When you first start using a new Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) tenancy, most organisations spend some time on architecture, design, and security before using it. A lot of organisations follow Oracle’s recommendations and use a Landing Zone as their starting point. However, after workloads are deployed on OCI, it is important to frequently validate the security posture of that OCI tenancy.
For validation of a security posture, ideally you need a good reference framework that tells you which configuration guidelines to follow in order to keep your tenancy secure. The Center for Internet Security (CIS) is an independent organisation that produces CIS Benchmarks that help protect against cyber threats. As part of these benchmarks, they publish the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Foundations Benchmark, Oracle Linux Benchmarks, Oracle Database Benchmarks, and many others which are all available for free.



A very useful exercise to do regularly is to compare the state of your security posture against their configuration guidelines. These benchmarks contain a lot of detailed recommendations, including how to check it and more importantly, how to adjust your configurations to become compliant.
How can this be done easily?
There are different tools available to help check against the CIS configuration guidelines, see this limited selection:
- Oracle provides Data Safe and the DBSAT tool for Oracle Databases, which provides prioritized recommendations on how to mitigate identified security risks.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers Cloud Guard, which can be used to detect threats, misconfigurations and monitor insecure activities. It also checks your tenancy against a selection of the CIS Benchmark recommendations for OCI (and for Oracle Linux when using Vulnerability Scanning Service and/or Instance Security). Cloud Guard also has the advantage of automatic remediation of the issues with a responder recipe, depending on which problems are detected.
- The OCI Security Health Check, for which Oracle has worked together with CIS, produces an automated way of quickly validating an OCI tenancy against compliance with the CIS OCI Foundations Benchmark.
As there are already several Oracle blogs about Data Safe (e.g. Oracle Data Safe Update Delivers a New Look and Enhanced Capabilities), DBSAT (e.g., Announcing DBSAT 3.1, DBSAT with Oracle Enterprise Manager) and Cloud Guard (e.g., Guard your Infrastructure with Oracle Cloud Guard, Discovering and fixing weak cloud security posture with Oracle Cloud Guard), we will focus the remainder of this article on the OCI Security Health Check.
OCI Security Health Check
The OCI Security Health Check is a freely available python script that can be downloaded and run, either locally or from within OCI Cloud Shell. It works in all Public Cloud Regions and Dedicated Regions, just ensure your Cloud Shell permissions allow Internet access. Within a few minutes it produces a report that has both summary and detailed results.
The most important difference compared to Cloud Guard, is that this script does a complete and exact comparison against all the recommendations from the CIS OCI Foundations Benchmark, making it easy to use as evidence for your compliance processes. Cloud Guard does a partial check against the CIS OCI Foundations Benchmark recommendations and currently only covers the Default Identity Domain for the IAM related checks. However, it is strongly recommended to have Cloud Guard enabled in your tenancy (this is also recommended by CIS) as it does check for many other security threats that are not part of the CIS OCI Foundations Benchmark.
The OCI Security Health Check script only reads the OCI control plane APIs to find the results. There is no impact on any resources in your tenancy as it does not connect to compute instances, databases, etc. If you want to run the OCI Security Health Check, you can follow the instructions, as documented on its GitHub page and summarised below:
- Login to the OCI Console and start Cloud Shell.
- Download the zip from the GitHub into Cloud Shell and optionally validate its checksum.
- Unzip the script and execute it.
- After a few minutes, a new zip file is created that has the report.
- Download the report zip file from Cloud Shell to your desktop and extract it.
Take action on the results
The report zip file contains a folder with your tenancy name and timestamp, and in this folder are several files. The recommended starting point is by opening the Compliance Report, which is named:
<tenancy name>_<timestamp>_standard_cis_html_summary_report.html
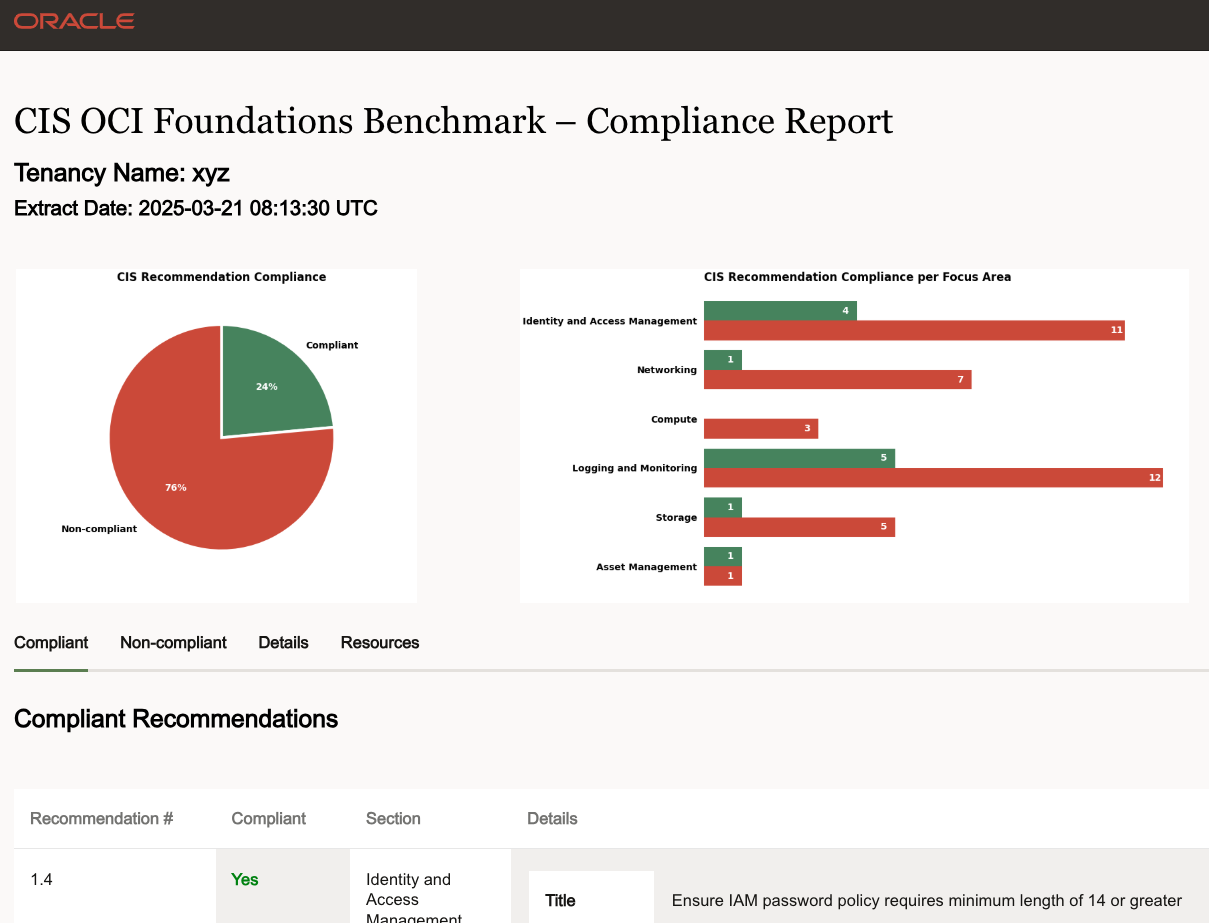
This Compliance Report is very usefull to get an overview of the state of your tenancy, browse the compliant and non-compliant findings, and read details of the recommendations.
Another file that is in the report zip folder is the consolidated findings excel document, named:
<tenancy name>_<timestamp>_standard_Consolidated_Report.xlsx
This excel file contains a structured list of all findings, and for all non-compliant configurations it has sheets with the details of the relevant OCI resources e.g., the OCID and name of the users, policies, instances, databases, etc. This detailed information of all relevant OCI resources is very helpful when improving your security posture and can be used together with the remediation steps as described in the OCI CIS Foundation Benchmark document. See the following example:

Finally, after remediating some or all the non-compliant findings, the script can always be re-run to verify the remediation actions have been applied correctly.
We recommend running this OCI Security Health Check regularly, e.g., once every month or always after applying new OCI configurations in your release cycle. And don’t forget to check frequently for updates on the GitHub page, as the script is actively maintained and follows new releases of the OCI CIS Foundation Benchmark.
For more information on the concepts in this post, see the following resources:
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Foundations Benchmark
- OCI Security Health Check
- Video: Assess your OCI Security Posture Against CIS Benchmarks for OCI
- Video: OCI Health Checks – Self Service
- CIS OCI Landing Zone Quick Start Template

