In 2017, we expanded our cloud database offerings from 1-node databases to ‘cloud-first’ Bare Metal 2-node RAC and Exadata systems, and most recently Virtual Machines. While launching new offerings across database shapes, database versions and editions, we also kept a focus on simplifying the lifecycle activities around creating, managing and updating Oracle Database in the cloud.
We are pleased to announce new Oracle-certified and access-controlled manageability features for patching, high availability and backup. The common underlying themes among these features are “automation” and “ease of use,” rooted in your need to invest time and resources in your core business rather than managing IT infrastructure and database fleet.
The following sections describe each new feature and outline how it simplifies your day-to-day database management tasks.
Patching
Oracle releases database patches containing feature upgrades, bug fixes and security fixes. These patches are often referred to as Patch Set Updates (PSU) or Bundle Patch (BP). Currently Oracle customers identify the right quarterly patch for their patch environment, download the patch and use manual tools like the OPatch utility to apply these patches and resolve any conflicts.
Now, the database service patching feature simplifies the steps required to patch a fleet of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure databases along with the underlying database system. You no longer need to find and manually install relevant patches on your database host. You can use the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console or Rest APIs to view the quarterly patch relevant to your database fleet and proceed to apply the patch. The service will then orchestrate the patch application steps and provide you with status. You can also view the history of patching jobs that were previously executed.
This feature is currently available for all bare metal database shapes (HighIO, DenseIO and RAC) and editions (Standard, Enterprise, Enterprise High Performance and Enterprise Extreme Performance). Database version 11.2.0.4 and 12.1.0.2 are currently supported. You can setup granular access control for the feature using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management. There is no additional cost associated with using this feature.
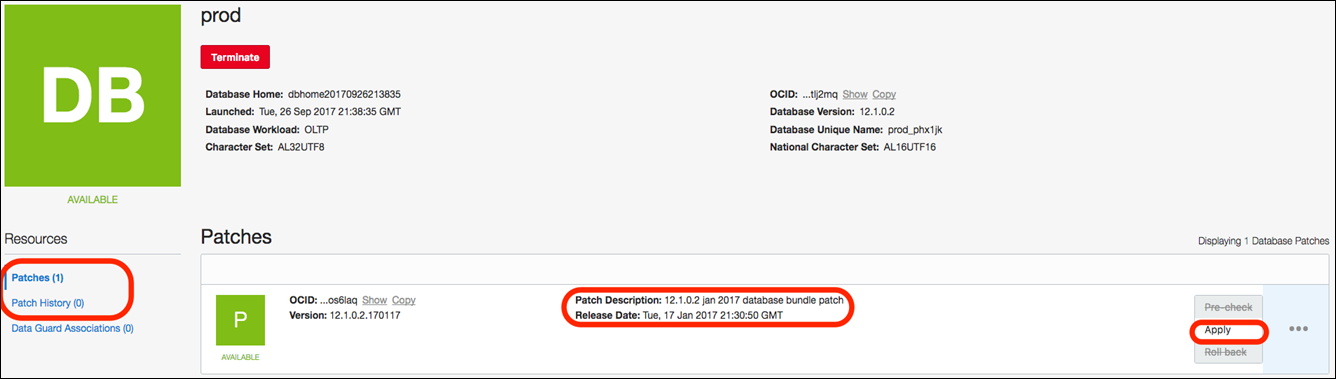
Below are the steps to apply a patch using the console:
Login to the console, select the database you want to patch and click on “Patches” under Resources. An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure database patch applicable to your database is displayed. Click the actions icon (“…“), and then click on “Apply”.
High Availability
Oracle Data Guard ensures high availability, data protection, and disaster recovery for enterprise data. Data Guard provides a comprehensive set of services that create, maintain, manage, and monitor one or more standby databases which can protect Oracle data from failures, disasters, human error, and data corruption. Data Guard is Oracle certified and follows standard Maximum Availability Architecture (MAA) best practices. Currently, Oracle customers use DGMGRL (Data Guard command-line interface) – a tool to manually manage Data Guard.
Now, you can manage your Data Guard configurations through the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console and Rest APIs. In a few clicks, you can enable Data Guard, view Data Guard configurations and perform switchover, failover, and reinstate actions.
This feature currently supports all bare metal database shapes (HighIO, DenseIO and RAC), database versions (11.2.0.4, 12.1.0.2 and 12.2.0.1) and all enterprise database editions (Enterprise, Enterprise High Performance and Enterprise Extreme Performance), along with granular access control using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management. When using this feature, you will be charged the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure database instance prices for your standby databases.
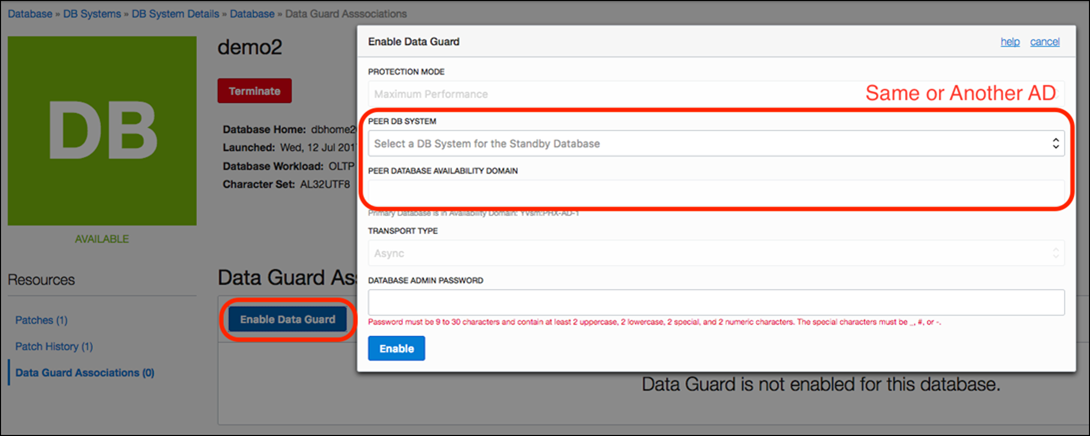
Below are the steps to enable Data Guard:
Login to the console, select the database that you want enable Data Guard for and click on “Data Guard Associations” under Resources. An option to enable Data Guard is displayed. Click on “Enable Data Guard” icon, select the “Peer DB System” under which you want to create you standby, enter the standby database password and click on enable “Enable”. A new standby database will be created under the selected Peer DB system and Data Guard association will be established between the primary and standby databases.
Backup and Restore
In every database system, the possibility of a data loss always exists due to the possibility of failures such as hardware failure, data corruption, or human error. If a failure occurs and affects the database, then the database must be recovered and normal operation should be resumed while insulating users from problems caused by the failure. This requires Oracle customers to constantly backup their production databases and restore from backups after a failure. Previously, many Oracle customers used RMAN (Recovery Manager) to manually setup and manage backup and restore.
Now, you can use the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console and Rest APIs to create and manage database backups. You can either enable an automatic incremental backup policy or create an on-demand full backup. The service orchestrates all the steps required to create and store the backup. You can later list your backups and restore the database to the latest, point-in-time or SCN (System Change Number) state. You can even create a new database from your on-demand full backup.
Here are the steps to enable automatic incremental backups, create a full backup, and restore a database from the console:
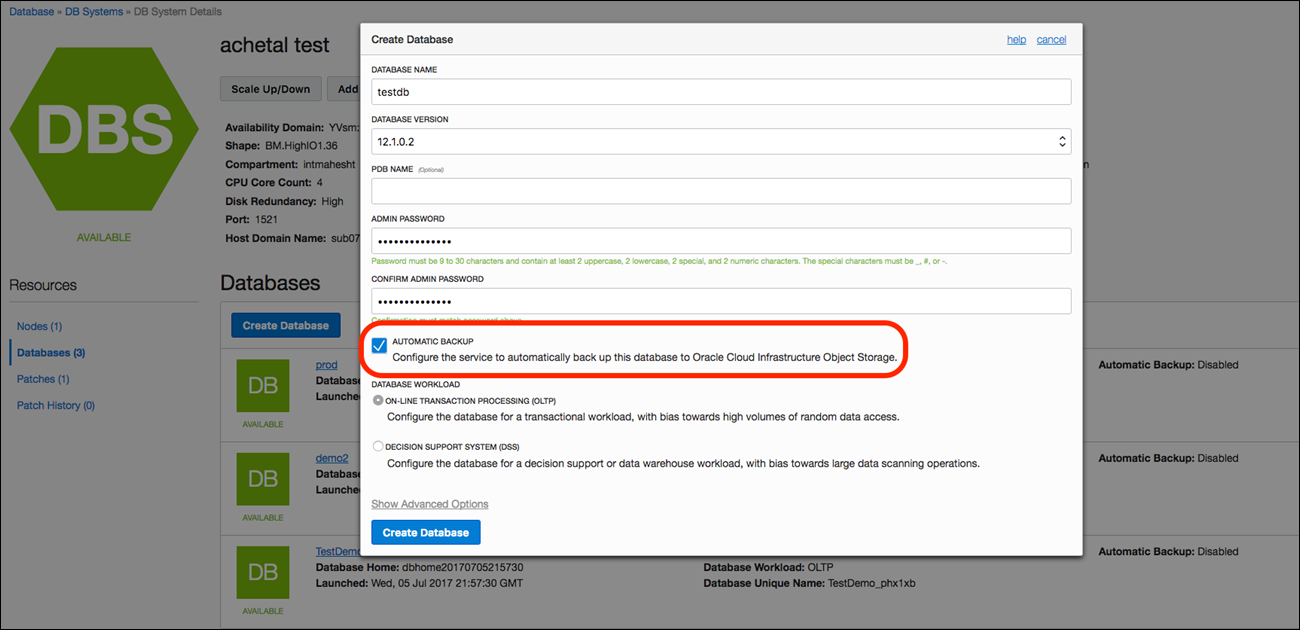
To enable automatic incremental backups, select “Automatic Backup” during database creation. If you select this option, automatic incremental backups will be setup on the database that was created.
To create a full back, choose the database you want to backup, click on “Resources” and select “Backups”. An option to “Create Backup” will be displayed.
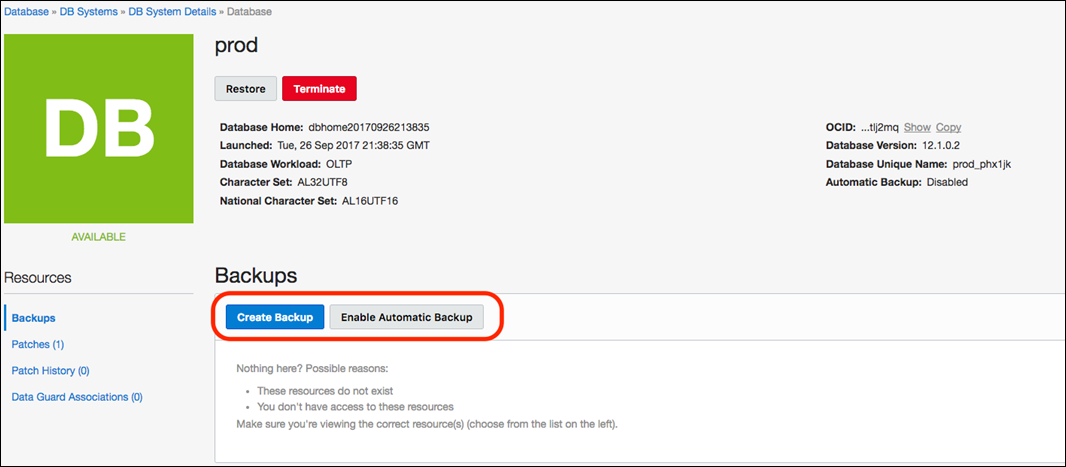
To restore a database from a backup, select the database that you want to restore and select “Restore”. You can restore the database either to the latest, point-in-time or SCN based state.
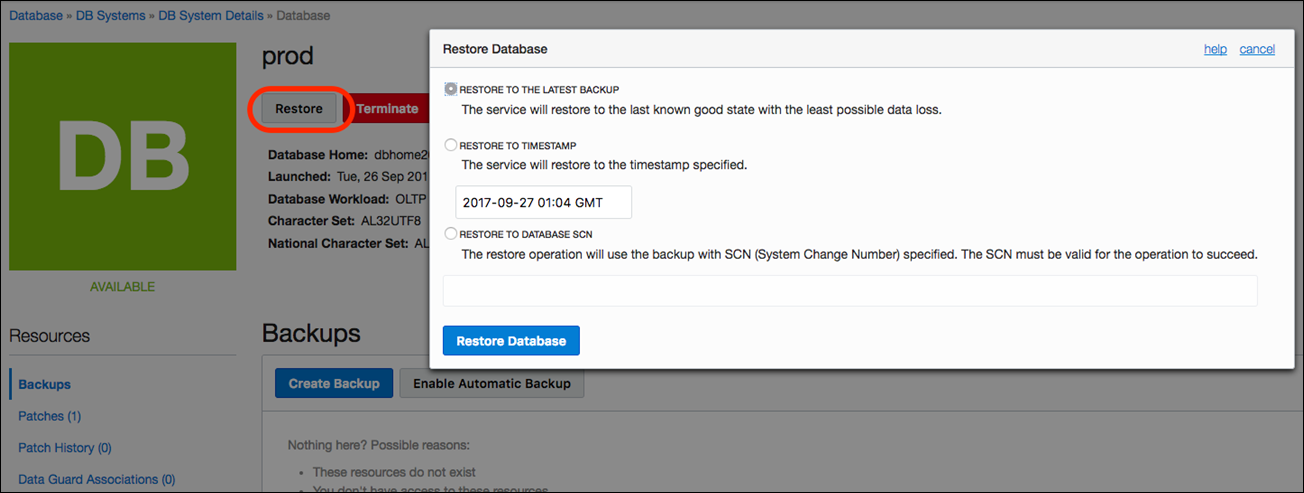
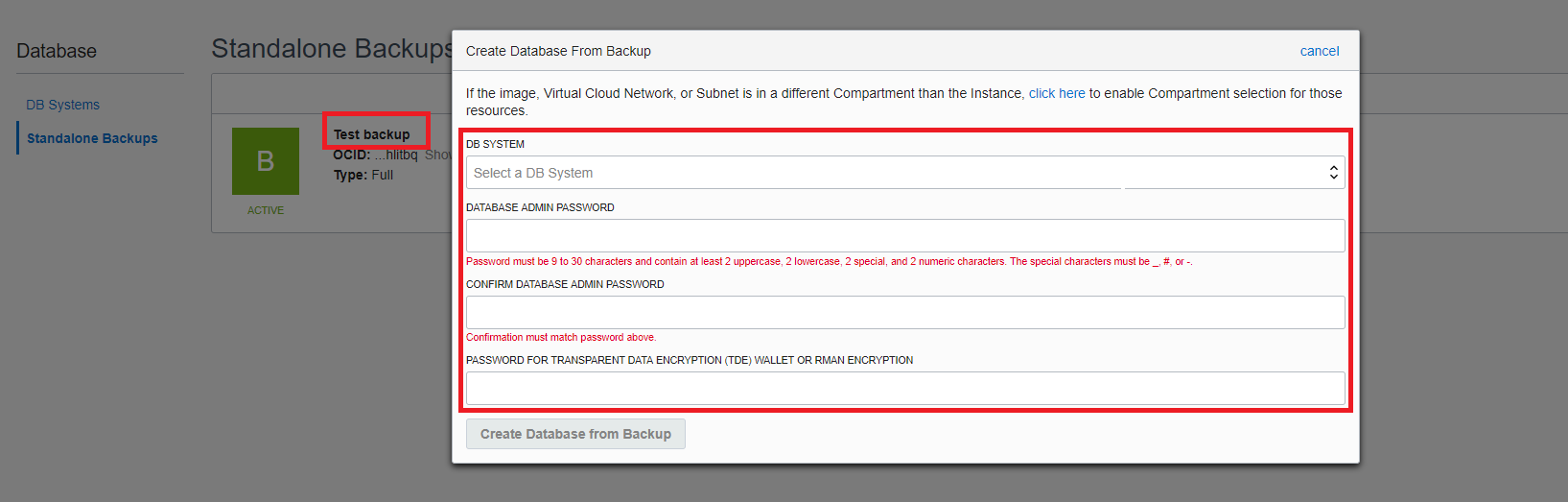
Below are the steps to view backups and create a new database from one of your on-demand backups:
On the main Database landing page, click on “Standalone Backups”. On this page you can view the on-demand full backups that you created. You can then select one of the standalone backups to create a new database. Select the DB System under which you want to create the database and enter admin and TDE password.
These backup and restore features currently support all bare metal shapes (HighIO, DenseIO and RAC), editions (Standard, Enterprise, Enterprise High Performance and Enterprise Extreme Performance) and database versions (11.2.0.4, 12.1.0.2 and 12.2.0.1), along with granular access control for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management Service. You will be charged the standard Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage rates for storing backups. There are no additional cost associated with using these features.
______________________________________________________________________________
All the above manageability features are now available in all OCI regions. For more details, please visit the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure documentation at https://docs.us-phoenix-1.oraclecloud.com/Content/home.htm
— Ashutosh Chetal, Principal Product Manager, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure