HeatWave is the only fully managed MySQL database service that combines transactions, analytics, machine learning, and GenAI services, without ETL duplication. It also includes HeatWave Lakehouse, allowing users to query data stored in object storage, MySQL databases, or a combination of both. Users can deploy HeatWave MySQL–powered apps on a choice of public clouds: Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure.
A DB system can be deleted by mistake due to human error or because of a failure or data corruption. In either case, the damage can be significant, with data loss ranging from minutes to hours. Our HeatWave customers can now avoid this situation. The HeatWave service on OCI supports backups (manual and automatic) that provide a recovery point objective (RPO) of 24 hours. All data can be restored up to 24 hours ago. Enabling point-in-time recovery (PITR) reduces the RPO, offering an RPO of up to 5 minutes.
And now, we are pleased to announce that PITR is available on a Deleted DB system. To benefit from this feature, you just need to enable PITR and automatic backup retention following the deletion of the DB system.
Introduction to PITR
With the PITR feature, customers can restore data from a specified DB system (DB1) to a new DB system (DB2) at a chosen point in time, anywhere from a moment in the past up to a certain point before the last update on DB1, typically 5 minutes or less.
PITR utilizes automatic backups for recovery. A DB system generates a binary log file and backed up if PITR is enabled on the DB system. The retention period for these binary log files is determined by the ‘retention-in-days’ variable, which the customer sets for automatic backups in the backup plan. These binary logs are crucial for the recovery process.
Understanding Backup Retention Support for PITR-enabled DB Systems
You can restore to any specific point-in-time within the earliest and the latest time window. The earliest and the latest time window is displayed in the Console under the Select a specific point-in-time option. The earliest available time depends on the backup retention period i.e. last configured when the DB system was active (or before deletion). For example, if you set the backup retention period to 12 days, the earliest available time is 12 days or the time when point-in-time recovery is enabled whichever is later.
Customers can restore a PITR-enabled DB system to a specific point in time within the retention period, even if they accidentally deleted the DB system after creation. Since a DB system has multiple automatic backups, each accompanied by corresponding binary log files, these files can be used for a restore operation. These binary log files are linked to the automatic backups and will be retained if the customer has set the DeletionPolicy to ‘RETAIN’.
In the event of an intermediate backup deletion request, the associated binary log files will also be retained and can be utilized as part of the PITR restore process.
Steps to Set Up a DB System for PITR support after deletion
The following steps outline how to set up a DB system to allow PITR support upon its deletion.
1. In the OCI console, open the navigation menu and select Databases. Under HeatWave, click DB systems.
2. Click on Create DB system to create a PITR-enabled DB system by following the next steps.
3. Scroll down to Configure backup plan, turn on the Enable Point-in-time recovery toggle, as shown in Figure 1.
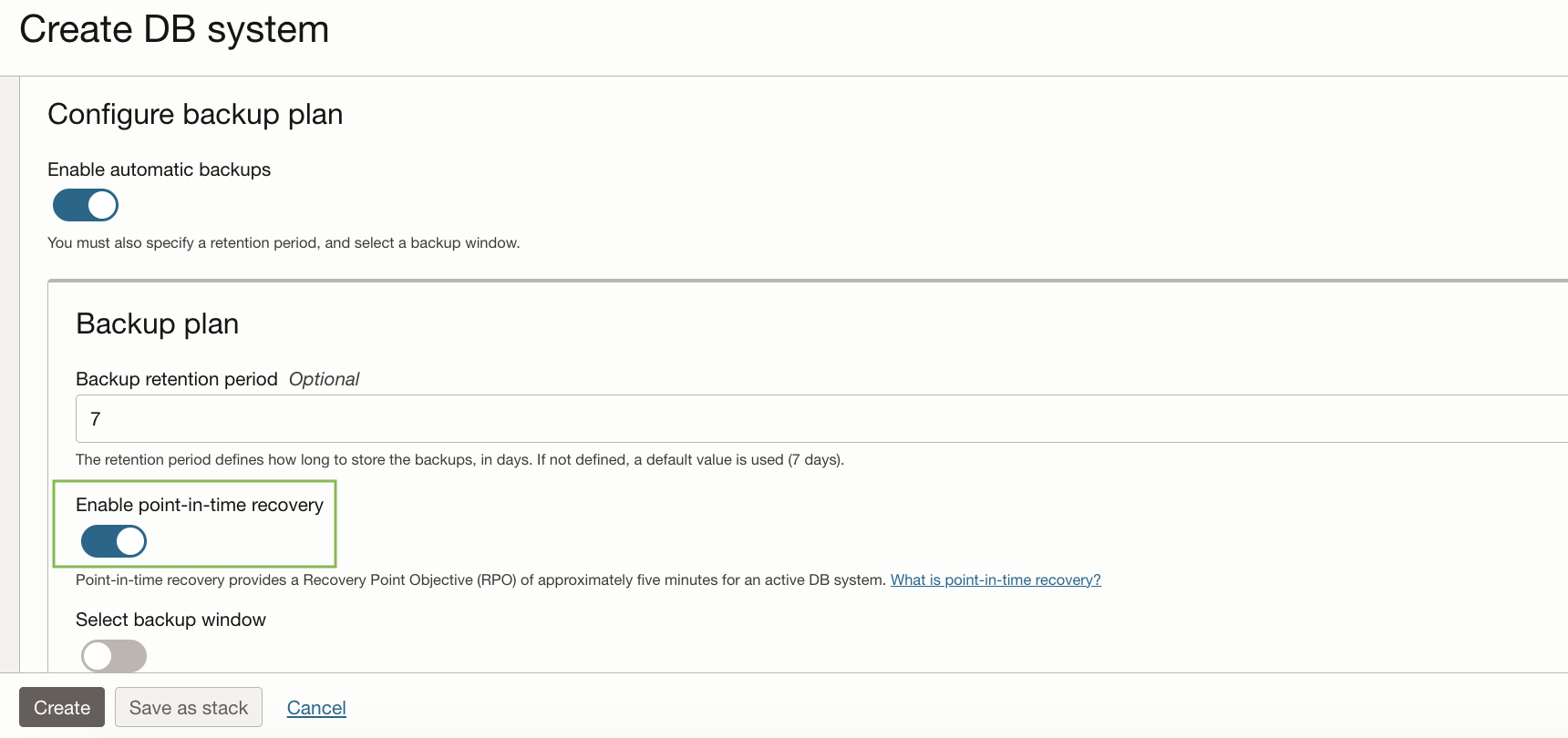
Figure 1. Enable PITR on a DB system
4. Scroll down to expand Show advanced options, open Deletion plan and set the Automatic backup retention toggle to Retain, as shown in Figure 2.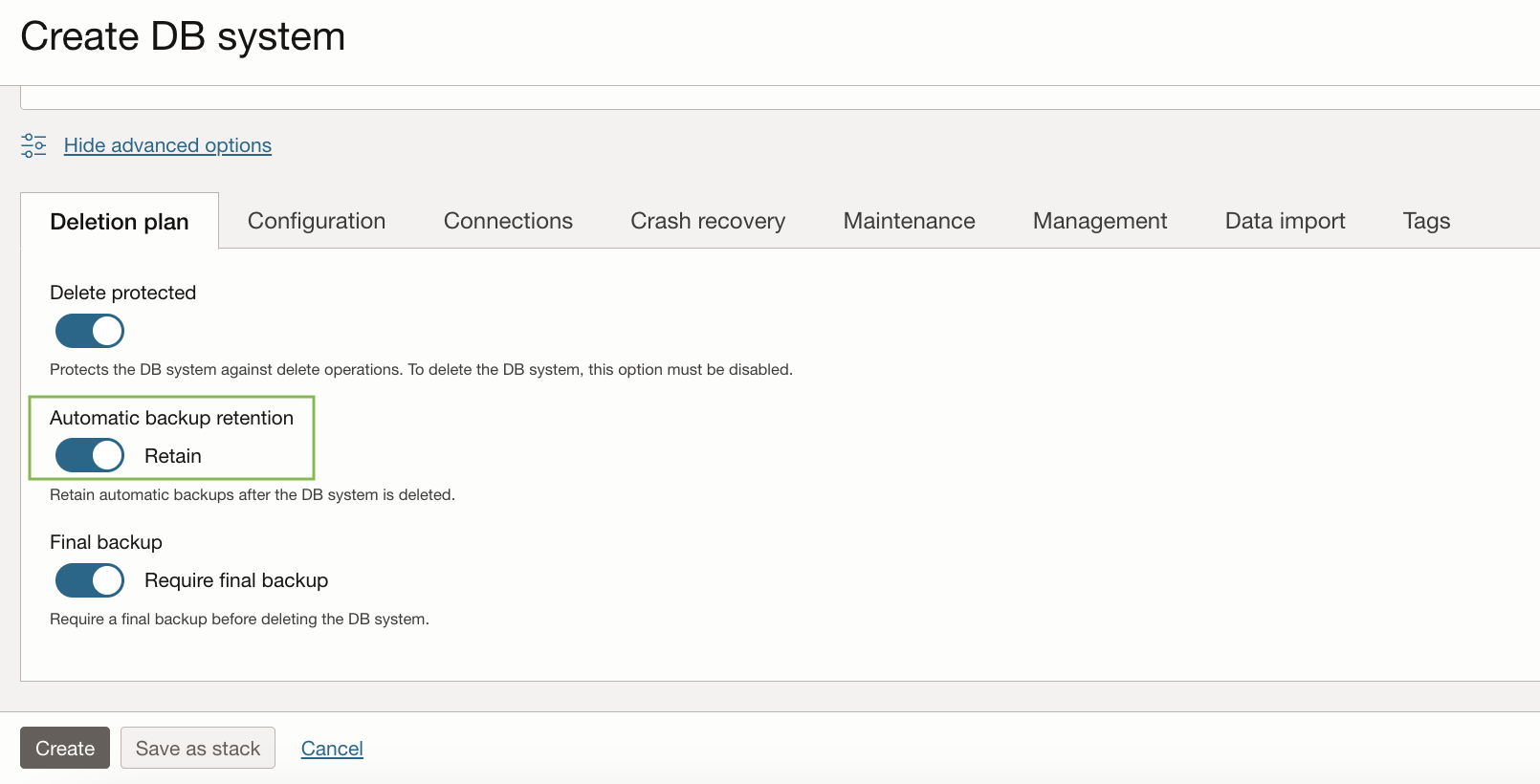
Figure 2. Configuring Automatic Backup Retention in DB system
5. After the DB system is created, scroll down to Backup plan. Verify that Automatic backup retention from the DB system deletion plan is set to Enabled, and Point-in-time recovery from Backup plan is set to Enabled, as shown in Figure 3.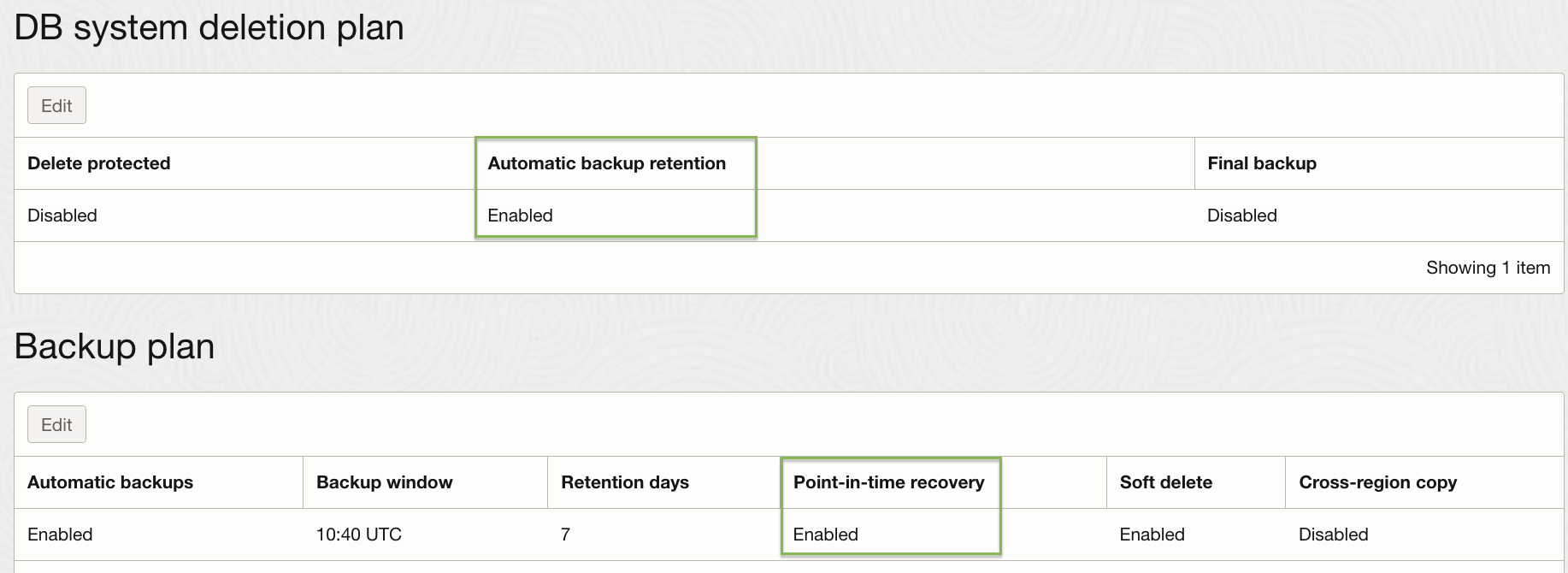
Figure 3. Verify Automatic Backup Retention and Point-in-time recovery is set to Enabled
Steps to restore PITR DB system on accidental deletion
The following steps show how a deleted DB system can honour PITR restore support, as per the given backup retention period.
1. Select the Deleted DB system, as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. DB system in Deleted state
2. Select Restore to a new DB system option from More actions dropdown list, as shown in figure 5.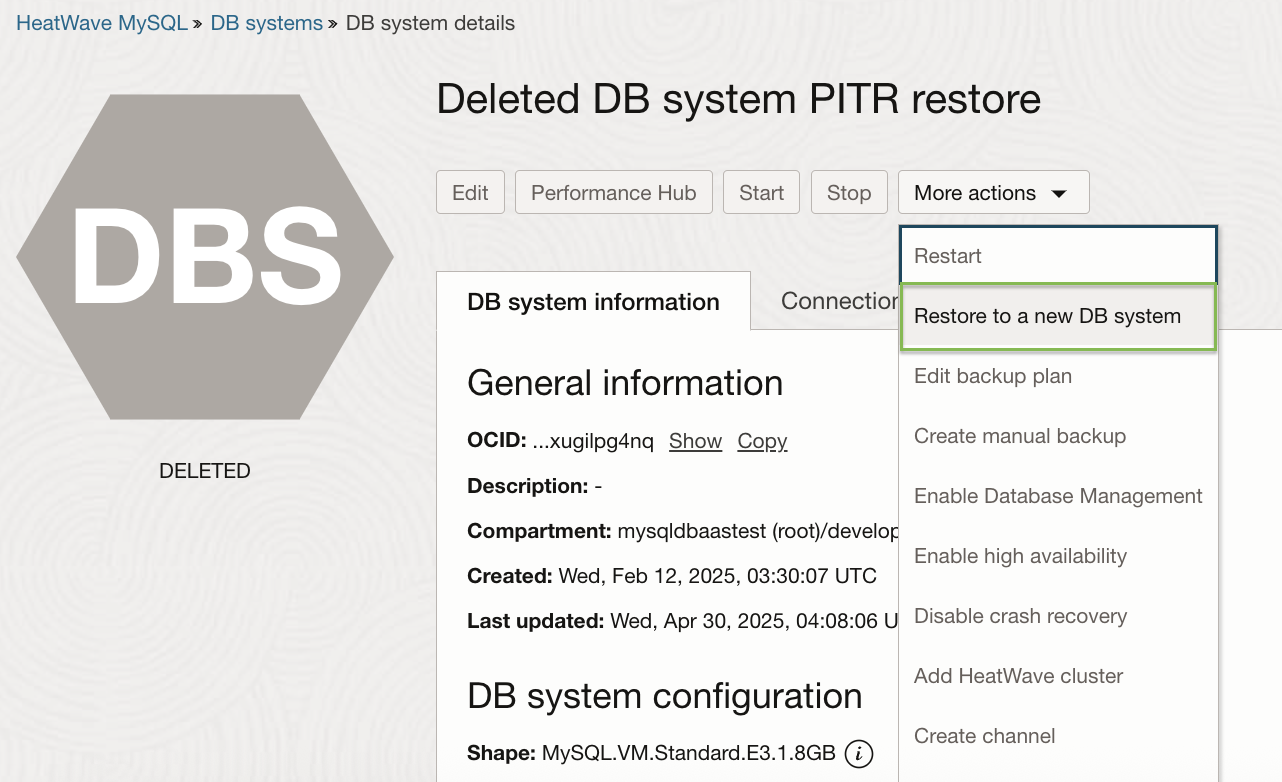
Figure 5. Restore option for Deleted DB system
3. The PITR-enabled Deleted DB system can be restored up to point-in-time, as shown in Figure 6.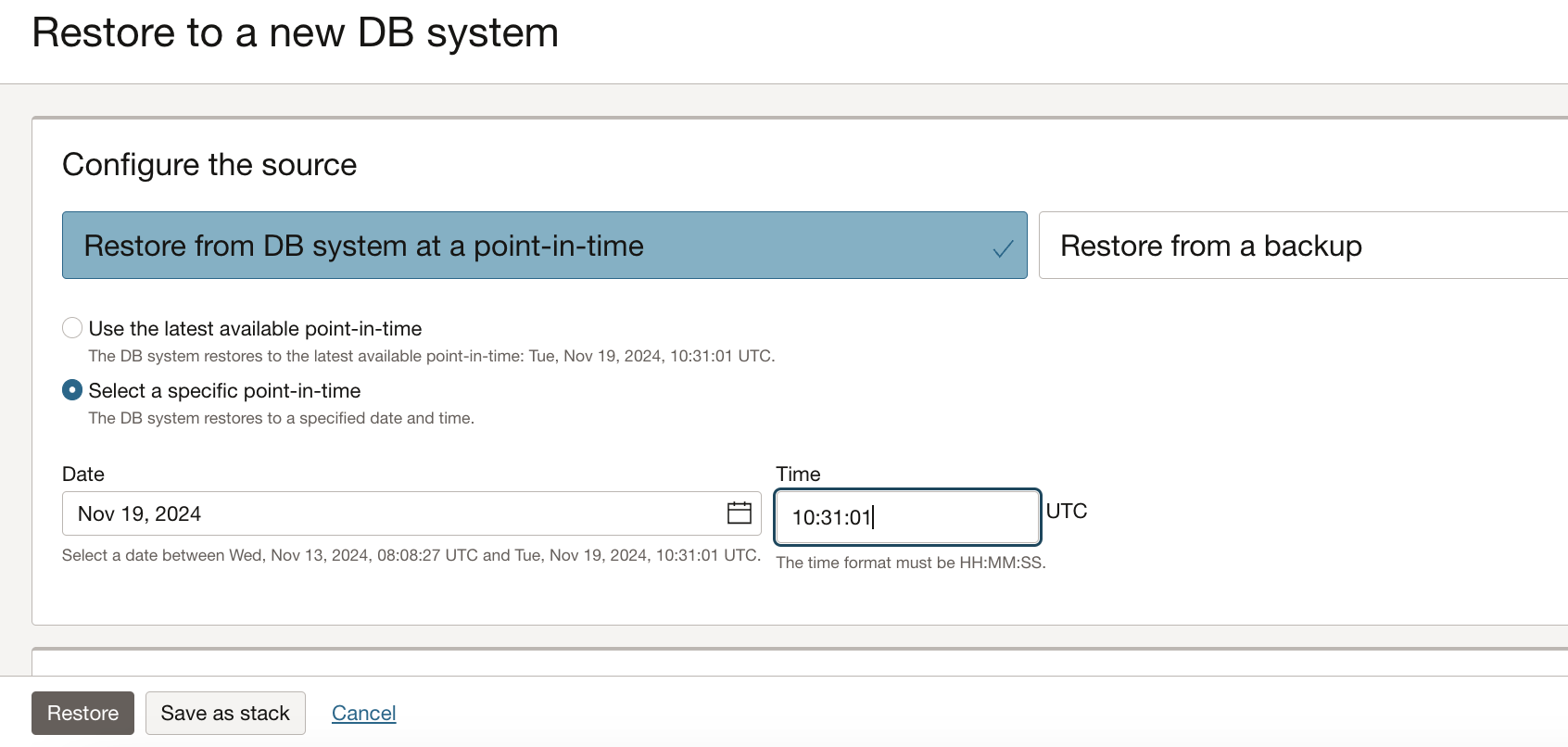
Figure 6. Restore PITR enabled Deleted DB system
4. Click on Restore button to create a new DB system.
5. A DB system restore operation is in progress, as shown in figure 7.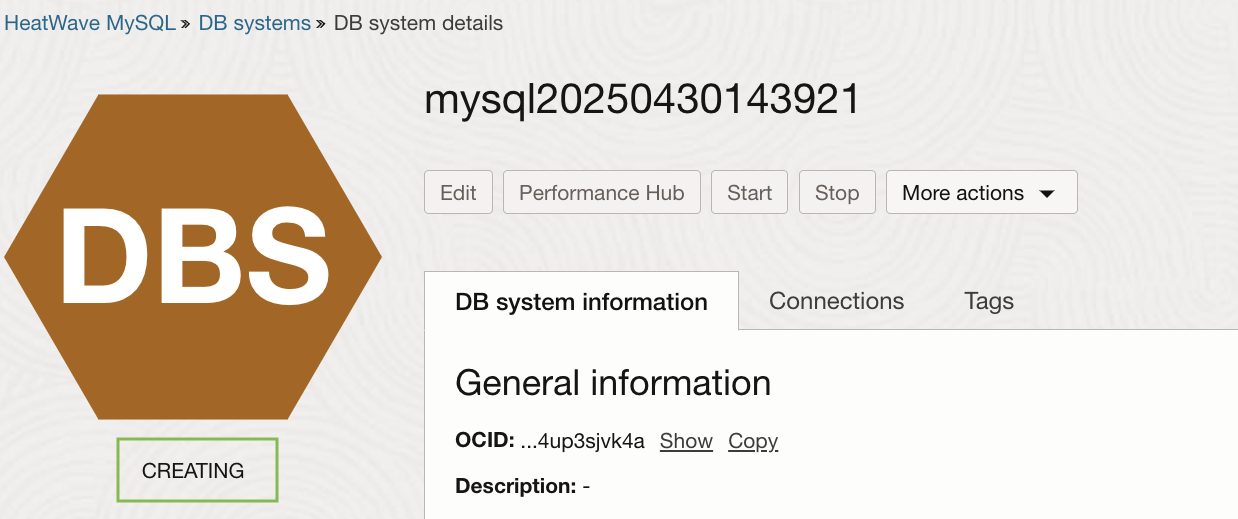
Figure 7. New DB system in Creating state
6. The DB system is successfully restored as shown in Figure 8.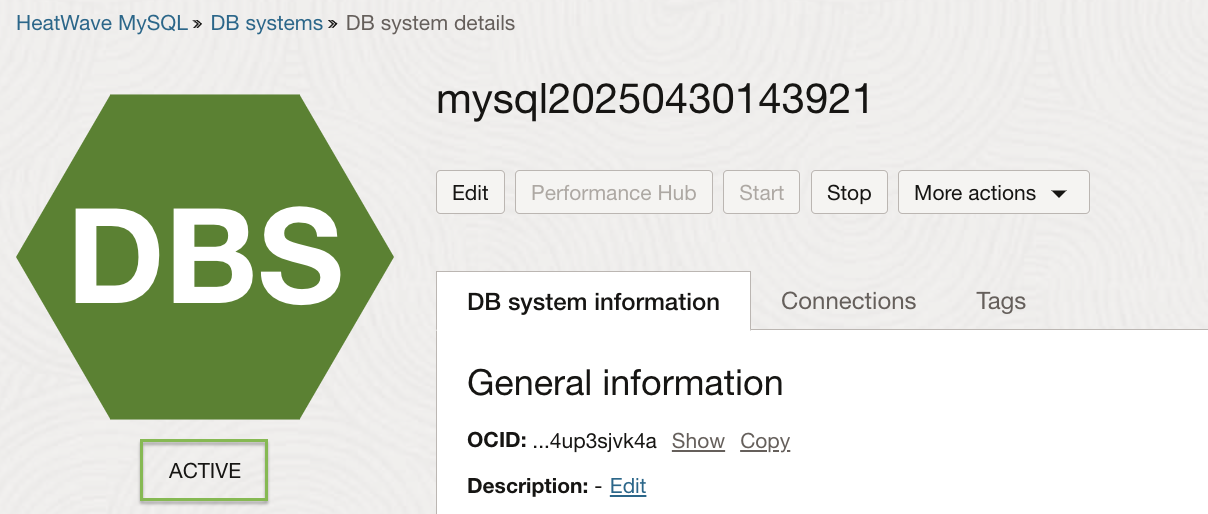
Figure 8. Restored Active DB system
Summary
We invite you to make use of the option to restore a deleted DB system using PITR data. In scenarios where accidental deletion, a failure, or corruption occurs, potentially leading to data loss ranging from minutes to hours, HeatWave now provides an RPO of up to 5 minutes. This feature will significantly aid in restoring a DB system with minimal RPO in such scenarios.
Your feedback is valuable for enhancing our services. Please feel free to share your thoughts or reach out to us for more information about this feature.
For further details, please refer to: Creating a DB System, Viewing DB System Details, Restore DB system using PITR.
