Oracle Linux 7 (OL7) support for ARM (aarch64) ended on January 1, 2025 and is not covered by OL7 Extended Support. As a result, security patches and bug fixes for OL7 on ARM have not been issued since. To align with this upstream status, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Kubernetes Engine (OKE) will begin deactivating the capability to create new OL7 ARM worker nodes. OKE will no longer build or ship new OL7 ARM images or support OL7 ARM platform images for creating new worker nodes. This change does not affect OKE control planes and applies only to worker node OS images on ARM.
This guidance applies to both managed node pools and self-managed worker nodes; OKE control planes are not affected.
Who is affected
This change affects OKE customers who run Kubernetes worker nodes on OL7 ARM (aarch64) – whether managed via OKE node pools or self-managed nodes. It also impacts any plans to create new OKE worker nodes from OL7 ARM images after the effective date. Customers using other architectures or already on OL8 ARM are not impacted by the deactivation of new OL7 ARM node creation.
What’s changing
OKE is ending support for creating new worker nodes based on OL7 ARM images. Specifically, OKE will stop building and publishing new OL7 ARM images and will deactivate the creation of new OL7 ARM worker nodes. Existing clusters and nodes that already use OL7 ARM images will continue to run until you take action; however, those operating systems will not receive upstream security patches or bug fixes.
Scope clarity
This change applies only to Kubernetes worker nodes that use OL7 ARM images. OKE control planes are not impacted. Oracle-managed serverless services, including Oracle Functions, are also not affected. If you operate mixed-architecture clusters, note that this action is limited to OL7 on ARM and does not alter policies for x86-based nodes.
Why this change
OL7 on ARM reached end of support on January 1, 2025 and is excluded from OL7 Extended Support. Without upstream support, OL7 ARM receives no new security patches or bug fixes, increasing exposure to unpatched vulnerabilities and operational risk. OKE is deactivating the creation of new OL7 ARM nodes to help customers maintain a supported, secure, and compliant environment and to guide migrations to OL8 ARM images.
Recommended customer actions
To maintain a supported and secure posture, begin planning and executing your migration to OL8 ARM without delay. Start with discovery, then move to a controlled, blue/green cutover to minimize downtime and risk.
- Migrate to OL8 as soon as possible.
- Inventory your environment:
- Review OKE clusters, node pools, and custom images to identify OL7 ARM usage.
- Confirm autoscaling groups and CI/CD pipelines aren’t pinned to OL7 ARM image IDs/OCIDs.
- Plan and execute an upgrade to OL8-based images for all affected node pools.
High-level migration path (OL7 ARM to OL8 on OKE)
Assess and plan
- Identify affected clusters/node pools, image references, and Ampere A1 shapes.
- Validate application compatibility with OL8 in a non-production environment.
- Estimate migration windows; typical migrations complete per node pool in hours, depending on image size, DaemonSets, and drain policies.
Prepare OL8 images and configuration
- Select a supported OL8 ARM OKE image. See the latest on OKE Supported Images and Running Applications on ARM-based nodes.
- Validate Kubernetes version skew between control plane and OL8 nodes is supported. See the latest Kubernetes skew policy.
- Confirm container runtime compatibility (containerd version and CRI config).
- Verify OCI CNI and CSI (Block Volume, File Storage) versions supported on OL8. the Compatibility matrix will help.
- Ensure Oracle Cloud Agent and required OS Management/OS Management Hub plugins are enabled on OL8 images. Use OS Management documentation to guide you.
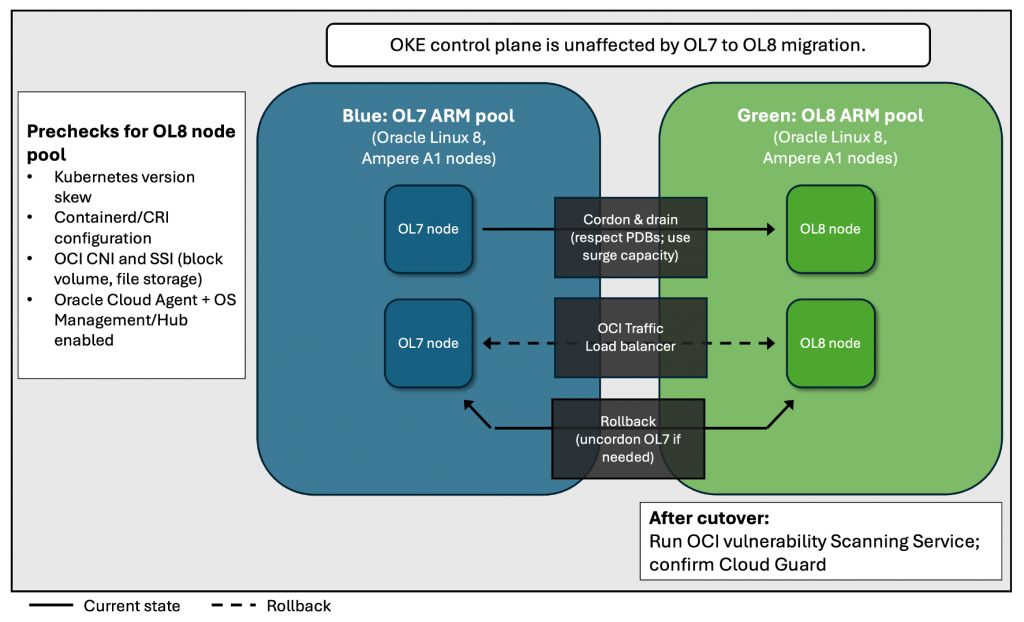
Create new OL8 nodes or node pools (blue/green)
Use a blue/green approach by running OL7 and OL8 side by side, shifting workloads to OL8, validating, then retiring OL7. The exact steps differ for managed node pools vs self‑managed nodes.
Managed node pools (recommended for most OKE clusters)
- Create a new OL8-based managed node pool in the same cluster with matching shape, labels, taints, and autoscaling policies.
- Apply equivalent networking and security (VCN/subnets, NSGs, security lists, IAM). Ensure Oracle Cloud Agent and required OS Management/Hub plugins are enabled on the OL8 image.
- Keep the OL7 node pool in place as rollback until SLOs are validated.
- For larger fleets, provision surge capacity or use rolling patterns. Validate CNI/CSI and containerd versions, and test Cluster Autoscaler scale‑out on the OL8 pool.
- OKE Upgrade Best Practices
- Drain OL7 nodes (respect PodDisruptionBudgets); observe rescheduling and autoscaler behavior before deleting the OL7 pool.
Self-managed nodes (created and operated outside of OKE’s managed pools)
- Provision new OL8 Compute instances with the supported OL8 image and required bootstrap to join the cluster (kubelet/kubeadm or your automation). Match shape, labels, taints, and node authorization. Working with Self-Managed Nodes
- Place nodes in the appropriate VCN/subnets with matching NSGs/security lists; configure routing and egress as needed (NAT/Service Gateway). Network Resource Configuration for Cluster Creation and Deployment
- Ensure Oracle Cloud Agent and OS Management/Hub (if you use it) are enabled; verify CNI/CSI and containerd compatibility.
- Cordon and drain OL7 self‑managed nodes to shift workloads to the OL8 nodes. Keep OL7 nodes available for a defined rollback window; then remove them from the cluster and decommission the instances.
- Note: Cluster Autoscaler manages capacity for managed node pools. For self‑managed nodes, use your external mechanism (Instance Configurations/Instance Pools/Autoscaling policies or your own scaling automation). Autoscaling Kubernetes Node Pools and Pods
For both scenarios
- Preserve labels/taints and PodDisruptionBudgets to meet SLOs during drain.
- Validate DaemonSets (CNI, CSI, logging/monitoring), ingress and load balancer behavior, storage mounts, and admission policies on OL8.
- Ensure Oracle Cloud Agent and OS Management/Hub (if you use it) are enabled; verify CNI/CSI and containerd compatibility.
- Provision new OL8-based nodes or node pools in the same cluster with matching shapes, labels, taints, and scaling policies.
- Nodes are for self-managed use cases
- Node pools are for managed node use cases
- Apply the same network/security configuration (NSGs, security lists, IAM).
- Keep the OL7 pool in place as a rollback path until you validate SLOs on OL8.
- For large fleets, use surge capacity or rolling patterns; adjust Cluster Autoscaler settings and test scale-out triggers on OL8 pools. See our documentation on Upgrade Best Practices.
Drain and migrate workloads
- Cordon and drain OL7 nodes; honor PodDisruptionBudgets and use surge capacity to meet SLOs.
- Monitor rescheduling: DaemonSets, ingress, storage (CSI), and sidecars.
- Validate containerd runtime behavior and CRI configuration on the new nodes.
Validate, secure, and cut over
- Run smoke and performance tests; verify logs/metrics and autoscaler behavior.
- Security verification:
- Scan new images/nodes with OCI Vulnerability Scanning Service (VSS). Enable or verify Cloud Guard detections for drift and configuration posture.
- Confirm image provenance/signing and restrict node image sources via IAM policies.
- Maintain a defined rollback window; when stable, remove OL7 node pools.
Operational tips
- Start with non-production clusters; promote the pattern to production after validation.
- Schedule a maintenance window and take snapshots/backups prior to upgrades.
- Update Infrastructure-as-Code (Terraform/Resource Manager) and CI/CD image references to OL8 image OCIDs; avoid “latest” tags.
- Expect temporary cost uplift while running dual node pools; right-size and tune scaling policies during migration.
- Self-managed bootstrap differences (kubeadm/cloud-init), node authorization, and Oracle Cloud Agent/OS Management enablement.
Security and compliance considerations
Remaining on OL7 ARM exposes nodes to unpatched vulnerabilities and increases risk of exploitation or unauthorized access. Adopt OL8 images, keep kernels and user-space current, and verify post-migration status with VSS and Cloud Guard. As part of your upgrade, review KMS/Vault usage for secrets, private cluster settings, WAF posture, and least-privilege IAM.
Frequently asked questions
- Does this affect the OKE control plane?
- No. This change applies to worker nodes using OL7 ARM images only.
- Are Ampere A1 shapes supported on OL8?
- Yes. Use the latest supported OL8 ARM OKE images. You can always check OKE Supported Images for the latest information.
- Can I still create new OL7 ARM nodes?
- Not after the effective date. OKE has begun to deactivate creation of new OL7 ARM worker nodes.
- Will my existing OL7 ARM nodes be shut down?
- No. Existing nodes continue to run until you remove or replace them, but the OS no longer receives upstream patches.
- Can I do an in-place OS upgrade from OL7 to OL8 on nodes?
- Not supported. Create new OL8 node pools and migrate workloads.
- What if I use custom images?
- Rebuild on OL8, validate required drivers and modules, and register with OKE. See Oracle Docs for Managing Custom Images for more information.
- Are x86 OL7 nodes affected?
- This notice applies to OL7 on ARM (aarch64) only. Review current Oracle Linux policies for x86 separately.
- Are Oracle Functions or other serverless services impacted?
- No action is required for Oracle Functions due to this change.
How to get help
If you’d like planning guidance or hands-on assistance, Oracle teams and programs are available to accelerate a safe migration.
- Contact your Oracle account team or Cloud Solution Architect for planning assistance.
- Open a support request if you encounter issues during migration. Oracle Support
- For complex estates or large fleet migrations, engage Oracle Consulting or a validated partner. Oracle Consulting
- Refer to the OKE upgrade runbook template (if available). OL8 and Upgrading Systems With Leapp
- Documentation and tutorials:
- OKE supported images/versions. Support Kubernetes VersionsOL8 documentation.OCI CNI/CSI version compatibility matrix. Documentation for Vulnerability Scanning Service and Cloud Guard.
- OS Management/OS Management Hub for Oracle Linux package management.
Please review your OKE environments for OL7 ARM usage now and schedule your migration to OL8 ARM. To remain supported and compliant, complete your migration to OL8 at your earliest opportunity. If you need guidance, reach out to your Oracle account team, open a support request, or engage Oracle Consulting.
