Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC) is a comprehensive platform that enables organizations to analyze data and gain insights in the moment. Performance testing is an essential step to ensure that OAC can handle the expected workload without compromising its performance.
Apache JMeter is an open-source tool for performance testing that allows you to simulate the real-world OAC users’ experience and measure the performance of your reports. This blog provides guidelines on using JMeter to perform real-world realistic performance testing for OAC.
A supporting post, Prepare Apache JMeter for Performance Testing of Oracle Analytics Platform Services, describes how to prepare for using Apache JMeter.
The diagram below illustrates the concept of performance testing process for OAC:
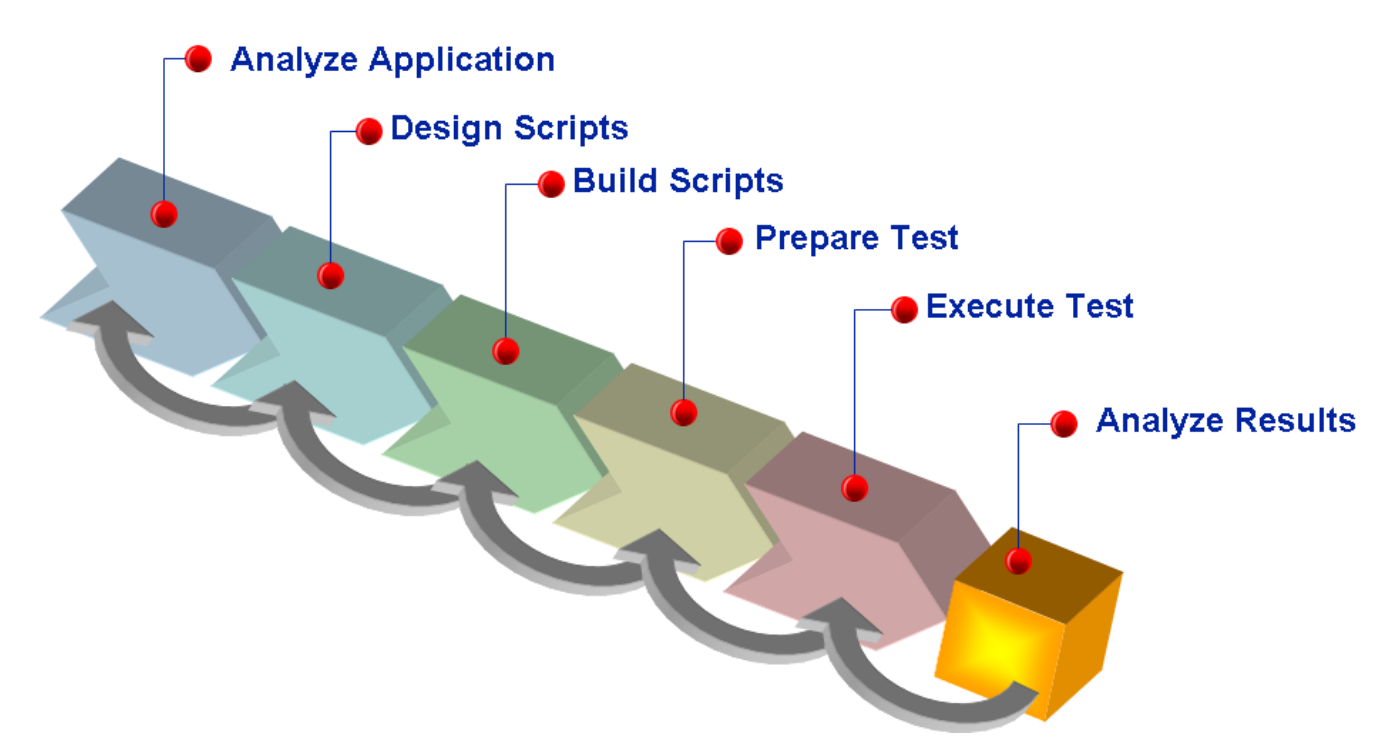
1. Design Your Performance Test Plan
Your test plan should be designed to simulate real-world scenarios and workload. This involves identifying the number of unique virtual users, the duration of the test, and the think-time between the requests. Ensure workbooks are optimized for single user performance (including various security roles), Define workload model during normal and peak usage. Simulate that workload using existing capacity/resources and scale points to achieve desired service level objective (SLO). The number of unique virtual users should be set to a realistic value that simulates your actual expected workload. The duration of the test should also be set to a realistic value that represents the period of time your users will be running reports. Think-time is the time a user takes between two requests, and it should be set to a realistic value to simulate real-world scenarios. Your test plan should also include pacing in the script to ensure that requests are sent at a realistic pace.
To achieve accurate and practical results, it is recommended to use different think times for different activities instead of using a fixed think time. For example, a short think time of 20 seconds is recommended for simple dashboard UI navigation, while a medium think time of 60 seconds for prompt selections. Similarly, when reports are displayed, it is advisable to use a large think time of 120-200 seconds with randomization. This approach ensures that the test accurately reflects the real-world user behavior and produces reliable results.
2. Correlation
Correlation involves capturing and replacing dynamic values in the script, such as access tokens, session state IDs, CSRF tokens, and other dynamic parameters. Failure to correlate these values can lead to errors and inaccurate results. Correlation is essential for cloud-based applications like OAC because they use dynamic values to maintain the session and handle user requests. To make this process easier, you can download a sample OAC correlation rules library COR file, which contains a pre-built set of correlation rules that can be used in creating test script for OAC.
3. Record and Replay Scripts
JMeter provides a feature to record user actions and convert them into test scripts. This feature can be used to record user actions in OAC and create test scripts that simulate real-world scenarios. The recorded scripts can be replayed multiple times to validate the report’s performance. The test scripts should be designed to simulate real-world scenarios, such as searching for data, generating reports, and visualizing data.
4. Test with Realistic Workload
To simulate a realistic workload, the number of virtual users should be set to a realistic value that simulates the expected workload. The workload should be gradually increased to identify the maximum capacity of the application. It is recommended to run the test for at least one hour to simulate real-world scenarios. The workload should be designed to simulate peak usage periods, such as the end of the month or the end of the fiscal year.
5. Analyze the Results
Once the test is completed, you’ll want to analyze results to identify the performance bottlenecks, which can include slow response times, high error rates, or excessive query capacity utilization. You can do this using available OCI metrics for OAC and JMeter’s built-in analysis tools. Once you’ve identified performance bottlenecks, you’ll want to act on your findings to improve the performance of the reports. This can include optimizing queries, improving system settings configurations, or changing to higher OCPUs shape.
If your reports fail to meet your performance goals, you can optimize them by identifying and addressing the bottlenecks. JMeter’s listeners can help you identify the slowest requests and you can analyze logs to determine the root cause of performance issues. You may need to optimize your database queries, adjust your caching settings, or scale up your infrastructure to improve OAC performance.
Helpful Monitoring Resources:
- Using OCI OAC Metrics.
- Using Usage Tracking.
- Set Up Usage Tracking in Oracle Analytics.
- Analyze Usage Tracking Data in Oracle Analytics.
- Using OCI OAC Logging.
- Step by Step Blog how to enable OCI logging.
- Watch Demo Video.
Summary
Performance testing using JMeter for OAC involves:
- Designing a plan to test those metrics
- Correlating dynamic values
- Recording and replaying scripts
- Testing with a realistic workload
- Analyzing the results
- Optimizing the appropriate areas based on the results of your analysis
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that OAC meets your performance requirements and provides a fast, seamless experience for your organization.
Conclusion
By following these guidelines and using JMeter to test real-world realistic performance for Oracle Analytics Cloud, you can identify and address reports performance issues before they impact your users.
Disclaimer
The guidelines provided in this blog post are intended to help to validate the performance of Oracle Analytics Cloud using Apache JMeter for performance testing purposes only. Oracle Corporation does not endorse or provide support for the use of third-party tools like Apache JMeter for testing Oracle Analytics Cloud. Users should exercise caution and follow best practices when testing production environments to avoid potential impact on users and data. Oracle Corporation is not responsible for any issues that may arise from the use of third-party tools for performance testing.
It is important to note that users of Oracle Analytics Cloud are strictly prohibited from utilizing any tools or services in a manner that performs Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks or simulations of such, or any “load testing” against any Oracle Cloud asset including yours. For further information, please refer to the Oracle Cloud Security Testing Policies.
