AI agents can improve operational efficiency and customer experience in business applications, as they can simulate human-like intelligence or perform tasks that would otherwise require human action. If you develop database applications and are looking for a simple way to leverage AI agents, Select AI Agent (autonomous agent framework) could be just what you’re looking for. The Select AI Agent framework enables you to build, deploy, run, and oversee AI agents – fully managed by Oracle Autonomous AI Database. You can develop conversational agentic workflows using a wide range of AI providers and AI models – including those you host via private endpoints – all from your Autonomous AI Database.
This blog explores how the Select AI Agent empowers organizations to build and deploy agentic AI solutions. You’ll learn what agentic AI is, how it’s different from traditional generative AI, and walk through a practical example of developing an intelligent, automated provisioning agent—all with simple integration.
Agentic AI use cases
AI agents can address a wide range of use cases that involve reasoning and action. For example, in customer support, AI agents can assist with troubleshooting issues, routing tickets, and escalating cases within the helpdesk process. By following a conversational flow, these agents can interact seamlessly with customers while accessing external information and systems using tools as permitted. Tools enable agents to, for example, retrieve customer data, view order history, consult knowledgebase articles, and even perform actions such as issuing refunds or updating service tickets—all in an automated, efficient manner.
Other use cases include:
- Financial research – an agent gathers and analyzes market data to produce briefs.
- Automated loan processing – an agent processes applications, verifies documents, obtains credit scores, and may even detect potential fraud. The goal is to accelerate loan approvals while reducing risk.
- Shopping assistant – an agent provides customized product recommendations, cross-sells options, and a streamlined checkout process.
- DevOps automation – an agent monitors system logs, detects issues, and applies fixes – automatically or with human approval.
How is agentic AI different from generative AI?
Before we dive into Select AI Agent’s capabilities, let’s clarify how agentic AI differs from traditional generative AI approaches. You may be wondering how AI agents differ from generative AI in general—or LLMs in particular. The main objective of generative AI, as found in large language models (LLMs), is in content creation—whether it’s text, image, audio, code, or SQL queries. In contrast, AI agents are not just chatbots: They focus on doing – being able to perform actions and make decisions to achieve specific goals with less human intervention. Agentic AI can help to automate complex business tasks, while being able to engage humans at critical points in a process to approve important actions.
In terms of autonomy, generative AI requires explicit instructions, and therefore lacks autonomy. Generative AI waits for user instructions or prompts and typically can work only on defined tasks. AI agents, on the other hand, can operate independently with minimal human guidance on multi-step tasks – even operating proactively.
Another difference involves their mode of interaction. Generative AI returns a single response to a specific prompt. Even if your chatbot supports conversations – where memory is maintained across individual prompts – the interaction is still “one prompt, one response.” AI agents, on the other hand, can handle complex communication involving multi-step scenarios to achieve goals. They can adjust their behavior in real time based on environmental feedback or data, along with solution evaluation.
In short, AI agents complement LLMs with additional capabilities:
- Autonomous decision-making: make decisions based on goals and constraints without constant human intervention
- Complex problem-solving: formulate, perform, and revise plans to solve problems
- Data access and tool use: call APIs, retrieve data, perform tasks, take actions
- Memory: have information and state from past interactions
- Environmental awareness: perceive and respond via integrated tools
- Goal-oriented: pursue longer-term objectives across multiple steps
Why Select AI Agent (autonomous agent framework)?
One approach to AI agent implementations may involve provisioning a VM, configuring and maintaining a container with necessary software packages, in addition to designing, implementing, and testing your agents. This approach may offer the most control over costs and security, it also could be complex and time-consuming. Alternatively, you could use a third-party agent service.
With Select AI Agent (autonomous agent framework), you can reduce development and operational overhead. For example, there is no need to download, install, or configure individual frameworks and provision compute resources. In addition, the Autonomous AI Database development tooling enables you to build and run agents managed by the database. Further, Select AI Agent doesn’t require data to be shipped outside the database to other frameworks or agent tools – offering greater security. In addition, Select AI Agent honors existing database security concepts such as role-based and code-based access control (RBAC and CBAC), system and object privileges, virtual private database (VPD), Oracle Real Application Security (RAS), data masking, and encryption features.
Select AI Agent key potential benefits include:
- Simplify orchestration of intelligent agents by using a unified framework that streamlines the coordination of agents capable of reasoning, acting, and learning from outcomes—reducing complexity in planning, tool integration, and reflective learning.
- Increase productivity with flexible tooling that allows you to build custom PL/SQL tools within your database, integrate external REST services, and utilize built-in tools—all without the need for additional infrastructure or custom orchestration code.
- Enhance user engagement and control by enabling agents to maintain context-aware, multi-turn conversations that support effective human-in-the-loop workflows through integrated short-term and long-term memory capabilities.
- Scale transparently to meet usage demand by running agent control flows natively within Autonomous AI Database, using auto-scaling to dynamically increase the number of concurrent agents or sessions.
- Maintain data security by running agents directly in the database, keeping data within the database and applying established security privileges and access controls.
- Speed up AI feature delivery with declarative agent definition using familiar PL/SQL, reducing development cycles. In addition, it enables rapid deployment across databases via Oracle’s Open Agent Specification.
How AI Agents with Select AI work
Select AI Agent concepts
Select AI Agent supports the definition of agent teams, agents, tasks, and tools. Like the AI profile, these reside in your database with the ability to create, drop, enable, and disable them.
Agent – an actor with a well-defined role that performs tasks using the LLM specified in your AI profile.
Task – a clearly defined set of instructions that may use one or more tools. You specify instructions for the LLM, which uses them to decide which tool(s) to use and when to accomplish the task. A task can be viewed as a step in a workflow or responsibility assigned to an agent.
Tool – used by a task to accomplish some behavior or action, especially when the task involves other systems like databases, email servers, web services, etc. Like tasks, you specify instructions for the LLM, which it uses to determine if a given tool is appropriate for the task. Built-in tools allow you to specify credentials and other details. Examples of built-in tools are:
- RAG – uses Select AI to perform retrieval augmented generation by querying a vector index specified in the AI profile.
- SQL – uses Select AI to generate and run SQL queries in your database using the specified AI profile.
- Web search – performs a web search using a third-party API, currently OpenAI with appropriate authentication credentials.
- Notification – enables sending Slack or email notifications with appropriate authentication credentials.
Agent Team – specifies one or more agents and assigns tasks to each of them. The agent team serves as the primary unit for deploying and managing agent-driven solutions.
Orchestration and control flow
Select AI Agent uses a solution framework based on the ReAct (Reasoning + Acting) agentic pattern, illustrated in figure 1. The ReAct pattern enables agents to iteratively reason about a user-provided prompt and use tools that act on some environment, which returns results or feedback for evaluation. The evaluation may determine if the agent has achieved its goal and return the final response or if it should continue to refine the solution—looping through the process until established exit criteria are met. In summary, each interaction follows the following sequence:
- Prompt: The user submits a prompt or question.
- Thought and action: The LLM reasons through the prompt and picks a tool to use on an environment for a given task, which may include human interaction for approval or additional input.
- Evaluation: after performing the task, assess whether the result or feedback meets established exit criteria and returns results.
Steps 2 and 3 repeat as needed, looping until the agent concludes with a final response that achieves the goal.
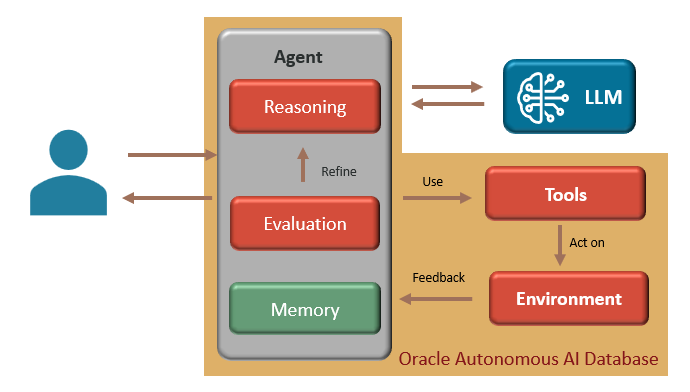
Figure 1: ReAct agentic pattern used by Select AI Agent (autonomous agent framework)
Security
To use Select AI Agent, an administrator must grant access to the DBMS_CLOUD_AI_AGENT package, which is an invoker’s rights package. The invoker must have privileges on the credential object for using AI providers, vector indexes, and data. Access is governed by the rights granted to the invoker in their schema.
Administrators can set up policies for personally identifiable information (PII) detection, masking, and audit trails using security features available in Autonomous AI Database. Data does not need to leave the database since agents based on Select AI Agent run natively in the database.
Agent developers can insert human-in-the-loop approval and confirmations as part of the agentic process. The ability to have human-in-the-loop interactions enables users to approve or confirm actions. This is essential for irreversible actions, but also enables escalation paths in agent processing.
Observability and evaluation
Select AI Agent provides visibility into the history of agent teams and tasks for individual users, through the USER_AI_AGENT_TEAM_HISTORY and USER_AI_AGENT_TASK_HISTORY views. There are corresponding DBA versions of these views, which provide administrators access to agent and task histories across users.
In the USER_AI_AGENT_TEAM_HISTORY view, each row represents a single agent team step and includes metadata such as the team name, job name, start and end timestamps, current state, error messages, etc. It acts as the top-level log that links to more granular task- and tool-level views for deeper analysis.
The USER_AI_AGENT_TASK_HISTORY view lists tool invocations. Each row records one invocation and includes detailed metadata such as the tool name, the agent and task that triggered it, team execution ID, specific step name, invocation timestamp, and input/output data passed through the tool. This view is essential for auditing how tools are used, monitoring integration behavior, and debugging issues related to tool results.
Example of a provisioning agent
In this example, we define an agent that interacts with a user to provision an Autonomous AI Database instance. Using the human-in-the-loop capability, the agent interacts with the user, asking for information needed to provision the database instance.
In the workflow, we define two tools: One to invoke the Autonomous AI Database Provision SDK, and another to list OCI regions. Select AI Agent automatically obtains the parameters needed to invoke these PL/SQL functions from the database procedure metadata. Where information is not already known, the agent asks the user for database configuration settings, like OCI region, the workload type (data warehouse or transaction processing), compute and storage requirements, and if Data Guard should be included.
Here is some of the code involved in defining the provisioning agent. We start with the DATABASE_ADVISOR agent:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI_AGENT.CREATE_AGENT(
agent_name => 'DATABASE_ADVISOR',
attributes => '{"profile_name": "GOOGLE",
"role": "You are a Senior Oracle AI Database Architect with expertise in Autonomous AI Database best practices, ' ||
'security configurations, and high availability solutions."}',
description => 'Expert database advisor for provisioning Autonomous AI Databases');
END;
Having defined a function to list the subscribed regions, we can define a tool that uses this function.
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI_AGENT.CREATE_TOOL(
tool_name => 'LIST_SUBSCRIBED_REGIONS_TOOL',
attributes => '{"instruction": "This tool lists all Oracle Cloud regions that are subscribed by current user tenancy. ' ||
'It helps users choose which region to deploy their Autonomous AI Database. ",
"function" : "list_subscribed_regions"}',
description => 'Tool for listing Oracle Cloud subscribed regions');
END;
Similarly, we define the ADBS_PROVISIONING_TOOL, which takes a set of parameters needed to provision an Autonomous AI Database instance.
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI_AGENT.CREATE_TOOL(
tool_name => 'ADBS_PROVISIONING_TOOL',
attributes => '{"instruction": "This tool provisions an Oracle Autonomous AI Database. ",
"function" : "provision_adbs_tool"}',
description => 'Tool for provisioning Oracle Autonomous AI Databases');
END;
The provisioning task, which uses these tools, may be described as follows:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI_AGENT.CREATE_TASK(
task_name => 'PROVISION_DATABASE_TASK',
attributes => '{"instruction":
"Help the user provision an Oracle Autonomous AI Database. ' ||
'Use LIST_SUBSCRIBED_REGIONS_TOOL to check all available regions that the user subscribes to. ' ||
'Use ADBS_PROVISIONING_TOOL to provision database only after you have gathered ALL required information. ' ||
'Must get final confirmation by summarizing all choices before provisioning. ' ||
'User request: {query}",
"tools": ["ADBS_PROVISIONING_TOOL", "LIST_SUBSCRIBED_REGIONS_TOOL", "HUMAN"]}',
description => 'Task for interactive database provisioning'
);
END;
Lastly, we define the agent team that associates the agent with the specific tasks it will perform.
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI_AGENT.create_team(
team_name => 'DATABASE_PROVISIONING_TEAM',
attributes => '{"agents": [{"name":"DATABASE_ADVISOR","task" : "PROVISION_DATABASE_TASK"}],
"process": "sequential"}');
END;
To run this agent team, we can use the SQL command line by first setting the team in our database connection session. Then, we can interact with our agent using the ‘agent’ action for Select AI:
EXEC DBMS_CLOUD_AI_AGENT.set_team(team_name => 'DATABASE_PROVISIONING_TEAM'); SQL> select ai agent create an Autonomous AI Database instance for me
Alternatively, we can use the RUN_TEAM procedure for full PL/SQL interaction and ease of integration in database applications.
DECLARE
v_response VARCHAR2(4000);
BEGIN
v_response := DBMS_CLOUD_AI_AGENT.RUN_TEAM(
team_name => 'DATABASE_PROVISIONING_TEAM',
user_prompt => ' create an Autonomous AI Database instance for me');
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(v_response);
END;
The interaction may look like the following:
SQL> select ai agent create an Autonomous AI Database instance for me You have access to the following regions, which would you like to use? SQL> select ai agent use Toronto What kind of workload type will this database be used for? SQL> select ai agent use OLTP workload type How many ECPUs and storage will be required for the database? SQL> select ai agent I want 4 ECPUs and 1 TB storage Would you like to enable Data Guard for high availability? SQL> select ai agent Yes, add Data Guard I started provisioning your Autonomous AI Database…
Get started
Select AI Agent (autonomous agent framework) offers a simple, secure, and scalable approach to building and managing intelligent agents within Oracle Autonomous AI Database. By enabling automation of complex workflows with integrated AI and robust governance, it accelerates innovation while helping to keep your data safe.
For more information…
- Try Select AI for free on OCI: Autonomous AI Database Free Trial
- Video: Getting Started with Oracle Select AI
- Documentation
- LiveLabs
