database’s CPU utilization or memory utilization is higher than 90% for more than 30 minutes.
Easy access to OS Management for OCI subscribers
OS Management Service is available at no additional cost for paid OCI subscribers and can be used with minimal configuration. Anyone who needs a scalable solution for maintaining and securing their OS instances can get immediate benefits from OS Management.
Resources
These features are available on all Oracle Linux-based OCI Compute instances that are managed by the OS Management service. For information on how to enable these features, refer to the following resources:
- Getting started with Resource Discovery and Monitoring (documentation)
- OS Management Service (documentation)
- Oracle Linux (web page)
