Every day, thousands of pages of Oracle’s product documentation are published to Oracle Help Center.
Oracle content developers must be able to publish content to Oracle Help Center (docs.oracle.com) at any time of the day, any day of the week. Keeping the infrastructure up and running and well maintained 24×7 to support the building and publishing of content to Oracle Help Center is critical.
Our content build-and-publish pipeline enables content developers to securely push content from Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) to a content delivery network service.
For these reasons, Oracle Help Center is fully powered and supported by Oracle Cloud.
The processes and tools we use for publishing content to Oracle Help Center
Oracle’s product content development teams create, develop, and publish a variety of content including product documentation, API documentation, articles, tutorials, hands-on labs, Reference Architectures, Solution Playbooks, graphics, and videos.
Oracle content developers create, review, and publish content to Oracle Help Center using a comprehensive set of publishing tools, including:
- A content build-and-publish pipeline
- Authoring and content management tools
- Archiver
- Metadata and product hierarchy systems
- Accessibility and compliance checkers
- Translation systems
Oracle content developers can publish documents to Oracle Help Center any time after the document has been reviewed in the document’s stage environment. A document can be published to Oracle Help Center within a few minutes.
The evolution of Oracle Help Center publishing operations
About two years ago, the infrastructure for our publishing tools and ecosystem was hosted in the Oracle on-premises data centers. Since then, our publishing operations and ecosystem migrated completely and seamlessly into Oracle Cloud. The overall migration project was complex but the availability of Oracle Cloud’s migration tools and services helped simplify the process. Now that we’ve migrated to Oracle Cloud, all compute resources, databases, and services that we relied on in the on-premises environment have been replaced with OCI resources and services.
Using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure as the pipeline host
The following architecture diagram shows the OCI resources that are used for hosting the content build-and-publish pipeline and tools that enables content developers to push content to Oracle Help Center:
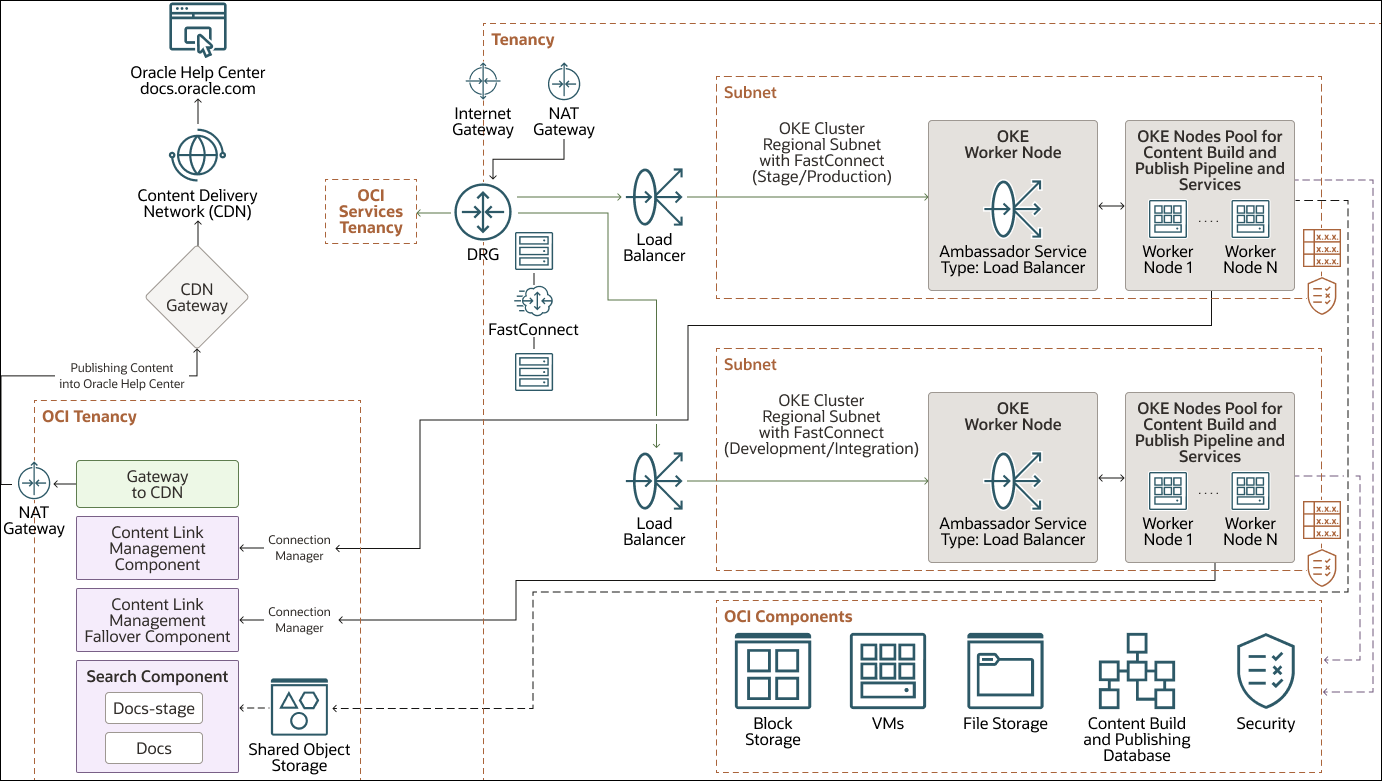
Making use of many Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources
We configured multiple OCI resources and services to set up the infrastructure for the publishing tools’ environments:
- OCI tenancy (compartments, network, load balancers and security policies)
- Compute resources
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Kubernetes (OKE)
- Databases
- Storage
- Monitoring
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancy, compartments, and security policies
We have a dedicated OCI tenancy set up and configured for hosting the publishing ecosystem. Compartments created within our tenancy are used to organize the multiple types of environments that are needed for developing and testing our publishing tools and reviewing content. We have set up distinct development, test, integration, and stage compartments for our application developers to access and do their work. We implement and test the publishing applications before we deploy them to the production environment.
A production compartment is set up to host the publishing tools when they’re ready for deployment and for content developers to use.
For security, we implement OCI security policies and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management entitlements to provide strong security enforcement and access restrictions to our tenancy. We adhere to the same OCI security controls and best security practices that we ask our OCI customers to follow.
Networking and load balancers
We make full use of the networking and load balancing services to handle the network traffic throughout our environments and availability domains. A private load balancer was created to direct incoming traffic in the stage and production environments and a separate private load balancer was configured to handle traffic for the development and integration test environments. A Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG), service gateway, and Network Address Translation (NAT) gateway have been set up to route traffic for the Kubernetes clusters in our tenancy.
Compute instances
The different types of compute shapes that are available in OCI give us great flexibility to provision and allocate compute resources that are needed for hosting our long running applications.
We set up clusters of Oracle Linux and Windows Server virtual machines (VMs) in our infrastructure; the VMs are configured with either Intel or AMD processors. We can quickly adjust the CPU and memory needs of each application with compute flexible shapes. This flexibility helps us to better plan for compute resource needs. It also helps with cost savings because we can easily reduce the size of a VM if we think that resources are over allocated.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Kubernetes
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Kubernetes (OKE) is one of the main cloud services that we use to support our publishing ecosystem. OKE is the main engine supporting our build-and-publish pipeline.
We use the OKE service to deploy our containerized applications to the OKE worker nodes cluster (Linux VMs). The compute resources used by our build-and-publish pipeline components are all provisioned using OKE. OKE is equally important for the support of our continuous integration effort to provide refreshes to our applications.
The following architecture diagram shows the OKE instances for our multiple publishing environments:
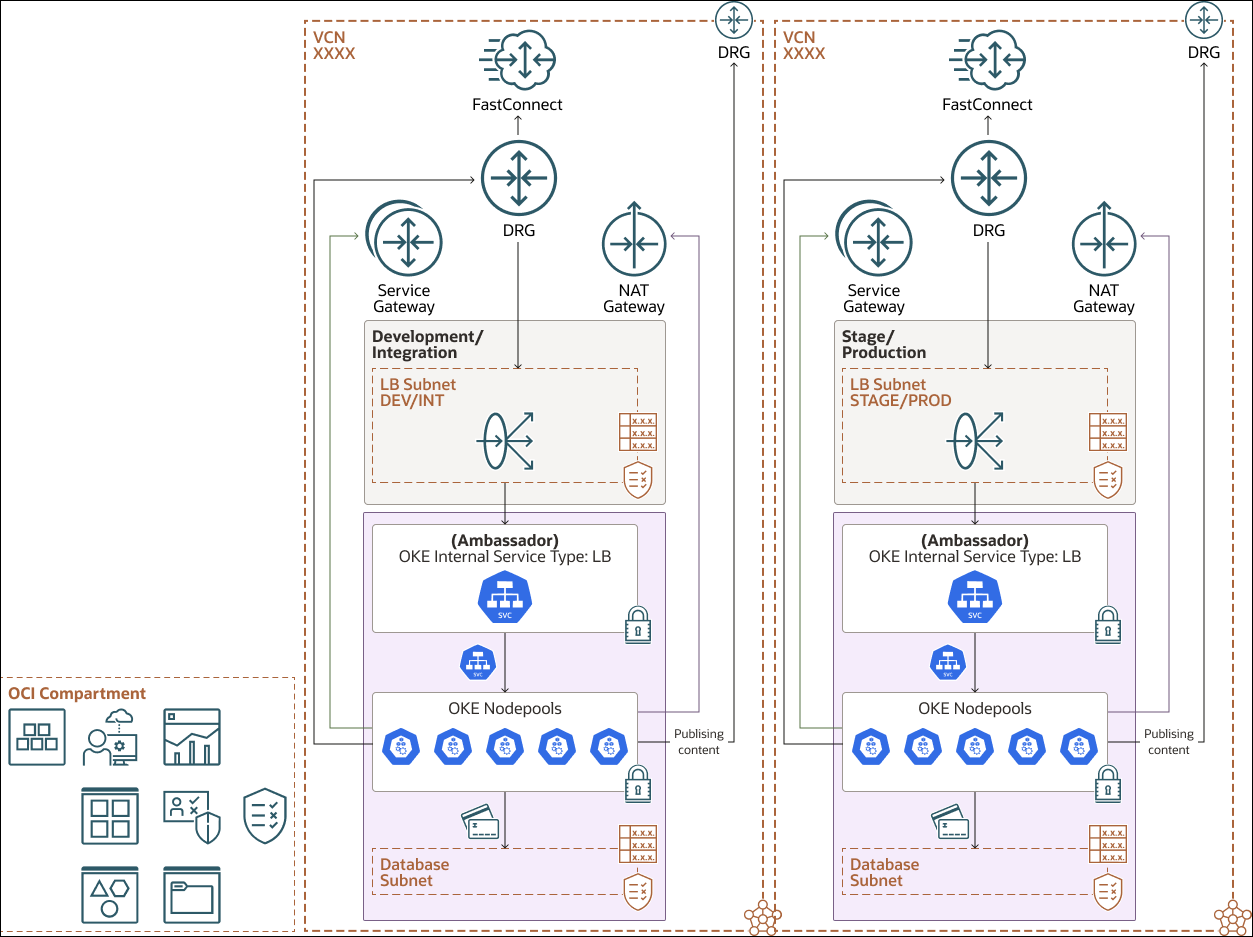
Storing content and data in Oracle databases
Documentation content and data are stored in Oracle databases in OCI. Our applications interface with Oracle Autonomous Database to store documentation data such as linking information and metadata.
The publishing application’s container database is set up with database compute resources and hosts a pluggable database for each application. The container database is configured as an OCI two-node database system. We use Real Applications Cluster (RAC), a cluster configuration where two instances of the same database are each on hosted different nodes (VMs) with nodes both accessing the same shared disks where the data is stored. The workload is distributed between the nodes.
Using storage services and data sharing
Our publishing applications use various types of storage services that are available in OCI. The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Block Volume service allows us to attach storage to VMs and to dynamically add storage as needed for our build applications.
We use network file storage (NFS) to enable data sharing between applications and object storage for bulk data storage such as search data snapshots.
Monitoring and provisioning our systems
OCI monitoring, Grafana, and Oracle Enterprise Manager are important tools that we use to help monitor the overall health of our systems and to manage all our compute resources in OCI. These tools provide usage and performance reports that enable us to tweak the performance of our applications and compute resources as needed. We dynamically configure and provision resources using the Oracle Cloud Console and Terraform scripts.
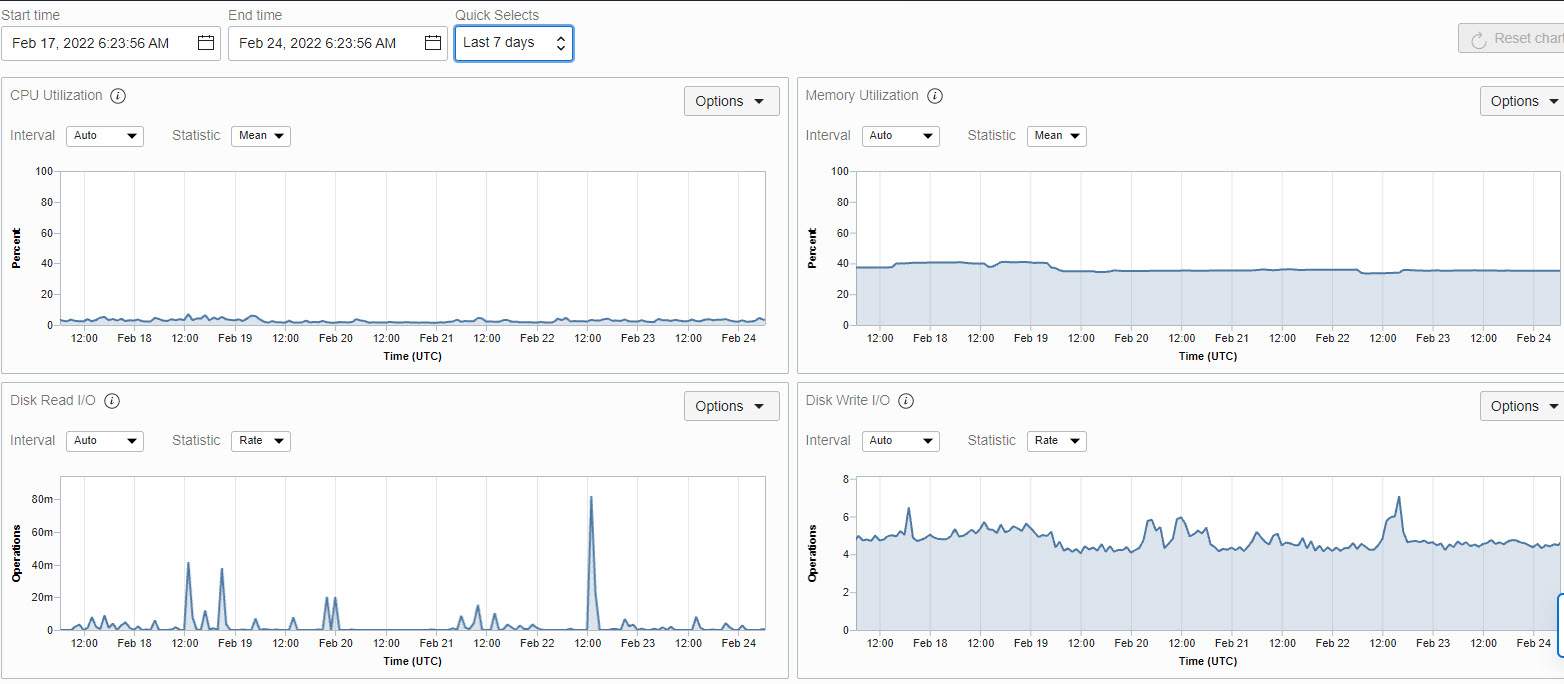
The following report shows weekly compute resource usage (CPU, memory, and disk) for one of our OCI OKE worker nodes. This report is available as part of the OCI Compute Instance metric reports:
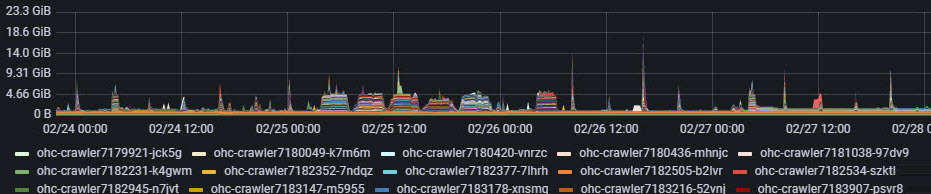
The following report shows Grafana memory usage for each of the Kubernetes node pods that are configured in our OKE instance:
Using the best tools and resources to bring customers the best experience
OCI provides the necessary monitoring and management tools to help our infrastructure team maintain our publishing environments. The OCI tools that are available also help us to do better capacity planning and future forecasting.
Using OCI tools and services, we plan and manage our publishing infrastructure in OCI with high efficiency and we can dynamically adjust OCI resources when necessary. We can easily innovate when new OCI services become available.
Overall, we reduced costs and achieved savings by moving our publishing operations from on-premises data centers into Oracle Cloud. And ultimately, this helps us create better and more innovative publishing solutions for our customers.
If you are looking for cloud services to host all types of application workloads, consider using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. For more information, see Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Documentation and Deploy Oracle Container Engine for Kubernetes.
