Workflow management is one of the industry’s most popular kinds of tools. You can describe almost any operational procedure in any industry as a workflow if it’s composed of repeatable steps that can range from running technical processes, such as orchestrating the scheduled startup and shutdown of servers, to business activities that can span a line of business, such as processing purchase orders, through to an entire enterprise. The ability to stitch activities or sequences of tasks quickly and easily into an automated workflow is essential to gaining speed and agility. As a result, workflow tools are widely available, a point confirmed by the fact that a quick search of “workflow engine” on GitHub brings back more than 1,000 results.
Today, we’re announcing the new Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Workflow service, a serverless workflow engine with a graphical flow designer that enables developers and architects to accelerate the creation and processing of application and business logic, automated IT tasks, data jobs, and orchestration of cloud services such as OCI Functions, Object Storage, API Gateway, Compute, and others. With OCI Workflow, creating composable applications is easy.
OCI Workflow limited availability program is presently paused. If you want to join the beta, complete this form and we will reach out once we resume.
Key capabilities
OCI Workflow enables you to design and run workflows easily and has the following key capabilities:
-
OCI service orchestration: Easily integrate components and orchestrate workflows across multiple OCI services, such as Compute, Networking, Storage, Functions, Oracle Container Engine for Kubernetes (OKE), Database, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), API Gateway, and more.
-
Schedule and event-based triggers: You can trigger workflows on a schedule defined using a cron syntax or by other events.
-
Visual design and monitoring: You can build workflows using a drag-and-drop visual designer, simplifying the creation process. Visualizing the workflow and watching the steps run allows you to verify your workflow and identify any errors or issues easily. When an issue or exception occurs, the visual designer makes it easy to pinpoint the error and examine the state of the workflow at the point of failure and detailed logs to aid with root-cause analysis.
-
Built-in flow controls: You can use out-of-the-box flow controls, saving time and effort, to write and maintain code to implement routing, looping, and parallelization.
-
Built-in retry logic and extensible error handling: You can configure error management for default or custom errors, which the service automatically catches. You can specify the logic of how these errors are handled using flow controls for retrying, exiting the workflow, transitioning to another state, or invoking custom error handling logic.
-
Context and data management: The workflow service maintains the workflow context and data as it moves between steps.
-
Data filtering: You can use JMESPath expressions to filter and modify as the data moves between the workflow steps.
-
Automatic versioning: Workflows have a concept of “latest” and “live” versions to differentiate between currently running workflows and those being designed and tested. Every time you edit the workflow, a new version is automatically created and identified as the latest. This functionality enables you to continue to iterate and enhance a workflow without impacting the process of its currently running live version. When development has been tested, you can promote the new workflow version to production.
Workflow scenarios
You can use workflows in various scenarios, but we see OCI Workflow being used in the most common scenarios: Service orchestration and task automation.
Service orchestration
-
Run a sequence of tasks to automate infrastructure provisioning, migrations, and patches
-
Multiple serverless functions that need to be processed in order
-
Machine learning sequence of tasks to train models with each step taking values from the next step and making decisions on which step to run next based on the output of a model step
-
Expose monolithic services to applications by orchestrating many small components, which can all be implemented by different microservices or serverless functions
Task automation
Many tasks needing human oversight, and interaction can be automated, including the following examples:
-
SecOps tasks, such as responding to detected security breaches or other incidents
-
Fraud detection or risk rating
-
Automate the processes involved in the training of ML models
Example application
The following example shows an application that we built using the Workflow service. This app workflow automates a loan-origination workflow and approves or rejects the user based on input criteria, such as proof of address, credit check, and so on. In a future blog, we share more info on how this app was built and capabilities of the Workflow service.
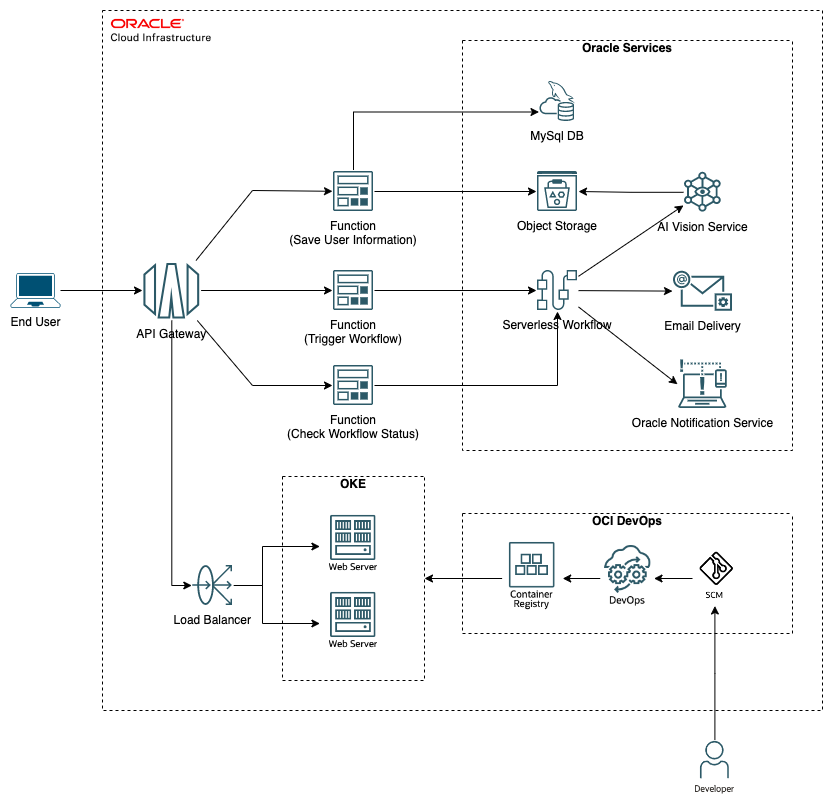
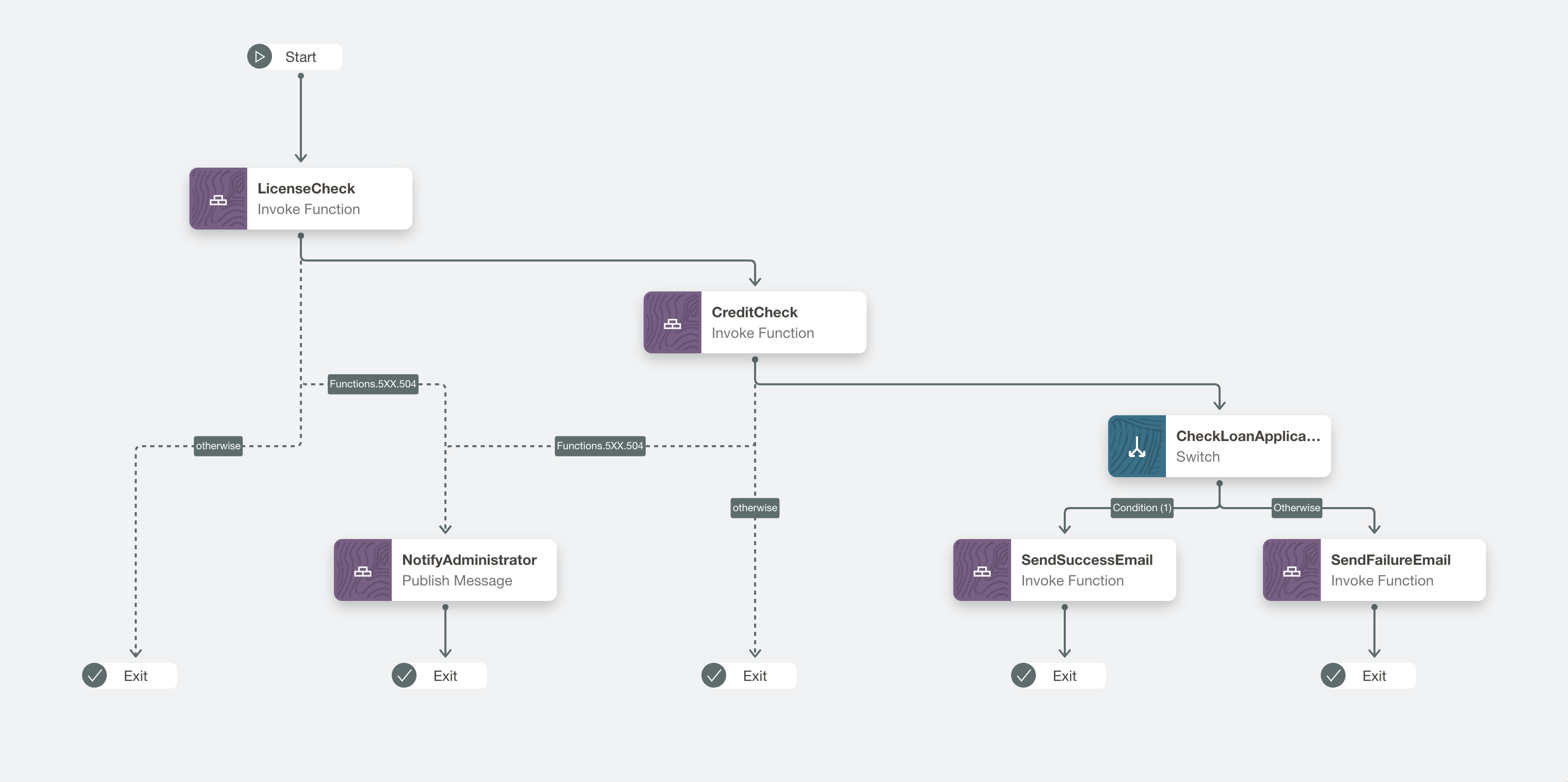
Getting started
OCI Workflow Limited availability program is presently paused. If you’re interested in participating in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Workflow limited availability program in the future, fill out this form. To learn more about the service, see the documentation
