The MySQL Server 8.1.0 release was published on July 18th, 2023 and it introduces the new MySQL Configurator tool for MySQL Server 8.1 and higher on Windows.
The MySQL Configurator application for Windows configures a MySQL Server installation in a series of basic steps. It can both configure and reconfigure the corresponding MySQL Server installation. Additionally, it can also remove a configuration it creates to allow a clean environment when removing MySQL Server from a system to start from scratch.
Distribution Methods
MySQL Configurator is included as part of the MySQL Server 8.1+ installation packages. Both the Server MSI and standalone zip archives include it as a mysql_configurator.exe executable.
How to execute the MySQL Configurator?
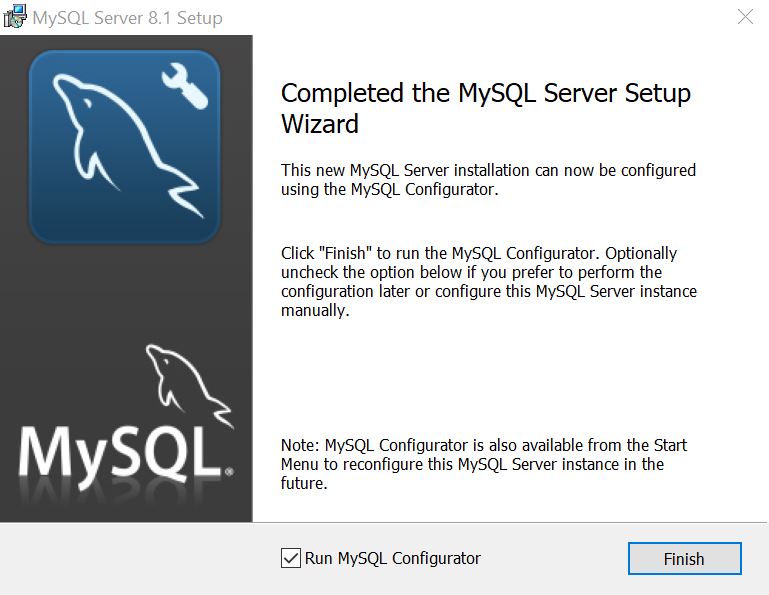
If installing MySQL Server using the MSI’s GUI, the final step of the MSI setup wizard’s process prompts to start the MySQL Configurator:
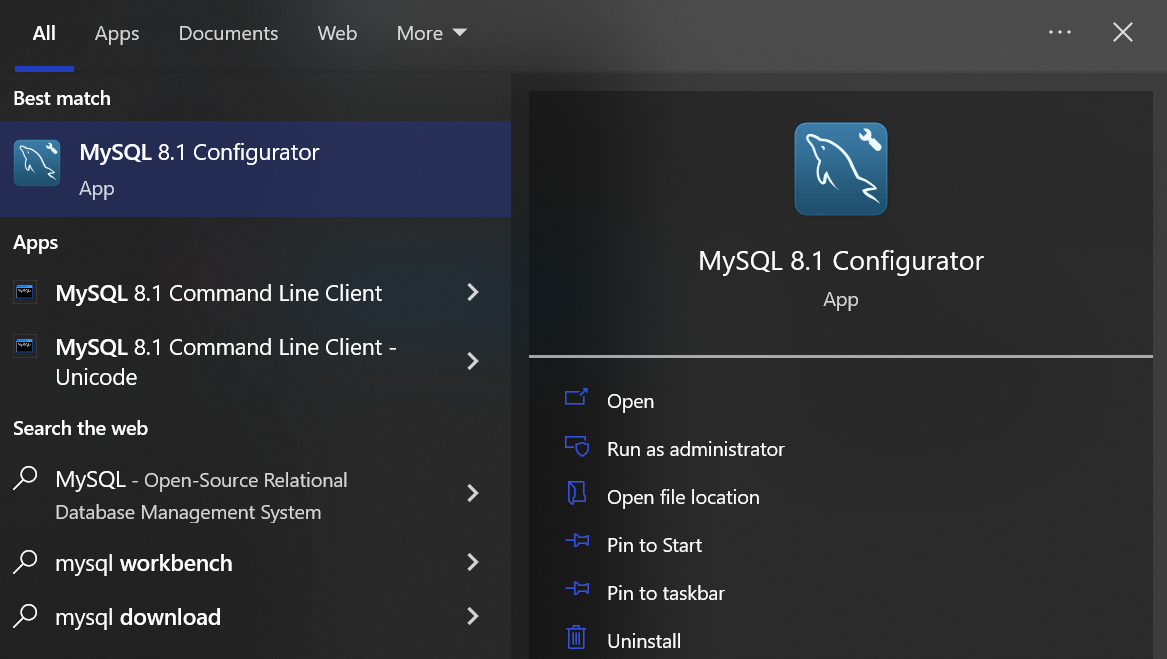
It also creates a Windows start menu shortcut that is able to launch the MySQL Configurator at any given time:
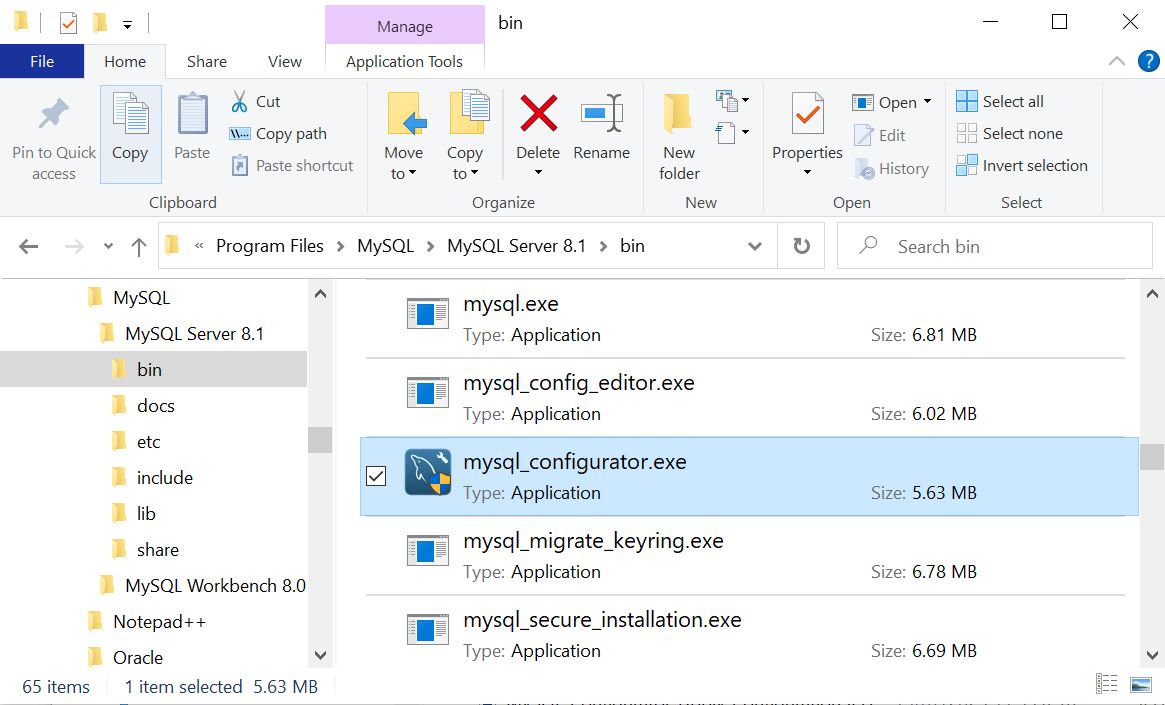
MySQL Configurator can also be found in the bin folder of the selected MySQL server installation folder. For standalone zip archive installations, look for the mysql_configurator.exe file located within the MySQL Server bin folder after extracting the files to the desired location:
As mentioned, MySQL Configurator is distributed as an executable file to execute anytime. If using Windows Explorer, double-click mysql_configurator.exe to configure or reconfigure the MySQL server installation.
To remove a configuration created by the MySQL Configurator in a previous configuration process, execute it with the “–remove” option. To do so, the easiest method is to open a command-line prompt and launch the executable while passing in the “–remove” option.
Note: MySQL Configurator requires administrative privileges to execute because it creates/deletes files and sets their file permissions.
What aspects of the MySQL server can be configured?
It configures options to create a running MySQL Server instance on the local machine. This involves defining protocols to access the MySQL server, creates a configuration file (my.ini) (usually in C:\ProgramData\MySQL) that contains the selected configuration options, creates and initializes the MySQL server’s data directory, adds the required firewall rules, configures the MySQL server to start as a Windows Service or process, and more. The configuration process includes the following stages:
Welcome Page
This page is only visible for a first time configuration, and not for a reconfiguration.
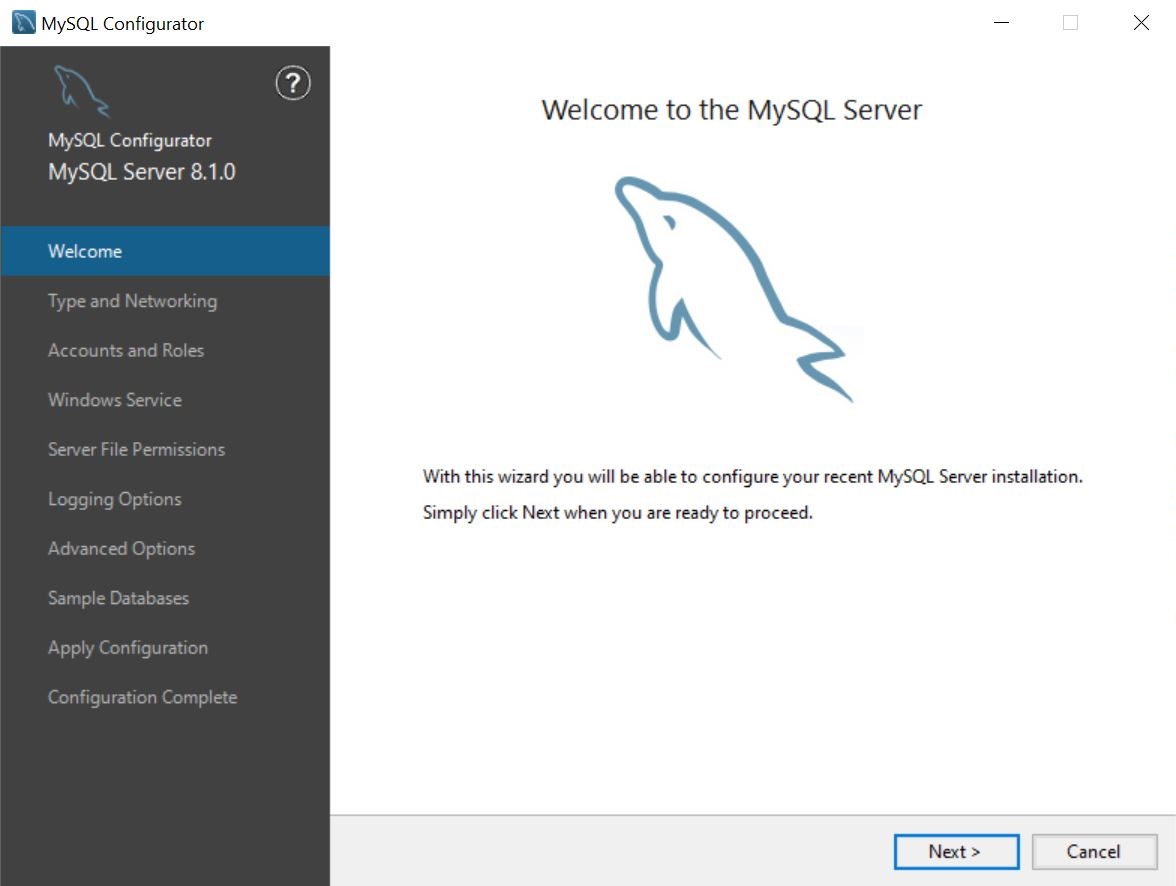
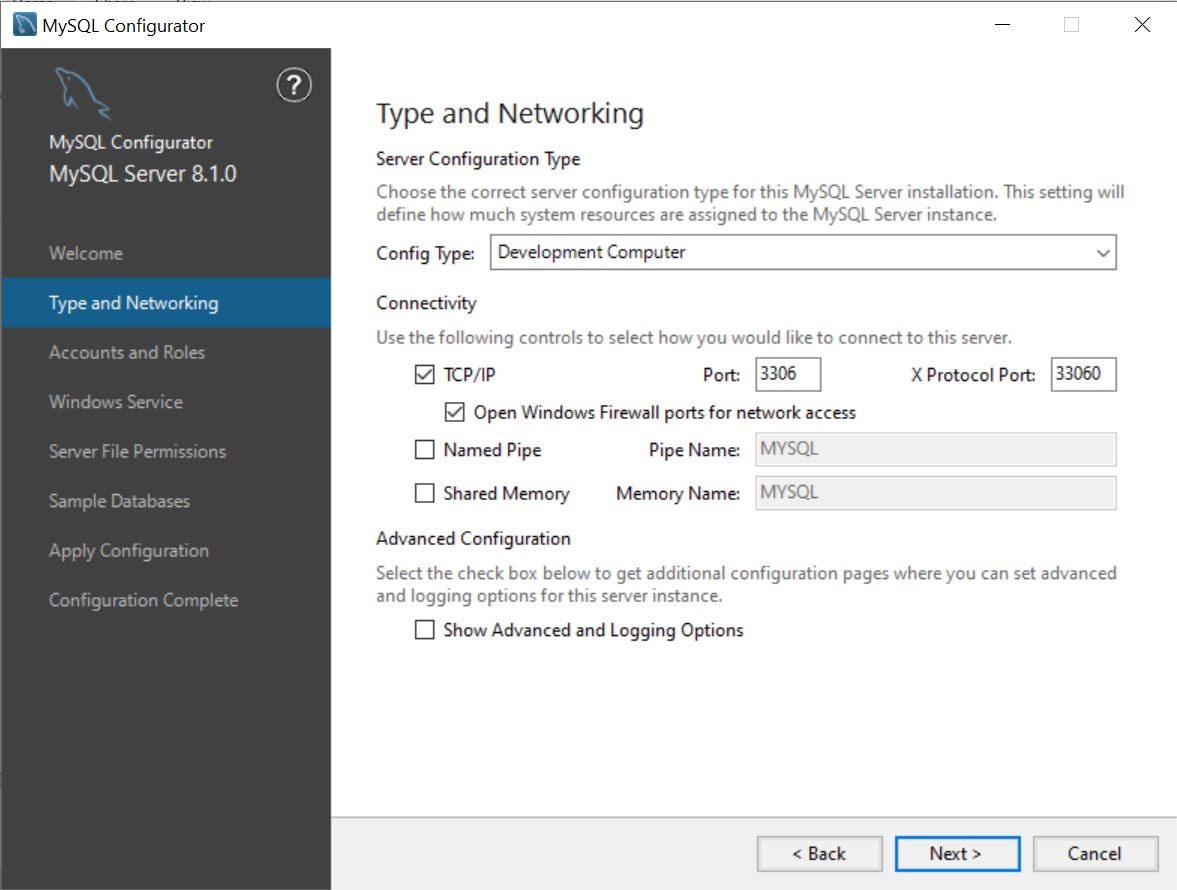
Type and Networking Page
This is where the configuration process begins. It first offers to select the main purpose of the MySQL server being configured by choosing the Server Configuration Type. Select the option that best reflects your intended use. Here you can also select the protocols used for connections. Finally, checking Show Advanced and Logging Options adds two additional configuration pages further down in the configuration process.
Accounts and Roles page
Here you assign the MySQL root user’s password. During a reconfiguration process, it prompts for the existing root user password rather than create a new one.
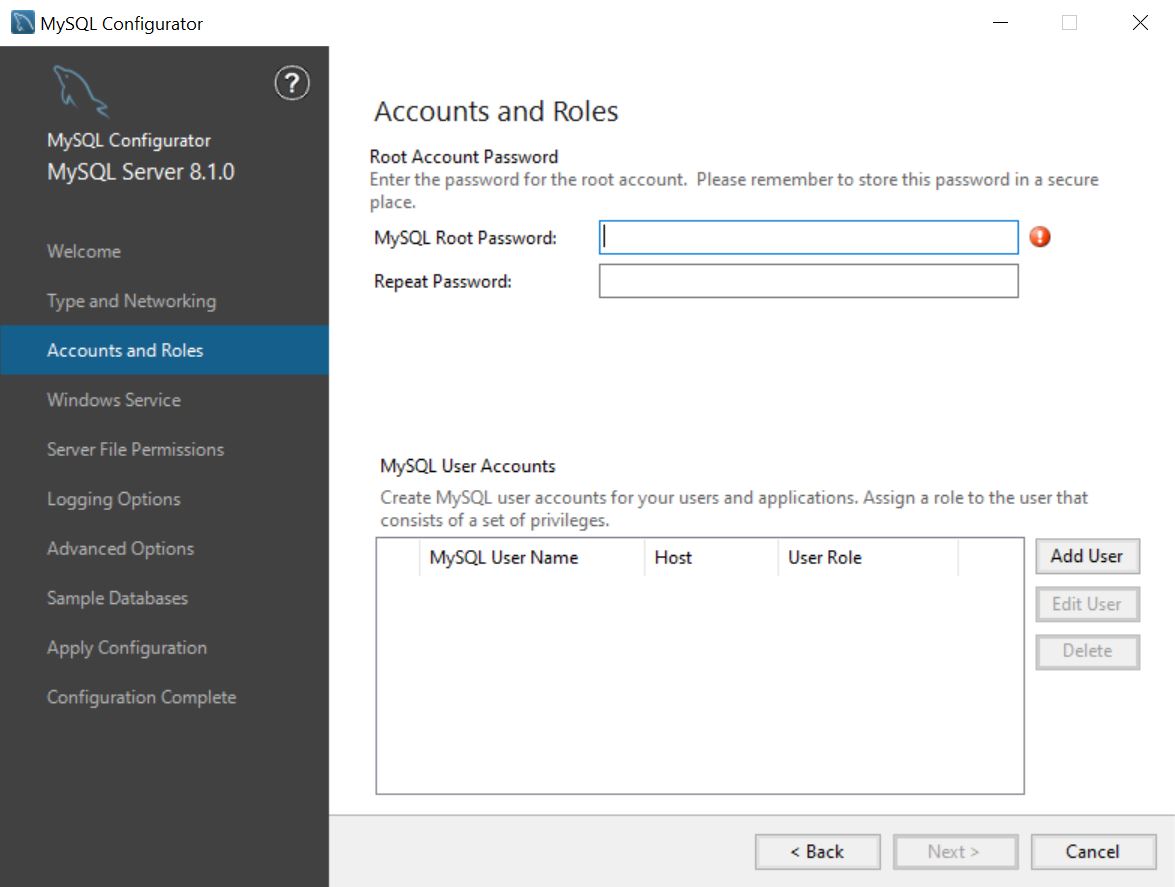
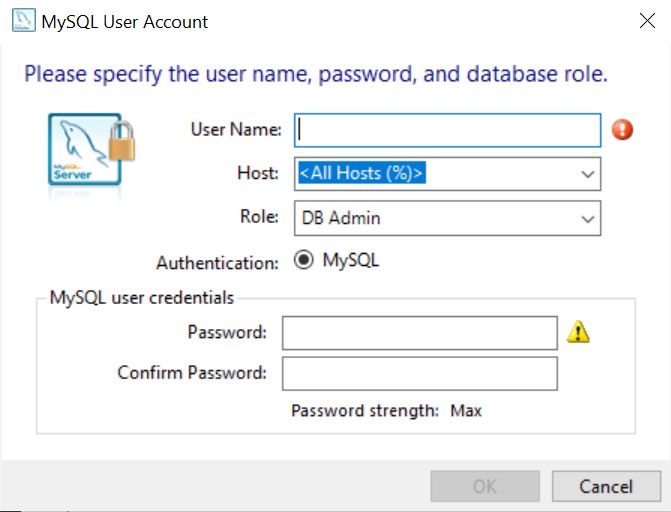
Click Add User to add additional MySQL users. These users are granted access to the MySQL server data based on the selected user role. Note that the creation of a user is currently only allowed during the initial configuration process and not for reconfigurations.
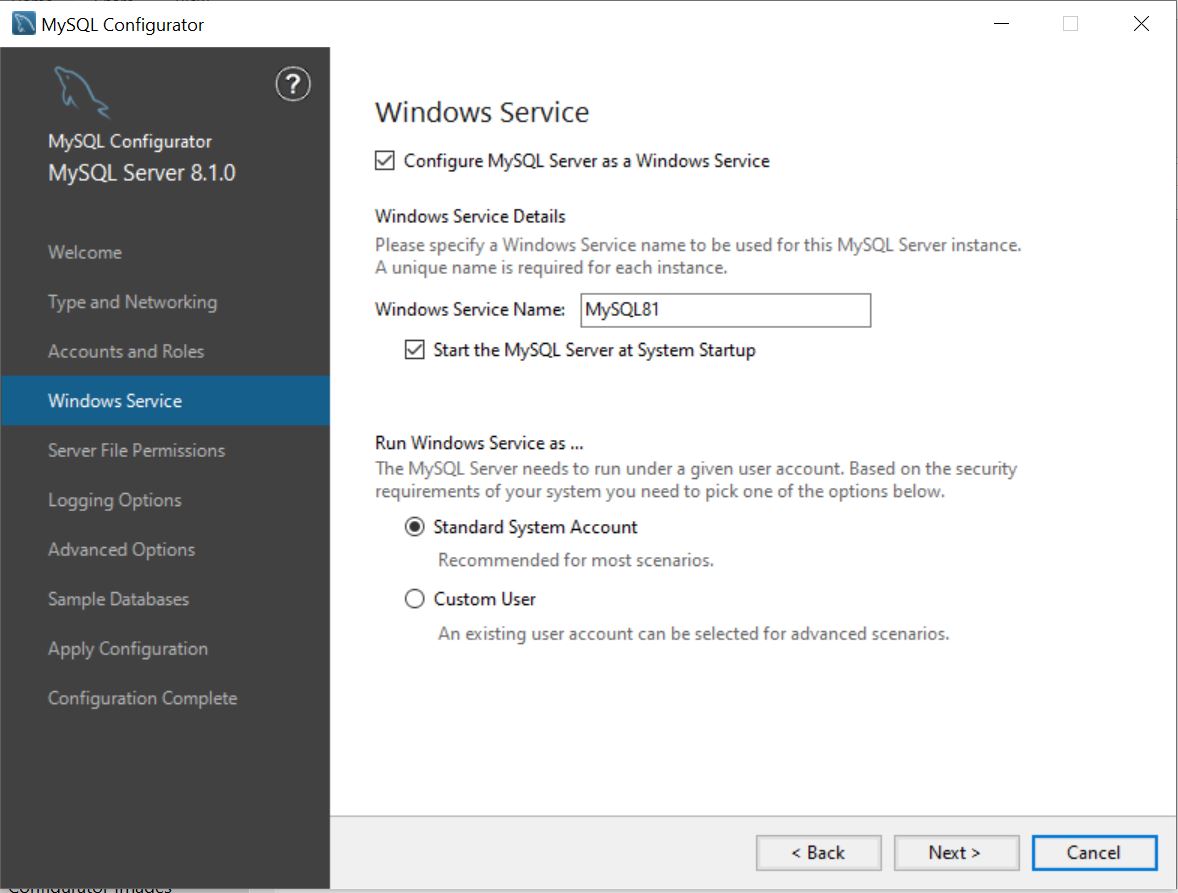
Windows Service page
By default, MySQL Configurator configures the MySQL server to automatically run as a Windows Service, or it can instead start it as a process. Starting MySQL as a process requires you to manually start the MySQL server after the host computer restarts or shuts down. When configured as a Windows Service, the Windows NETWORK SERVICE account is assigned to start the service but using a different account is optional.
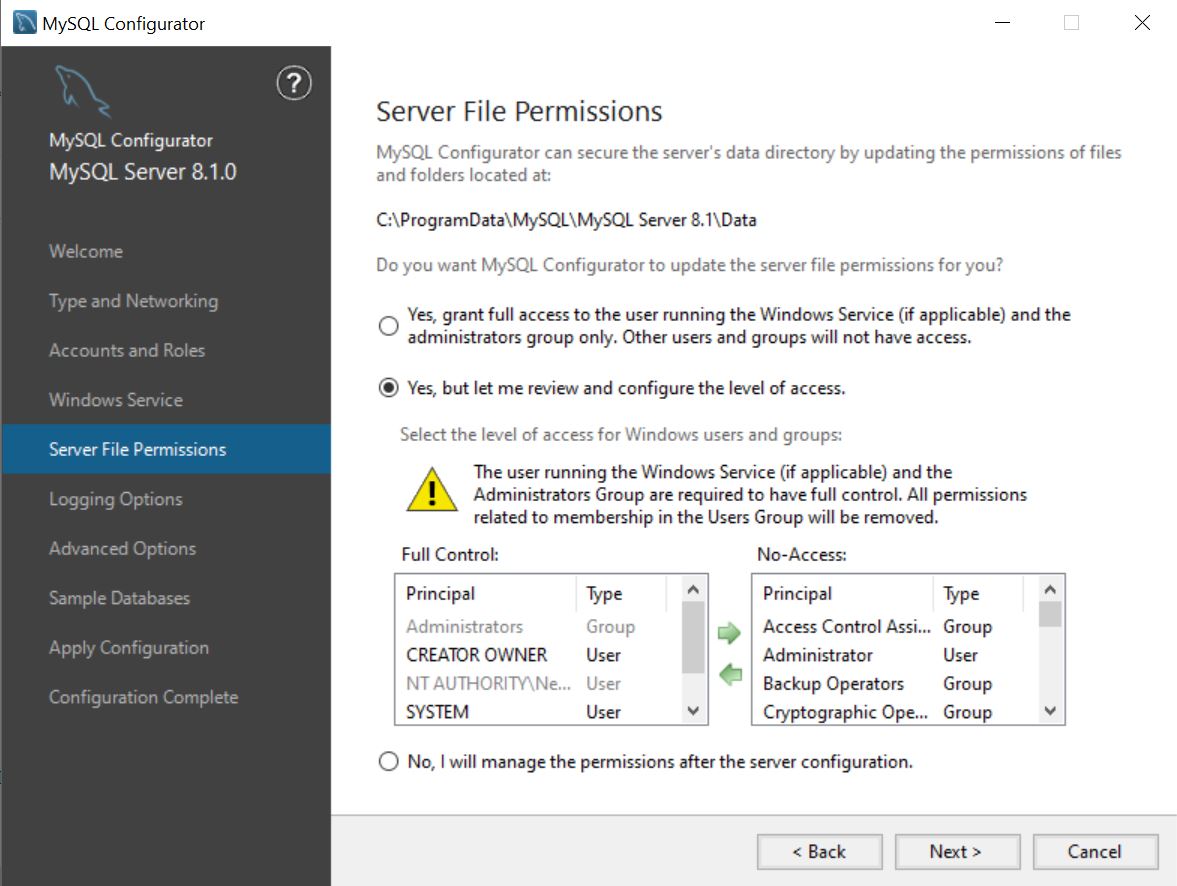
Server File Permissions page
Security of the MySQL server’s data directory is imperative, hence the need to configure which users have access to it. By default, the configuration process grants the minimum needed permissions, but you can configure access in a different way using this configuration page by either selecting users to gain access or to allow you to manually configure the permissions after the configuration process ends.
The next two pages are only visible if the Show Advanced and Logging Options checkbox was checked in the Type and Networking page:
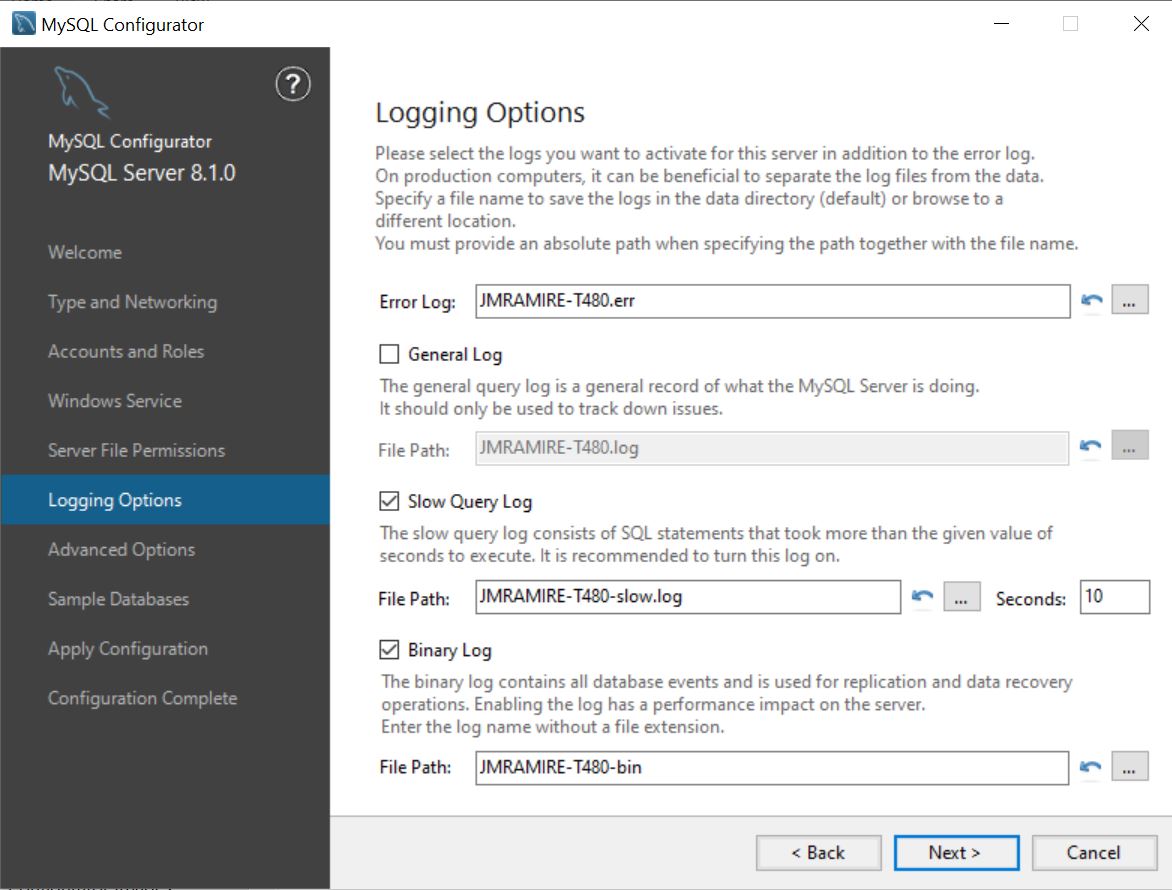
Logging Options page
Select different paths for the MySQL server logs, and it can also enable or disable log types.
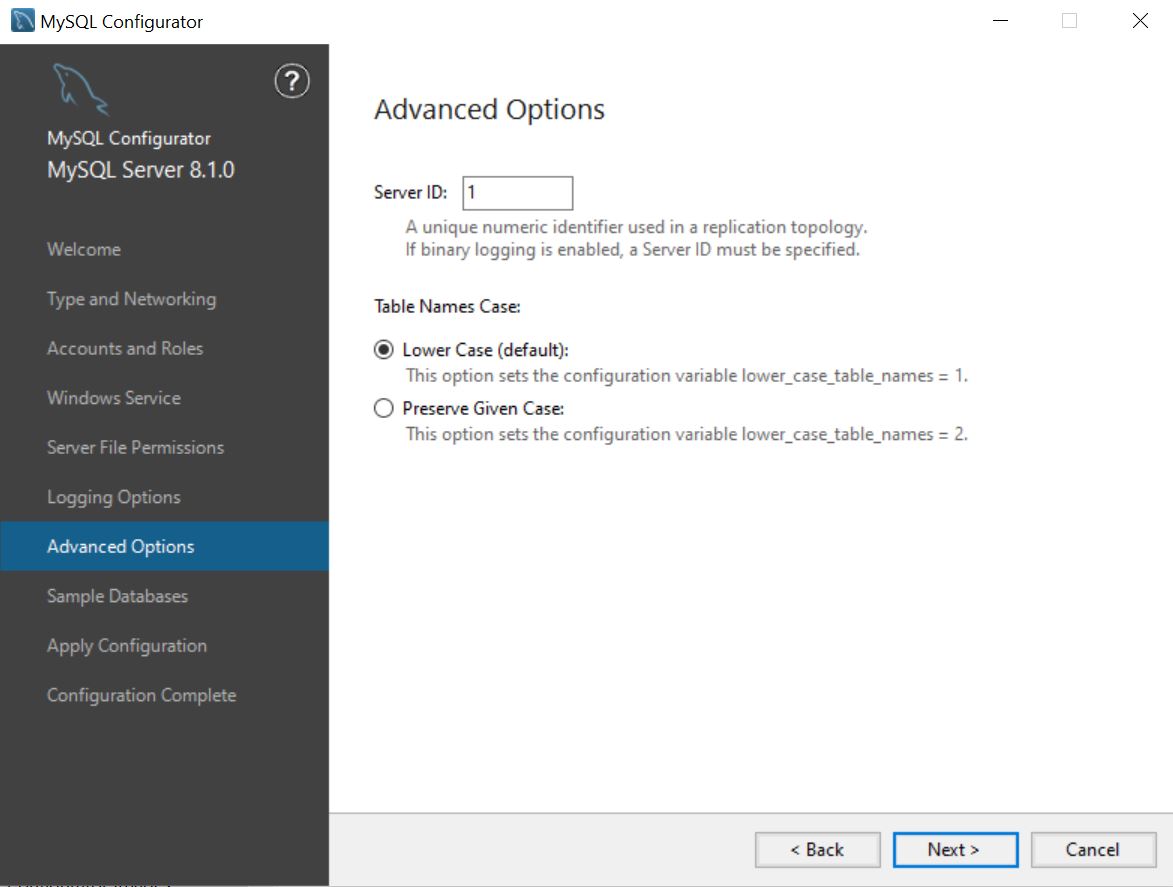
Advanced Options page
Allows you to specify a MySQL server ID (probably needed if there are plans to implement an InnoDB cluster in the future) and to select the casing behavior when the server deals with table names.
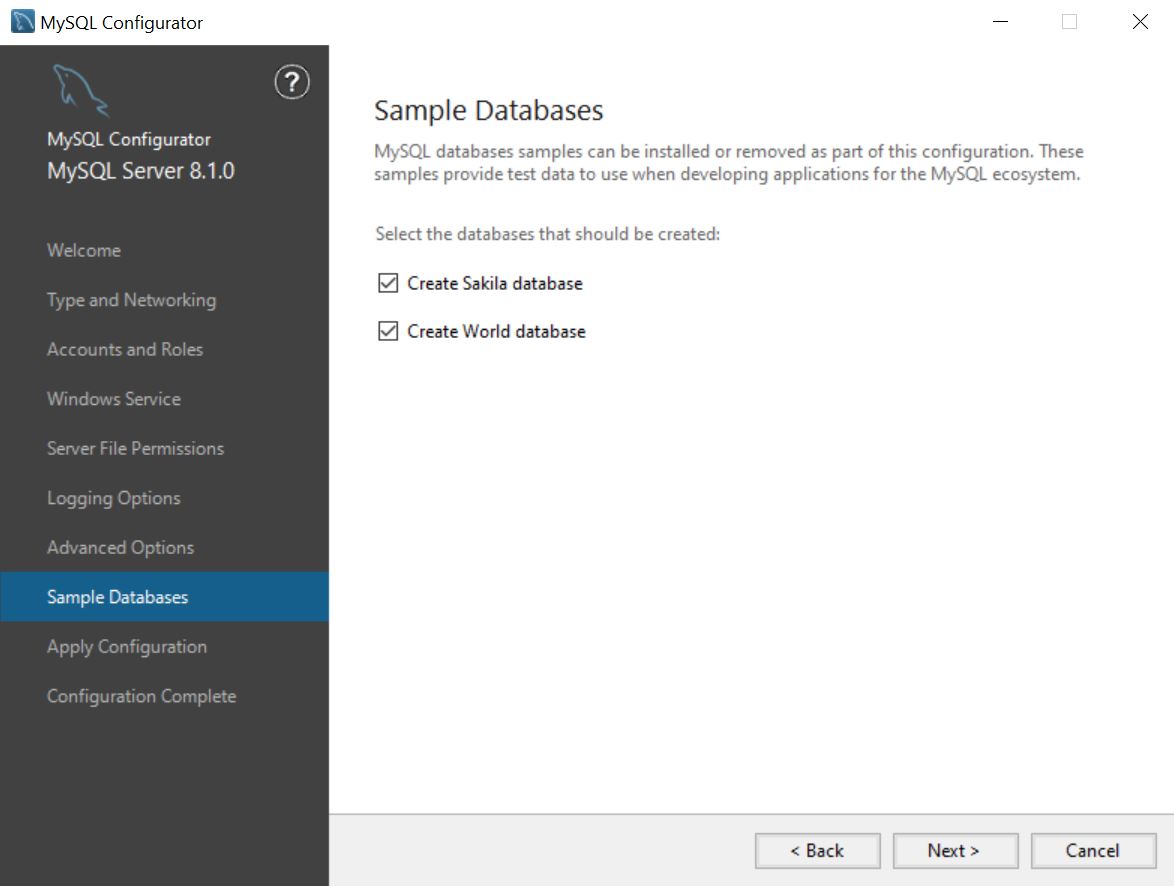
Sample Databases page
MySQL offers sample databases to test your applications. Select your desired sample databases to create either during initial configuration or reconfiguration.
Apply Configuration page
After selecting the desired configuration option, click Execute to configure your MySQL Server instance.
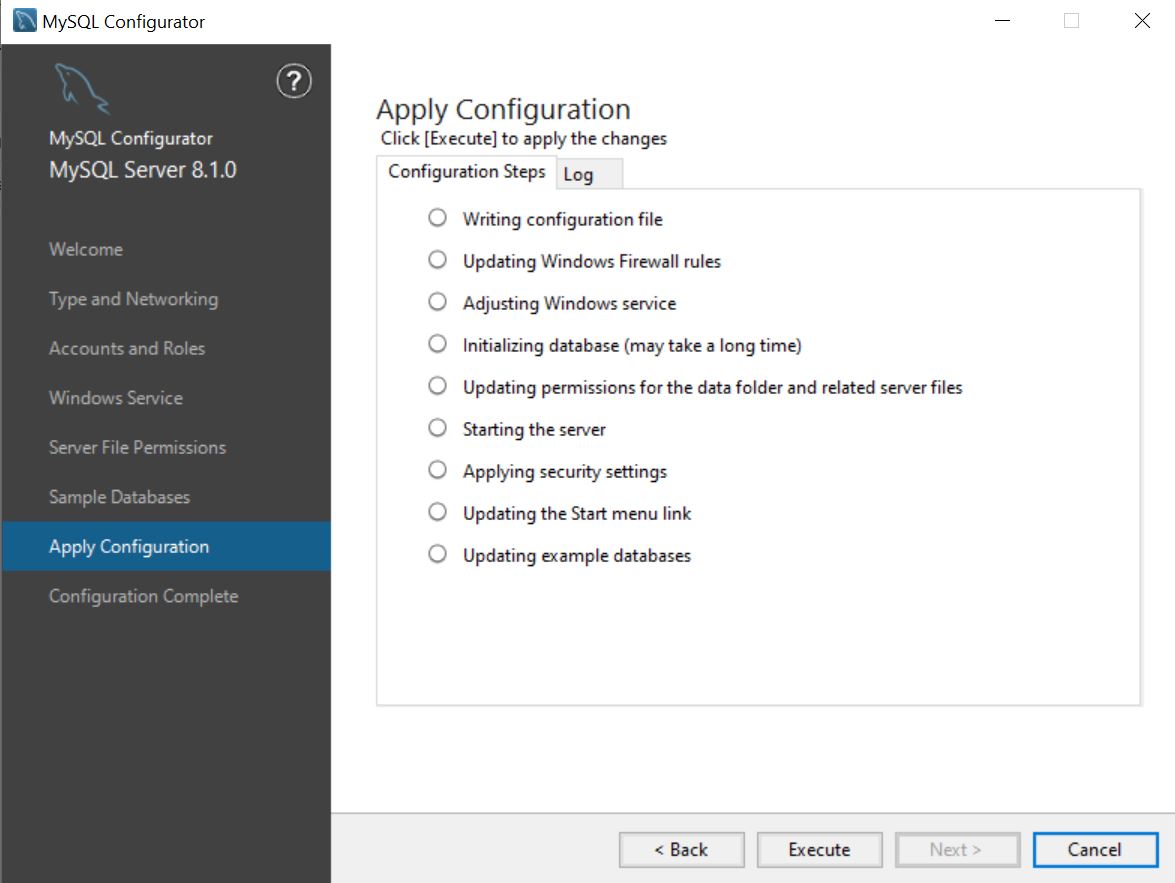
Note that start menu shortcuts are only created for MSI installations, meaning the Updating the Start menu link step is not shown during the configuration of a zip archive installation.
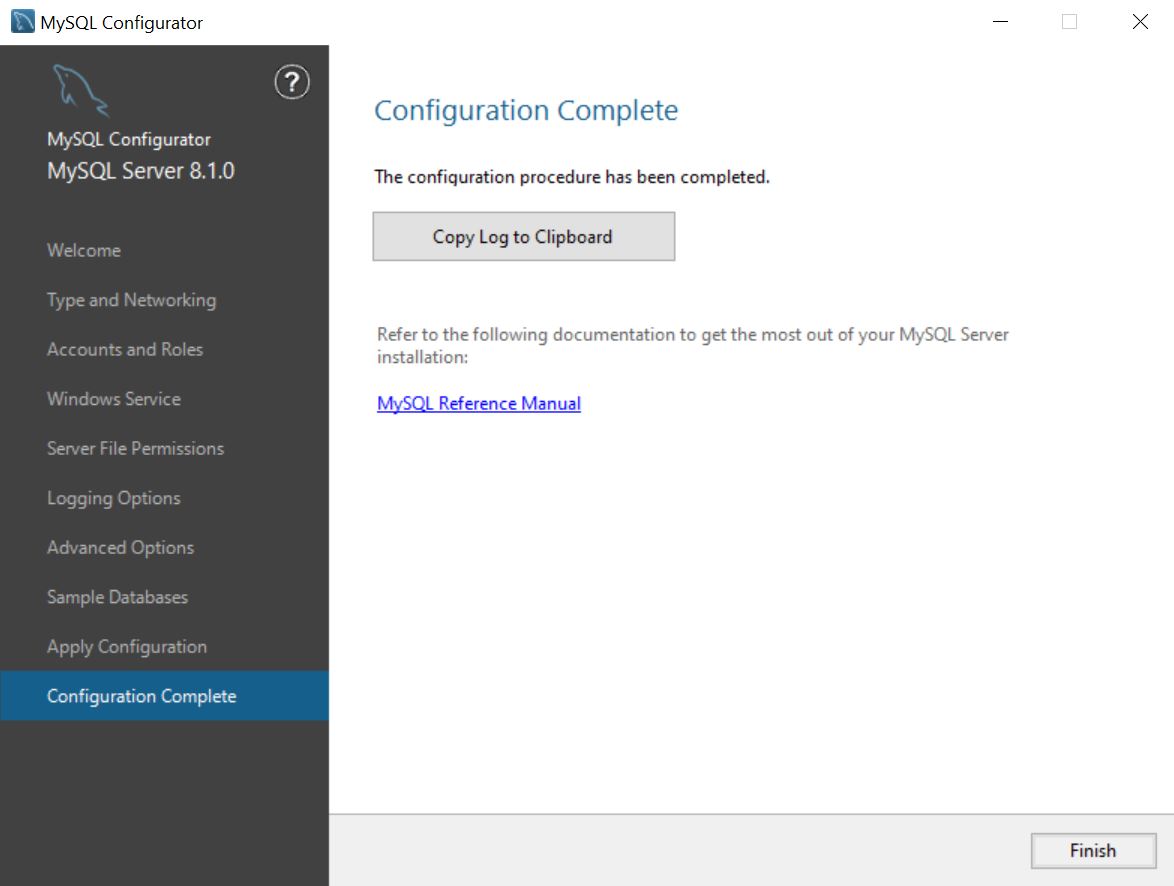
Configuration Complete page
Finally, review the log (if not done already as part of the Apply Configuration page) and refer to the official MySQL documentation. Reaching this page means that the configuration process completed as intended, and that you can proceed using your MySQL server instance.
Reconfiguration
MySQL Configurator is available anytime after the initial configuration, and allows you to automatically identify the previously selected configurations. From here a configuration can be changed if needed.
Removal Mode
When uninstalling MySQL Server using the MSI or through the Windows Control Panel, the uninstall process will automatically launch MySQL Configurator in removal mode to allow removal of the configuration created by MySQL Configurator. Zip archive installations should manually launch MySQL Configurator in removal mode before removing the server files to ensure there are no leftover files.
Running MySQL Configurator from the command-line and passing in the “–remove” parameter makes it run in removal mode. This option is useful to start over from scratch or to remove the MySQL server.
Running in removal mode prompts whether the data directory should be removed or not. Opting to not remove it means that the data directory is intended for use with a future installation. Note that MySQL Configurator does not currently support reusing an existing data directory during a first-time configuration process.
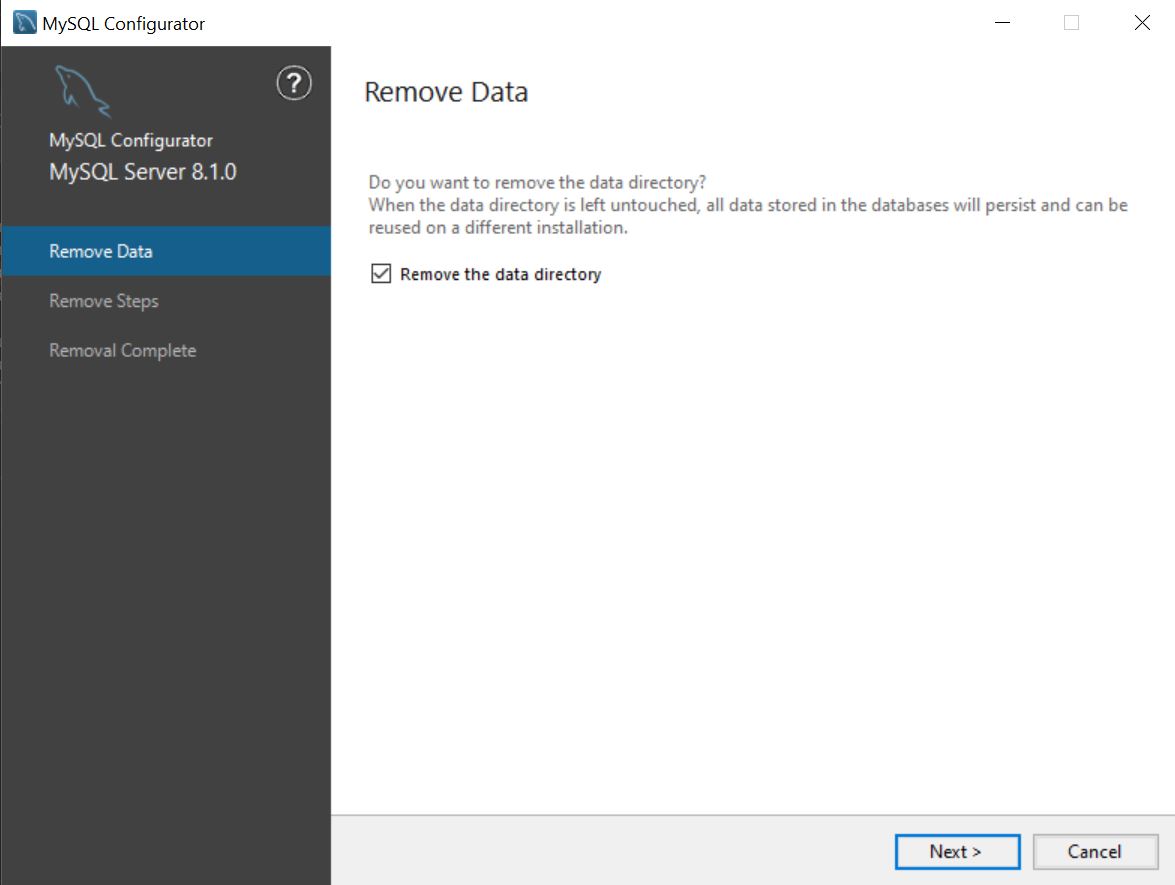
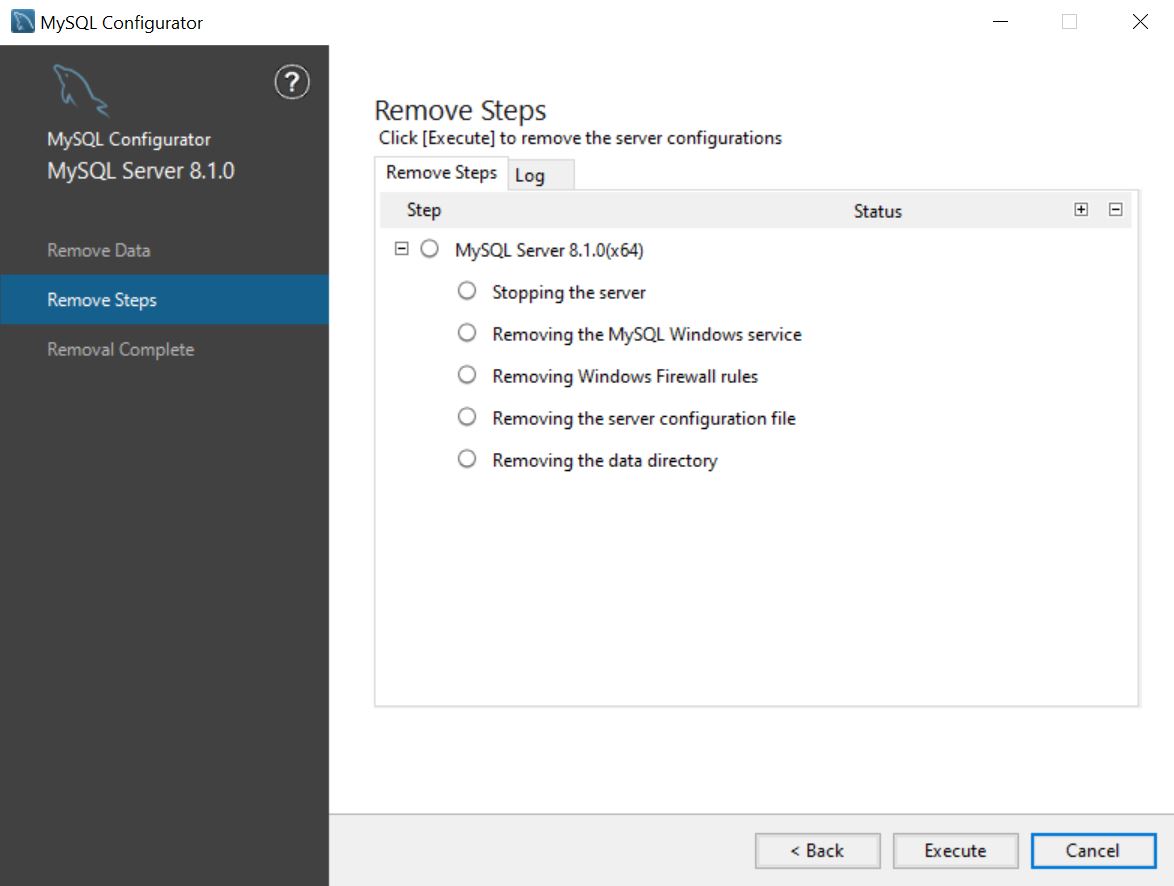
After choosing whether the data directory should be removed or not, proceed to execute the removal steps.
Download
As previously mentioned, MySQL Configurator is part of the MySQL Server 8.1+ installation package. To download the latest version of MySQL Server, refer to this official downloads page.
Bug Reporting
For any issues or incorrect behavior, please file a MySQL Configurator bug report. Access MySQL Bugs and raise a new bug under the MySQL Server: Install Configuration Tool category. Ideally, first check that a similar issue has not yet been raised. Also, please provide easy to follow steps for reproducing the issue.
Contributing Code
The code for the MySQL Configurator tool is publicly available in the official Github repository. Developers interested in contribuiting to this project should follow these steps:
- Make sure to have a user account at bugs.mysql.com. The account will need to be referenced when submitting the OCA (Oracle Contributor Agreement).
- Sign the Oracle OCA. Instructions related to this step can be found at the OCA page.
- Develop the pull request.
- Validate the pull request by making tests that sufficiently cover the functionality.
- Submit the pull request. While the pull request can be submitted with Github, it can also be submitted directly with bugs.mysql.com.
We truly believe in the principles of open source and appreciate any and all contributions to our projects.
Thank you for using the MySQL products!
We hope MySQL Configurator will ease your MySQL server configuration experience and meet your expectations. Future releases will add more configuration capabilities to ensure that we’re always up to date with the latest MySQL offerings to fit your needs.
