Overview
OCI MySQL Heatwave allows customers to use OCI user accounts to authenticate using authentication_oci plugin. Up to MySQL 8.0.32, this required an API Key pair. Starting with MySQL 8.0.33, the plugin also supports the IAM Security token generated using the OCI CLI.
Since only local and provisioned users have access to the API Key-Pair, federated users can greatly benefit from our new feature, because credentials used to generate the IAM Security Token can use integration with external identity provider. This enables DBAs to leverage the Identities and Group Memberships of any OCI user (Local, Federated or Provisioned) for authentication into MySQL Instances.
Using this feature, a MySQL instance can validate a connecting user via the IAM security token which is generated by the user through OCI CLI using the same credentials that they use to sign in to the OCI Console.
Prerequisites
To use authentication_oci plugin for IAM security token based authentication, you require following:
- A Local, Federated or Provisioned user account which allows you to login to OCI console either through Direct Sign-In or Single Sign-On.
- A correctly configured OCI CLI.
- The following policy statement defined in each tenancy you intend to connect:
- A running DB system.
- A correctly configured VCN granting command line access to the DB system either from a compute instance or a local machine.
- A correctly configured mysql command-line client.
Database Administrator’s Task
A Database Admin can create mappings which can allow a single OCI user or a group of OCI users to login to MySQL using IAM Security Tokens.
Mapping a MySQL user to a single OCI user
This mapping provides the OCI user the identity and privileges of a MySQL user.
Mapping a MySQL user to a Local user
This requires the OCID of the local user and the tenancy in which the user is defined.
Connect to the DB system as the administrator and run the following command to create and map the MySQL user, <MySQLUser> to the local user with OCID, <UserOCID>.
Mapping a MySQL user to a Federated/Provisioned user
This requires the User ID of the federated/provisioned user from the identity provider domain and the tenancy OCID.
Connect to the DB system as the administrator and run the following command to create and map the MySQL user, <MySQLUser> to the federated/provisioned user with User ID, <UserID>.
Notice the difference in terms of using <UserOCID> for local user v/s <UserID> for federated/provisioned user.
Mapping a MySQL Proxied User to an IAM Group
This mapping provides all the users of the IAM group the identity and privileges of the MySQL proxied user.
Connect to the DB system as the administrator and do the following to create and map MySQL proxied users <pUser1>, <pUser2> and <pUserN> to IAM groups <IAMGroup1OCID>, <IAMGroup2OCID> and <IAMGroupNOCID> respectively:
- Create MySQL users <pUser1>, <pUser2> and <pUserN> to proxy:
- Grant required privileges (such as database privileges, table privileges, and column privileges) to the MySQL proxied users using the GRANT Statement.
- Map the MySQL proxied users to IAM groups:
If an IAM user is a part of more than one IAM group, and if you map these IAM groups to different MySQL proxied users, then the IAM user is mapped to the first MySQL proxied user (that corresponds to the IAM group of which the IAM user is a part) defined in the group_mapping field. For example, if an IAM user is part of both <IAMGroup2OCID> and <IAMGroupNOCID>, then it is mapped to the first MySQL proxied user, <pUser2>, that corresponds to the first IAM group of which the IAM user is a part, <IAMGroup2OCID>.
- Grant proxy privileges to the anonymous user created in step 3:
MySQL proxied users <pUser1>, <pUser2> and <pUserN> are mapped to the IAM groups, <IAMGroup1OCID>, <IAMGroup2OCID> and <IAMGroupNOCID> respectively, enabling the IAM group members to access the MySQL Server with all the identity and privileges assigned to the MySQL proxied users.
Connecting to the DB System
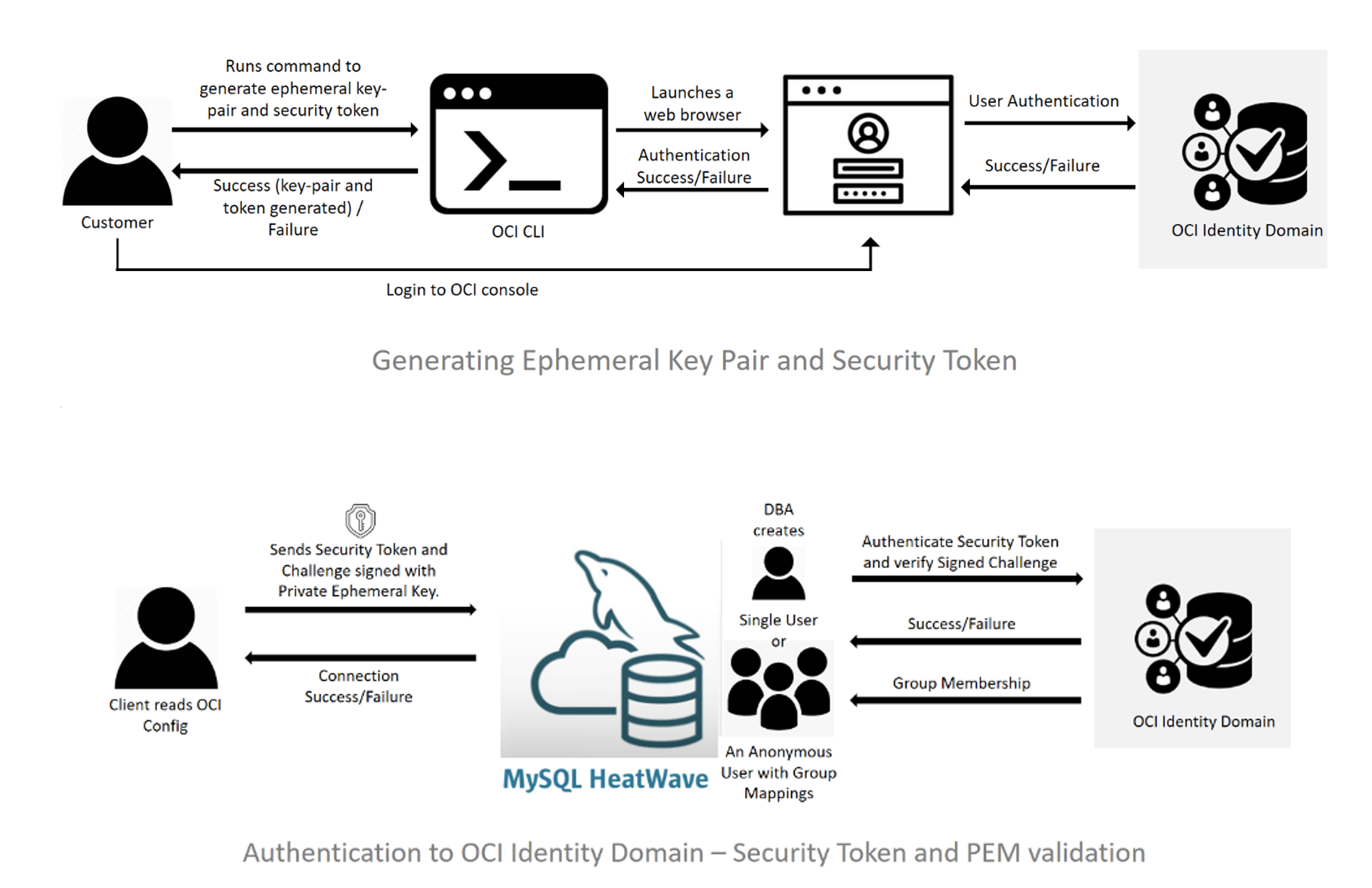
Generating IAM Security Token
Use the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure command-line interface to generate an IAM Security Token.
- Run the following command in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure command-line interface:
A web browser is launched.
- In the browser, enter your user credentials and login to OCI console.
The IAM security token is generated along with a session (or ephemeral) key pair. The authentication information is saved to the .config file. By default, the IAM security token expires in one hour.
- To refresh the IAM security token (within the validity period), run the following command:
You can refresh the token up to 24 hours.
Connecting with a Mapped MySQL User
From MySQL client, run the following command to connect to a DB system as a MySQL user who is mapped to an OCI user:
Connecting with a Mapped Proxy User
From MySQL client, run the following command to connect to a DB system as a MySQL proxied user who is mapped to an IAM group:
Here, <UserIdentifier> is the User OCID for a Local user and User ID from Identity Provider’s domain for a federated or provisioned user.
Conclusion
MySQL Heatwave allows users managed in OCI or an external Identity Provider to login an MySQL instance using IAM Security Tokens. This offers improved security and ease in user management.
Additional References
- MySQL Database
- Connecting to a DB System
- Authentication using authentication_oci plugin
- Identity and Access Management
- Understanding User Types
