There are releases, and then there are major releases. Oracle. Big Data service just had a major release that brings several key features that our customers have been asking for. Big Data service version 3.0.7 (and later) with Oracle Distribution of Hadoop now offers the following new features.
Autoscaling
Big Data autoscaling enables you to create autoscaling rules to automatically scale a cluster horizontally or vertically using CPU utilization metric. With autoscaling, you automatically get more resources and performance when you need and automatically reduce your consumption to optimize for costs when you don’t need them. Autoscaling works with both standard and AMD Flex shapes.
With vertical autoscaling, you can change the shape of nodes in your cluster based on the rules specified.
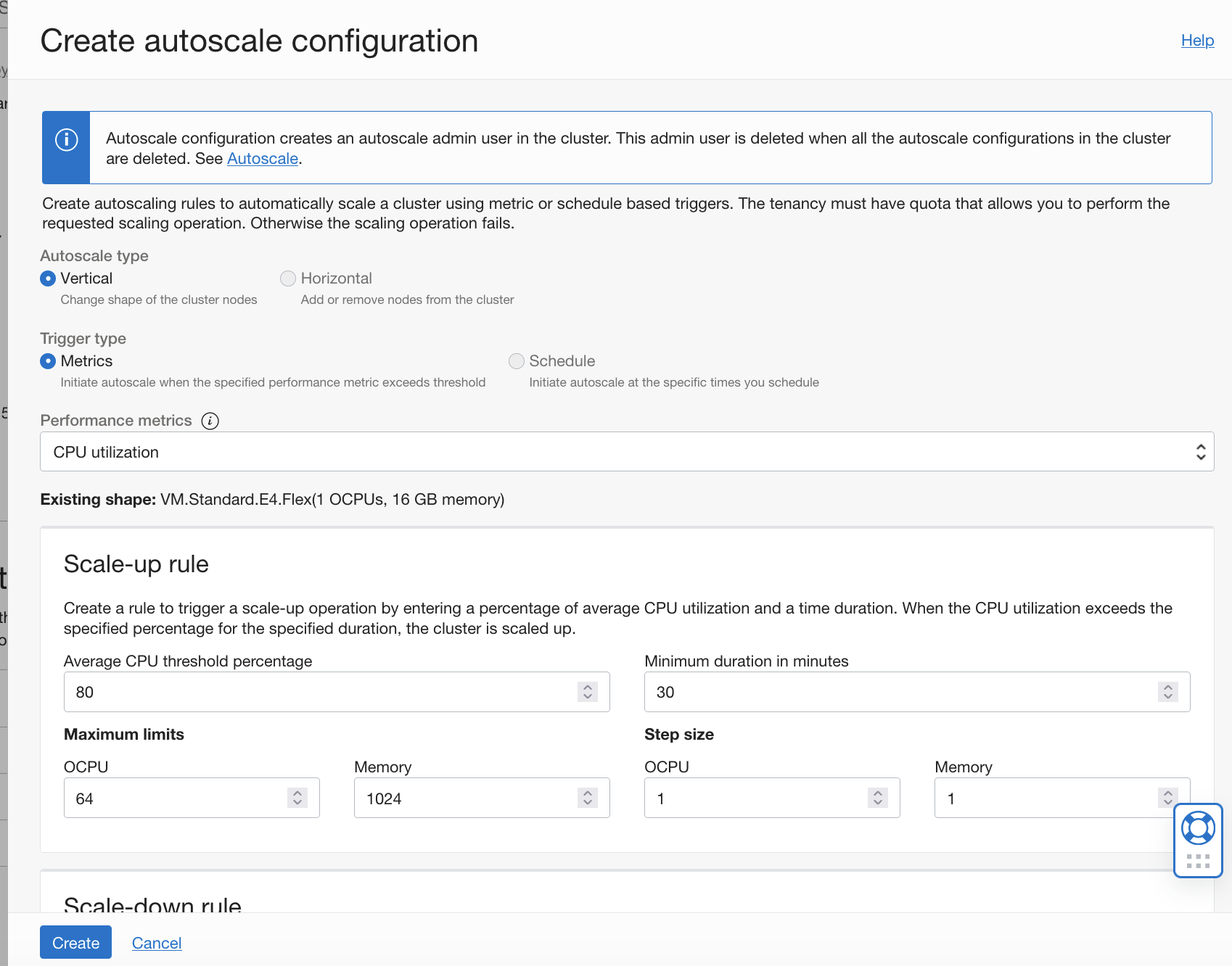
With horizontal autoscaling, when thresholds are met, the number worker nodes in the cluster are automatically added (scaled out) or removed (scaled in), depending on the configured rules.
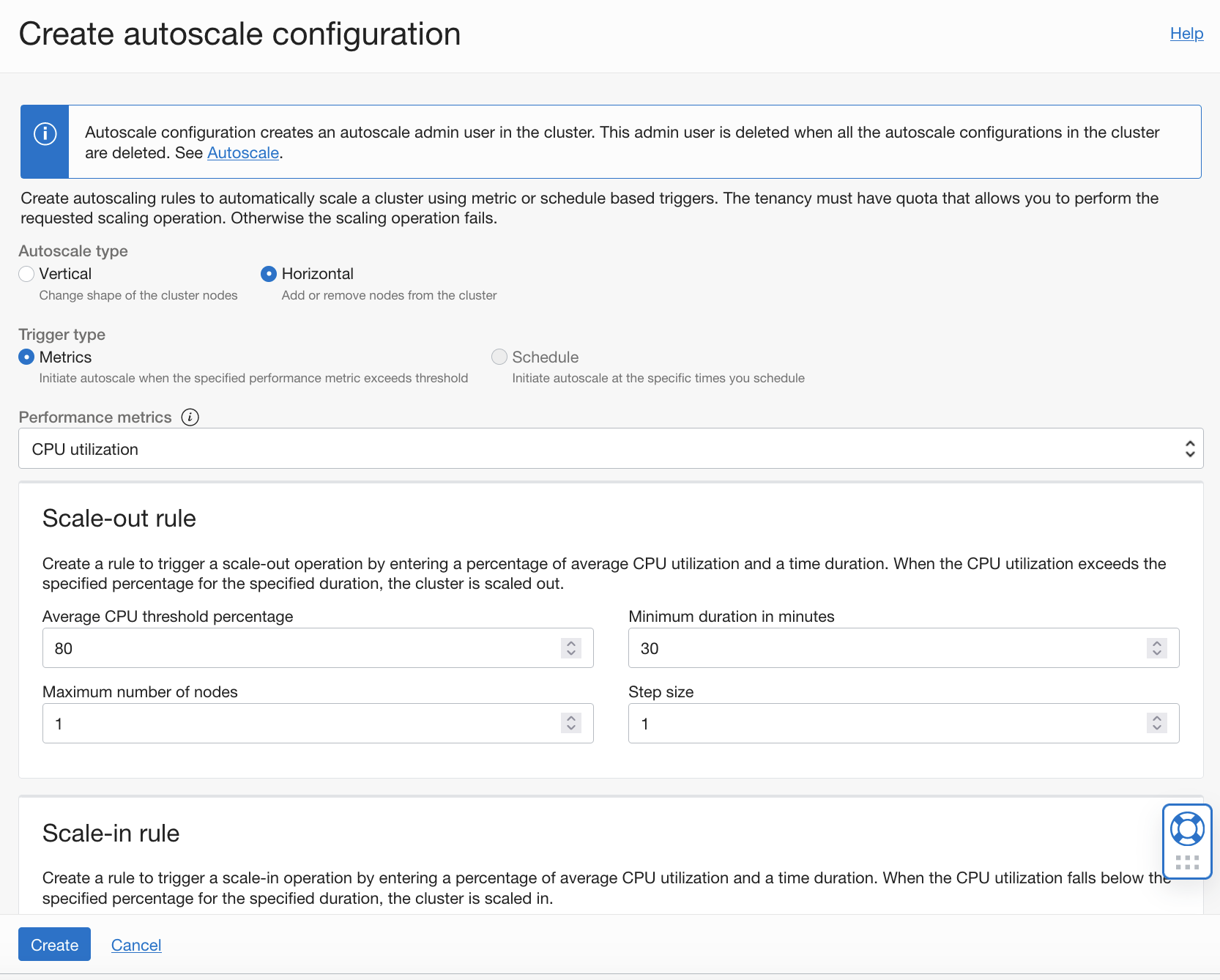
For more information, see Autoscaling a Cluster.
AMD Flex shapes
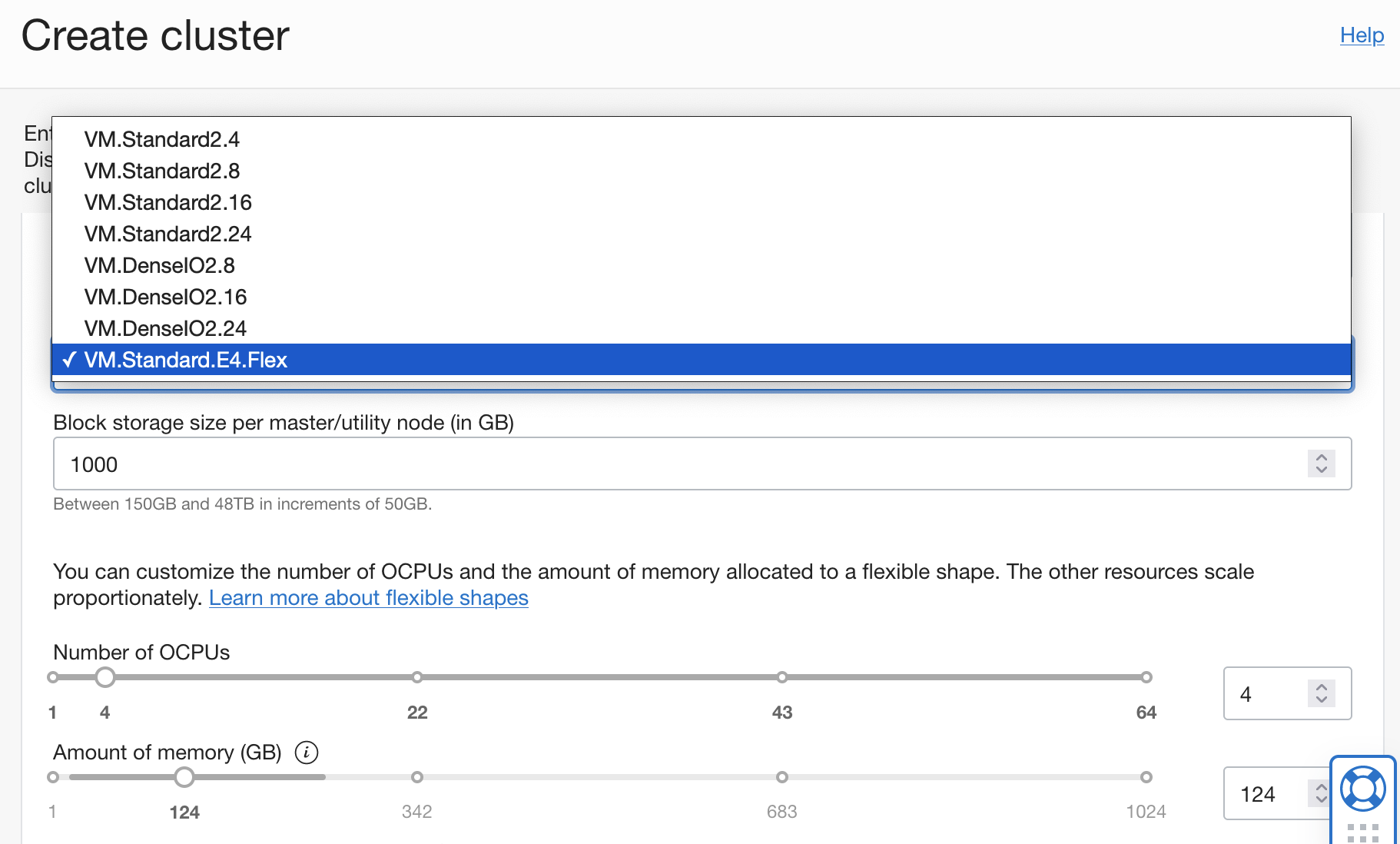
Big Data now supports VM.Standard.E4.Flex (AMD) shapes. When you create a Big Data cluster with this shape, you select the number of OCPUs and the amount of memory that you need to match your workload, enabling you to optimize performance and minimize cost.
Presto (Trino)
Trino is a distributed SQL query engine designed to query large data sets in Big Data Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Object Storage. Presto is now preconfigured in Big Data clusters and can be managed through Ambari.
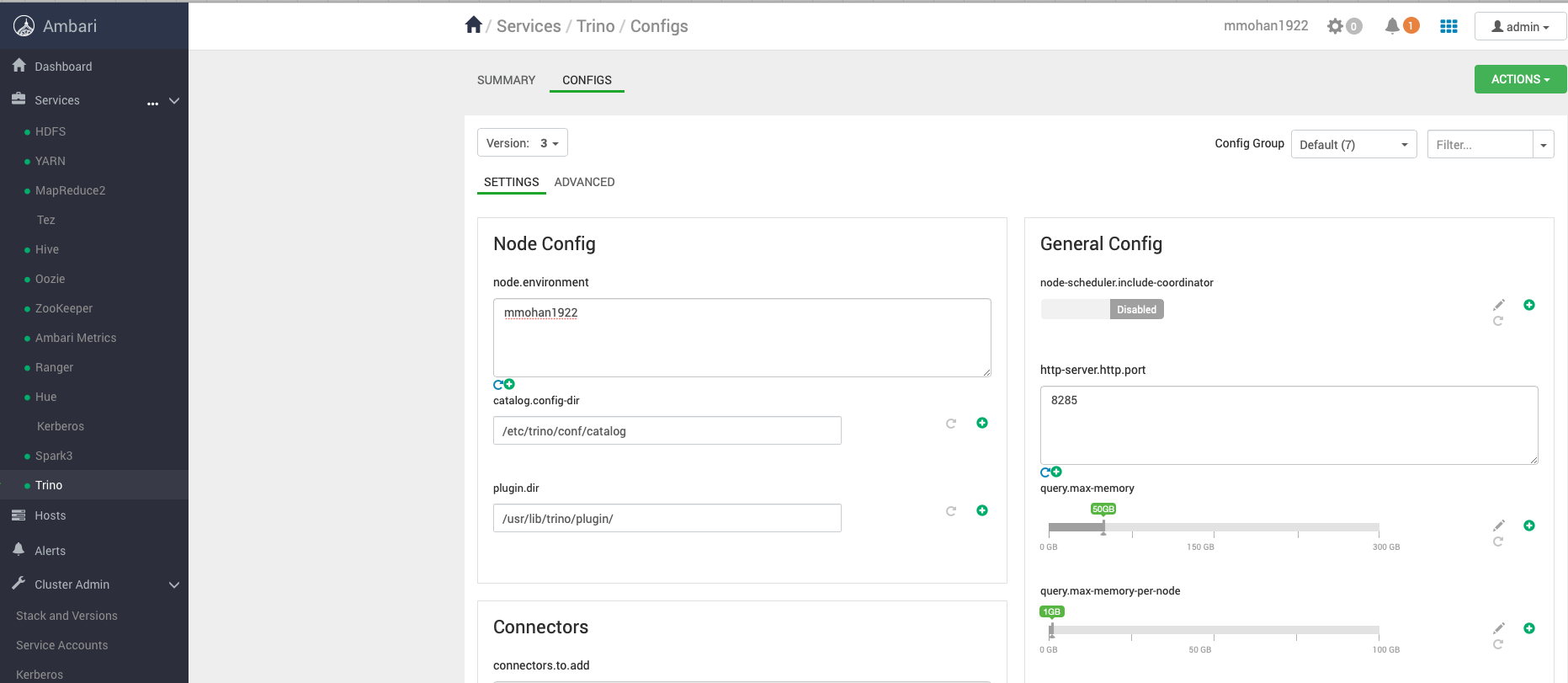
For more information, see Managing Clusters.
JupyterHub
JupyterHub is a popular open source project that enables multiple users to work together by providing each with their own Jupyter notebook on shared resources managed together. Big Data now comes preconfigured with JupyterHub
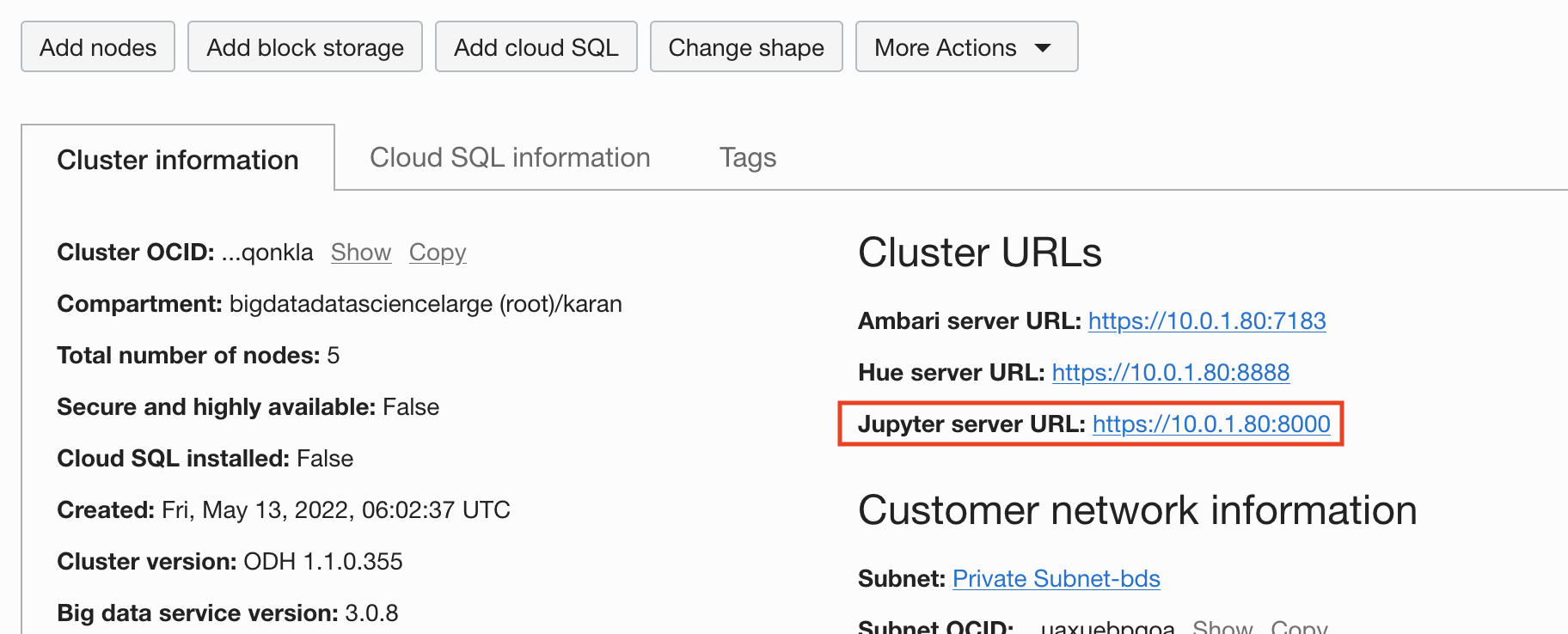
From the URL provided in the Oracle Cloud Console, you can access Jupyterhub to deploy a notebook server and launch page.
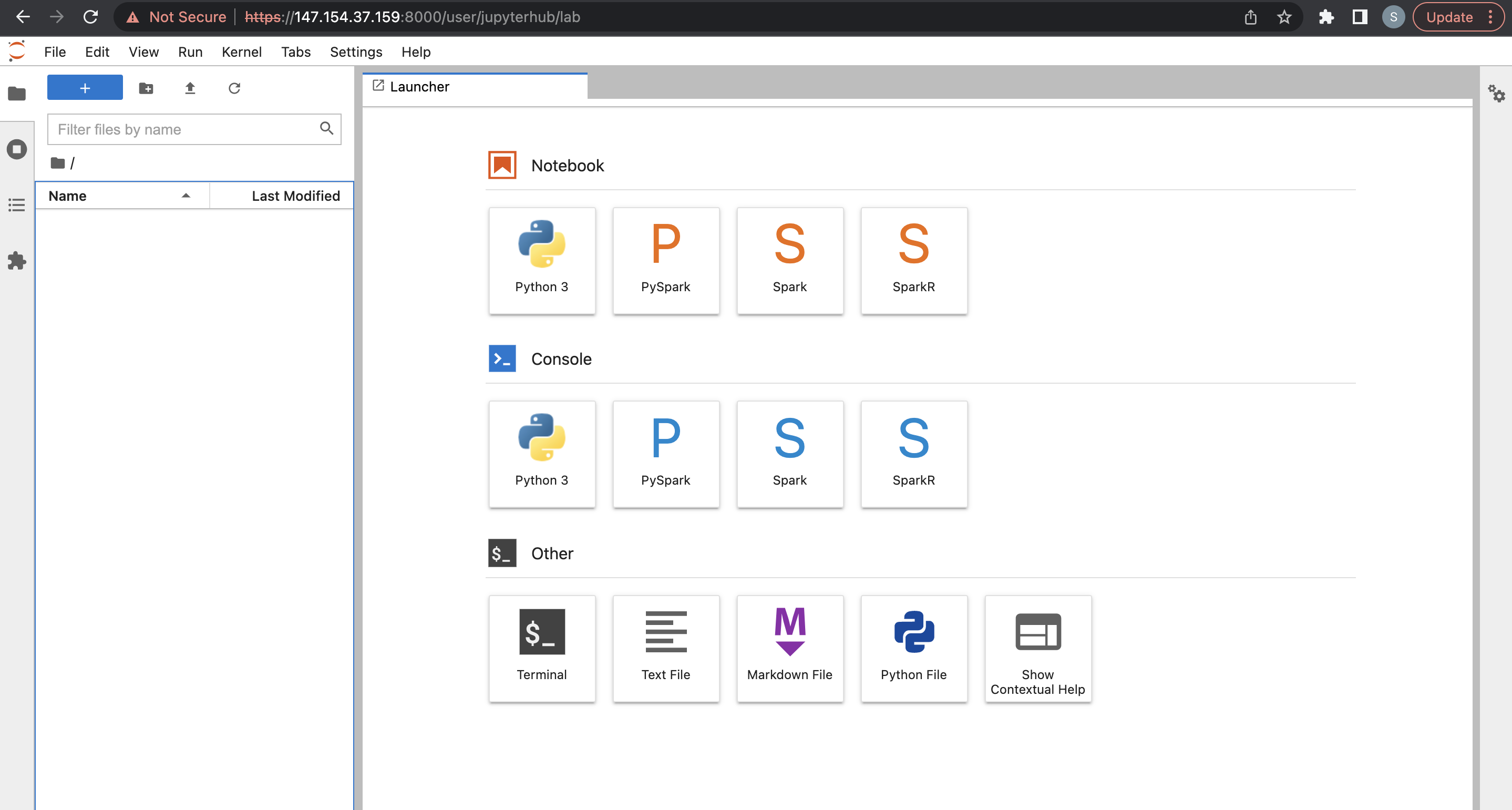
From there, you can deploy one of the multiple kernels available by default, such as Python, PySpark, Spark, and SparkR.
For more information, see Using Jupyterhub.
Bootstrap scripts
Bootstrap scripts enable easier configuration and automation with Big Data. You can run a bootstrap script on all the cluster nodes after a cluster is created, when the shape of a cluster changes, or when you add or remove nodes from a cluster. You can use this script to install, configure, and manage custom components in a cluster.
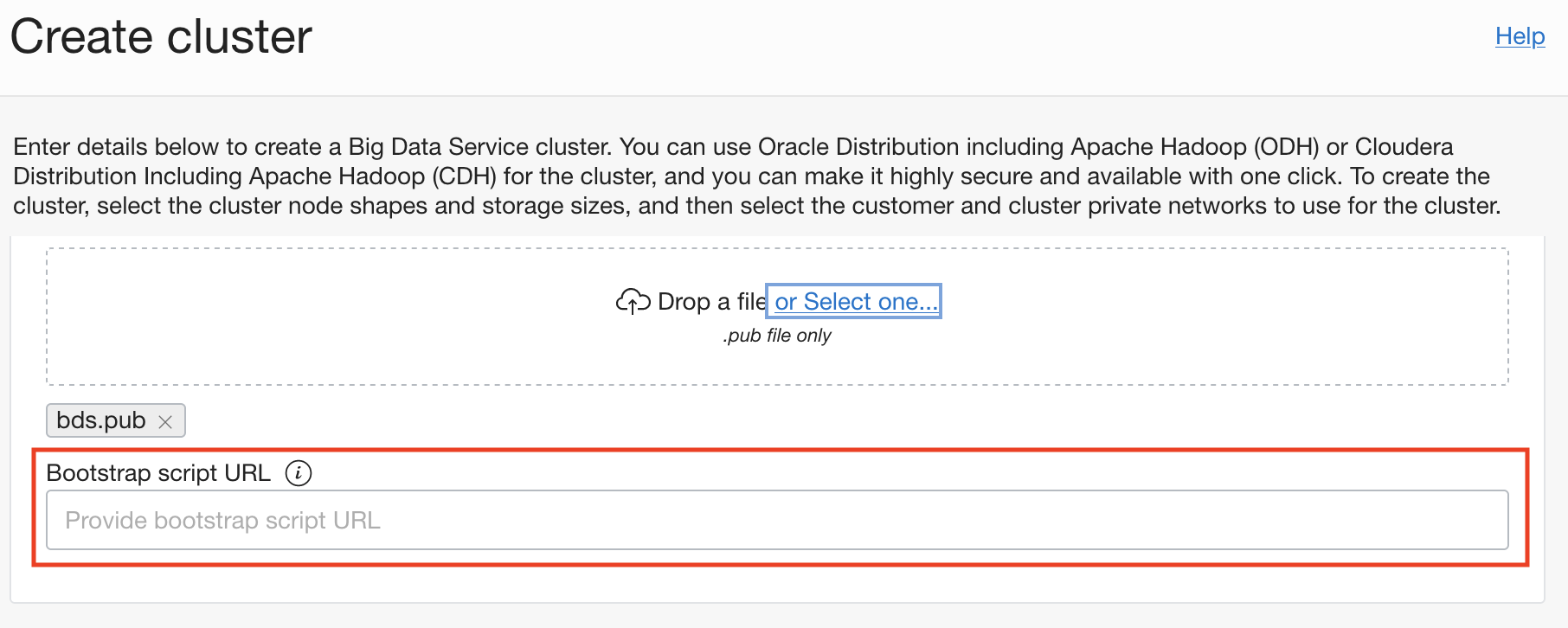
Bootstrap scripts can also be updated after a cluster has been created.
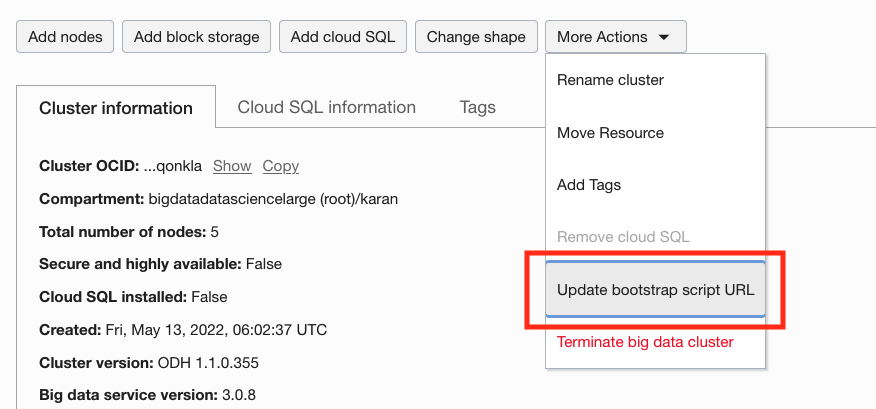
For more information, see Updating bootstrap script URL.
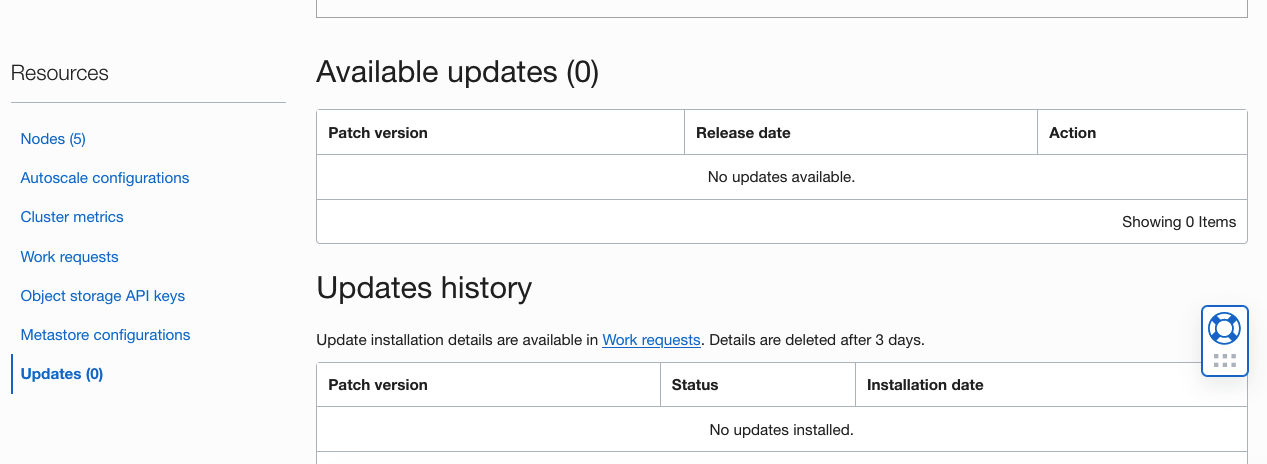
Patch management
The Big Data Console page has a new Updates link in the Resources column. Click this link to view the available updates and installed updates for the cluster. This link allows you to easily manage and apply Big Data patches and review the history of the patches that were previously applied.
Custom Kerberos realm names
You can now specify your own custom Kerberos realm name while creating a Big Data cluster.
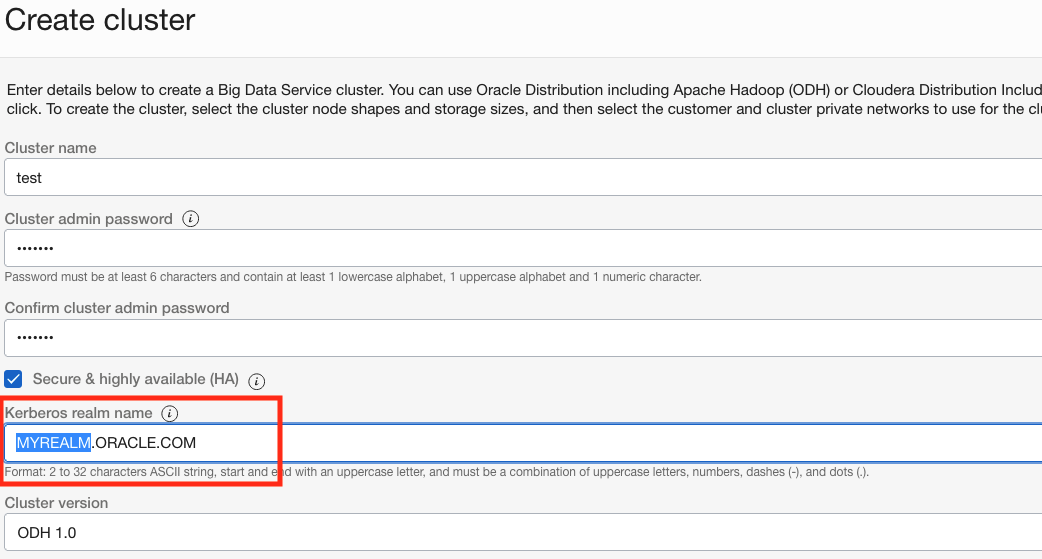
Enterprise customers can now use their own trusted realms and more easily integrate Big Data with their preexisting Kerberos.
For more information, see Creating a Cluster.
Other features
With this release comes the general availability of the following features:
-
Add compute-only worker nodes to your cluster.
-
Delete any worker node from your cluster.
-
Hue comes preconfigured in the cluster.
-
Livy comes preconfigured in the cluster.
Conclusion
All the features in this Big Data release help enable enterprises of all sizes to use the power of managed open source software in Big Data more easily and efficiently to build their data lake, extract, transform, and load (ETL), querying, processing, and machine learning platforms. Future blogs cover some of these new features in more detail.
