Transitioning a candidate from an external applicant to a full-time employee should be seamless, but what happens when their temporary onboarding account creates unexpected risks? Without proper identity boundaries, pending workers might inadvertently access resources meant only for employees, exposing organizations to compliance challenges and leaving them open to threats.
In Oracle Fusion Cloud Applications, managing identities during these transitions is critical. By separating pending worker identities from employee accounts, organizations can establish a secure framework that protects sensitive resources, simplifies onboarding workflows, and maintains clear role distinctions. This approach is especially important for organizations relying on other external identity services, such as Microsoft Entra ID, a dedicated identity domain helps maintain controlled access during onboarding.
The Challenge: A Single Identity Store is Not Enough
In Oracle Recruiting Cloud, external candidates follow a structured process: They apply, accept offers, and transition into the “pending workers” category. These accounts are provisioned with roles, such as the Oracle-provided ORA_PER_PENDING_WORKER_ABSTRACT or a custom role like GSE_Onboarding_Job, to facilitate onboarding tasks. On the hire date, these pending workers automatically convert to employees, and their onboarding roles are removed.
Despite the structured process, using a shared identity store for all users, including pending workers, employees, and even suppliers, introduces risks. Without clear separation, external candidates can gain unintended access to internal resources, undermining security, and compliance efforts.
Creating Boundaries with External Identity Domains
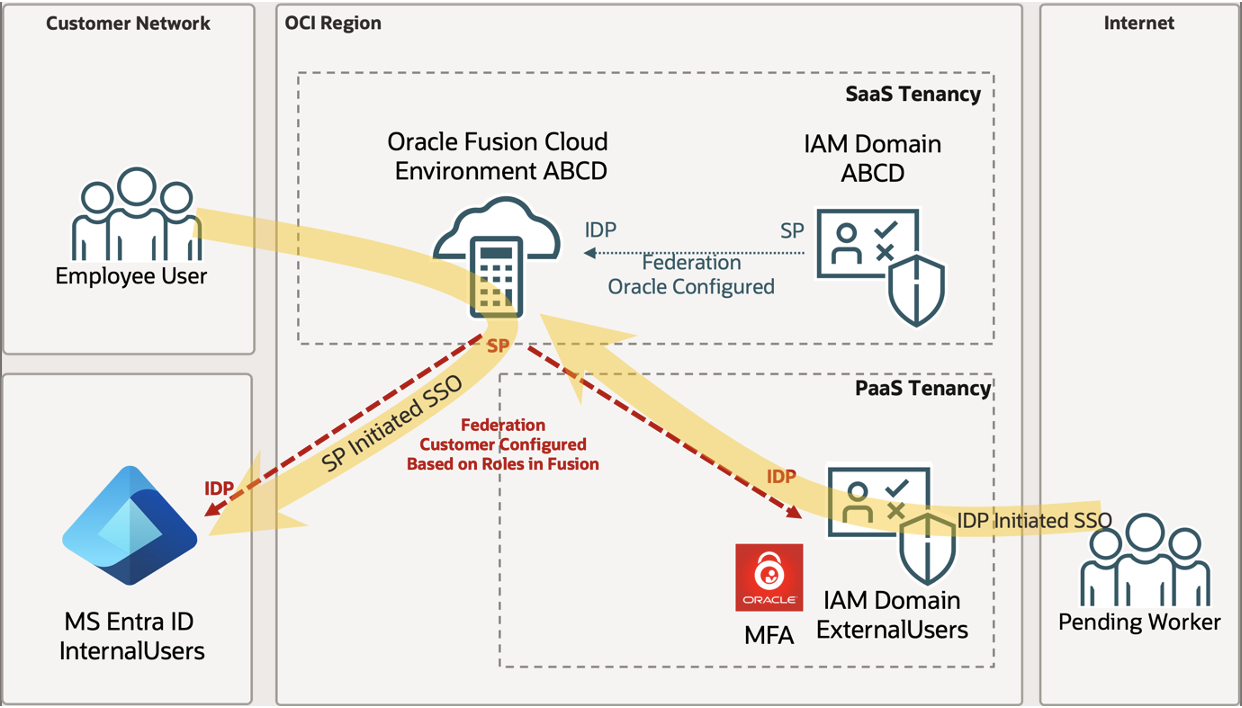
A dedicated external identity domain within Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Identity and Access Management (IAM) isolates onboarding accounts, prevents unauthorized access to internal resources, and helps streamline the onboarding process.
Candidates are directed to this external domain through a special link with identity provider (IdP)-initiated single-sign-on (SSO) , which is automatically sent to them. Only accounts assigned an onboarding role, such as GSE_Onboarding_Job, synchronize to this external domain, helping pending workers remain isolated.
As pending workers transition to employee status, Fusion’s automatic provisioning rules revoke their onboarding roles. During the next synchronization cycle, the external domain identifies this change and automatically deletes the temporary account, preventing overlapping access and maintaining strict role-based permissions.
Facilitating Identity Synchronization Across Systems
A seamless onboarding process relies on identity separation and keeping identity attributes synchronized across external directories and Oracle Fusion Cloud Applications in the following areas:
- Username and email updates: Often, corporate directories, such as Microsoft Entra ID, supply work emails and network IDs. To maintain consistency across systems, synchronize these attributes with Oracle HCM. Using the employee’s corporate email as the username simplifies SSO and streamlines password resets, helping achieve a smoother user experience.
- Integration with Microsoft Entra ID: When discrepancies arise between directories and Oracle HCM, such as email or phone updates, Microsoft Entra ID can push these changes into Oracle HCM using file-based integrations. This synchronization helps keep all systems aligned. For more details about the implementation, see Part 1 : Oracle Fusion Cloud Applications SSO with Microsoft Entra ID.
By keeping identities separate and synchronized, organizations improve security, prevent access issue, and simplify employee lifecycles.
Architecting Identity Separation
A key component of this solution is the integration of an external identity domain within OCI IAM, allowing pending worker accounts to operate in a separate environment. In many customer environments, Microsoft Entra ID serves as the central Identity store. Organizations often implement best practices to restrict the creation of nonemployee accounts within Entra ID, further reinforcing security policies.
The synchronization process for the external identity domain relies on the custom GSE_Onboarding_Job role, specifically designed for pending workers. This role helps ensure that only relevant accounts are included in the external domain, for strict alignment with organizational policies. For detailed guidance on setting up external identity domains, see Securing Oracle Fusion Bill Management with IAM Domains.
The following configuration highlights how the GSE_Onboarding_Job role is central to this solution and how it supports secure synchronization to the external domain:
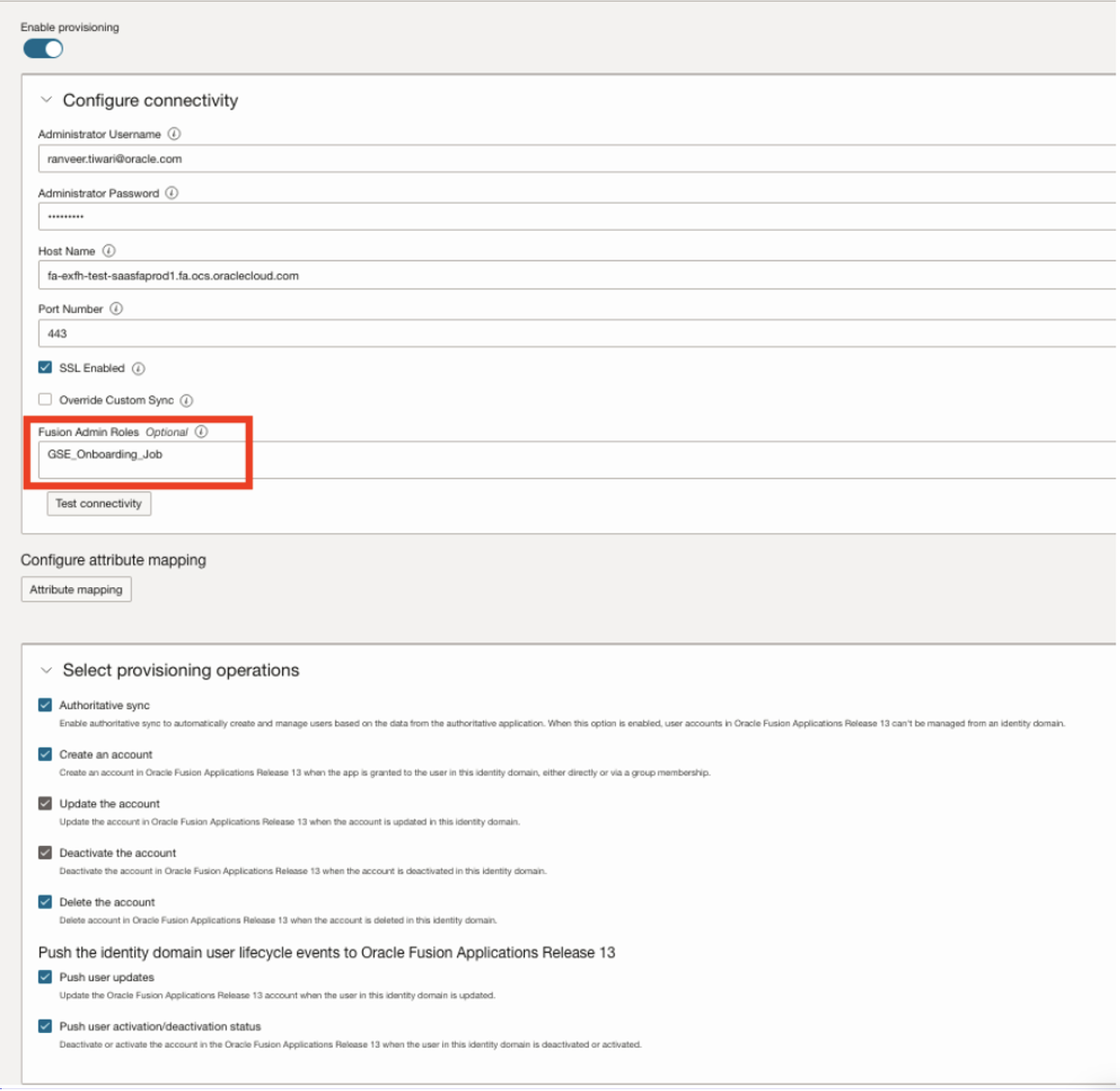
This role is revoked through the autoprovisioning rule. When in place, synchronization to the external IAM domain no longer finds the GSE_Onboarding_Job role, leading to automatic user account deletion. For detailed steps, see How You Convert Pending Workers.
Conclusion
A separate identity domain for external candidates enhances identity management practices within Oracle Fusion. This strategy prevents pending workers from gaining unintended access to employee-level resources, while simplifying deprovisioning when they transition to employees.
The result is a more secure, compliant, and efficient workforce identity lifecycle. Importantly, this configuration is transparent to all users of Oracle Recruiting Cloud, requiring no extra administrative effort from recruiting managers or candidates.
For more information about the concepts in this blog post, see the following resources:


