Introduction:
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) within Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC) brings powerful automation capabilities that help organizations streamline business operations without restructuring their existing systems. By combining RPA’s ability to replicate human actions with OIC’s strong integration, workflow, and API-driven orchestration, enterprises can automate repetitive tasks across disparate applications—both modern and legacy. RPA enables end-to-end automation by bridging systems that lack APIs or modern integration interfaces, ensuring seamless data flow across applications, SaaS systems, and legacy environments. The combined approach accelerates digital transformation, lowers operational costs, ensures better compliance through governed automation flows, and expands automation possibilities where traditional API-based integrations fall short.

Technical Approach:
Before initiating any development activities in Oracle Robotic Process Automation (RPA), it is essential to verify that both the RPA Browser Extension and the Robot Agent are installed and updated to their latest versions. This ensures compatibility, prevents runtime failures, and guarantees that all new features are available during automation development.
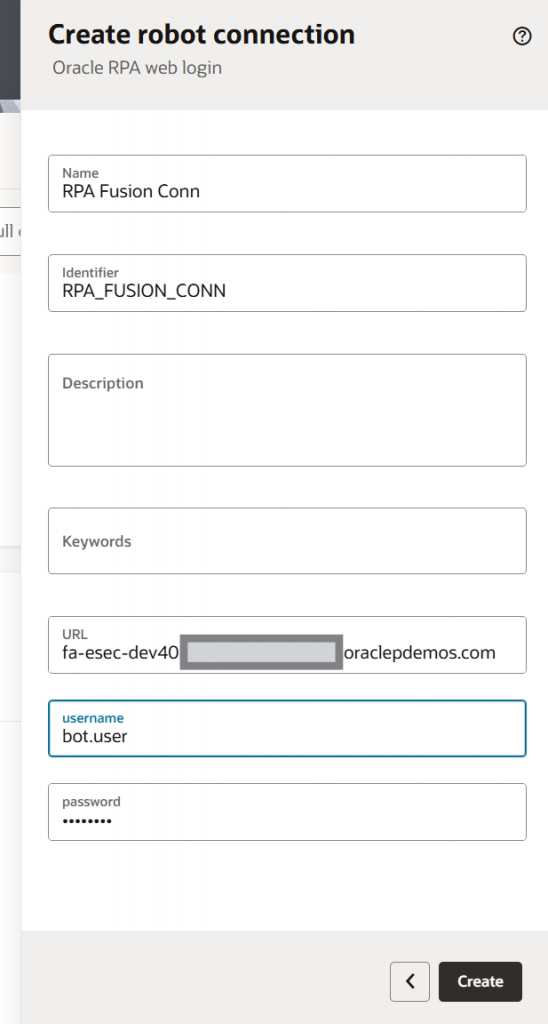
- Define Robot Connections:
You can store information, like URL and credentials, in the robot connection. Inside the Robot, you can use that information directly from the connection. When you need to update the value in the future, you need to update only the robot connection, rather than every robot that uses the connection.
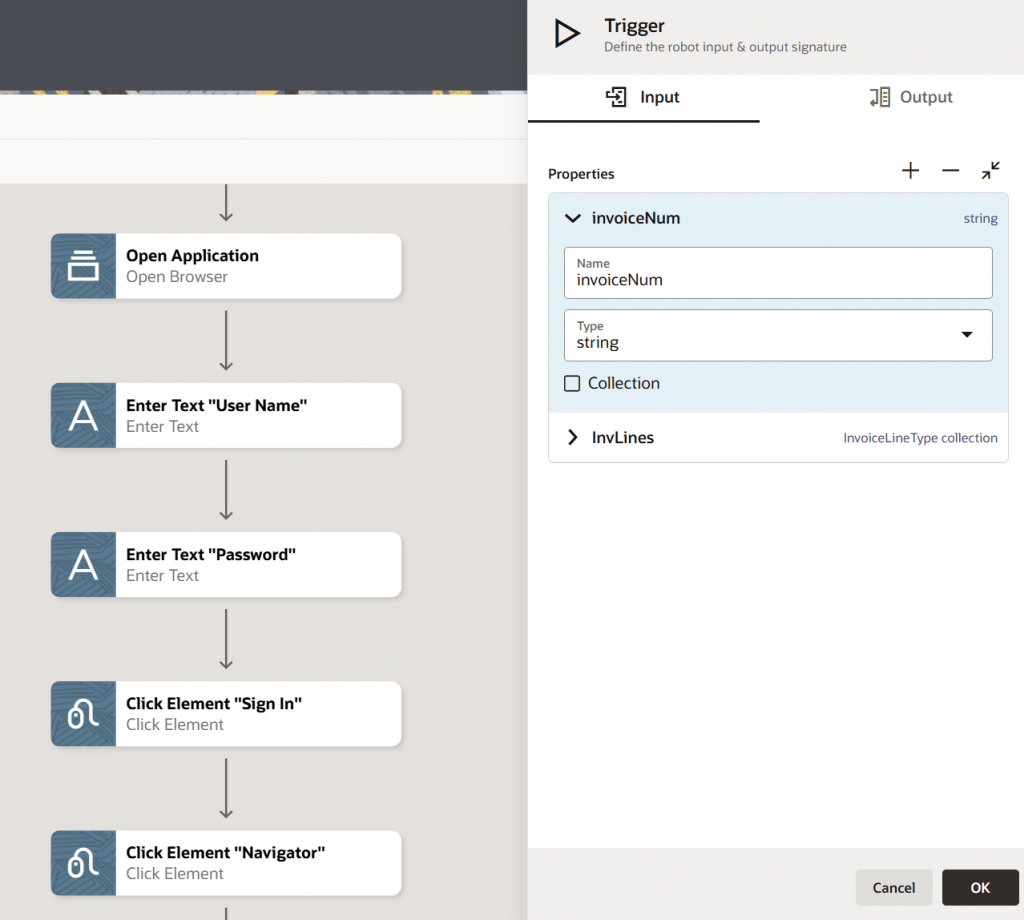
- Define Input/Output parameters:
You can define input and output parameters in RPA. These parameters can be used as input arguments after the robot is activated. For example, if a bot processes invoices, instead of coding a fixed invoice number, you can pass the invoice number as an input parameter every time the bot runs.
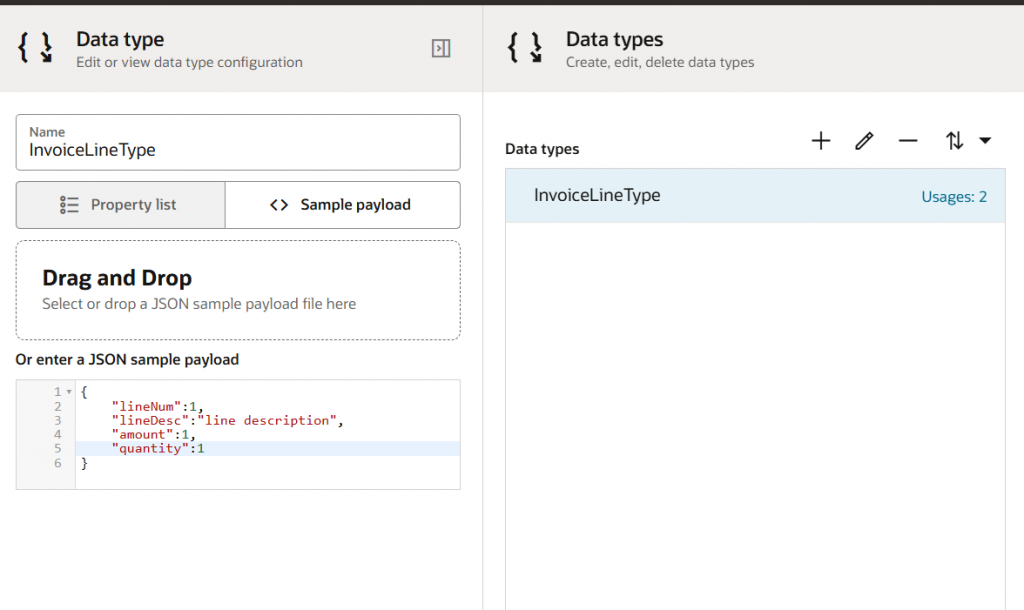
- Define Complex Data Types:
You can define complex input parameters & variables within RPA. You must create a Data Type to accomplish this. Either you can define the property list one by one, or you can use a sample JSON payload to create the data type.
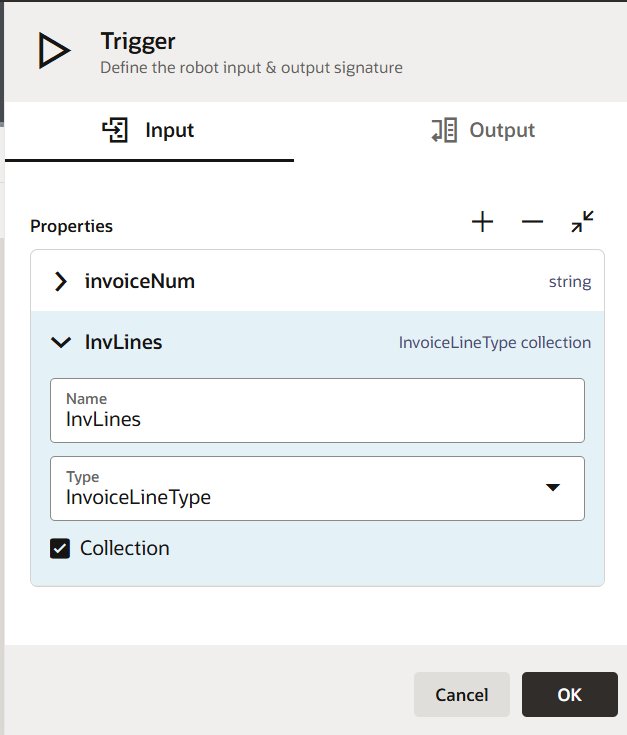
Once the data type is created, it will be available as a Type while creating any variable. In order to utilize a complex type as an input parameter, you must choose that type. For example, if you need to update several invoice lines, you can construct an input parameter called invoiceLine with the type invoiceLineType. Make sure the Collection option is selected before passing an array of invoice lines as an input parameter.
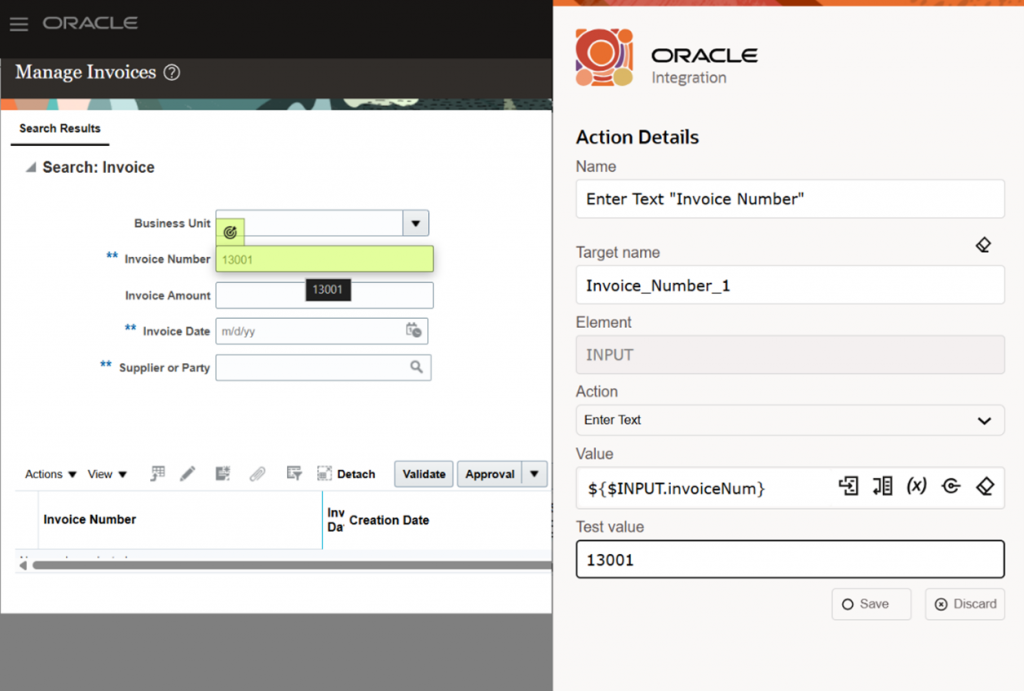
- Search invoice with Enter Text:
RPA allows you to “Record after the selected action” Record or by adding required Actions or Flow Control manually. For that, you need to make sure Browser extension is installed as a prerequisite. Once you reach the search invoice page, you can use the Enter Text option, where you provide the invoice number as an input parameter. Make sure one valid test data is available to you, which you can mention in “Test value.” This will assist you to update the respective field and help you to navigate to the next step.
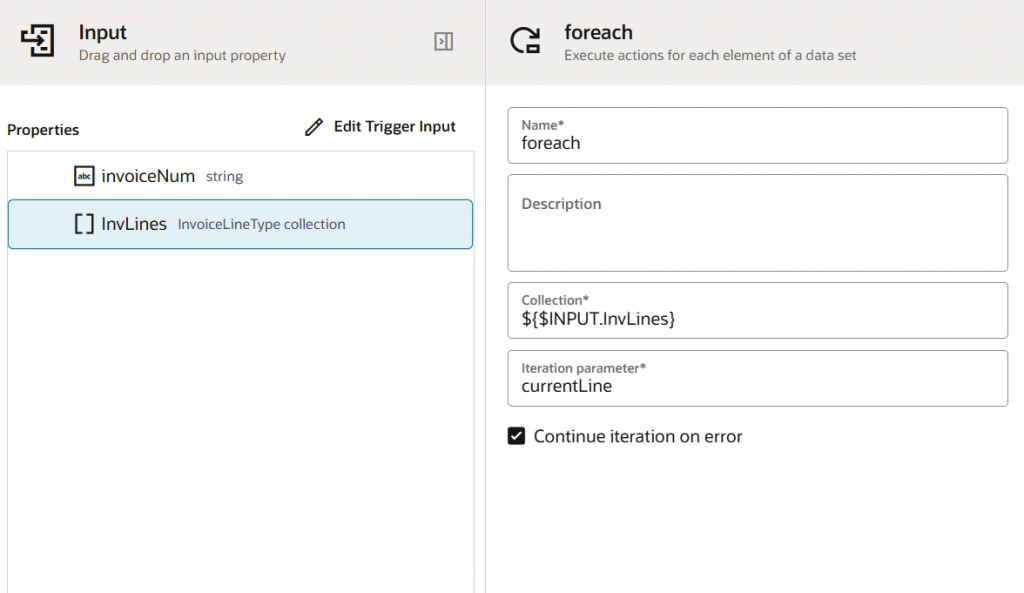
- Add a Foreach Loop:
When a robot performs the same actions for multiple items, add the actions to a foreach loop. Consider an organization that needs to manually update several invoice lines. We generated an input parameter collection called invoiceLine, as seen in the previous step, and we will use a foreach loop collection & in the iteration parameter, enter the name to give to every record in the collection. As per business requirements, you can check Continue iteration on error.
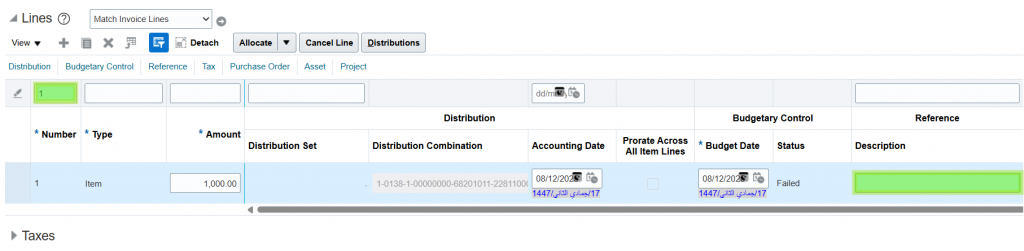
- Use Iteration parameter inside foreach:
As part of a repetitive task, if you want to filter with a line number, you can use the Enter Text activity to search with each line number.
But in the UI, the filter reflects only after you click Enter. For this reason, RPA offers the “Press ENTER Key to finish action” checkbox. This is not available in recorder mode, but you need to update your activity and change it. For better troubleshooting, it’s recommended to enable screenshots before & after the action.
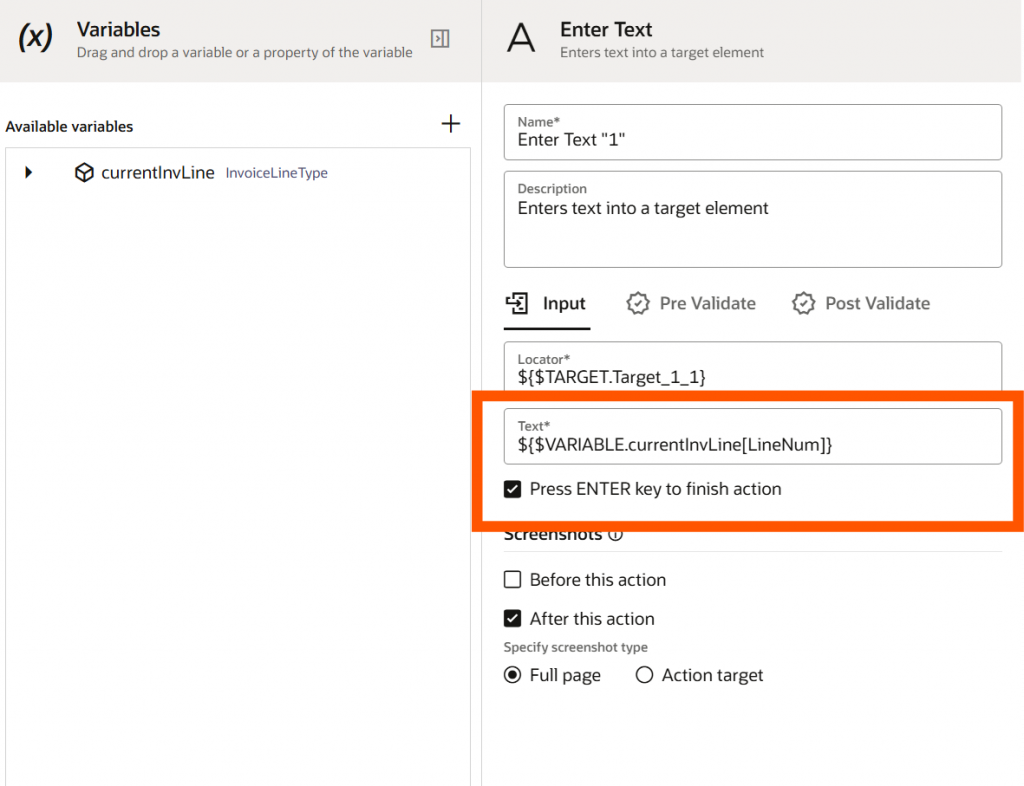
Similarly, you can update other invoice line attributes. RPA provides a wide range of actions that users utilize daily in their everyday activities, such as Checkbox, Click Element, Radio Button, Get Text, etc. Once all action has been taken care of, you can use the Click Element action for Save and Close.
- Web Table Definition:
We will set up another ROBOT to retrieve the recent currency exchange rate from a bank’s website, which does not provide an API for this purpose. The bank website maintains the currency name along with buy/sell rate in tabular format. In Oracle Robotic Process Automation, a Web Table Definition is a way to identify and interact with those HTML table elements on a web page during automation. OIC RPA offers a structured way to define the web tables using “Target a Page Element” in which you must choose all necessary columns and two sample rows for each column, as demonstrated below.
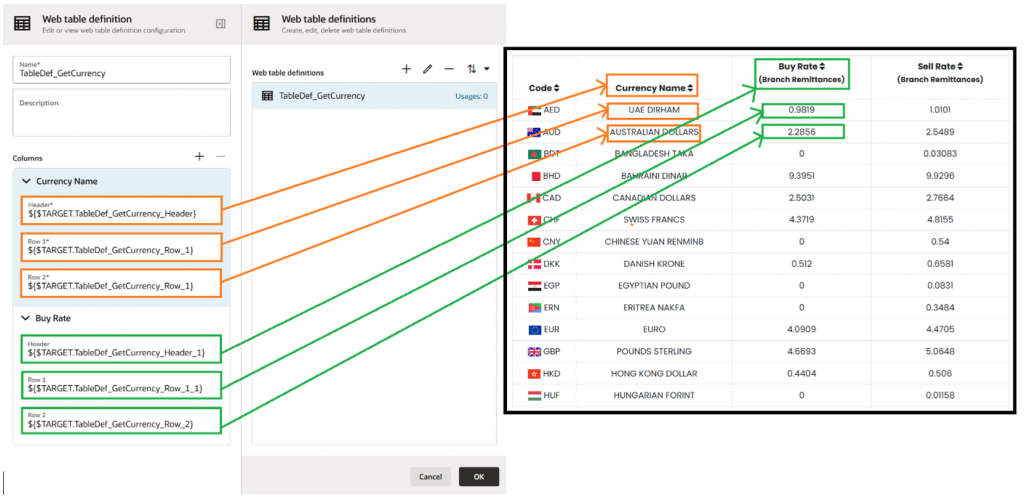
In our use case, we need only the Buy Rate for the respective Currency Name, but if you need more columns for business automation, you must select all required columns. Now we will be using the Web Table activity, where an already defined web table will be used. In the output section, one variable will be generated automatically that will hold the current entire table elements.
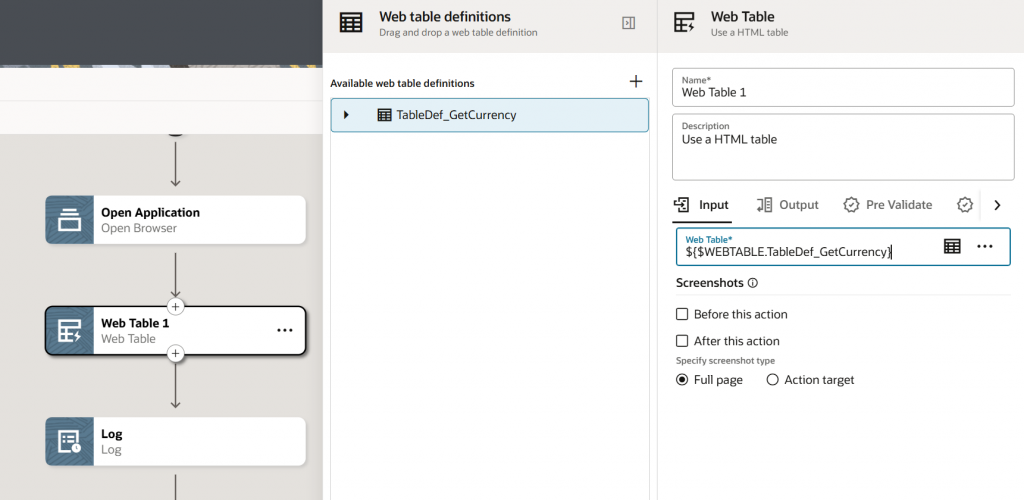
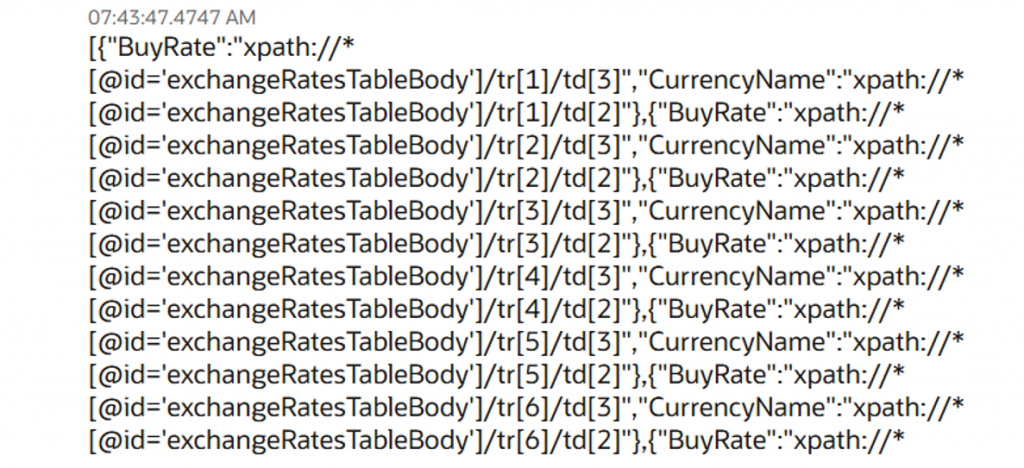
To confirm if the Web Table is configured correctly or not, you can log the output variable and run the Robot. For successful configuration, you will be able to see the XPath of the table content.
We have now set up the currency input variable, from which the buyRate output parameter will be retrieved. Then we will be utilizing the flow control capability foreach to iterate through each line of the WebTable output variable.
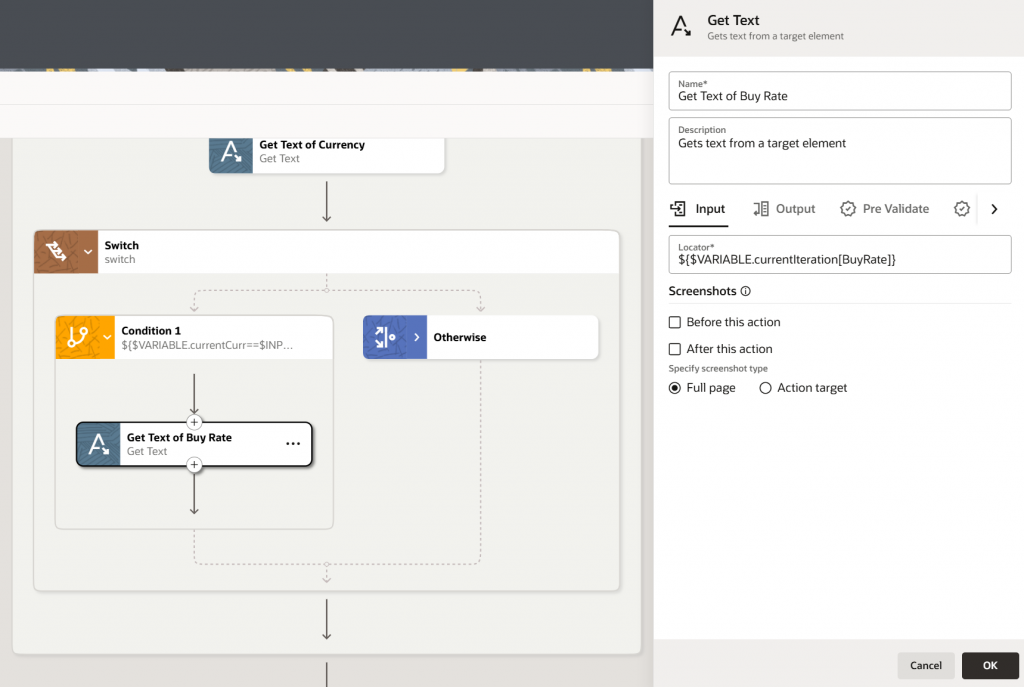
- Get Text of current iteration:
We created one variable currentCurrency to hold the currency of the current iteration. We will use the Get Text action to copy the currencyName from the current iteration of the webtable output variable to currentCurr local variable.
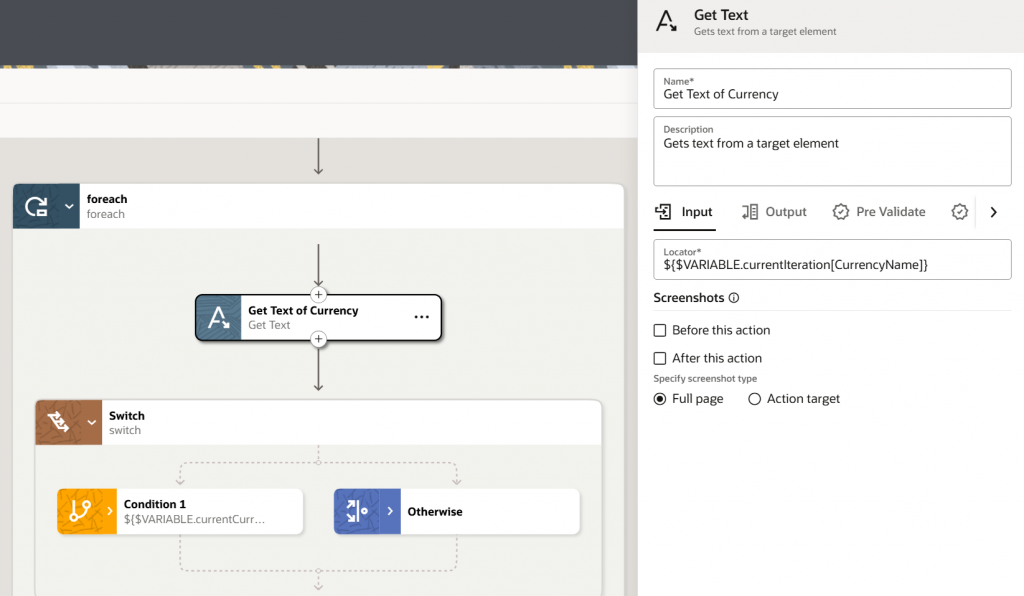
- Leverage Switch Flow Control
Now we have leveraged another flow control feature, Switch. A switch condition has the capability to evaluate one or more conditions and then take the appropriate action. The condition might include an expression to determine whether the value held by currentCurrency is equal to input_Curr coming as an input parameter.
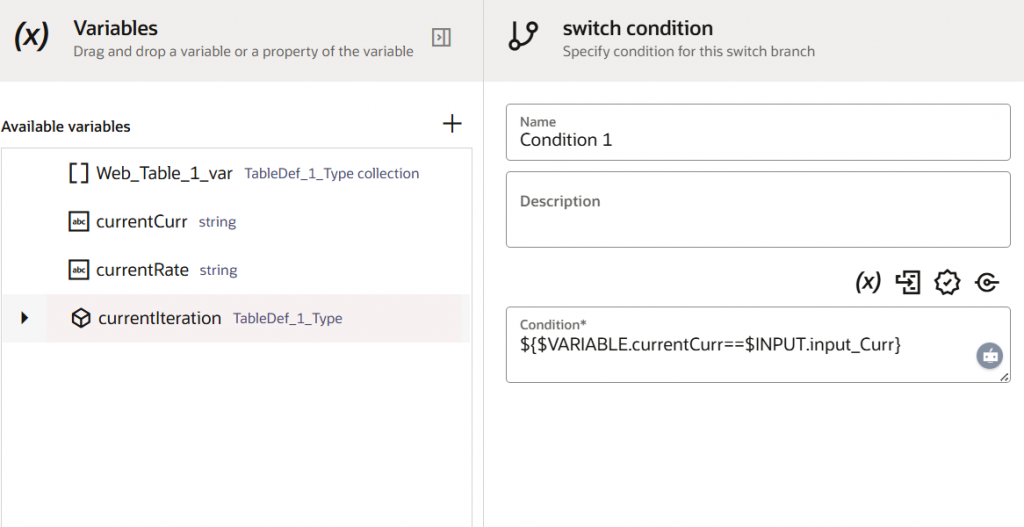
Whenever the condition is fulfilled, we will be copying the BuyRate of the current iteration into the output variable. Once done, save the robot. Every time you save a robot, Oracle Integration validates the robot and identifies its errors, if any exist. After you finish building a robot, activate it. Afterward, you can test and run the robot.
Execution:
Robots run on environments, which are the computers or virtual machines (VMs). Environment pools are collections of these computers. To run a robot on a real-world environment, you must associate the robot with an environment pool. Then you can activate your robot. The input for a robot contains a number of properties you configured during build time. To test the Robot, you can simply click Run as shown below.
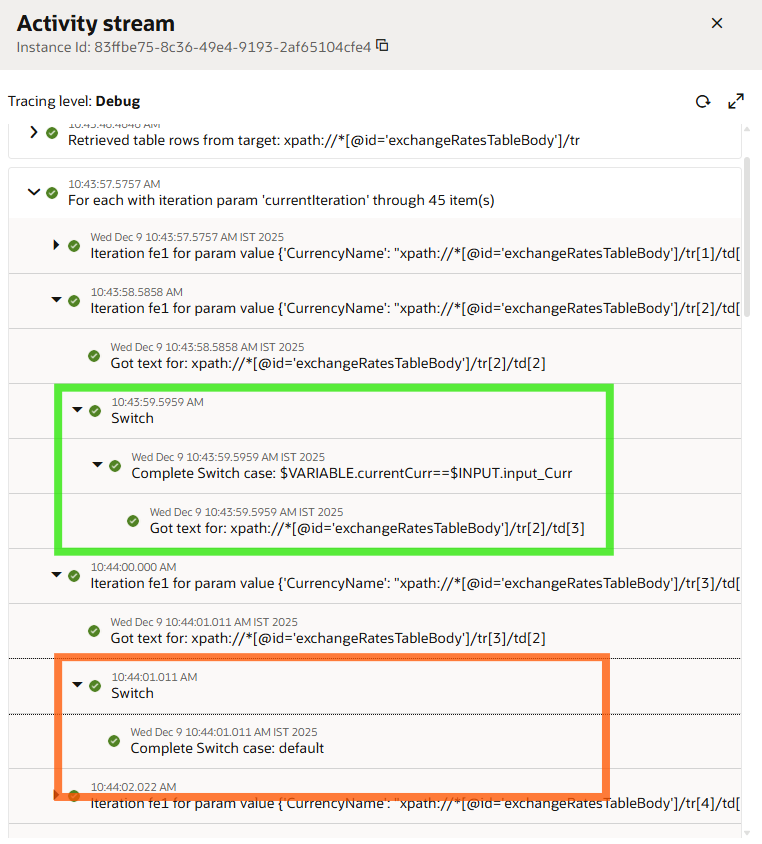
You can design an integration within the same project that calls multiple robots in accordance with the requirements. OIC provides Native Action “Robot flow” which can be used to invoke robot with required input parameters. In our use case, we have designed the integration in such a way that it will invoke the getCurrency Robot to retrieve the exchange rate for a certain currency, compute the amount that needs to be updated in the invoice, and then call the updateInvoice Robot. You can review the activity stream for the Robot under the Observe tab in the project. Check whether each step ran correctly: Green checkmarks indicate that the action was completed successfully. A red X indicates that the robot wasn’t able to complete the action. In the below activity stream of the GetCurrency robot, you may observe the robot is comparing currency names in each iteration. Once the condition is fulfilled, it’s using the Get Text action to retrieve the respective exchange rate & map to output parameter.
Under Observe you can monitor environments and environment pools within a project. You can identify shared environment pools, find environments that require updates to the robot agent, and check whether an environment pool has enough environments to handle its robot instance load. Hence, it’s recommended to download the latest agent, install it, and add it into the environment pool.
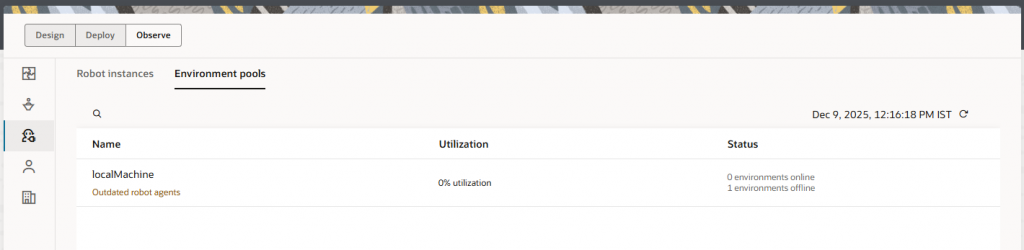
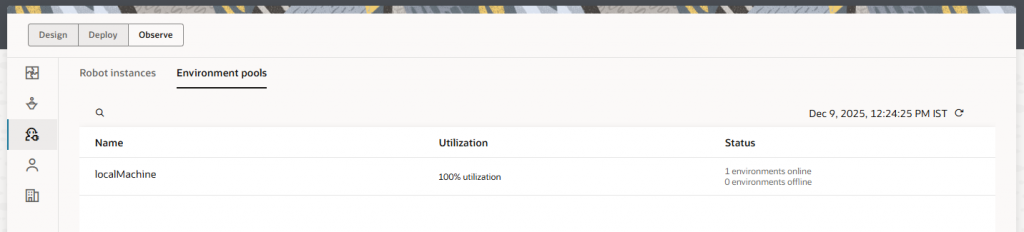
After adding the latest agent into the environment pool, you can see the warning is not coming anymore. Also, you can monitor the utilization during the robot execution.
Conclusion/Key Takeaways:
- Legacy System Enablement: RPA bridges gaps where APIs are not available – especially in legacy, other web-based applications – ensuring end-to-end automation without major system upgrades.
- Cost Efficiency: Automation reduces operational costs by minimizing manual labour, improving turnaround times, and optimizing resource utilization.
- Scalability & Reusability: Once built, RPA components and integration flows can be reused across multiple processes, helping organizations scale automation quickly.
- Reduced Errors & Higher Accuracy: Robots follow deterministic workflows, significantly reducing manual errors and improving data quality across processes.
- Seamless Integration with OIC: OIC acts as the central orchestration layer, enabling bots to work in harmony with APIs, applications, file-based systems, and event-driven flows.
References / Useful Links
References / Useful Links:

