Do you know how to search in Oracle Database? Oracle database contains a full-text search, called Oracle Text, that is fully integrated and provides even extensions for text mining, classification, clustering etc. You can start immediately in a “normal” database schema. The simplest use case is to perform a full-text search within a single column. But even more complex cases are supported: Search within multiple columns in the same data source and also searches within multiple data sources are supported.
In Oracle Database 23, there is a new feature called Ubiquitous Database Search which makes it very easy to search in different data sources. Only one command is needed to create a self managed index and another one to add different sources. Without writing additional PL/SQL code or having any deep knowledge about Oracle Text datastores etc. you can include data sources in your search. Ubiquitous Database Search is implemented via the API DBMS_SEARCH. It’s a JSON search index with a predefined set of preferences required for searching documents with contents in different columns, tables, and views.
How can you use this functionality? Of course you can use it in your SQL application and in tools such as SQL*Plus, SQL Developer, SQLcl etc., but also with the APEX.
As with other interesting database features like JSON dataguide, REST etc. the APEX development team implemented this 23 functionality as well. Therefore in APEX 23.3 you can find a very intuitive implementation of Ubiquitous Database Search.
When talking with Florian Grasshoff from the APEX development team we decided to write a posting in a joint effort 🙂
First let’s illustrate which steps are required when using SQL linemode tools.
Note: The table data comes from the Movie Database.
1. Create an index with index _name TMDB_SEARCH.
execute DBMS_SEARCH.CREATE_INDEX(index_name => 'TMDB_SEARCH');
2. Add data sources tables MOVIES and SHOWS.
execute DBMS_SEARCH.ADD_SOURCE(index_name =>'TMDB_SEARCH', source_name => 'MOVIES'); execute DBMS_SEARCH.ADD_SOURCE(index_name =>'TMDB_SEARCH', source_name => 'SHOWS');
3. Review the document.
select DBMS_SEARCH.GET_DOCUMENT(INDEX_NAME=>'TMDB_SEARCH', DOCUMENT_METADATA=>METADATA) as output from TMDB_SEARCH;
4. Search with queries.
SQL> select metadata as output from TMDB_SEARCH where CONTAINS(data,'fuzzy(gumb)') > 0; SQL> select title from movies where id in ( select json_value(metadata, '$.KEY.ID') from tmdb_search where contains(data, 'fuzzy(gumb)') > 0 and owner = 'OH' and source = 'MOVIES' );
In the posting New full-text search in 23ai: Ubiquitous Database Search you can find a detailed description about the required steps.
Now let’s demonstrate how easy it is to do the same thing with APEX release 23.2. Kudos to Florian who put the following tutorial together. 🙂
In APEX, no knowledge of the DBMS_SEARCH package is required; existing ubiquitous search indexes and sources in the database can simply be selected in the UI and used for searches. It is also not necessary to write SQL statements using the DBMS_SEARCH.GET_DOCUMENT function, for example, as the SQLs are generated by APEX.
With the APEX Application Search feature it is declaratively possible to query different data sources in one search, no matter if the data source is a table, a view, a remote database or a REST API.
In APEX 23.2 we are now supporting ubiquitous search indexes and their sources.
1) Login to your workspace and create an app
2) Under “Shared Components” -> “Navigation and Search” -> Choose “Search Configurations”
This shared component defines the data source to be searched and the way results should be displayed.

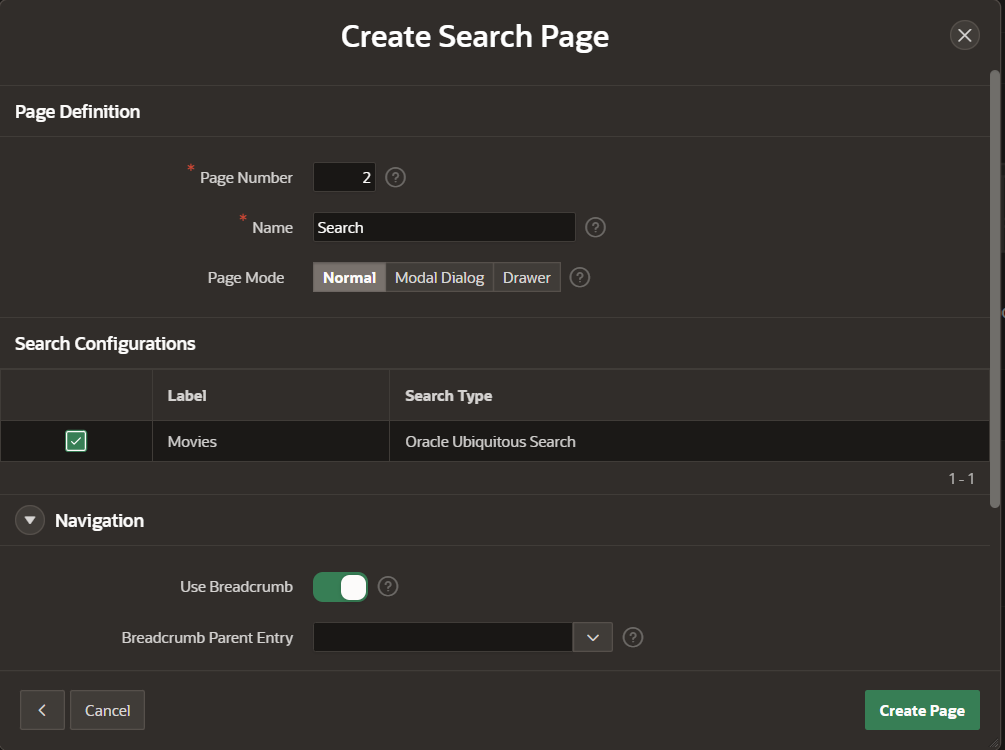
3) Create a new Search Configuration, give it a name, e.g. “Movies” and select the new search type “Oracle Ubiquitous Search”
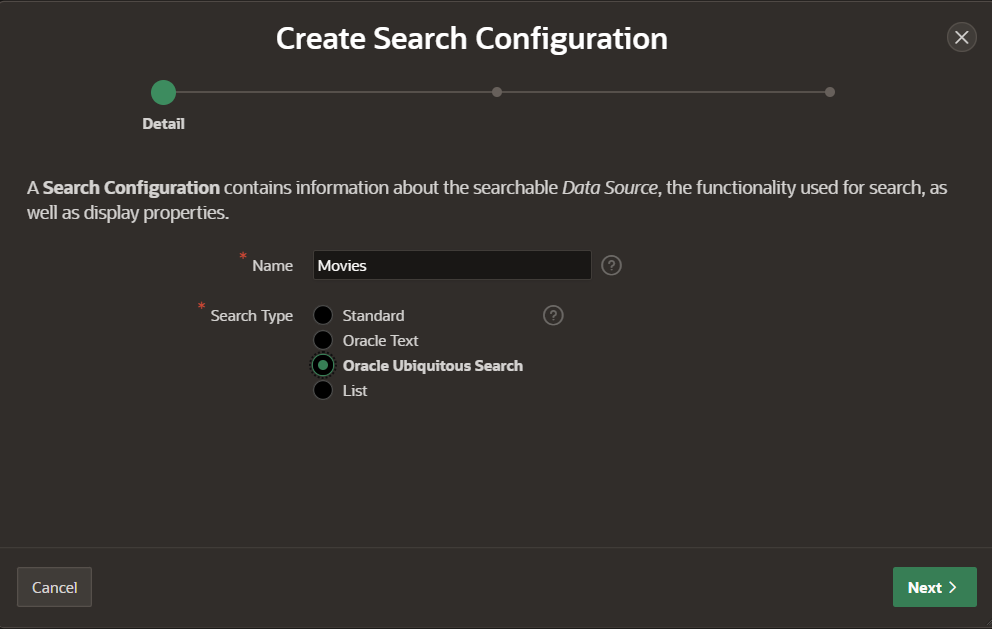
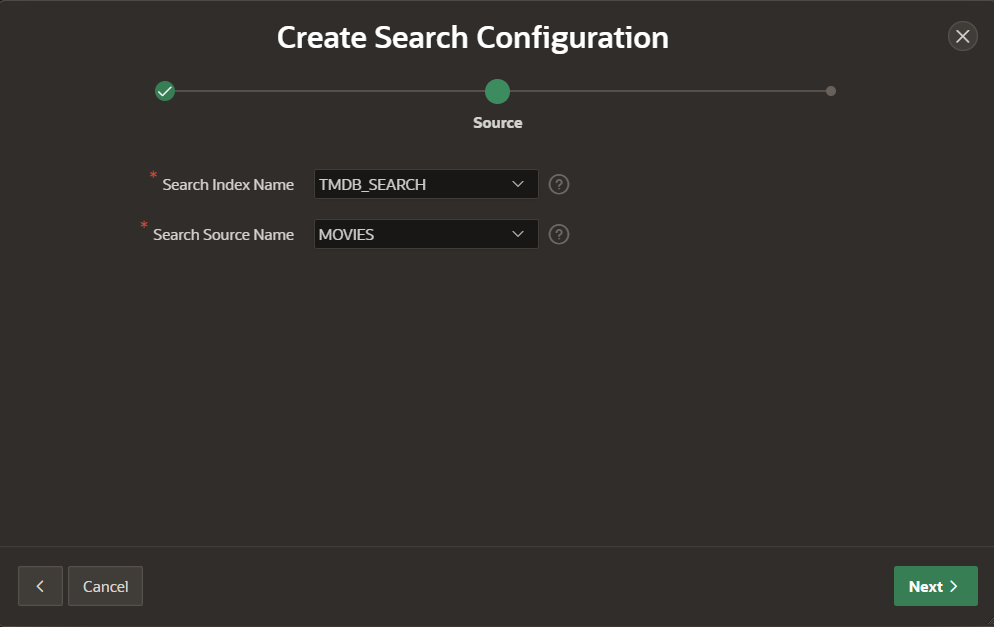
4) Select the ubiquitous search index and source
5) Map a column for the title and description of the search result UI
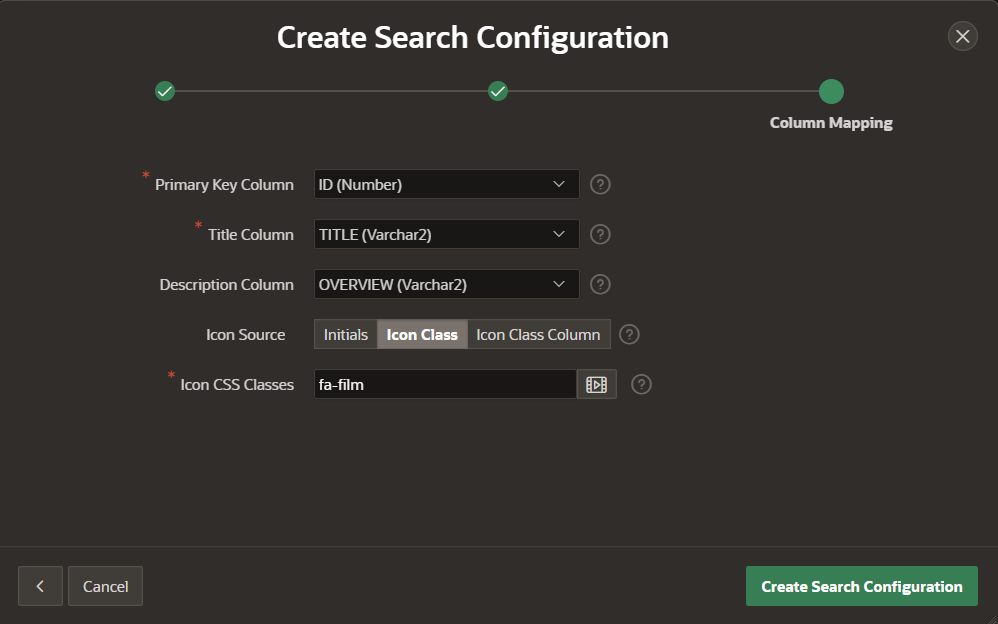
At this point we have created a basic search configuration and the easiest way to use it for searches is to use a pre-built search page.
6) Create a new page and use the “Search Page” component
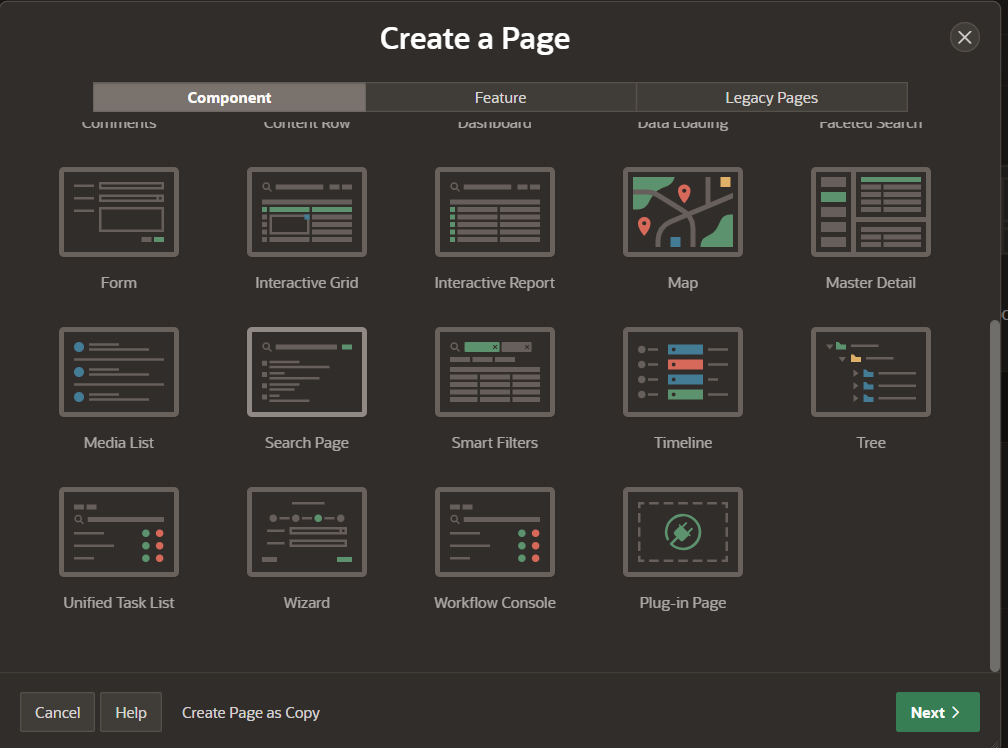
7) Choose any name and select the search configurations to be used for the search
8) Run the page and perform a search
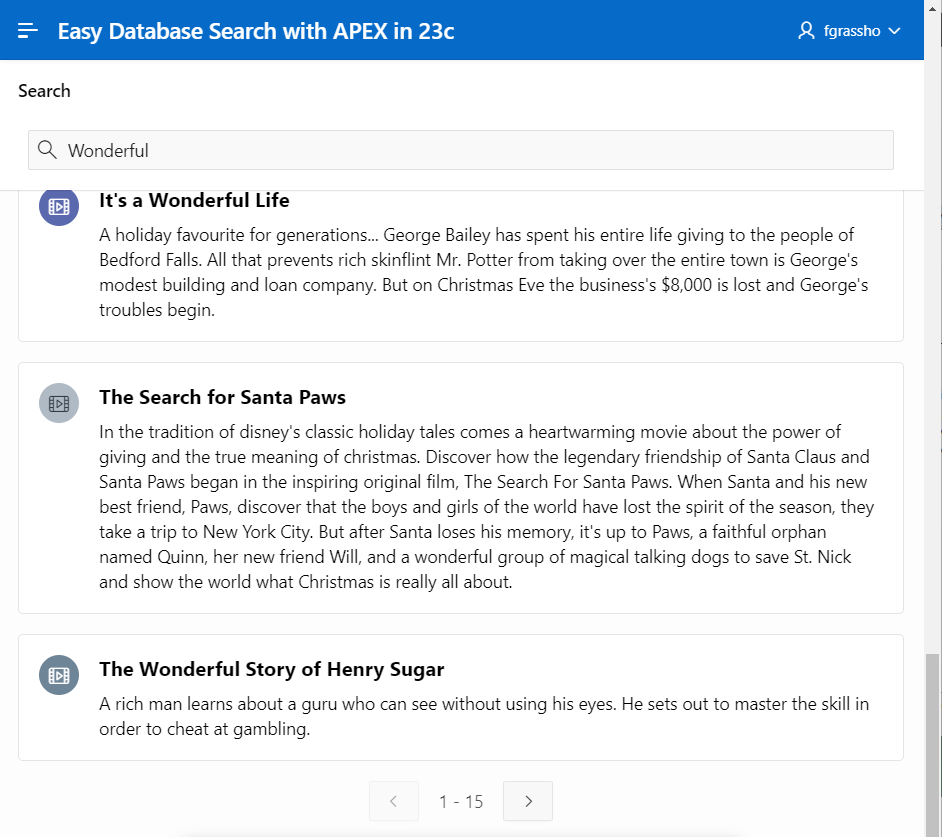
With just a few clicks, we were now able to use Ubiquitous Database Search in APEX. We defined a search configuration, built a page for executing the search in our application and already searched in our data.
Everything we saw before in the SQL examples is now automatically executed in the background.
We can of course make further settings in the search configuration to customize the search result, for example by displaying additional data from the data source and an image instead of an icon.
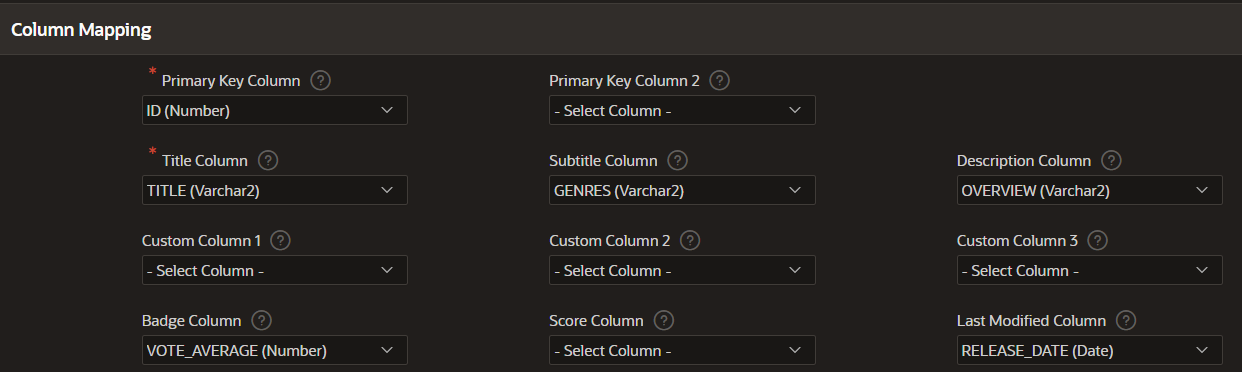
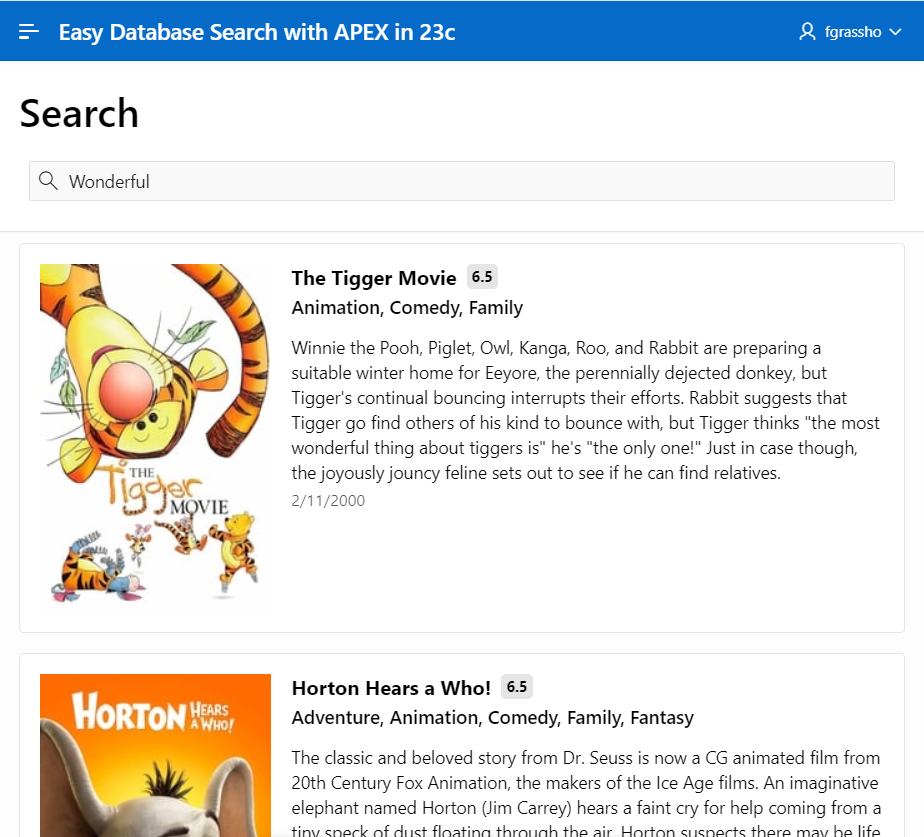
In this example, we are mapping our columns “VOTE_AVERAGE”, “GENRES” and “RELEASE_DATE” from the movies search source to display values for the badge, subtitle and last modified columns of the search result. We also use the URL from the “POSTER_URL” column to load the corresponding image for each movie.
![]()
Now we run the same search in our application and our changes are visualized.
For each film, the corresponding image is loaded and we can now see the genres, ratings and release date in addition to the title and description.
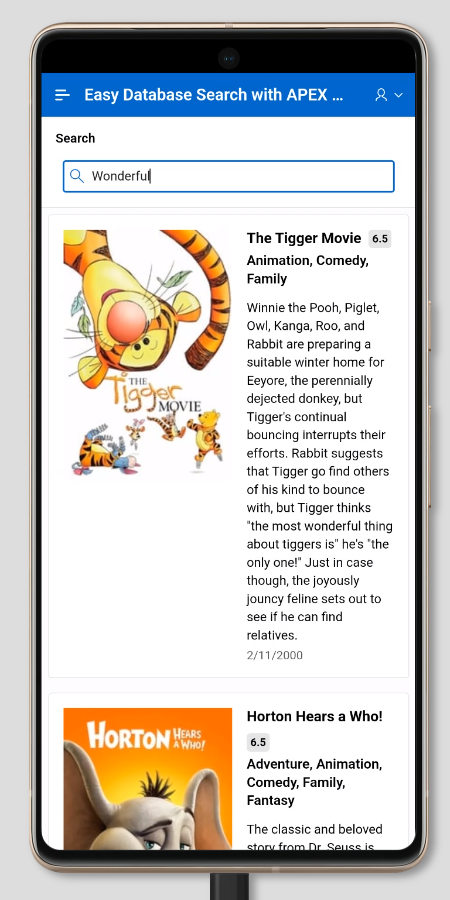
Our application is responsive by design, here in the example with a Pixel 7 Pro.
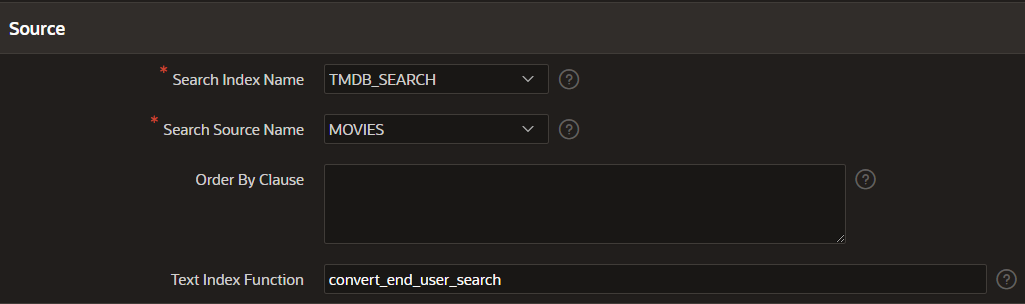
At the moment, the complete search term is used for the search by applying a contains expression. In the search configuration, you can specify your own “Text Index Function” that transforms the search term and applies a fuzzy search, for example.
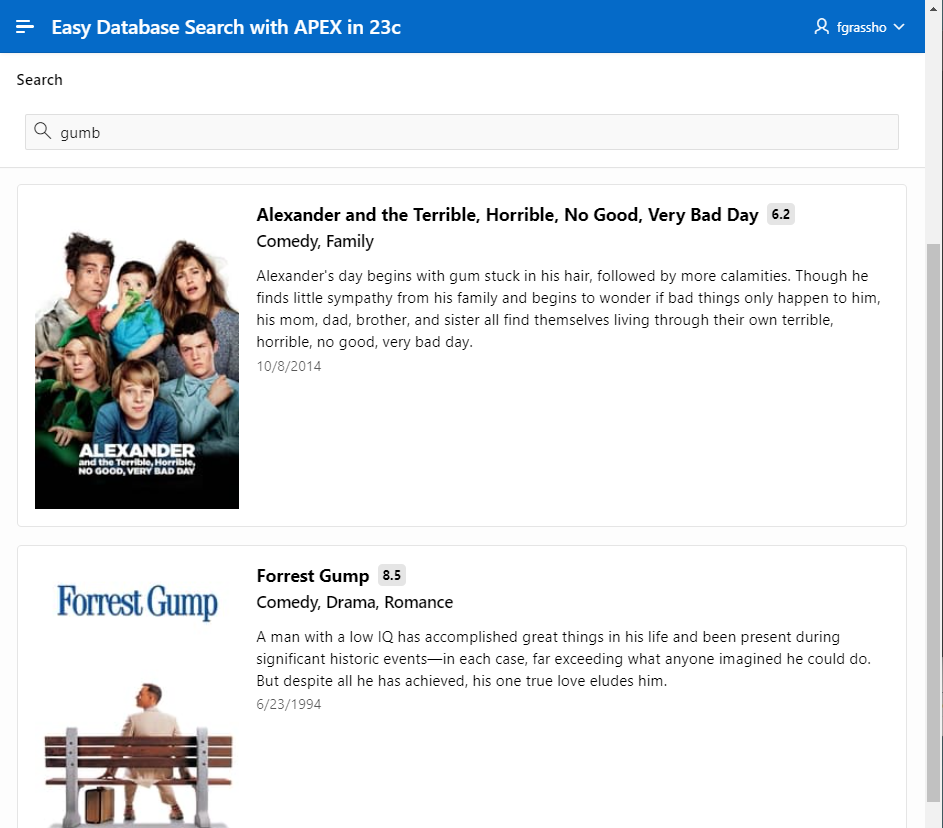
We take our previous example and are looking for the movie “Forrest Gump”, but the search term “Gumb” is used, and we still get our desired result thanks to the fuzzy search.
APEX also provides an API to use the search configurations in SQL or PL/SQL.
With the API, it is therefore possible to use the search configurations in all APEX components that support SQL statements as a data source. It is also possible to build your own search applications or to access the search configurations directly in the database with SQL or PL/SQL code.
select * from table ( apex_search.search(apex_t_varchar2('movies'), 'wonderful') );
With Oracle database version 23, we get a fantastic feature called Ubiquitous Database Search, which makes searching our data much easier. In combination with APEX, we can visualize our search results beautifully without writing a single line of code. Best, you try it out yourself!
Further reading

