Monitoring MySQL replication is key to maintaining data consistency, troubleshooting issues, and ensuring smooth failover across environments. It helps confirm that your replication topology is running as expected, assists in identifying delays or failures, and gives control to manage increasingly complex deployments.
Understanding MySQL Replication types:
- Asynchronous Replication: Traditional MySQL replication, which enables data from one MySQL server, which is known as a source, to be copied to one or more MySQL servers known as replicas. Replication is asynchronous by default; replicas need not be connected permanently to receive updates from a source.
- Group Replication: High Availability solution that enables a set of MySQL servers to function as a cohesive group, ensuring data consistency and fault tolerance. Each MySQL server maintains a complete copy of the data, and communicates with other group members through message passing. The communication layer provides a set of guarantees such as atomic message and total order message delivery.
Asynchronous replication can be configured to establish pathways for data transfer in the following ways:
- Inbound Replication: Inbound replication uses a replication channel configured in the MySQL DB system (HeatWave or External) to copy transactions from another MySQL source into the target DB system.
- Outbound Replication: Outbound replication uses a replication channel to copy transactions from a MySQL DB system (HeatWave or External) to another MySQL source.
In an asynchronous MySQL replication environment, detecting failures in the replication channel is critical to prevent data lag and maintain consistency across systems. OCI Database Management makes it easy to create custom alarms for these issues using built-in metrics, with no extra setup required.
In this post, we’ll guide you through setting up a custom alarm for Channel Failure, a metric that indicates when a replication channel is down. This enables your operations team to react swiftly to potential disruptions through email alerts. Similarly, you can set up alarms for other critical metrics important to your team, like replication lag or thread status, ensuring thorough and proactive database monitoring.
Setting Up Custom Alarm for Channel Failure
Prerequisite:
Before getting started, ensure Database Management (DBM) is enabled on your MySQL HeatWave DB system. This allows the DBM agent to collect metrics for ChannelFailure and stream them to OCI Monitoring to create alarms. Also, ensure that the inbound replication is set up on the MySQL HeatWave DB system to monitor the replication channel.
Note: ChannelFailure alarms should be set on the replica DB system, where replication threads operate.
Step-by-Step: Creating a Channel Failure Alarm
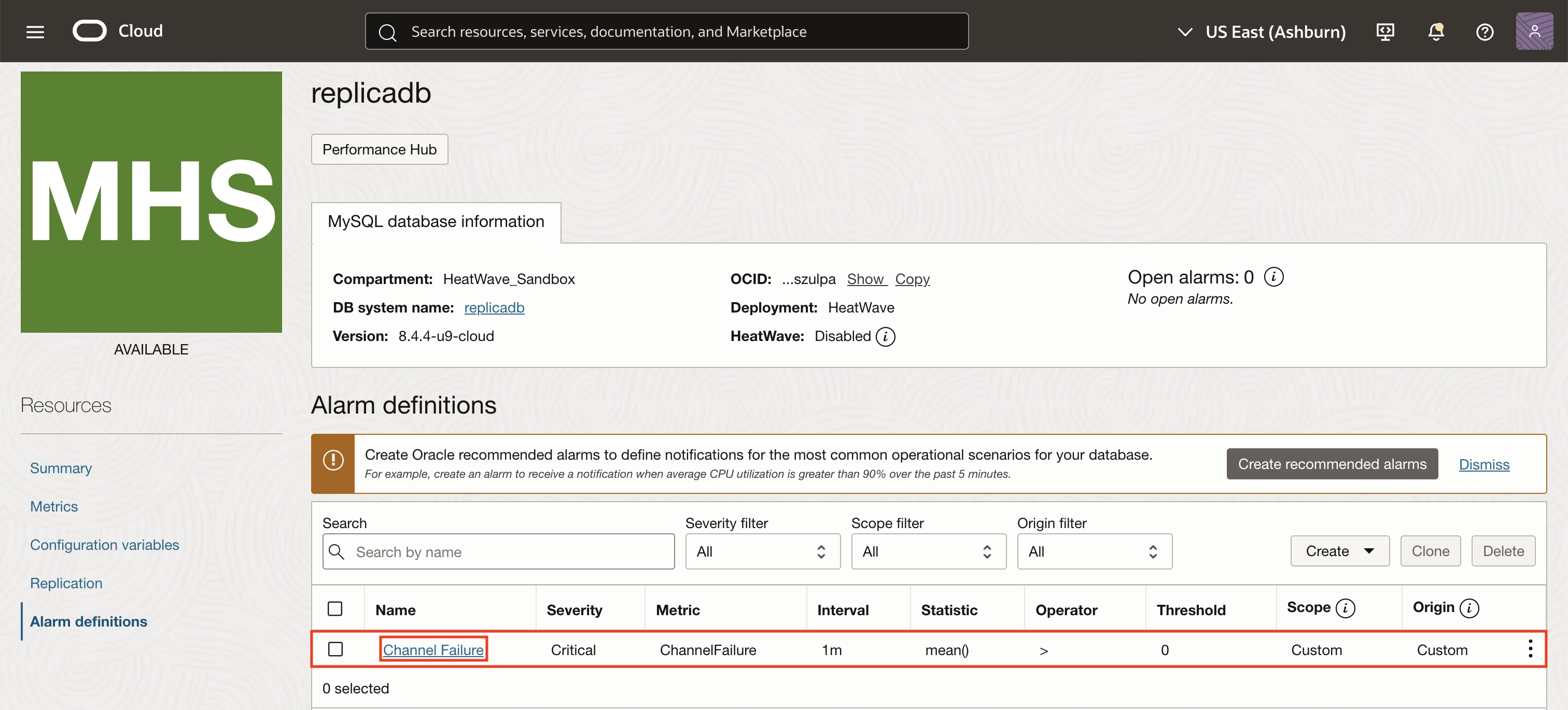
From the OCI console, navigate to Observability & Management -> Database Management, and select HeatWave and MySQL. Click on the name of your DB system from the fleet where you can find Alarm definitions listed in the Resources section.
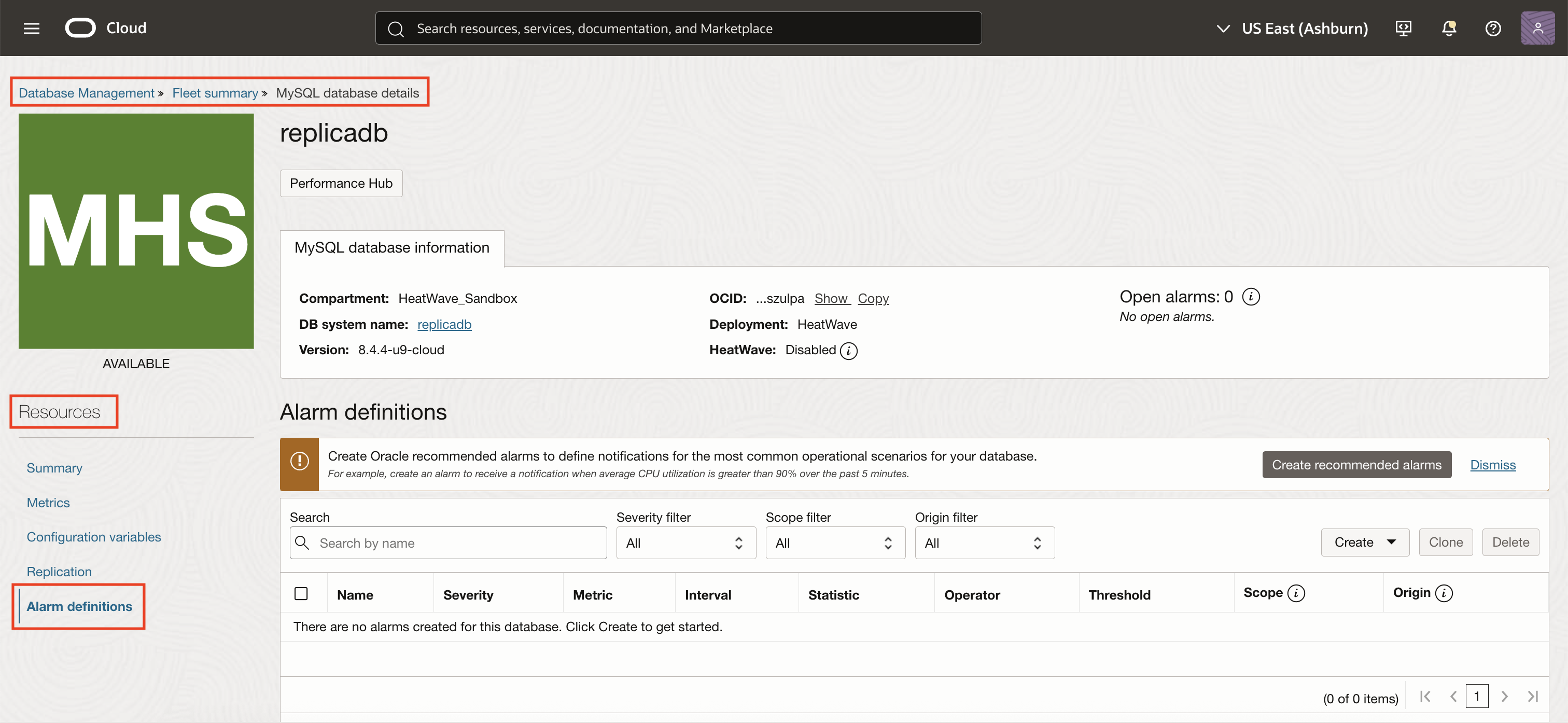
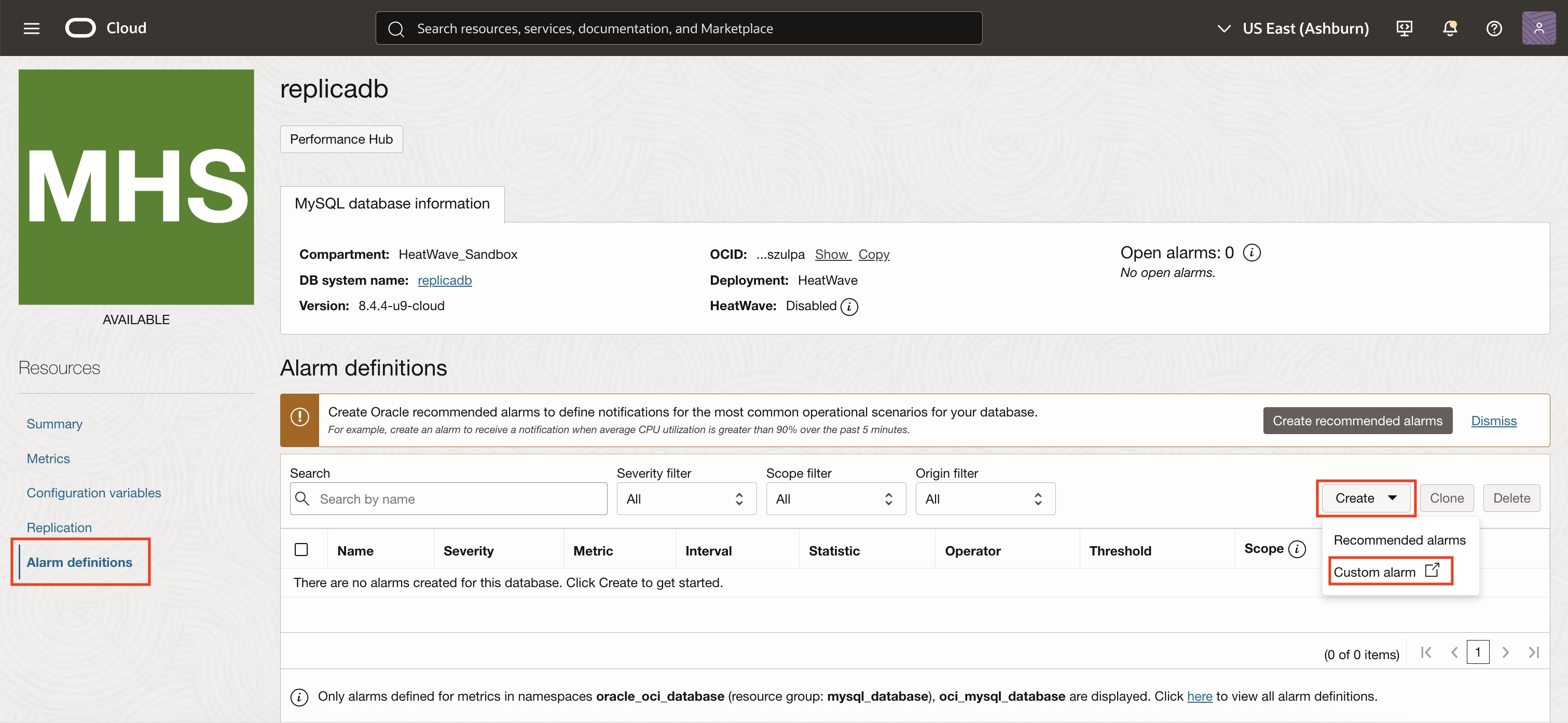
Click Create to start defining a new alarm. Select Custom alarm from the dropdown menu to access the complete set of alarm creation options in the OCI Monitoring service.
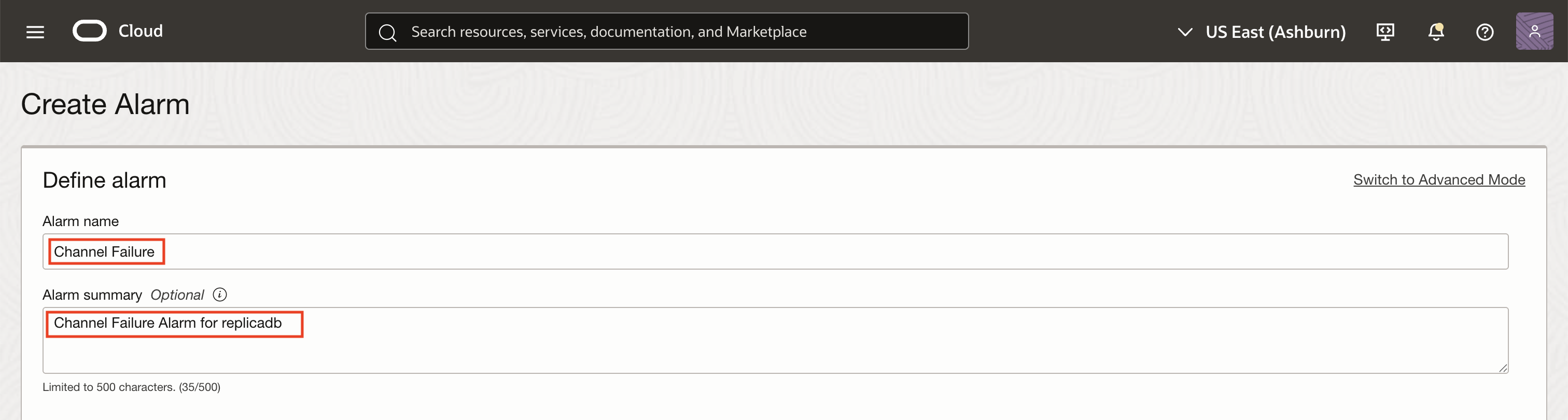
Enter an alarm name and summary for triggering an alert if replication channel fails on the MySQL HeatWave DB system.
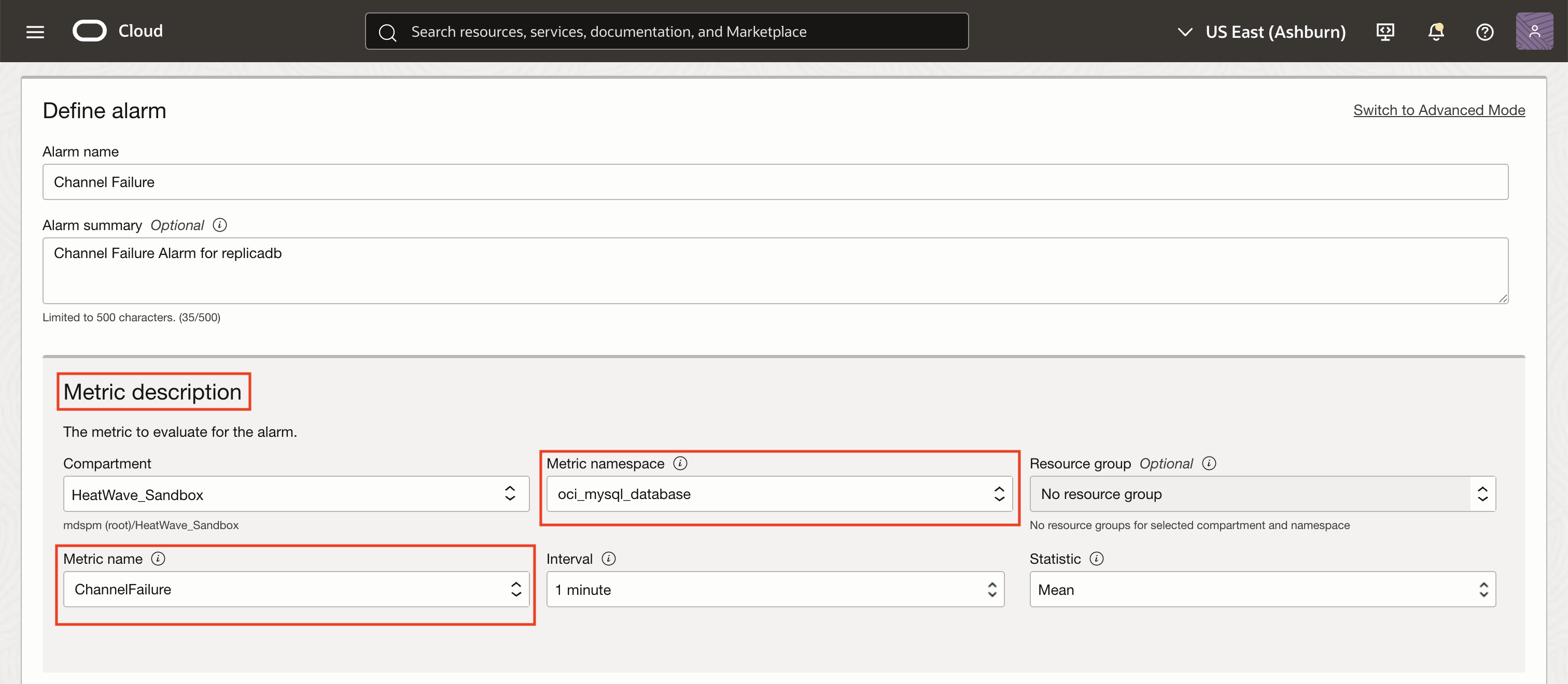
In the Metric description section of the alarm creation page, set the Metric namespace to oci_mysql_database and the Metric name to ChannelFailure that will be evaluated by the alarm. Set the collection interval to 1 minute to ensure near real-time detection.
Under Metric dimensions, select filter as dbSystemId and enter the OCID of your MySQL HeatWave DB system. This ensures the alarm only monitors the intended replica.
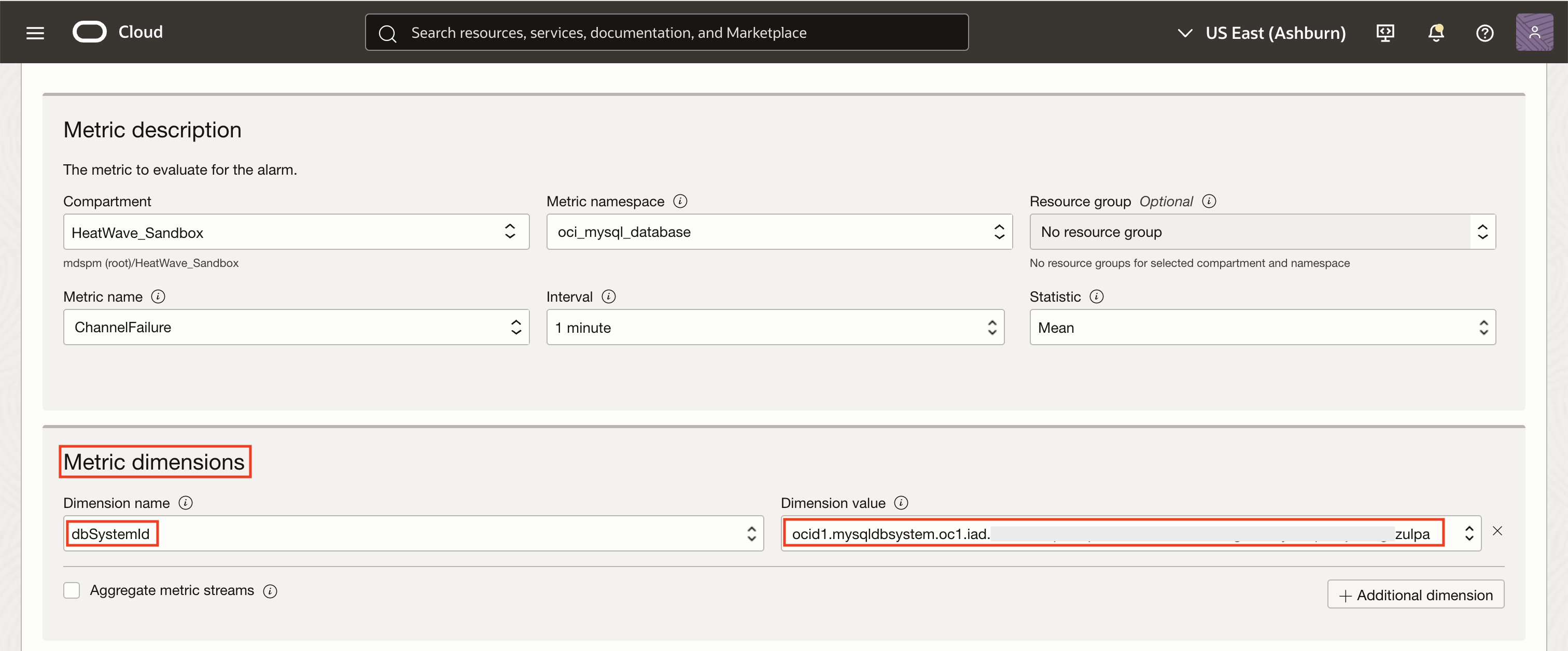
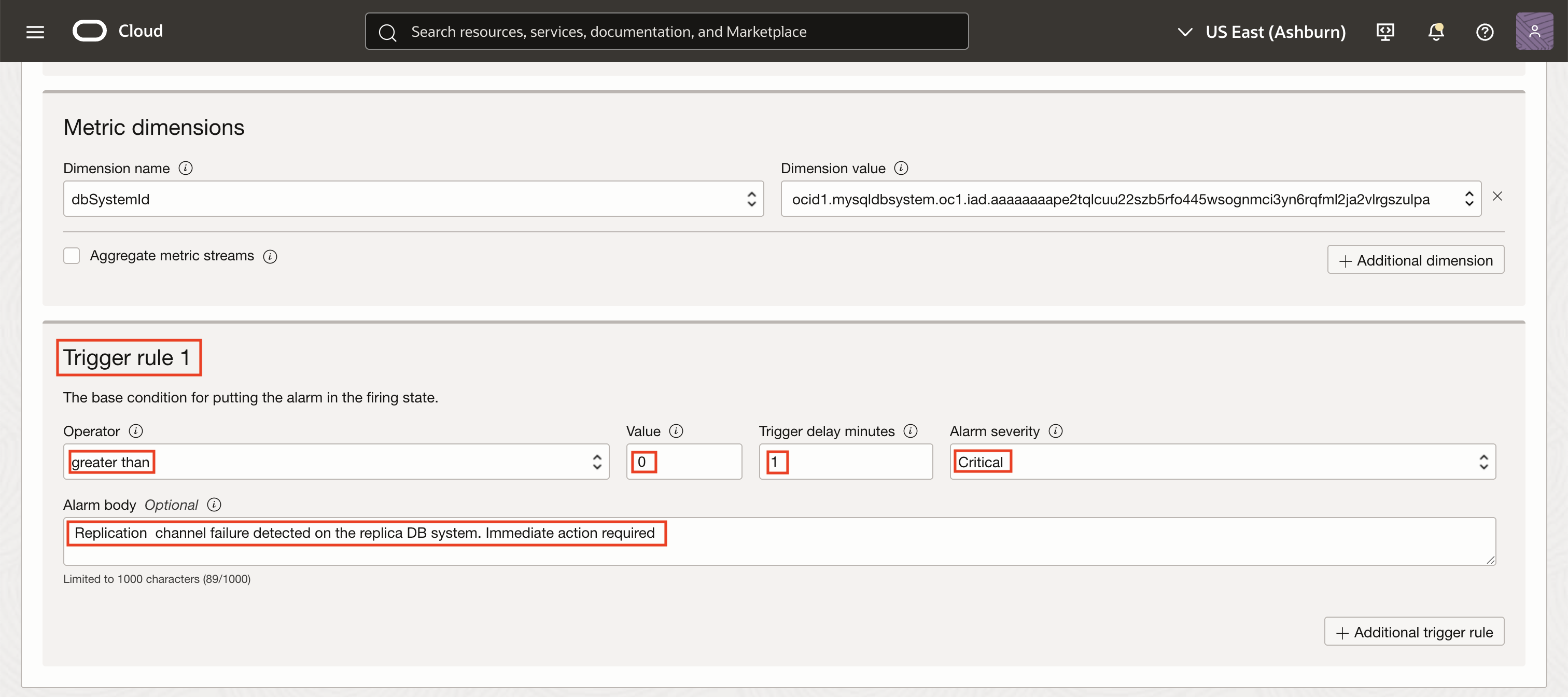
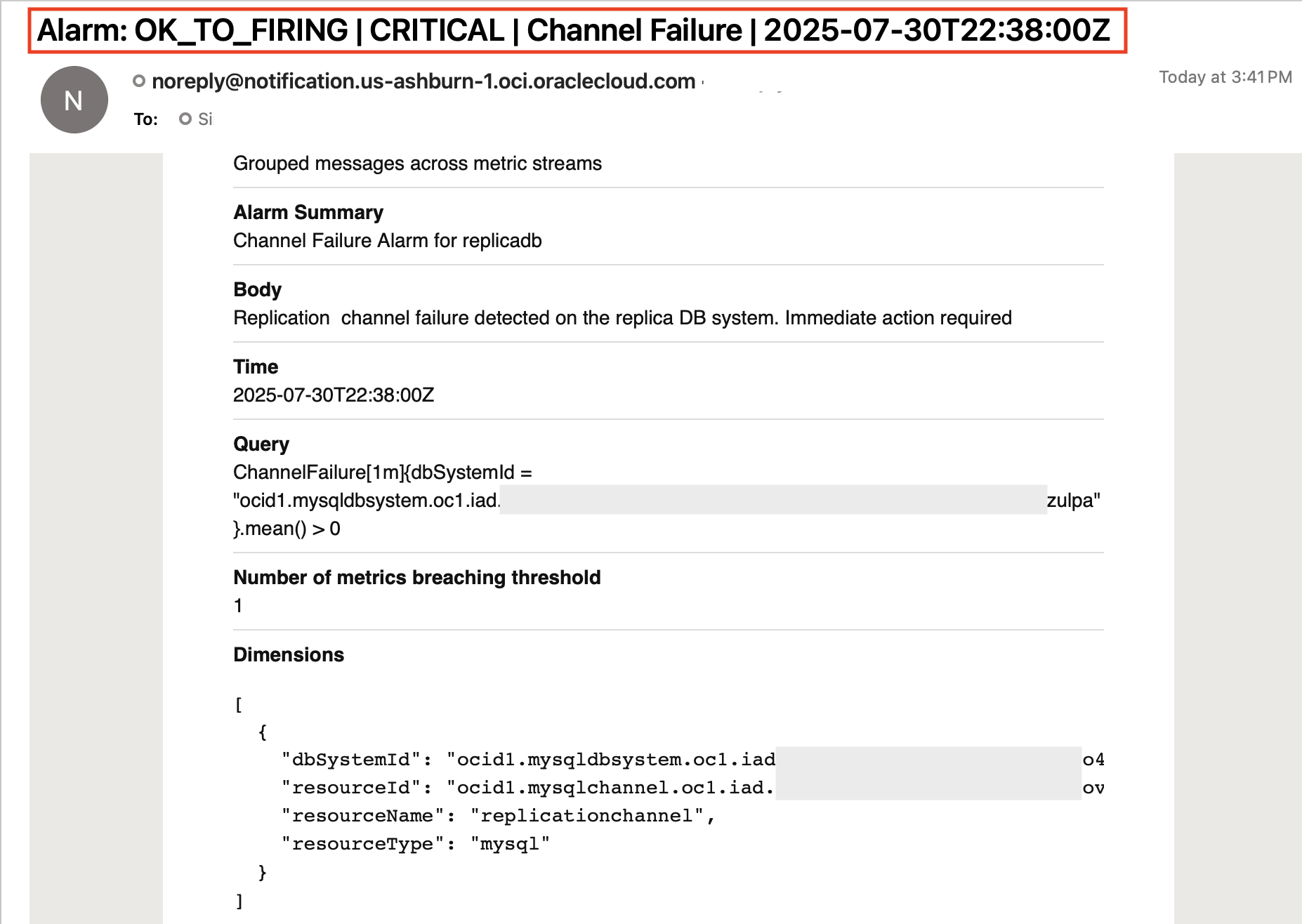
Define the trigger rule so that the alarm fires when the ChannelFailure metric value is greater than 0, indicating a failure. Set a trigger delay of 1 minutes to avoid false positives, and assign the severity level as Critical. Optionally, you can add a message in the alarm body such as, “Replication channel failure detected on the replica DB system. Immediate action required.”
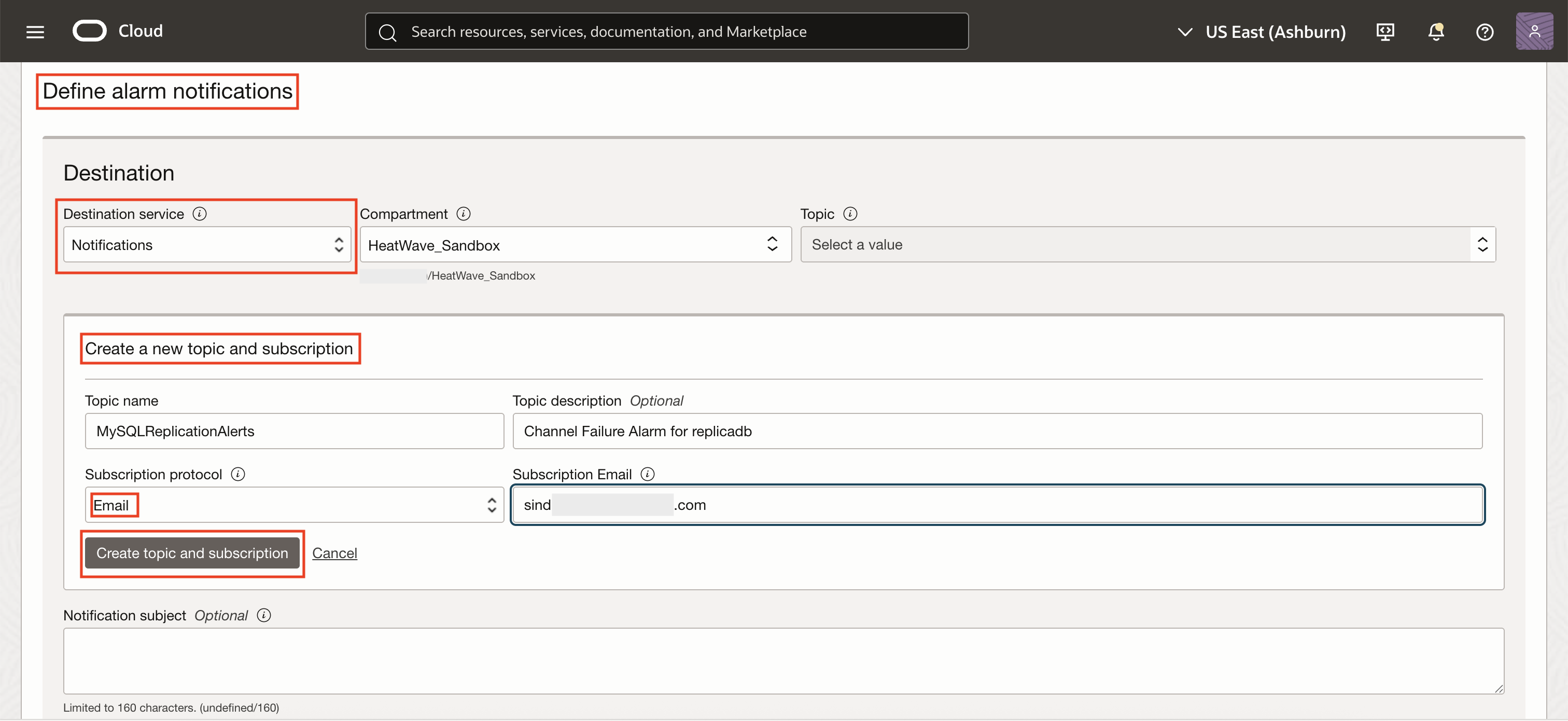
To receive alerts via email, navigate to Define alarm notifications and create a new topic (e.g., MySQLReplicationAlerts). Add an email subscription to the topic, and confirm it from your inbox. Then, return to the alarm definition and set this topic as the alarm destination, ensuring your team will be notified the moment a channel failure occurs.
Once all configurations are complete, click Save to activate the alarm.
From this point onward, OCI will continuously monitor the ChannelFailure metric for your replica DB system. If the replication channel fails, the alarm will trigger based on your defined condition and send a notification to the subscribed email, enabling rapid responses.
Operational Impact
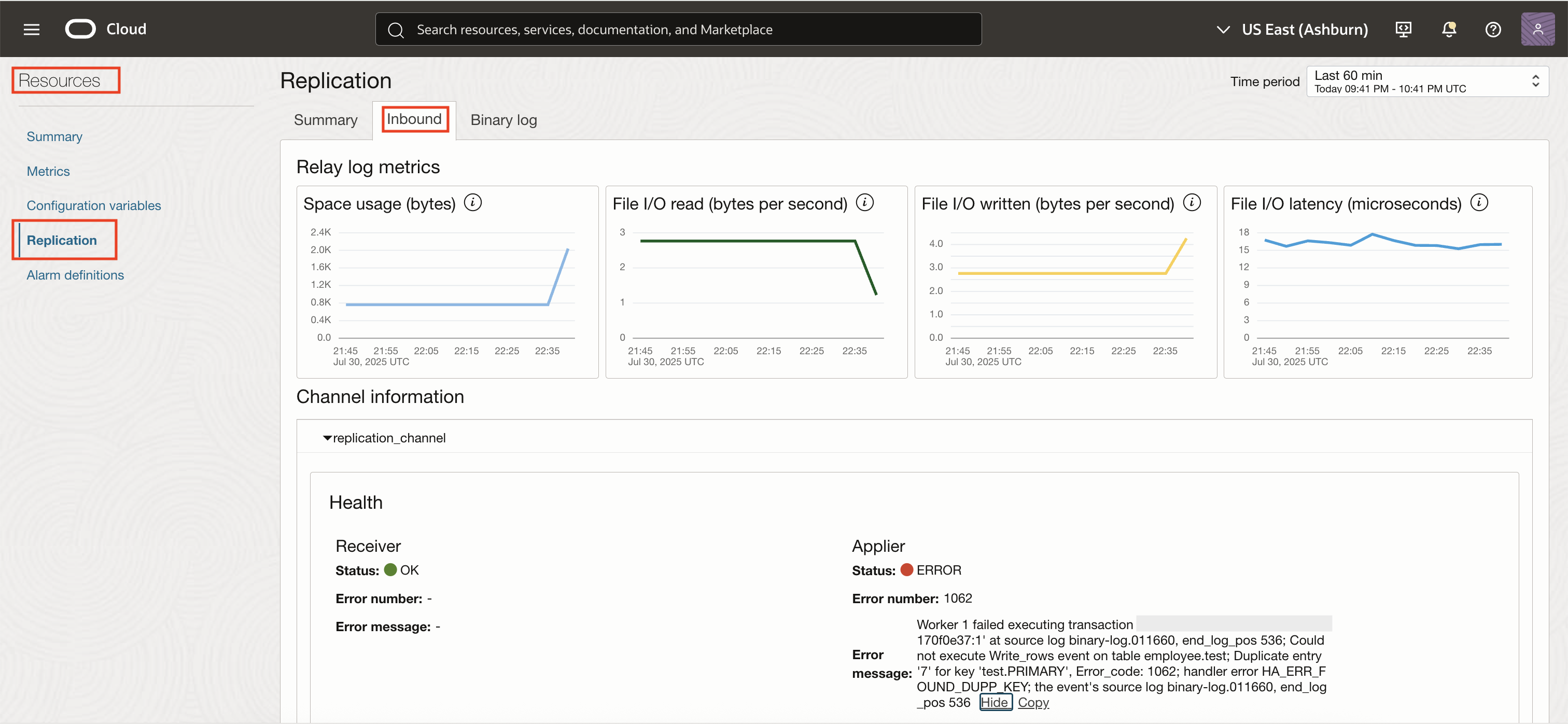
With these alarms in place, you receive immediate notifications about replication disruptions, enabling you to respond quickly and reduce the risk of data inconsistencies. In addition to alarms, OCI Database Management provides real-time replication monitoring, which becomes available when you enable Full Monitoring. Once Full Monitoring is enabled, simply navigate to the Replication tab under Resources to monitor channel status, track replication lag, and access key diagnostic details, all available in a user-friendly interface.
Conclusion
Proactive monitoring and alerting for MySQL replication is essential to ensure high availability and data consistency, especially as your operations scale. By tapping into OCI’s built-in capabilities, without the hassle of custom scripts or external solutions, you’re staying one step ahead of potential problems and minimizing business risks.

