Preemptible instances offer up to 50% cost savings compared to on-demand compute but can be reclaimed at any time.
These instances can be an economic offering for non-production, stateless, fault-tolerant, and check pointable workloads such as CI/CD jobs, batch jobs, and stateless microservices.
Let’s examine the design principles that enable reliability at scale, including capacity flexibility, graceful shutdowns, and resilient orchestration.
Designing for Capacity Flexibility
OCI regions consist of multiple ADs (Availability Domains). Each is an independent data center with its own compute capacity, further segmented by capacity (i.e. E5, E6, etc).
Deploying preemptible instances with strict constraints on ADs and shapes can significantly reduce available capacity. Therefore, design deployments to be flexible across shapes and ADs.
Here are some example strategies:
Distributing Across ADs
If you request E6 preemptible capacity in AD-1 and capacity is unavailable, deploying the same shape in AD-2 or AD-3 may succeed. Preemptible capacity is allocated independently per AD, so spreading workloads across ADs improves availability.
Mixing Compute Shapes
When E6 isn’t available, switching to an alternative shape, such as E5, can often secure capacity with performance tradeoffs. Different shapes draw from separate capacity pools, offering more flexibility.
Combining Strategies
Combination of AD flexibility and shape substitution typically provides the fastest path to successful deployment. For example, if AD-1 lacks E6 capacity, you would have the option to try E6 in alternative alternative ADs or E5s in any AD.
In addition to architectural considerations, please consult with your OCI account team for proactive capacity planning discussions.
Graceful Shutdown: Handling Preemption Gracefully
Preemptible instances can be terminated at any time due to capacity needs or scheduled maintenance. It is critical to understand how to capture termination events, cleaning up state, and resuming later.
Monitoring Instance Termination
OCI provides multiple ways to detect impending instance termination:
Instance metadata service (IMDS): Query for preemption notices from within your instance by polling one of these endpoints:
A JSON payload with key ‘instancePreemptionAction’ will be returned at least two minutes before termination begins. Example:
{
"agentConfig": {
},
"availabilityDomain": "DEGj:US-ASHBURN-AD-1",
"canonicalRegionName": "us-ashburn-1",
"compartmentId": "ocid1.compartment.oc1..aaa",
"definedTags": {
"Oracle-Tags": {
"CreatedBy": "default/admin@email.com",
"CreatedOn": "2026-02-02T22:03:31.538Z"
},
},
"displayName": "instance_name",
"faultDomain": "FAULT-DOMAIN-3",
"hostname": "hostname",
"id": "ocid1.instance.oc1.iad.anu…",
"image": "ocid1.image.oc1.iad.aaa…",
"instancePreemptionAction": {
"preemptionAction": "terminate"
},
"metadata": {
"ssh_authorized_keys": "<your_ssh_key>"
},
"ociAdName": "iad-ad-3",
"region": "iad",
"regionInfo": {
},
"shape": "VM.Standard.E5.Flex",
"shapeConfig": {
"maxVnicAttachments": 2,
"memoryInGBs": 12.0,
"networkingBandwidthInGbps": 1.0,
"ocpus": 1.0
},
"state": "Running",
"tenantId": "ocid1.tenancy.oc1.. ",
"timeCreated": 1770069812085
}
This serves the use case for in-instance scripts, such as flushing logs and managing checkpoints.
OCI Events: Use OCI Events to track instance lifecycle via email notifications or function invocation. Email notifications will be delivered at least 2 minutes before termination.
- For Example: https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Events/Reference/eventsproducers.htm#computeevents__compute_instance
Paired with Functions, OCI events can be used as a component for orchestrating preemptible nodes. This will be explored later.
Ways to Manage Graceful Shutdowns
Design your systems to manage termination proactively. Common patterns include frequent checkpointing and central event management.
Frequent checkpointing: Regularly save intermediate state or progress to persistent storage (i.e. file storage).
The following example demonstrates how an in-instance daemon can detect preemption events and persist timestamps to File Storage:
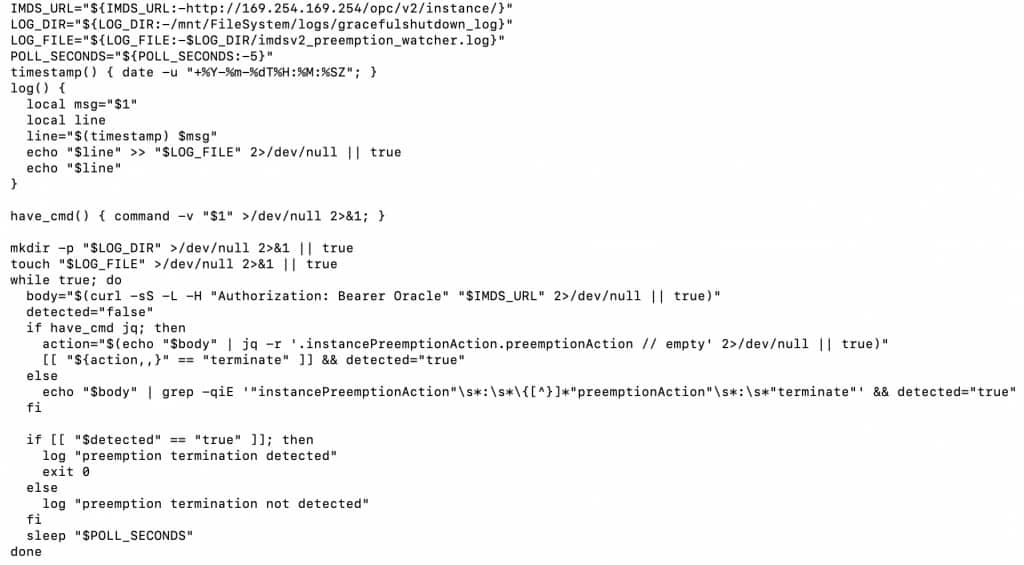
Running the script above, in a preemptive instance from a custom image, provided the following output:
2026-02-06T07:50:34Z preemption termination not detected
2026-02-06T07:50:39Z preemption termination detected
….
2026-02-06T07:55:01Z preemption termination detected
*log ends hereNote that daemon was configured to always restart. Therefore, the script would run until instance termination. With this method, logs describe instance termination occurred five minutes after notification via IMDS, providing a window to stop accepting new requests, complete in-flight work, flush logs, and finalize checkpoints.
Central Event Management: Use either or both methods of capturing termination to signal drain/reschedule workloads. The method varies amongst orchestration systems. For example, OKE supports this natively: https://docs.oracle.com/en us/iaas/Content/ContEng/Tasks/contengusingpreemptiblecapacity.htm
You may also rely on pairing OCI events with functions to capture terminated nodes and respond with deploying new nodes. Let’s explore that below.
Designing Orchestration
Resilient orchestration requires an automated pipeline to deploy new preemptible instances after termination.
Other than OKE, OCI Functions can act as a custom orchestrator that position these instances as an elastic infrastructure rather than fragile resources:
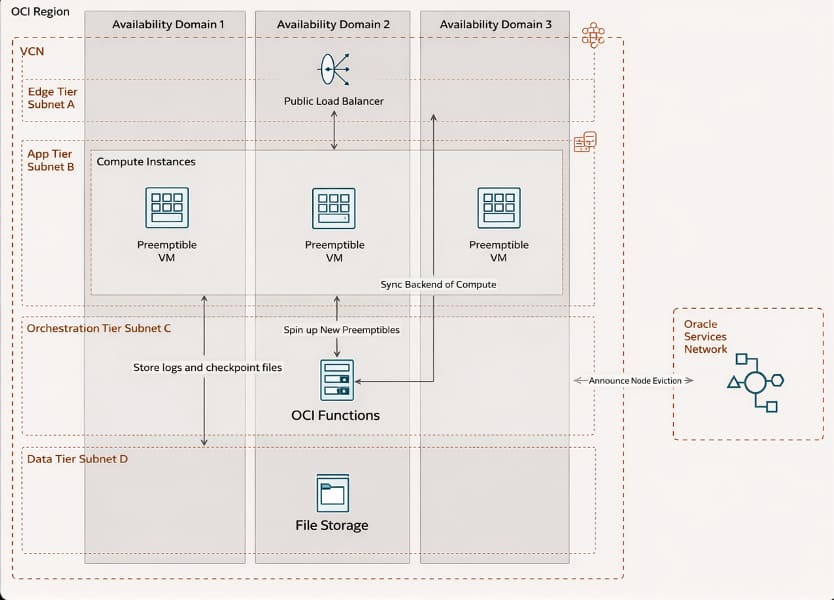
Networking: Load Balancer defines three instances in a backend set to handle failover and routing between ADs.
Compute: Distributed preemptible instances across multiple ADs with graceful shutdown logic.
To support graceful shutdowns across preemptible nodes, implement a daemon that polls IMDS and add filesystem in fstab.
For scalability, consider creating a custom image with the daemon and fstab configured.
Event Service: Detects and announces instance termination / deletion to functions.
Functions: Acts as a central orchestrator that calls OCI SDK to launch replacement instances, adding to the existing backend set while ensuring backend set is healthy
For example, develop a resilient python function that combines the strategy of checking every AD and compute shape (i.e. E3, E4, and E5) for available capacity:

Example above is designed for a maximum of 3 retries of a shape in SHAPE_OPTIONS (in this case E3, E4 and E5) in each AD. If all capacity options are exhausted, Functions’ scheduler feature can periodically reconcile desired vs. actual instance counts and relaunch missing nodes.
In addition to managing compute, consider implementing a logic to maintain a healthy backend set at the load balancer (i.e. remove IPs associated to terminated instances): https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/api/#/en/loadbalancer/20170115/Backend/DeleteBackend
File Storage: A persistent storage to store checkpoints and logs.
Logging (Optional): Insightful to debug functions invocations.
Wrapping Up
Designing for fault tolerance, graceful shutdown, and resilient deployment transforms how you use OCI. You’ll not only save costs by leveraging preemptible instances, but you’ll also gain operational resilience and scalability at cloud scale.
Engage your OCI account team to explore how preemptible capacity can support your workloads and business objectives.
Learn More
List of Supported shapes: https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Compute/Concepts/preemptible.htm
