Ensuring the reliability and performance of database backup and recovery operations is mission-critical for any enterprise. MySQL HeatWave Service already provides robust support for Manual, Automatic, and Operator backups. To further enhance the integrity and efficiency of backup operations, we are excited to introduce two new features: Backup Validation and Backup Preparation.
Why Backup Validation and Preparation Matter
For many organizations, maintaining regular backups and validating their integrity is not just a best practice—it’s often a regulatory requirement. Data protection standards and compliance frameworks (such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC) frequently require enterprises to retain validated, restorable backups to ensure business continuity and auditability.
Traditionally, the process of backup validation can be time-consuming and complex:
-
Customers must restore the backup to a separate environment
-
They then run various queries and checks to ensure data integrity and consistency
-
Post-validation, customers need to manually delete the temporary database resources they created for this purpose
The new Backup Validation and Prepare Backup features in MySQL HeatWave Service simplify and automate this workflow:
-
Usability: With just a click of the Validate button, customers can initiate a thorough integrity check no manual restore, or data queries required
-
Reduced Complexity: The entire validation and preparation process is managed by the service. Customers no longer have to provision, monitor, or tear down validation resources manually
-
Automatic Cleanup: All resources used for validation are automatically deleted after the process, eliminating orphaned or forgotten instances and saving costs
-
Future-Ready Backups: Prepared backups are optimized for faster restores. Pending redo and undo log changes are applied in advance, reducing recovery times and ensuring that your backups are truly ready whenever you need them
-
Overall, automated Backup Validation and Preparation take the guesswork, manual effort, and risk out of maintaining compliance-ready, easily restorable backups—making your database operations both simpler and safer.
Feature Highlights
Backup Validation
Backup Validation is designed to proactively confirm the integrity and restore-readiness of your backups. Here’s what it brings:
-
Reliability Confirmation: Ensures backups can be reliably restored.
-
Corruption Detection: Validates that backup files are complete and free from corruption.
-
Configuration Error Detection: Regular validation helps detect configuration or environmental issues early.
How it Works:
-
Restore the backup to a temporary validation environment.
-
Run internal consistency and integrity checks.
-
Tear down the validation environment.
-
Update the backup record with the validation outcome.
Backups that are detected as invalid are marked as FAILED, halting further size metering and triggering appropriate flags for remediation.
Prepare Backup
Prepare Backup enhances recovery speed, especially for transactionally active DB systems. Here’s how:
-
Accelerated Recovery: Applies all pending redo and undo log changes ahead of time. This reduces the InnoDB crash recovery at the time of restore.
-
Minimized Downtime: By reducing post-restore recovery operations, the overall impact of data loss events is minimized.
When to Use Prepare Backup
The Prepare Backup feature is particularly beneficial for transactionally active databases—those with frequent data changes—where InnoDB crash recovery can significantly increase restore times. By applying all pending redo and undo log changes ahead of time during backup preparation, the time required for crash recovery at restore is minimized. This means you can bring your database online much faster in the event of a data loss or migration event.
For databases with light workloads or those that are mostly idle, the advantage is less pronounced, as there are fewer changes pending and crash recovery is already quick.
Note:
Backup preparation is not instantaneous; the time required to prepare a backup is primarily determined by the volume of uncommitted changes and the size of the database. This preparation process essentially shifts the time and compute resources from the point of restore to the point of validation/preparation. In other words, by investing the time upfront to prepare the backup, you are making future restores faster and more predictable, especially important when business continuity demands minimal downtime.
This allows organizations to plan and control when the extra preparation workload occurs, avoiding surprises during critical restore events.
Steps: Validating and Preparing a Backup in MySQL HeatWave
1. Open the Navigation Menu
In the Oracle Cloud Console, click the navigation menu.
Select Databases.
Under MySQL HeatWave, click Backups.
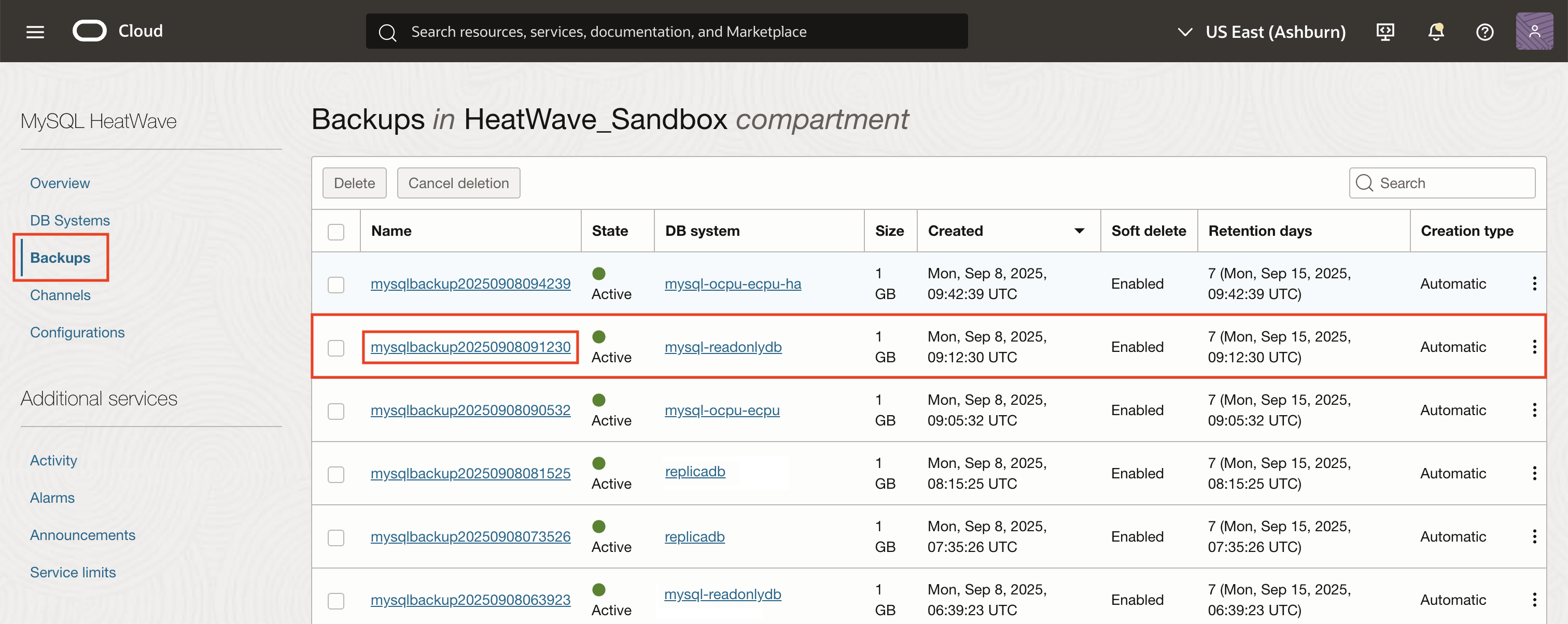
2. Locate and Select the Desired Backup
On the Backups list page, browse or search for the backup you want to validate.
Click on the backup entry to highlight/select it.
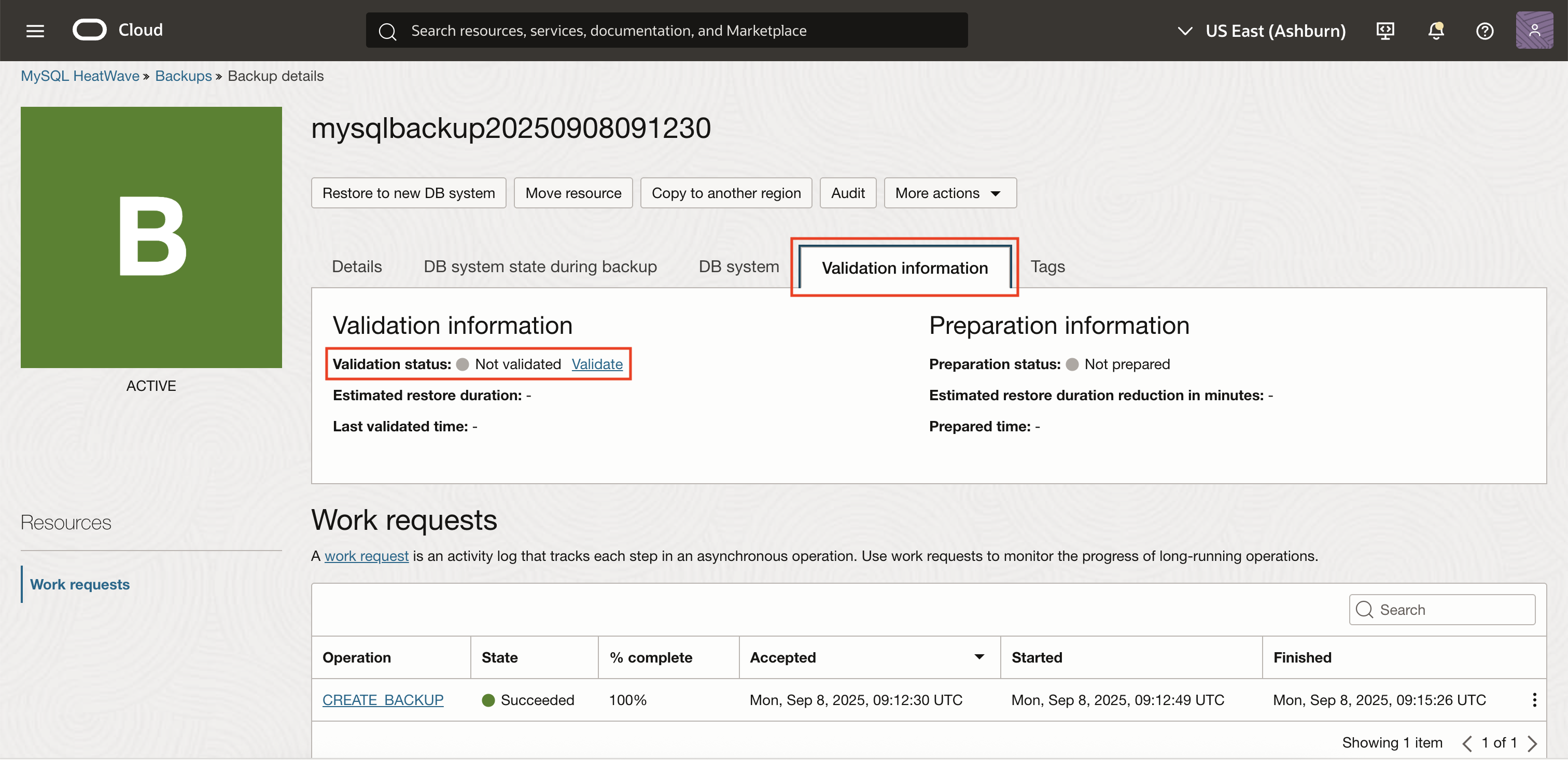
3. Initiate the Validation Process
With the desired backup selected, click Validate at the top of the page.
4. Enable “Prepare Backup” (Optional)
In the Validate backup panel that appears, you will see an option labeled Prepare backup.
If you want to enable backup preparation (and the backup hasn’t been prepared before), check the Prepare backup option.
Note: Prepared backup applies pending redo and undo log changes, making future restores faster.
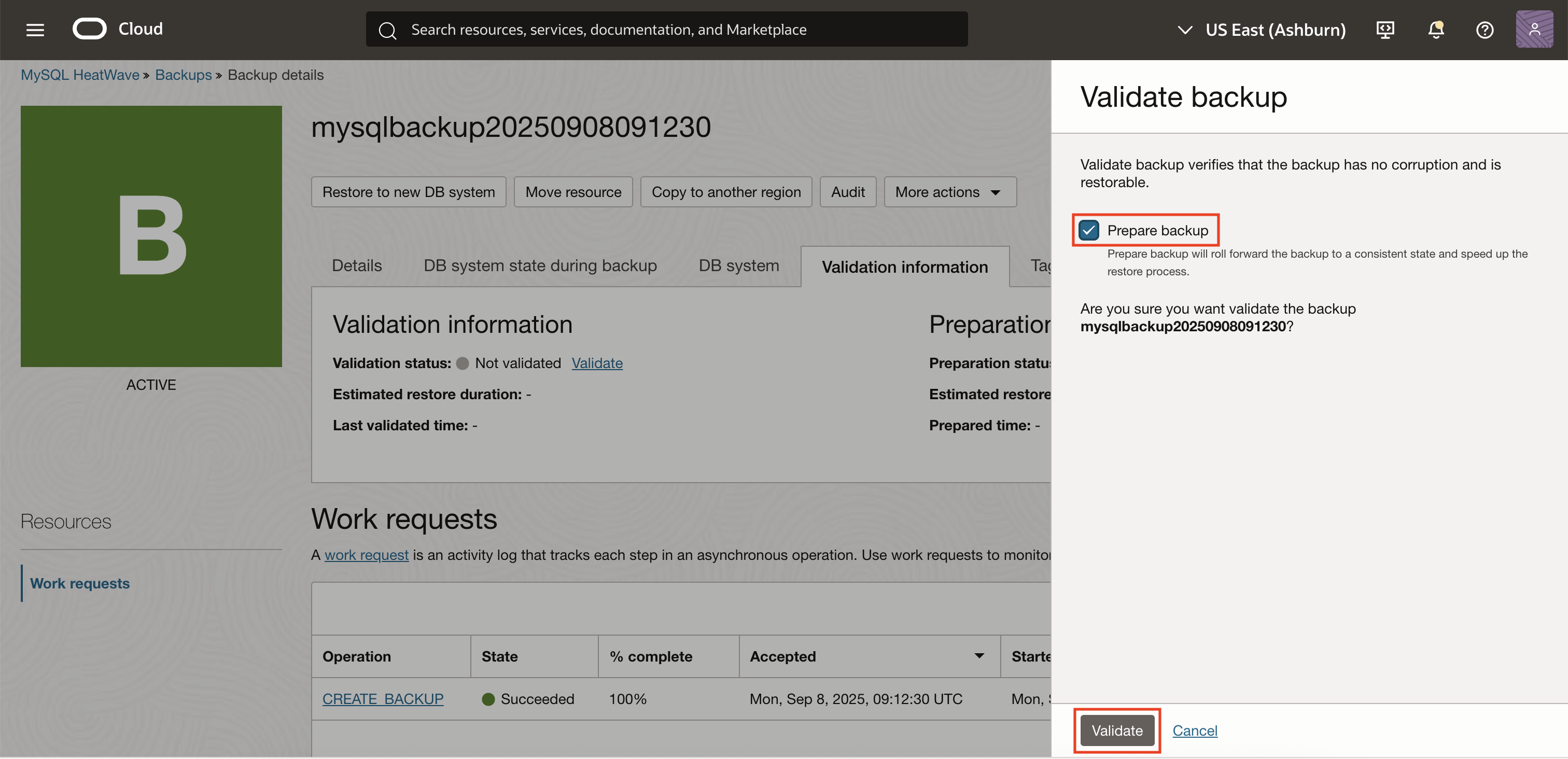
5. Confirm and Start Validation
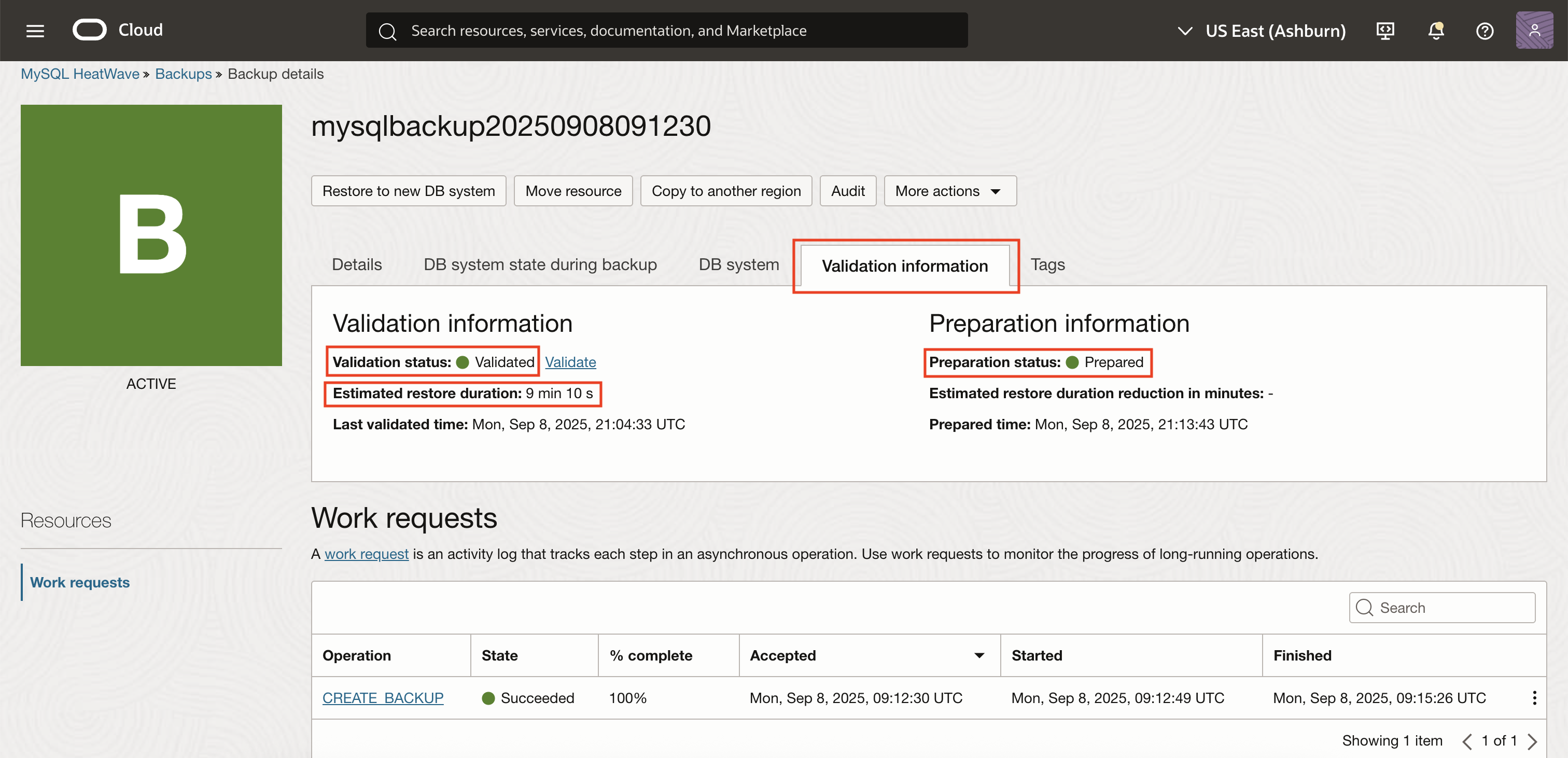
Click Validate to start the backup validation (and preparation, if selected).
The process will execute, and you can monitor status updates in the interface.
Billing Model
-
Customers are billed for compute and storage consumed during validation and prepare backup operations.
-
Compute shape matches that of the original DB System.
-
Validation and prepare backup processes are transparent (no customer-visible DB Systems are created for these operations).
-
DbSystemBackup OCID is used for metering rather than the MysqlInstance OCID.
-
In Prepare Backup, two validation environments are created sequentially:
-
First, an environment is provisioned to validate the original backup
-
Once this step completes, a second environment is created to validate the prepared backup
These environments are not active at the same time; instead, each is created and metered one after the other. As a result, customers are only billed for the compute resources of one validation environment at any given moment, not both concurrently.
-
-
Billing starts when resources are provisioned and stops upon their deletion.
Backup Size Metering
-
Backups that are detected as invalid are set to a FAILED state, immediately stopping storage metering.
-
Prepared backups will have full data with all pending logs applied; even if the backup Type is incremental on preparing, the backup size will increase to full size; metering updates accordingly after preparation
Conclusion
With Backup Validation and Backup Preparation, MySQL HeatWave Service customers can be confident that their backups are not only intact but also primed for fast, reliable restores. These features help ensure business continuity, minimize downtime, and protect critical data assets essential in modern enterprise environments.
References
