MySQL continues to gear up innovations and now includes rich procedural programming capabilities inside the database. Developers can now write JavaScript stored programs (functions and procedures) in the MySQL database server. The stored programs will be run with the GraalVM run time. This is available as a Preview in MySQL Enterprise Edition and can be downloaded via Oracle Technology Network (OTN). MySQL-JavaScript is also available in the MySQL Heatwave cloud service on OCI, AWS and Azure.
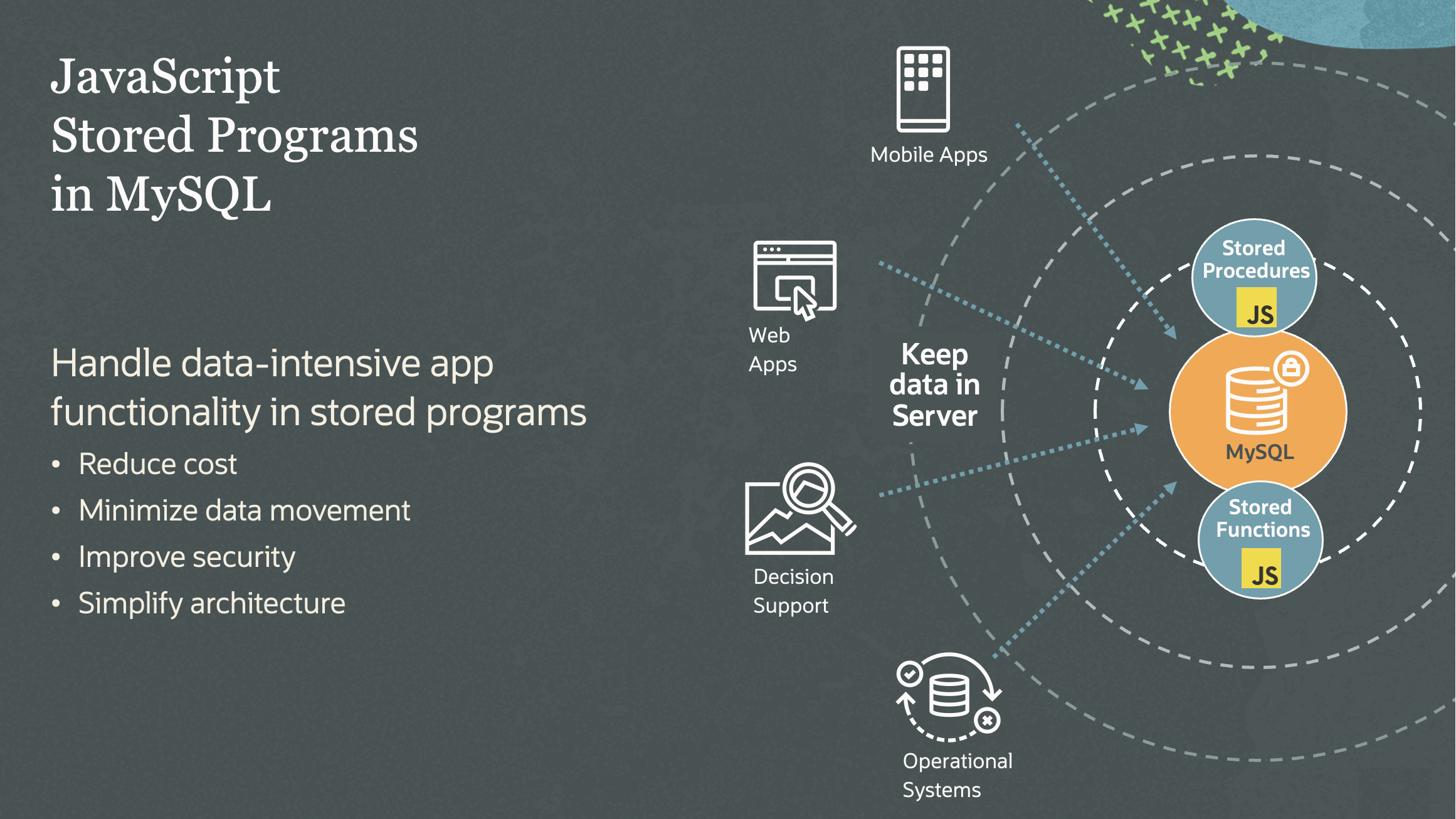
Why JavaScript Stored Programs?
JavaScript is the most popular programming language among developers. Besides the simpler syntax and the support for modern language features, a key factor in its popularity is the rich ecosystem which provides a multitude of reusable code modules.
When in need for persistent storage, MySQL, the most popular open-source database, will be a natural choice for JavaScript developers. By supporting JavaScript in stored programs, developers will be able to write MySQL stored programs in a familiar language and take advantage of the extensive JavaScript ecosystem!
The support for JavaScript stored programs, will not only improve developer productivity by leveraging the large ecosystem; more developers will now possess the necessary skills to write stored programs. In other words, organizations may now tap into a broader range of developer talent by utilizing the widely accessible JavaScript skill set for backend development.
Stored programs offer a key advantage by minimizing data movement between the database server and applications. Transferring large amount of data, especially for batch-processing, can be problematic for many reasons:
- It is time consuming and can cause significant network overhead.
- Increased latency may become noticeable when applications are “chatty”.
- Processing large data volumes in the mid- or application-tier requires large amounts of memory and storage, adding cost.
- Data transfer between machines, especially in cloud environments, often must be avoided due to security risks and data protection requirements.
- Moving large amount of data outside the database service, will increase egress costs.
Using stored programs to process data within the database is a common solution to these problems.
New Use Cases
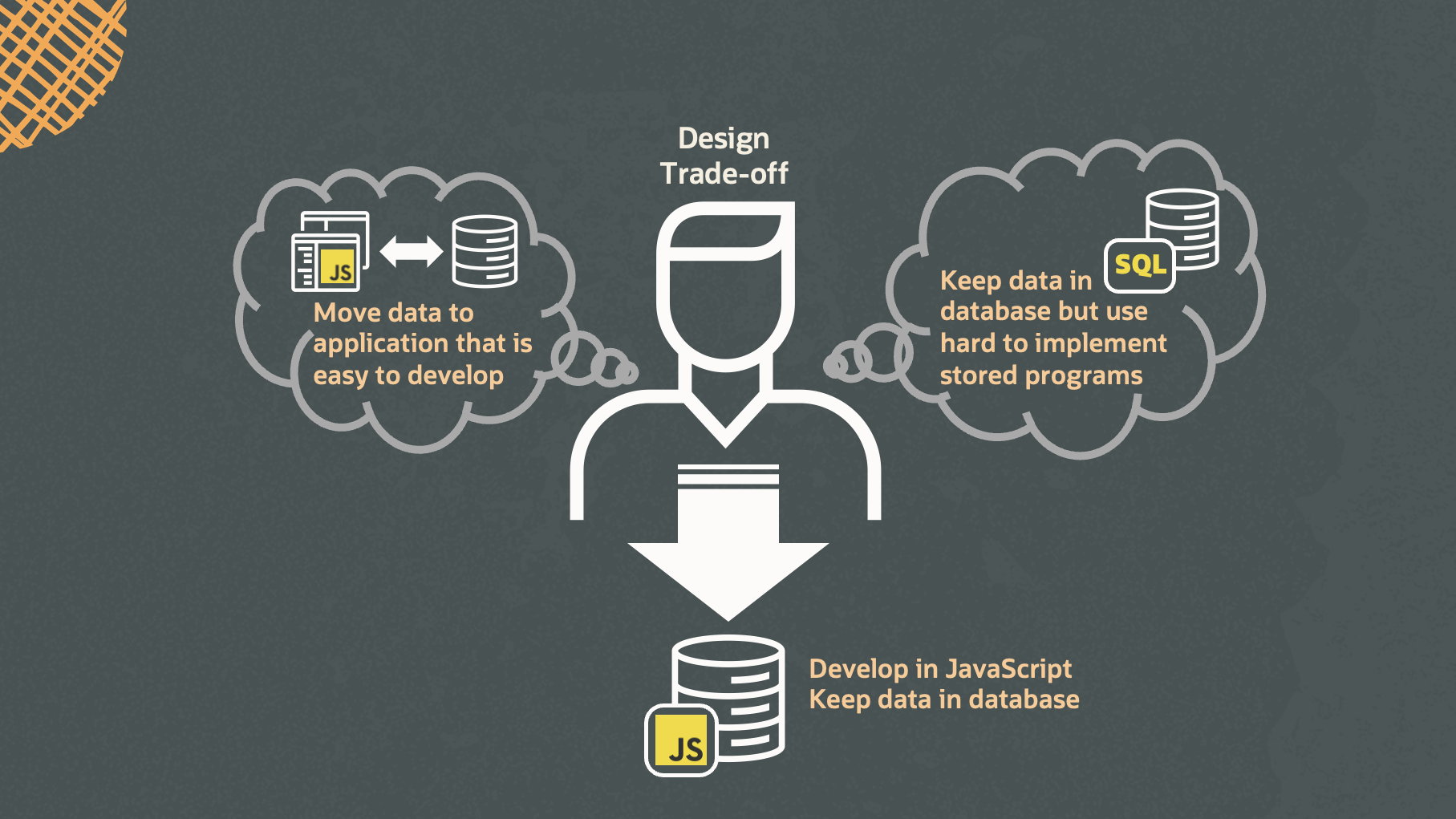
MySQL-JavaScript unlocks new opportunities in application design that were once constrained by a trade-off. JavaScript stored programs empower developers to sidestep data movement and seamlessly implement advanced data processing logic inside the database with ease. Some examples of simple use cases are listed below:
- Data extraction: Extract information from commonly used complex objects in databases, for example, URL strings.
- Data formatting: Generate formatted strings using widely used templatization schemes such as, JavaScript Mustache package.
- Approximate search: Use similarity scoring functions in SELECT queries, for example, retrieving similar strings from a table.
- Data Validation: Clean data using complex validation rules. For example, using JavaScript Validator package.
- Compression / Encoding: Use custom algorithms, not included in MySQL, for data compression and encryption.
- Data Transformation: Change data representation such as converting column of strings into sparse-matrix representation used in feature engineering.
The examples provided are just a glimpse into the potential of this feature. More intricate use cases exist, like deploying complete data pipelines and setting up staging environments for machine learning applications.
MySQL-JavaScript
MySQL is introducing support for JavaScript stored programs. Users can now express rich procedural logic inside the database. The JavaScript runtime is integrated via GraalVM, where the user can use all GraalVM’s Enterprise Edition (EE) features such as compiler optimizations, performance, and security features at no additional cost.
This release has support for:
- JavaScript language based on ECMAScript 2021
- Stored Procedures and Stored Functions
- MySQL datatypes such as all variations of integers, floating point, and CHAR/VARCHAR types
The ECMAScript standard library includes many basic usage operations and data structures that makes implementation easy and expressive. The developer can also reuse millions of available 3rd party packages from online package managers such as “npm”.
What is GraalVM?
GraalVM is an Oracle compiler eco-system that includes JDK, language implementations such as JavaScript, R, Python, Ruby and Java. It includes just-in-time (JIT) and ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation technology. It also provides a fully managed virtual machine with sandboxing capability and tooling support. MySQL-JavaScript is integrated with GraalVM Enterprise edition.
Defining JavaScript Stored Programs
To create a JavaScript stored program in MySQL, you can use a variant of the same SQL statements that are used for traditional stored functions and procedures:
CREATE FUNCTION gcd_js (a INT, b INT) RETURNS INT LANGUAGE JAVASCRIPT AS $$ let [x, y] = [Math.abs(a), Math.abs(b)]; while(y) [x, y] = [y, x % y]; return x; $$;
As seen from the above example, the JavaScript code is embedded directly in the definition of the SQL-callable function. The names of the arguments can be referred directly in the JavaScript code, and when the function is called, there will be an implicit type conversion between SQL types and JavaScript types. To call JavaScript stored procedures, the CALL statement should be used, similar to the regular SQL stored procedures. Both input and output parameters are supported for stored procedures.
Executing JavaScript code inside SQL statements
A JavaScript function may be called from SQL statements anywhere a traditional SQL function may be called; in SELECT expressions, WHERE, GROUP BY, and ORDER BY clauses, DMLs, DDLs, Views, and others. Here is an example of an SQL statement that calls the function we defined above:
SELECT col1, col2, gcd_js(col1,col2) FROM my_table WHERE gcd_js(col1, col2) > 1 ORDER BY gcd_js(col1, col2); CREATE TABLE gcd_table AS SELECT gcd_js(col1,col2) FROM my_table;
Debugging JavaScript code inside MySQL
Debugging goes hand-in-hand with the software development. The MySQL-JavaScript feature exposes additional SQL interfaces to aid troubleshooting, while the JavaScript program runs in the database.
CREATE PROCEDURE division (IN a INT, IN b INT,
OUT result DOUBLE) LANGUAGE JAVASCRIPT AS $$
function validate(num) {
console.log("validating input value: ", num);
if (num === 0) throw ("Division by Zero!");
}
validate(b);
result = a / b;
$$
JavaScript exceptions to MySQL errors conversion happens transparently. Developers can also access JavaScript stack traces, in addition to standard output.
CALL division( 5, 0, @res);
ERROR 6000 (HY000): JavaScript> Division by Zero!
SELECT mle_session_state("stdout");
validating input value: 0
SELECT mle_session_state("stack_trace");
<js> validate(division:9:187-214)
<js> division(division:11:222-232)
<js> :anonymous(division:15:256-265)
Security
JavaScript support in MySQL offers highest levels of security, isolation, and data protection. JavaScript for MySQL relies on the industry-proven Oracle’s GraalVM security guarantees.
The VM sand box ensures that malicious code cannot compromise other modules of the MySQL server. Every Stored Program is parsed and executed in its own context. This isolation policy does not allow one stored program to read or modify other stored program’s data or code. Spawning or manipulating threads from JavaScript user code is restricted, and JavaScript user code has no access to network communication or file system.
JavaScript stored programs builds on the standard MySQL privileges model. Only privileged users are allowed to create stored programs. The access to the SP can also be controlled by privileges. One user may define the stored programs that can be executed by others.
Compatibility
JavaScript stored program work seamlessly with traditional SQL stored programs. The feature is agnostic to storage engine, data can be accessed transparently from InnoDB, Lakehouse, and HeatWave.
MySQL Heatwave Service now comes with pre-installed and configured JavaScript on OCI, AWS and Azure service deployments. For MySQL Enterprise Edition, the feature requires manual installation and configuration.
Performance
MySQL-JavaScript integration uses a custom-built VM for its specific use-case to allow the best end-to-end performance. This customization is based on GraalVM’s ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation where the language implementation is compiled down into a native binary representation for fast processing.
GraalVM has its own JavaScript implementation based on ECMAScript 2021 standard. The language implementation is competitive in terms of performance although it is implemented using GraalVM’s Polyglot framework which focuses on supporting multiple programming languages within the same VM.
Lastly, the MySQL-JavaScript feature benefits from various state-of-the-art optimizations that come with enterprise edition of GraalVM, such as compiler optimizations including aggressive inlining and partial escape analysis. This also includes a profile guided just-in-time (JIT) compiler that switches between interpreter and native compilation at runtime.
Conclusion
MySQL-JavaScript enables developers to express complex programming logic directly inside the MySQL server. This allows developers to push data-intensive parts of their applications close to their data, reducing data movement cost. Use of JavaScript based on ECMAScript 2021 prevents vendor lock-in issues, while the developer enjoys all the benefits of GraalVM (Enterprise Edition) at no additional cost. To try out MySQL-JavaScript for free, download MySQL Enterprise Edition from Oracle Technology Network (OTN). MySQL-JavaScript also integrates seamlessly with the MySQL HeatWave cloud service where the latest innovations are available to the developers at their fingertips.
Want to learn more?
For details refer, User Manual (JavaScript Stored-Programs Section 25.3)
