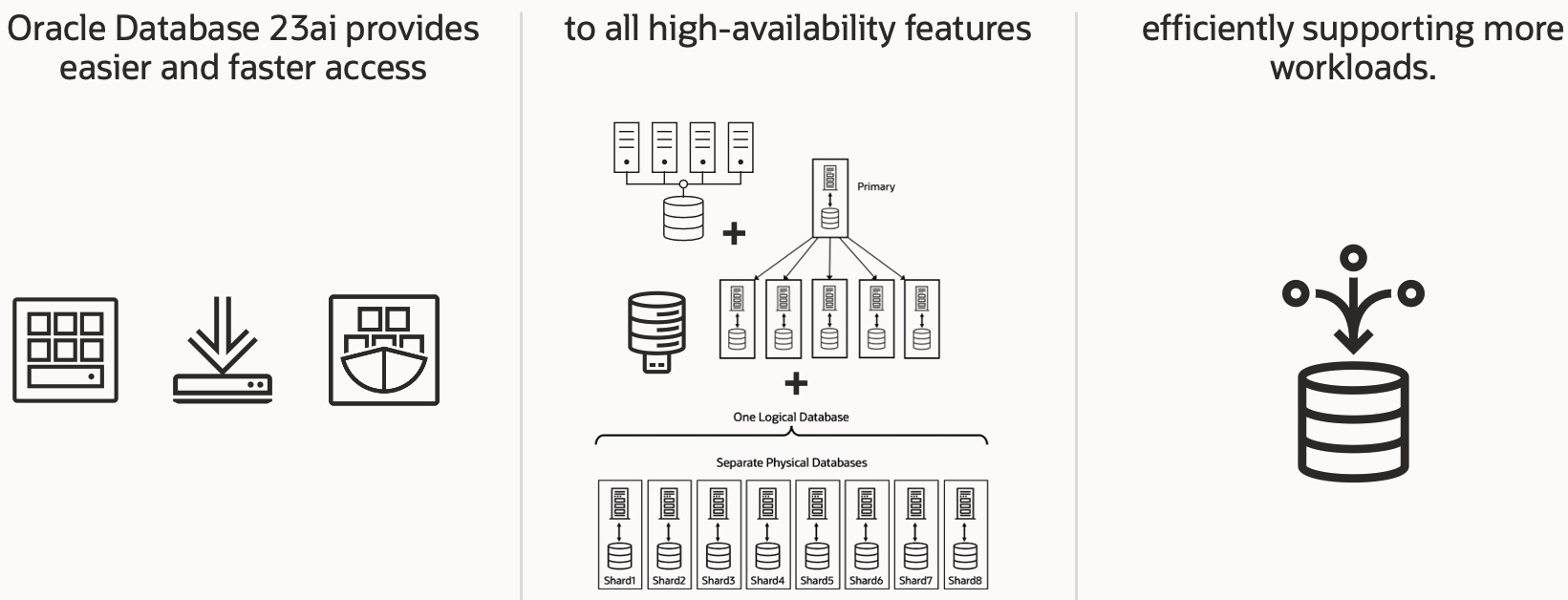
Oracle Database 23ai is the latest Oracle Database version, providing unprecedented features and capabilities for developers and database administrators. In addition, this release focuses on delivering Oracle’s exceptional high availability (HA), scalability, and disaster recovery (DR) features in a faster, more reliable, integrated, massively scalable, and efficient way, ensuring that easy access to high availability must never be an afterthought when using Oracle Database.
Why Oracle Database 23ai for HA, Scalability, and DR?
Data, one of any business’s most valuable assets, expands rapidly. Companies use more databases and tools to integrate and protect their data in different pools and containers to manage the data sprawl. Oracle’s Converged Database supports multiple workloads and various data types and has many built-in or addable HA features. Using Oracle Database will enable Oracle’s customers to analyze their data more efficiently, develop and deploy applications faster, and grant them immediate access to various integrated HA features.
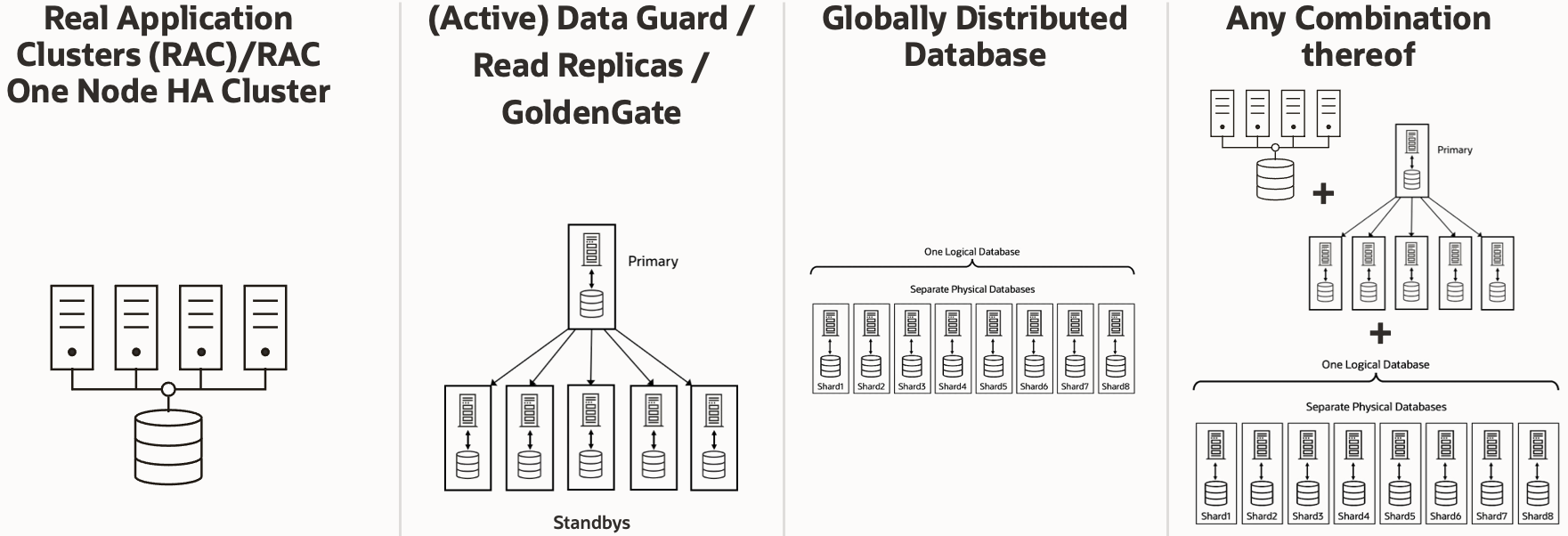
Oracle Database 23ai, unlike any other database on the market today, supports all common high availability and scalability architectures; starting with Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC), Oracle’s award-winning, all-active, shared-disk database implementation, over (Active) Data Guard and GoldenGate meeting any replication need, to any combination of those technologies. The latest supported architecture is Oracle’s Globally Distributed Database, which allows Oracle’s customers to address data sovereignty use cases conveniently and provides a hyper-scale architecture for applications that can support database sharding. With Oracle Database 23ai, the same applications can use built-in RAFT-based replication integrated with transaction execution, providing a fast and automatic sub-three-second failover with zero data loss.
According to Oracle customers, high availability issues – unplanned outages due to failures – are no longer the top pain points regarding database availability. Patching and upgrading, often called planned maintenance, have been named the most common pain points in recent surveys by the Maximum Availability Architecture (MAA) team. The need for regular patches/updates and frequent functional enhancements resulting in “patching” is considered the leading cause of maintenance-related downtime in approximately 30% of the cases.
Rolling maintenance across systems has long been the answer to reducing maintenance-related downtime, requiring an auxiliary database or a multi-node cluster like Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) – until now! Oracle Database 23ai can offer the same maintenance benefits as a multi-node cluster on a single server. The feature enabling this capability is called Single Server Rolling Database Maintenance. It allows rolling-applicable patches and updates to be applied on a single server only using a special Oracle RAC One Node implementation. Oracle RAC supports a similar feature called Local Rolling Database Maintenance, preventing planned maintenance from interfering with the workload on remote nodes in the cluster.
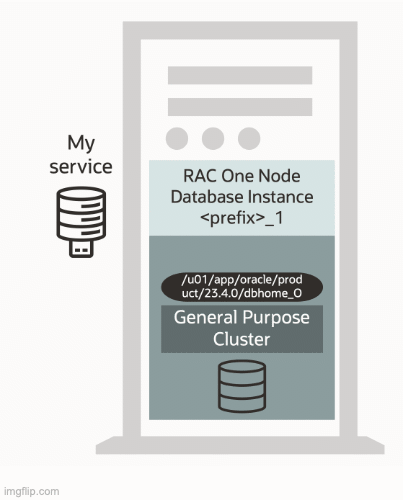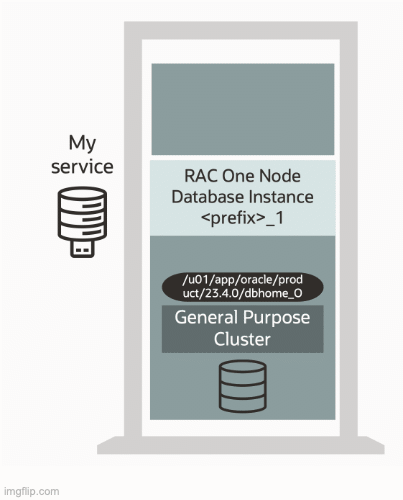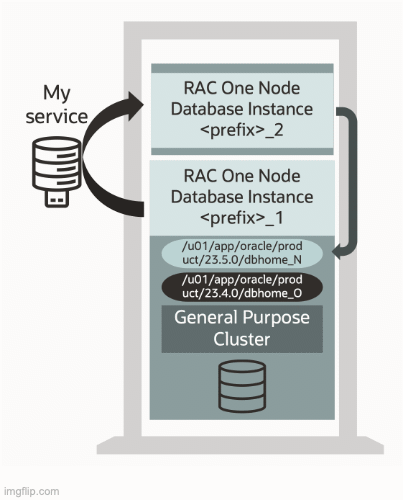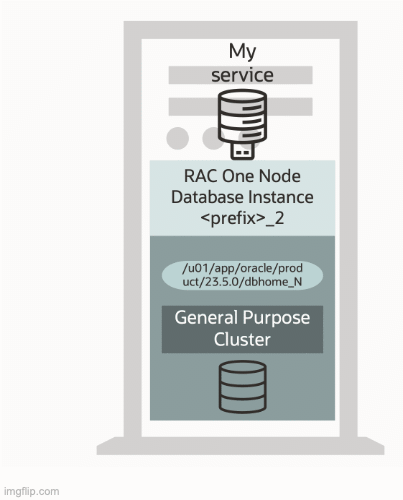
As data sprawls, so does the requirement to access HA features fast and whenever needed. With Oracle Database 23ai, all HA architectures can be combined (“don’t replace; add-on”) and accessed quickly, as “faster access to high availability” was another focus area for the latest release of the Oracle Database.
One of the main features in this focus area is not related at first – a significantly reduced Oracle Grid Infrastructure disk footprint. Oracle Grid Infrastructure is the basis for Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) databases and needs to be deployed before any Oracle RAC database can be deployed. With Oracle Database 23ai, the Oracle Grid Infrastructure disk footprint has been reduced by half (a more than 2x reduction in disk space compared to Oracle Grid Infrastructure 19c), allowing for a much faster initial deployment (up to 33% faster than for a two-node cluster compare to Oracle Grid Infrastructure 19c) and “add node” due to a more than 2x faster unzip and software copy to nodes.
![]()
Another benefit of reduced disk footprint is the easier deployment of Oracle RAC environments in containers. Oracle Database, including Oracle RAC, has been supported in containers for the longest time. For example, Oracle RAC in Docker Containers has been fully supported since Oracle Database 19c https://blogs.oracle.com/maa/post/oracle-rac-on-docker-now-with-full-production-support.
Support for Oracle RAC on Podman was added later, allowing for a fast, lightweight deployment of Oracle RAC 19c, 21c, and 23ai on Oracle Linux 8 as the first container environment to support this Linux release. A base Oracle RAC Podman image is available on GitHub and the Oracle Container Registry. Customers can manually apply RUs to the base image and create custom images as needed.
Oracle Database 23ai adds the long-awaited Oracle RAC on Kubernetes support. Technically, Oracle Database 23ai is not a requirement to run Oracle RAC on Kubernetes, as Kubernetes orchestrates the deployment of Oracle RAC container images across a pod. Still, testing and specific enhancements will only be available with the latest Oracle Database release. One of those enhancements is the Oracle Operator for Oracle RAC on Kubernetes support: https://www.oracle.com/database/kubernetes-for-container-database/#database-operator
Continuous Integration and Innovation
Regarding providing the most reliable database architecture – Oracle Maximum Availability Architecture (MAA) – it’s not always the significant enhancements and innovations that matter. Integration with existing features and minor enhancements are equally important. Oracle Database 23ai includes many such integration features and minor improvements across different areas, making a huge difference.
Take the integration with Oracle’s unique Pluggable Databases (PDBs) for example. PDBs, a.k.a. Multitenant Container Databases, have long provided a simplified database lifecycle management for never-down applications, an HA area that is increasingly important for Oracle’s customers. Following Oracle’s “don’t replace; add-on” paradigm, all Oracle Database 23ai HA architectures fully support and can be used with Pluggable Databases. In the context of Oracle’s Globally Distributed Database, shards can be Pluggable Databases in different CDBs. Since Oracle Database 21c, Oracle offers a new Data Guard per Pluggable Database feature that allows PDB-level disaster protection with two Container Databases (CDB) actively running workload. Oracle Multitenant and Oracle RAC have had a symbiotic relationship since the release of Oracle’s Pluggable Database architecture more than ten years ago.
With Oracle Database 21c and Oracle Database 23ai, the integration of Pluggable Databases with Oracle RAC has been taken to the next level, as Pluggable Databases are now a first-level entity managed in Oracle Clusterware. In other words, a Clusterware resource is used for managing PDBs, not a database service acting as a proxy for the PDB placement, starting with Oracle Clusterware 21c. In Oracle Database 23ai, the next long-term support release, the focus was on stabilizing and optimizing those enhancements. The Fast Pluggable Database Open feature is one outcome of such efforts, enabling an up to two times faster PDB open by performing an “open in parallel” with DLM reconfiguration.
Some of the other minor improvements making a considerable difference include, but are not limited to, the following:
-
Automatic Self-Correction of Host Configurations – The Configuration Verification Utility (CVU) provides more than verification by correcting file permissions in the Grid Infrastructure home and adjusting OS kernel parameters to recommended values.
-
Expedited Fencing on Exadata Database Machine – A single process stuck in the OS kernel could stall RAC reconfiguration, even on Exadata. Oracle RAC instance and node reconfigurations are now integrated with Exadata’s fencing optimizations, allowing for expedited fencing.
-
Last Node Standing despite the loss of wire – Oracle Clusterware will prevent a node eviction of the last node in a cluster due to a private interconnect failure as much as possible.
-
Oracle RAC Fast Start Reconfiguration – Instead of pausing work for reconfiguration and instance recovery after an instance crash, Oracle RAC Fast Start Reconfiguration allows work to start on clean blocks immediately, leading to work resuming up to six times faster and instance recovery completing in three-fourth of the time compared to Oracle RAC 19c.
The most significant continued innovation feature attesting to the fact that “integration with existing features” is one goal that Oracle will continue to pursue is the new support for AI vector search within the Oracle database and its integration with Oracle RAC. Vectors are used in AI to represent the content of unstructured data such as images, documents, and videos. Each vector is a sequence of numbers called dimensions, which capture the critical features of the unstructured data. In Oracle Database 23ai, a native Vector datatype and optimized vector similarity search indexing have been added to greatly enhance query performance. New SQL functions and operators will make creating, manipulating, and querying vectors easier. In Oracle RAC, Oracle transparently scales vector processing across the cluster or isolates it to a subset of nodes in the cluster, as Juan Loaiza stated in his Oracle CloudWorld 2023 keynote.
Don’t Hesitate, Upgrade!
There are many good reasons to upgrade to Oracle Database 23ai – the new high availability, scalability, and disaster recovery features discussed in this blog post are only some. We are pleased to announce that the latest version of the world’s most powerful database, Oracle Database 23ai, is now generally available on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. MAA on-premises customers will need to wait until the release of Oracle Database on-premises, which will follow soon. At that time, you will benefit from faster and easier access to all high availability, scalability, and disaster recovery features, including (Transparent) Application Continuity Support for DBMS_ROLLING, by simply and smoothly upgrading to Oracle Database 23ai. Until then, follow this blog for the latest updates.