OCI GoldenGate deployment backups are key to troubleshoot issues. Deployment Backups are automatically created daily. You can also create manual backups at any time, and save them to your OCI Object Storage. The manual deployment backup contains the full GoldenGate deployment directory structure and files, including log and trail files.
Currently there are several ways you can access the OCI GoldenGate deployment backups:
- Use Cloud Shell directly inside the Oracle Cloud Console
- Use OCI Console to access the OCI Object Storage, and then download the backup locally.
- Use OCI SDKs or the OCI Rest API to access the OCI Object storage programmatically.
OCIFS provides an alternate way to access OCI GoldenGate backups within OCI Object Storage through a filesystem. With OCIFS, Object Storage data becomes accessible as regular files that you can read, write or modify with standard shell commands (ls, rm, cat …).
Prerequisites:
- Provision a OCI Compute Instance using the pre-built Oracle Linux Cloud Developer Image
OR Quickly install and configure the OCI Command Line Interface (CLI) on a current OCI Compute Instance - Set up API Key on above OCI Compute Instance. Refer this link for more details.
- Create a OCI object storage dedicated for OCI GoldenGate backups , if not created already
- Test Connectivity to OCI Object Storage
-
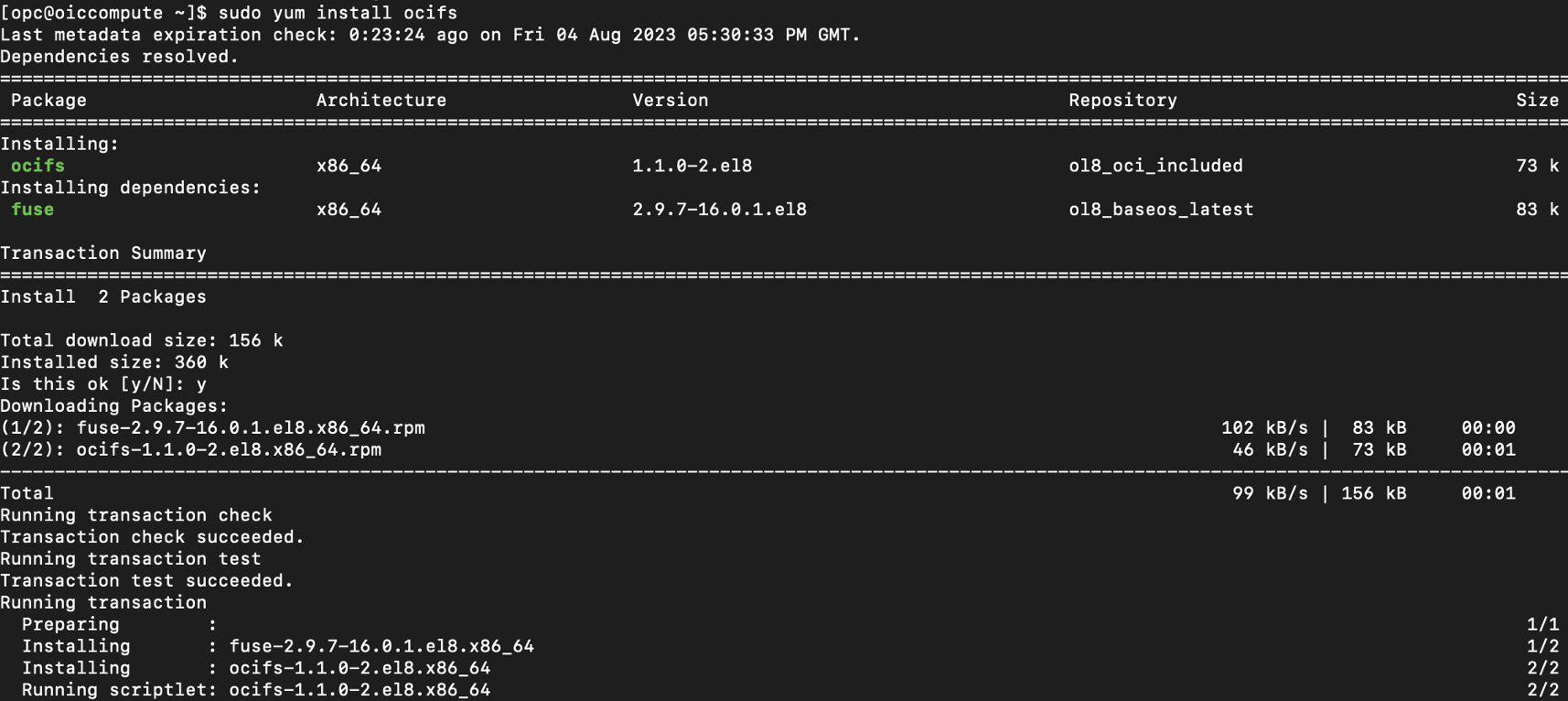
Install the OCIFS Utility
Use the below command to install the OCIFS utility
- Mount the OCI Object storage bucket using OCIFS
OCIFS lets you mount OCI Object Storage buckets to be used as file systems, and lets you manage the objects i.e. OCI GoldenGate deployment files in the mounted buckets as regular directories and files.
Here is an example to mount the OCI Object Storage bucket (OCIGGBD) on the ~/myociggbkp directory.
$ ocifs OCIGGBD ~/mydir
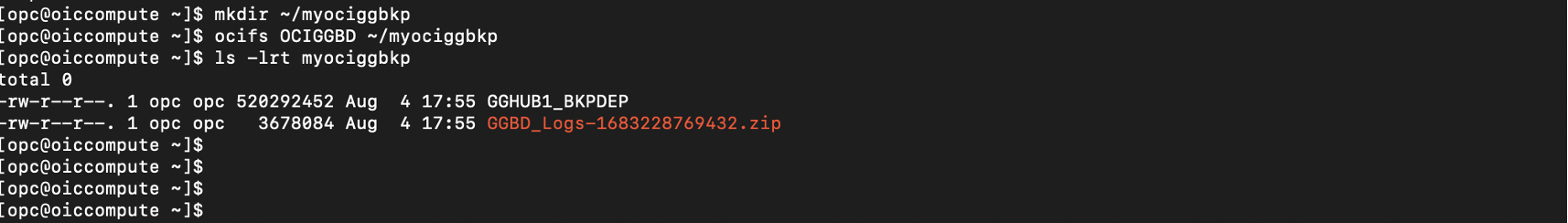
- Accessing OCI Object Storage Data as Regular Files
After the OCI Object Storage bucket containing the OCI GoldenGate deployment backup is mounted, OCI Object Storage data is accessible as regular files. Now you can use your regular shell commands to read, write, modify or add OCI Object Storage data.
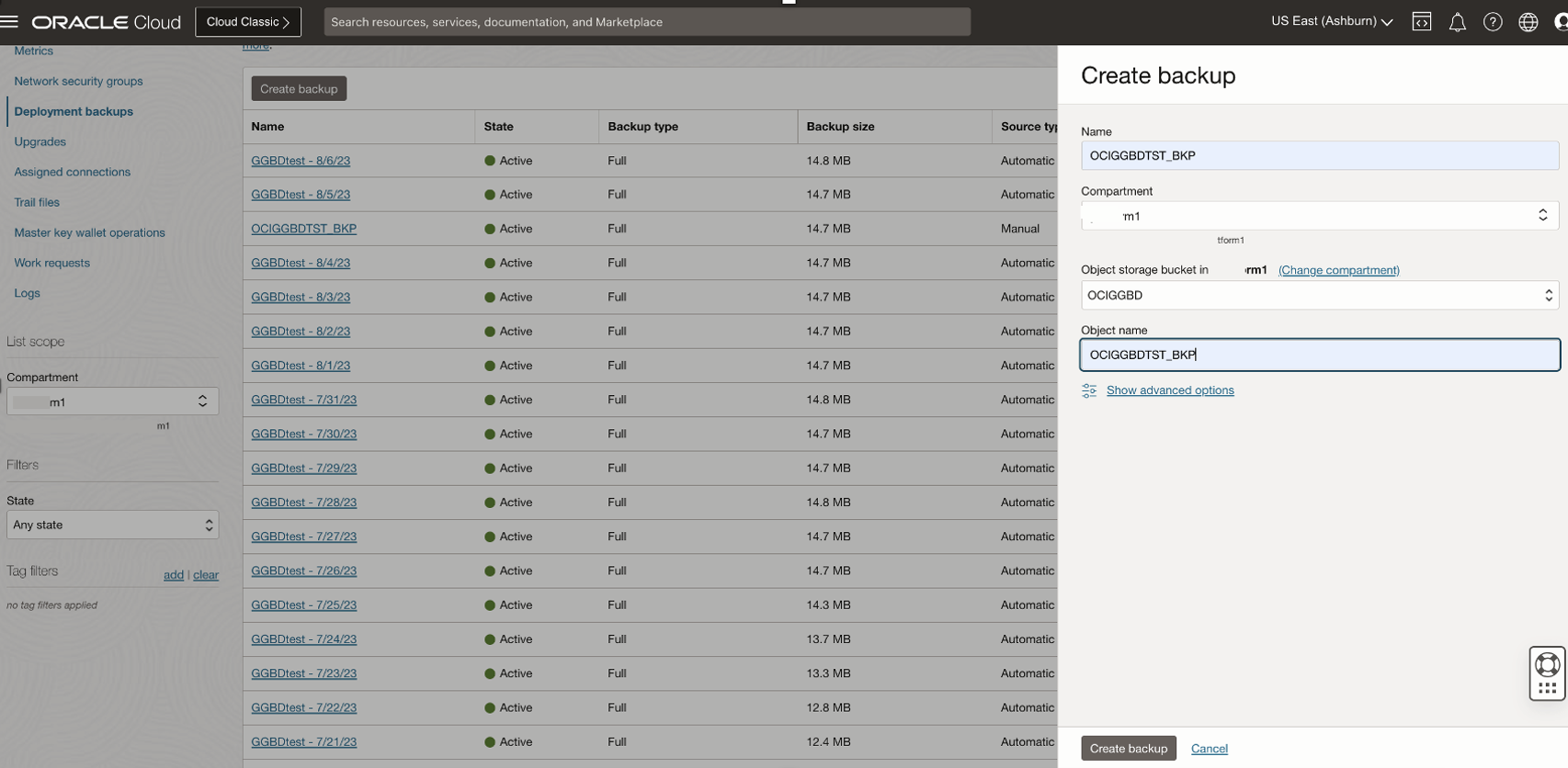
You can initiate a new manual backup for your OCI GoldenGate deployment using OCI console or OCI CLI command:
OR
CLI Command :
oci goldengate deployment-backup create --display-name <name> --compartment-id <compartment OCID> --deployment-id <deployment OCID> --namespace-name <namespace> --bucket-name <object storage bucket name> --object-name <backup filename>
- Once the deployment backup is completed , you should be able to see the same reflected in your mounted directory
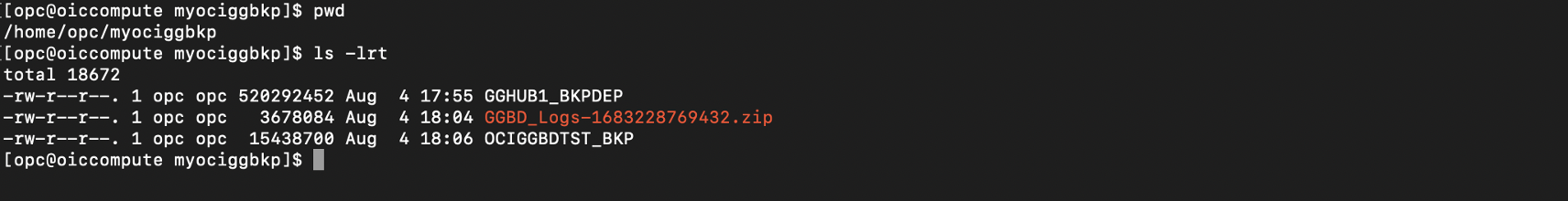
- Copy the OCI GoldenGate deployment backup to a different location using cp command and extract the backup using the tar command
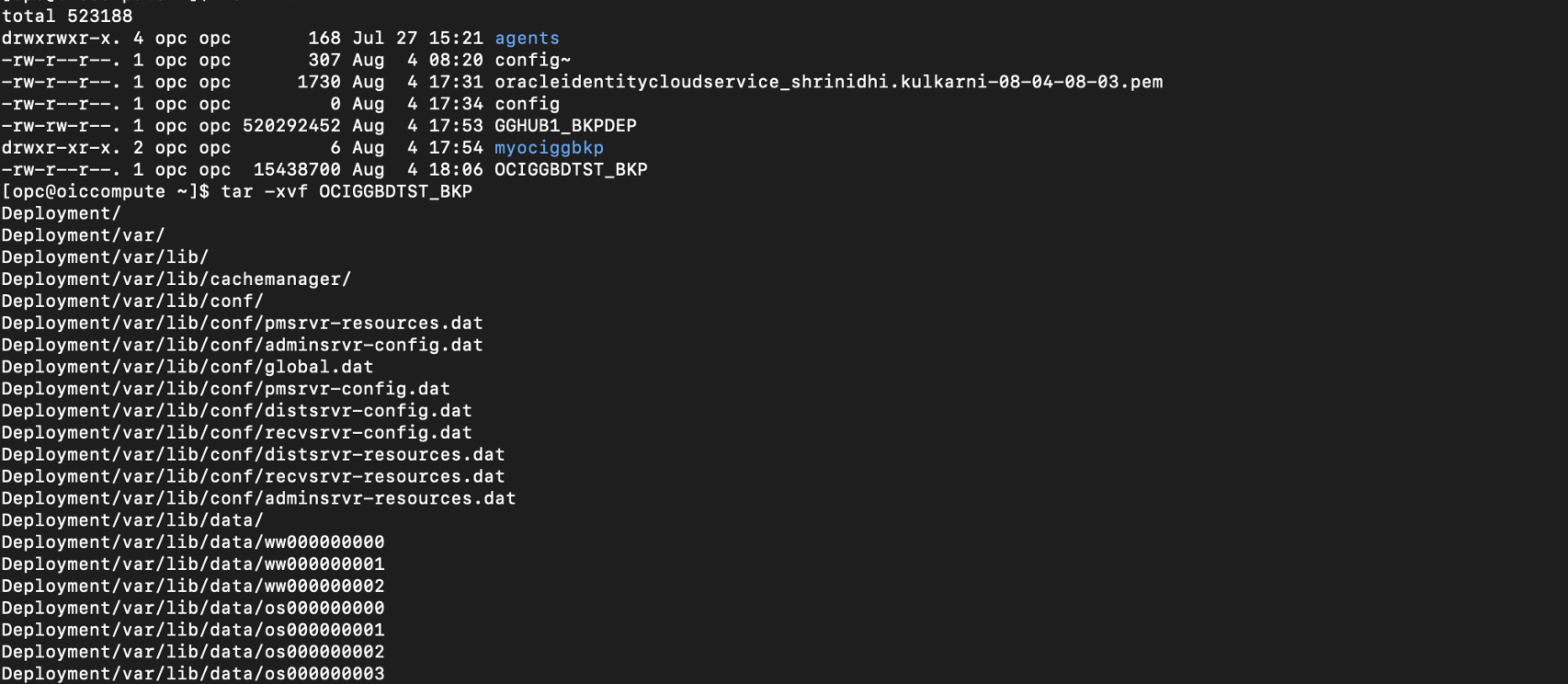
- The manual deployment backup contains the full OCI GoldenGate deployment directory structure and files, including log and trail files. The directories and files that are helpful for troubleshooting are available under Deployment:
/etc/ogg: parameter files
/var: log files, checkpoint, trail files, and so on
/var/checkpt: checkpoint
/var/data: trail files
/var/report: report files
Unmount the OCI Object Storage bucket
Unmounting an OCIFS file system removes its corresponding cache directory, unless the file system is mounted with the cache-keep option. See OCIFS Cache Options.
Learn More:
