Security and risk management are now shared priorities among the C-suite. As organizations migrate more of their data and infrastructure to the cloud, questions concerning security have become more widespread. These questions are especially relevant for databases, where breaches can result in significant liability for organizations.
CISOs manage risk for customers, partners, and the organization in a way that enables the business to succeed and innovate. Most of today’s business processes, including database security, can be further improved through intelligent automation.
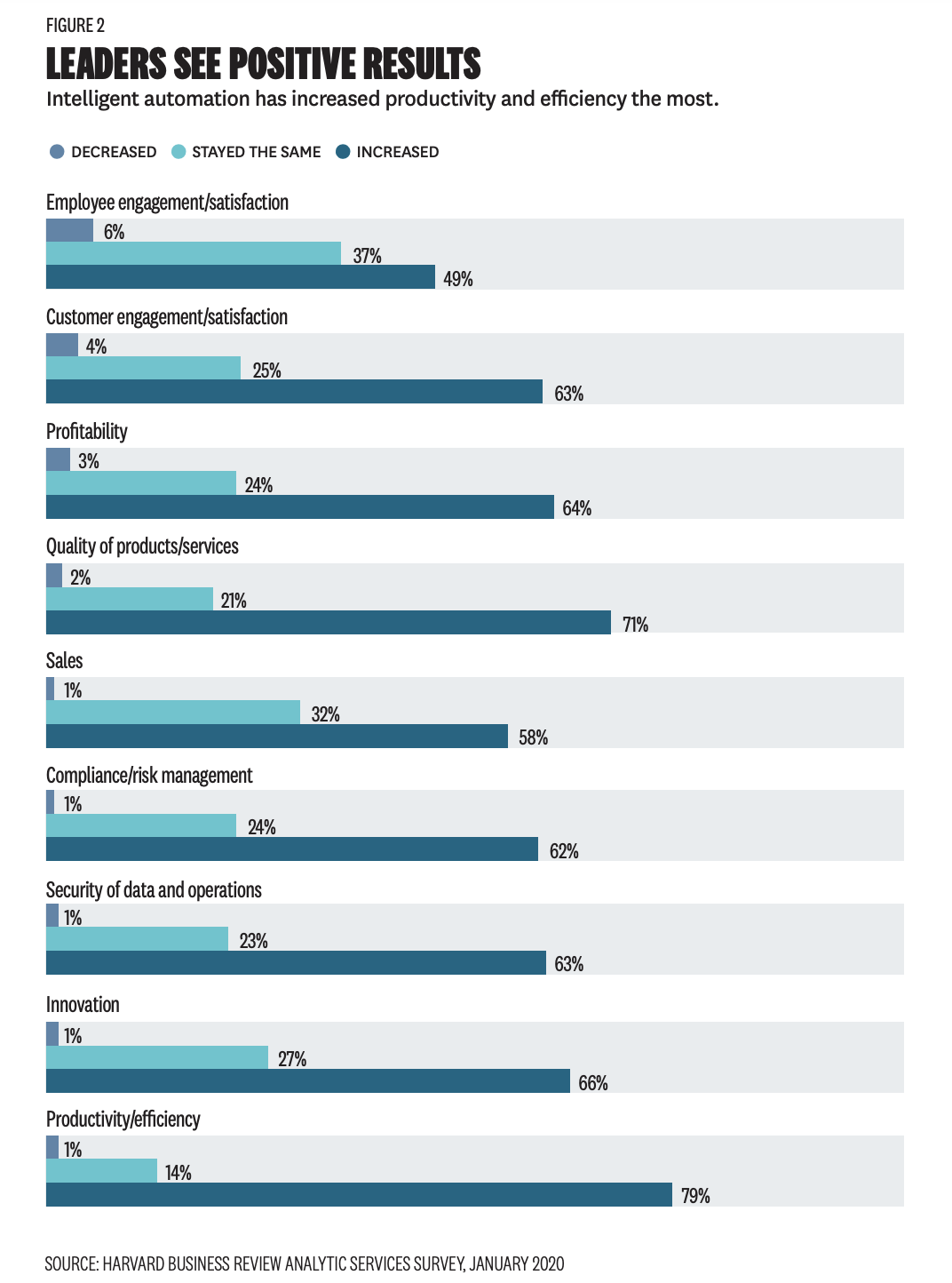
Research conducted by Harvard Business Review Analytic Services shows that 80% of respondents deemed intelligent automation (IA) very important to the success of their organization. And people implementing IA are seeing positive results.
Untimely database patching can have costly security risks
Patching is the process of improving, updating, and securing computer software and databases. You can patch to fix a known problem, create an enhancement, or remove a security vulnerability. Security patching is essential for keeping your data secure.
Patching normally requires taking a database server offline while modifications are made. This downtime can cause some organizations to delay patching, which can result in outdated code bases, unavailable improvements, and most importantly, the potential for vulnerabilities to be exposed. When vulnerabilities are exposed, hackers on the lookout for weaknesses that haven’t been patched can discover them.
With the security risks posed by untimely security patching, 51% of IT teams reported deprioritizing other projects to address patching priorities. This reprioritization results in delayed innovations and updates, putting your competitive advantage at risk.
Cloud security can help address the problem of untimely patching, but not entirely
Cloud security refers to a set of policies, controls, and technologies that work together to help data, infrastructure, and applications stay secure. While some aspects of cloud security can help address the problem of timely patching, they don’t address the issue in its entirety.

A foundational component of cloud security is the shared responsibility between the cloud provider and the customer, which conveys the division of labor between the cloud service provider and service subscriber. But even managed cloud database providers that offer full software support for a database server might still need to schedule patching with customers, because the patching operation can cause an interruption in service.
48% of CIOs report that their administrators are unable to patch on time because of how the required downtime impacts service level agreements. The only way to ensure the timely application of patches is to use a service that offers a nondisruptive patching process. With intelligent automation, the advantages of cloud computing can be achieved while also protecting sensitive and regulated data—without the need to schedule patching.
Oracle patches for security vulnerabilities automatically, helping prevent hackers from accessing your database.
Oracle Autonomous Database has built-in security with intelligent automation
Oracle Autonomous Database is a managed cloud database service offered on Oracle’s next-generation cloud infrastructure. If you need to keep data in your data center, for either legal or operational reasons, Oracle also offers a solution: Oracle Cloud@Customer is situated locally in your data center but managed remotely by the Oracle Cloud team.
Oracle Autonomous Database offers the following benefits:
- Automatic patching: With Oracle Autonomous Database, security patches are automatically applied without application downtime, making your database more secure than a manually operated database.
- Encryption: Oracle offers always-on encryption for data at rest and in motion. Data is transferred from storage to processing nodes encrypted and kept encrypted in cache.
- Separation of the duties of data management and database administration: Oracle uses features, such as Database Vault and the pluggable database lockdown profiles, to isolate database administration managed by Oracle from data administration managed by the Autonomous Database customer.
- Audits: Database activity auditing is automatically configured, enabled, and in constant operation. The database system records any suspicious patterns of access and allows for the flexibility to extend analysis of the collected data to other services or to on-premises security information and event monitoring (SIEM) systems.
- Dedicated infrastructure: Oracle offers customers the option to request infrastructure dedicated your databases only, delivering physical isolation required by some data security regimes.
- Data Safe: Data Safe is a unified database security service that detects risks introduced by users, data, and configurations through continuous monitoring. Data Safe is offered free of charge for all Autonomous Database customers.
Focus on the future of your organization with intelligent automation
According to the 2020 Cloud Threat Report, within the next three years, most cloud-resident servers plan to take advantage of intelligent and autonomous patching and updating.
At Oracle, we want every organization to take advantage of the cloud’s agility, flexibility, and scalability without compromising their own data, or their customers’ data. That’s why we bake security and automation into our cloud solutions, helping ensure full-stack protection and a platform that’s secure by design.
Organizations that adopt IA can have the advantage of solutions like automated patching that enable them to spend less time on security risks and more time on building innovations that provide the best solutions for their customers. Learn more about Oracle Cloud services.
For more information, see the following resources:
