HeatWave is the only fully managed MySQL database service that combines transactions, analytics, machine learning, and GenAI services, without ETL duplication. HeatWave also includes HeatWave Lakehouse, allowing users to query data stored in object storage, MySQL databases, or a combination of both. Users can deploy HeatWave MySQL–powered apps on a choice of public clouds: Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure.
Database systems by default, and independent of the cloud provider, are read-write and can be accessed by any defined user account with the required privileges and valid access credentials. Nevertheless, in some cases, users might want to make a database read-only or restrict its access only to administrators, for security reasons or to preserve data integrity. It is possible to find ways to achieve this using some alternative strategies, such as: changing all individual users’ account privileges only to allow reads or changing the settings of the network resource used to connect to the database to restrict connections. However, the application of those strategies can be cumbersome and error-prone, especially when they need to be performed in a short amount of time. Wouldn’t it be better to have a safe and straightforward database option that allows this?
For HeatWave database systems on OCI (DB system), we’ve solved this challenge by introducing two new DB system properties, namely the database mode and access mode. The database mode allows the user to set a DB system as READ-WRITE (allowing reading from and writing into the DB system) or READ-ONLY (allowing only reads from the DB system, writes will not be permitted except those done via an inbound replication channel). The access mode allows the user to set a DB system as UNRESTRICTED (allowing all valid accounts with the required privileges to connect to the DB system) or RESTRICTED (allowing only valid administrator accounts to connect to the DB system).
Motivation
In a nutshell, the main reason to configure a database as read-only is to preserve its data integrity, protecting it against undesired data changes. Several use cases can be found where this might be needed:
- Historic or archive purposes: Some databases might only be used for historical and archive purposes, keeping data that should not be modified and only used for reporting or auditing.
- Maintenance and security: Administrators might be required to prevent data changes or even restrict access to the database while performing some critical maintenance task (e.g., upgrading the application) or for security reasons (e.g., when suspecting that the application or some component might be compromised).
- Disaster Recovery (DR): In a DR setup, an active DB system on a given region can replicate to another stand-by DB system in a distinct region. Should any disaster happen on the active DB system region, making it completely unavailable, the warm stand-by DB system is then ready to take over. The replica DB system should be set as read-only (only accepting transactions from the replication channel) to avoid accidental writes to it, preventing the data from diverging from the primary DB system. The access to the replica DB system can also be restricted to administrators to block connections to the wrong DB system, fencing the applications and other users from accessing the replica DB system.
What changes on MySQL instances
In practice, changing the database mode corresponds to setting the super_read_only MySQL system variable, and changing the access mode corresponds to setting the offline_mode MySQL system variable. Changes to the database mode or access mode are applied to all the MySQL instances of the DB system, including the associated managed Read Replicas (RR). However, in the case of RR which are read-only by definition, setting the database mode to READ-WRITE will have no effect and the RR will remain read-only. Thus, only the access mode setting is effectively applied to RR instances.
In more detail, the following setting will be set on the MySQL instances, according to the database mode and access mode values of the DB system:
- Database mode:
- READ-WRITE: super_read_only = OFF (except for RR);
- READ-ONLY: super_read_only = ON;
- Access mode:
- UNRESTRICTED: offline_mode = OFF;
- RESTRICTED (Administrators only): offline_mode = ON;
Managing the database mode and access mode
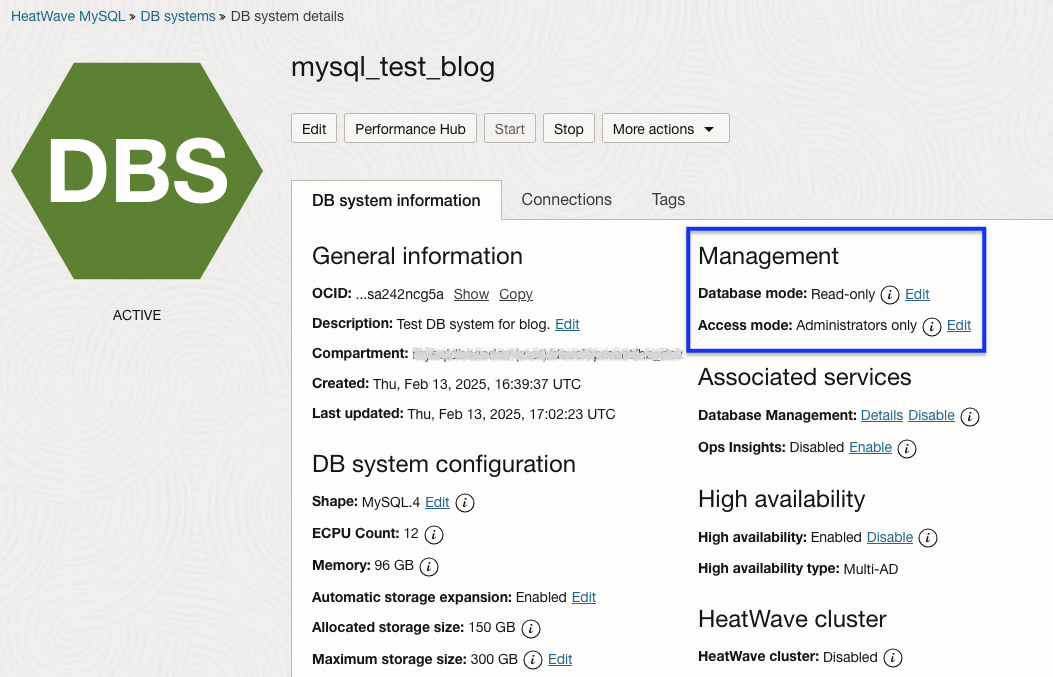
To check the database mode and access mode of a DB system, access the OCI Console and navigate to the target HeatWave DB system:
- Go to the Database section;
- Under the HeatWave MySQL category, click DB Systems;
- Click on the Name of the desired DB system in the list;
- The DB system details will be displayed;
- The Database mode and Access mode configuration can be observed in the Management section;
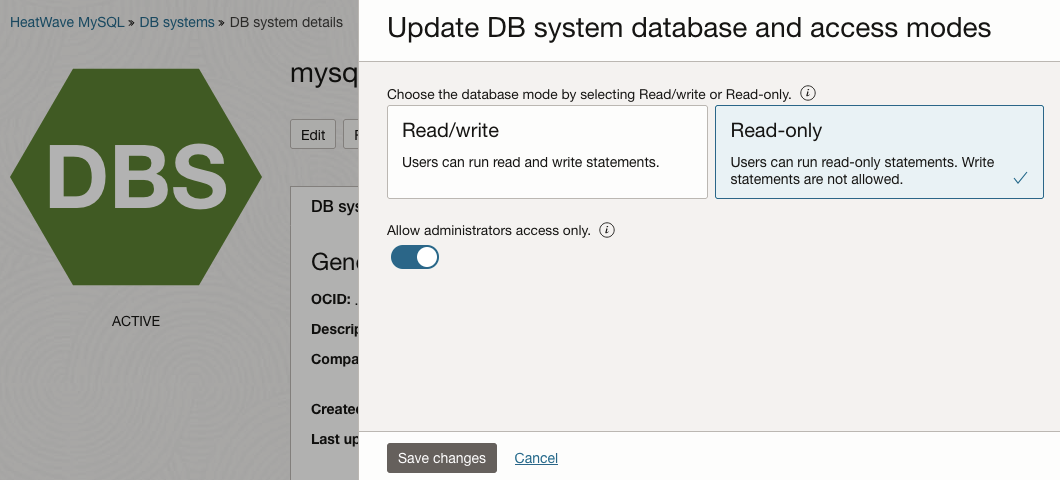
To change the database mode and access mode of the DB system, from the DB system details page of the desired DB system:
- Click the Edit link next to the Database mode or Access mode value;
- Choose the desired Database mode:
- Click Read/write option to allow read and write statements;
- Click Read-only option to allow only read statements;
- Choose the desired Access mode:
- Disable Administrators access only toggle button to allow access to all users;
- Enable Administrators access only toggle button to allow access only to administrators;
- Click Save change button to update the DB system database mode and access mode;
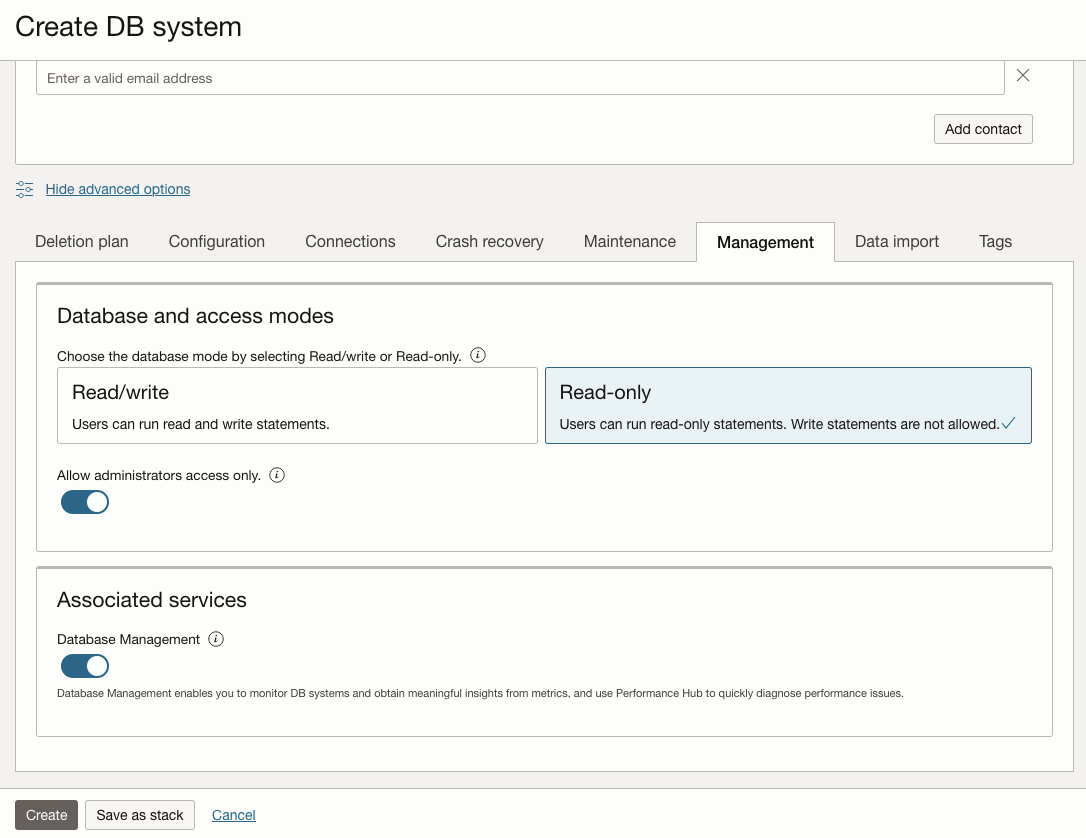
It is also possible to create a new DB system with custom database modes and access mode values from the OCI Console:
- Go to the Database section;
- Under the HeatWave MySQL category, click DB Systems;
- Click the Create DB system button;
- Fill in the details and set the desired options for the new DB system that you want to create;
- Click Show advanced options link (at the bottom);
- Select the Management tab;
- Choose the desired Database mode:
- Click Read/write option to allow read and write statements;
- Click Read-only option to allow only read statements;
- Choose the desired Access mode:
- Disable Administrators access only toggle button to allow access to all users;
- Enable Administrators access only toggle button to allow access only to administrators;
- Click Create button to create the DB system;
NOTE: You cannot enable the HeatWave cluster if you want to make the DB system read-only (and vice-versa).
Summary
Now, the HeatWave Service in OCI provides a simple way to configure a database system as read-only or restrict connection only to administrators. This is achieved by setting the database mode and access mode properties of the DB system. Customers on the HeatWave Service in OCI can make this change in an easy, fast, and safe way, simply by switching the value of a DB system property. These new modes help improve the efficiency and safety of maintenance tasks and enable the creation of more advanced Disaster Recovery setups. Start using this new feature today and take advantage of the additional level of control that it provides over the data integrity and access to the database.
To try HeatWave Service and explore its capabilities, visit oracle.com/heatwave/free.
For more information about HeatWave Service, visit oracle.com/mysql.
