Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC) empowers organizations with modern, AI-powered analytics — delivering dynamic visualizations, interactive dashboards, and real-time insights that drive confident, data-informed decisions across the enterprise.
Built on Oracle’s secure and scalable cloud infrastructure, OAC unifies data preparation, semantic modeling, machine learning, and governed self-service analytics into one platform. It enables everyone — from business users to data engineers — to work with consistent, trusted data while exploring insights interactively.
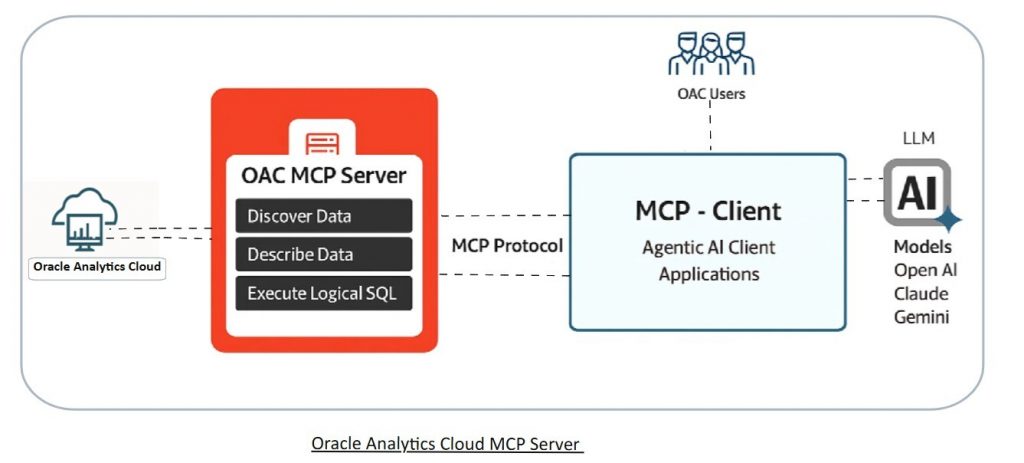
The Oracle Analytics Cloud November 2025 update introduces a new capability: the Oracle Analytics Cloud Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server. This feature connects OAC with external AI clients such as Claude Desktop, Cline (VS Code extension), and GitHub Copilot, enabling users to explore governed data through natural-language conversations. The MCP server also integrates with agentic workflows and automation platforms such as n8n and LangChain, opening new possibilities for AI-driven analytics automation.
OAC already includes powerful AI features such as the AI Assistant, which allows users to ask natural-language questions directly within Oracle Analytics Cloud. The Oracle Analytics Cloud MCP server complements these capabilities by extending OAC’s reach into external AI ecosystems and agentic workflows.
The key difference: The AI Assistant provides conversational analytics inside OAC’s user interface, while the MCP Server enables external AI agents and automation workflows to query and analyze governed OAC data from outside the platform — effectively bridging enterprise analytics with autonomous AI agents and intelligent automation workflows.
⚠️ Important Note on Security and Data Handling
Before connecting external AI clients, it’s important to understand how security boundaries are maintained.
The Oracle Analytics MCP Server provides secure, token-based access to governed data within OAC. However, once data leaves OAC and is processed by an external AI client or agentic workflow, the data becomes subject to that client’s own data-handling, storage, and governance policies. Customers must ensure that any connected MCP client or automation platform complies with their organization’s security, privacy, and AI-use policies. While OAC enforces governance during data access, what happens to the data after it leaves OAC depends entirely on the external system’s configuration and policies.
Feature Overview: Oracle Analytics Cloud MCP Server
The OAC MCP server bridges governed enterprise analytics and conversational AI. Built on the Model Context Protocol (MCP) — an open standard that enables secure, context-aware communication between AI systems and enterprise applications — the OAC MCP server allows users to query and explore OAC content using everyday language.
Core Capabilities
- OAuth 2.0 authentication: Standards-based, secure token authentication ensures only authorized users can access data.
- Dynamic query generation: Natural-language questions or prompts are converted into Logical SQL (LSQL) dynamically by the connected LLM on the fly. The generated LSQL is then sent to OAC where governance is enforced during execution.
- Governance enforced during execution: When LSQL queries are executed in OAC, role-based and row-level security are applied according to existing user permissions.
- Trusted data access through the semantic layer (if present): When a semantic model (RPD) is deployed in OAC, it provides a trusted business abstraction layer, ensuring consistent metrics, calculations, and business logic across all LLM-generated queries. Where no semantic model exists, datasets (XSA) serve as the governed access layer, applying the same role-based security and permissions framework to ensure controlled access to underlying data sources.
🔍 Discover · Describe · Execute
At the core of OAC MCP server are three foundational tools that define the conversational analytics workflow.
- Discover (
oracle_analytics-discoverData): Lists available datasets and subject areas, helping AI clients identify what data exists. - Describe (
oracle_analytics-describeData): Retrieves dataset metadata (tables, columns, measures, and hierarchies) helping the AI understand relationships and business meaning. - Execute (
oracle_analytics-executeLogicalSQL): Executes Logical SQL (LSQL) generated dynamically by the connected LLM, applying OAC’s role-based security, filters, and caching. Depending on configuration, the query may run through the semantic model or directly against a XSA dataset, but in all cases, OAC enforces governance and access control at execution.
Additional MCP tools will become available in the future to extend these capabilities.
📘 Resource: Logical SQL Grammar Reference
Alongside the three tools, OAC MCP server provides a key resource — the Logical SQL Grammar Reference. This resource helps AI clients:
- Understand and construct valid OAC logical SQL syntax.
- Generate queries aligned with OAC’s semantic model and business rules.
- Ensure consistency and accuracy when transforming natural-language questions into executable queries.
How it works: The LLM uses this grammar reference along with metadata from Discover and Describe operations to dynamically generate LSQL queries. The generated LSQL is then sent to OAC, where it is validated and executed within OAC’s governed environment. When a semantic model is used, it adds an extra abstraction layer that shields underlying schemas and enforces consistent business logic across queries. When datasets are used directly, OAC’s security model continues to govern access.
🔐 Security note: While OAC enforces complete governance during query execution (authentication, authorization, row-level security), the LSQL itself is generated by the external LLM. Once query results are returned to external AI clients, data handling depends on those clients’ retention and processing policies. For sensitive data environments, consider using enterprise LLM configurations with zero-retention policies or deploying local or OCI-hosted LLMs within your own infrastructure.
User Benefits
| Persona | Benefit |
| Executives | Ask business questions conversationally — get governed answers instantly. |
| Analysts | Extend self-service analytics using natural language, accelerating insight discovery. |
| Developers | Embed conversational insights into applications and build AI-powered analytics experiences. |
| Data Engineers | Validate data quality and troubleshoot issues conversationally, reducing time to resolution. |
| Automation Teams | Integrate OAC into agentic workflows (n8n, LangChain) for intelligent, data-driven automation. |
Setup Guide (15–20 Minutes)
Prerequisites
- Oracle Analytics Cloud instance
- Claude Desktop, Cline, or Copilot (the setup example uses Claude Desktop)
- Node.js v18 or higher
- Windows, macOS, or Linux
Step 1 – Generate Access Tokens
- Log in to OAC using
https://<your-oac-host>/ui. - Navigate to your User Profile, and then the Access Tokens section.
- Click Download Tokens.
The file automatically downloads as tokens.json.
Sample tokens.json:{
“accessToken”: “eyJ4NXQjUzI1NiI6...”,
“refreshToken”: “AgAgNzRjNDQxOWI...”,
“expiresIn”: xxxxx
}
🔐 Access tokens inherit your OAC privileges, so be sure to store them securely. If you use the MCP Connect script instead, you can sign in interactively — no manual token file is required, and token refresh is handled automatically.
Step 2 – Download the MCP Connect Package
- In OAC, navigate to your User Profile, and then the MCP Connect section.
- Click Download.
- Extract the downloaded ZIP to a local path such as
C:\MCP\oac-mcp-connect\(on Windows) or~/MCP/oac-mcp-connect/(on macOS/Linux).
The extracted package includes:
oac-mcp-connect.js–Node.jsimplementation of the OAC MCP server.oac_mcp_connect_config-template.json– Sample configuration file.README.md– Comprehensive setup and usage documentation.lib/– Required dependency libraries
Once extracted, this folder serves as your working directory for running the OAC MCP server and connecting OAC with external AI clients.
Step 3 – Install Node.js
- Download and install
Node.js(v18+) from nodejs.org. - Verify the installation by opening a terminal/command prompt:
node -v
npm -v
Both commands will return version numbers to confirm successful installation.
Step 4 – Configure Claude Desktop
- Edit your Claude configuration file:
– Windows:C:\Users\\AppData\Roaming\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json
– Mac:~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
- Add the OAC MCP server configuration in
claude_desktop_config.json.
- Restart Claude Desktop (quit and reopen).
The OAC MCP Server supports two authentication methods: browser-based and token-based.
Browser-Based Authentication (recommended)
This method authenticates interactively through your browser when Claude Desktop starts.
Windows example:{
"mcpServers": {
"oac_mcp_connect": {
"command": "C:\\Program Files\\nodejs\\node.exe",
"args": [
"C:\\MCP\\oac-mcp-connect\\oac-mcp-connect.js",
"https://<OAC-INSTANCE>.analytics.ocp.oraclecloud.com"
],
"description": "Oracle Analytics Cloud MCP Server - Browser Auth"
}
}
}
MacOS example:{
"mcpServers": {
"oac-mcp-connect": {
"command": "node",
"args": [
"/path/to/oac-mcp-connect.js",
"https://<OAC-INSTANCE>.analytics.ocp.oraclecloud.com"
],
"description": "Oracle Analytics Cloud MCP Server - Browser Auth"
}
}
}
How the browser-based method works:
- On first use, a browser window opens for OCI/IDCS login.
- Tokens are automatically cached and refreshed.
- No manual token management is required.
Token-based authentication
This method uses pre-configured OAuth tokens stored in a JSON file and is useful for automation or environments without browser access.
Windows example:{
"mcpServers": {
"oac_mcp_connect": {
"command": "C:\\Program Files\\nodejs\\node.exe",
"args": [
"C:\\MCP\\oac-mcp-connect\\oac-mcp-connect.js",
"https://<OAC-INSTANCE>.analytics.ocp.oraclecloud.com",
"C:\\MCP\\tokens.json"
],
"description": "Oracle Analytics Cloud MCP Server - Token Auth"
}
}
}
MacOS example:{
"mcpServers": {
"oac-mcp-connect": {
"command": "node",
"args": [
"/path/to/oac-mcp-connect.js",
"https://<OAC-INSTANCE>.analytics.ocp.oraclecloud.com",
"/Users/<username>/oac-mcp-connect/tokens.json"
],
"description": "Oracle Analytics Cloud MCP Server - Token Auth"
}
}
}
How the token-based method works:
- Reads tokens from the specified JSON file.
- Automatically refreshes expired access tokens using the refresh token.
- Updates tokens.json with new tokens after refresh
d. For both methods, restart Claude Desktop completely (quit and reopen).
Step 5 – Verification
- Open Claude Desktop and start a new chat.
- Look for the Search and Tools section in the chat interface.
- Click oac_mcp_connect (or your configured MCP server name) and expand it.
You should see these OAC tools:
✅ OA: Discover Data — Lists available datasets and subject areas.
✅ OA: Describe Data — Retrieves dataset metadata and structure.
✅ OA: Execute Logical SQL — Executes natural-language queries using LSQL.
When all three tools display as Connected, your integration is ready to use.
Next Steps: Start Exploring Conversational Analytics
Once the connection is established, you can immediately begin exploring your data through your AI client. Try these conversational prompts to validate your setup:
Discover:
“What datasets are available in my OAC environment?”
→ Returns available subject areas and datasets.
Describe:
“Describe the Sales Overview dataset.”
→ Lists dimensions, measures, and hierarchies.
Execute:
“Show total revenue by region for 2024.”
→ LLM generates LSQL, OAC executes the query with full governance enforcement, and returns results.
You can continue the conversation contextually — by asking follow-up questions, drilling into details, or exploring different aspects of your data.
Authentication and Token Management
The OAC MCP server authenticates clients using OAuth 2.0 access tokens, ensuring secure, standards-based access to OAC.
When launched through the MCP Connect utility, a browser window automatically opens for secure sign-in, and token acquisition and refresh are handled transparently for the user session.
Alternatively, users can manually download an access token file (tokens.json) from their OAC user profile page and provide it to the script for testing or automation scenarios.
Token expiration information can be viewed in OAC under Access Tokens. For sessions started using MCP Connect, token refresh is handled automatically.
For detailed authentication configuration, advanced parameters (--insecure, --chrome-path, --service-instance-key), and troubleshooting guidance, refer to the README.md file included with the MCP Connect utility.
Data Security Considerations
For sensitive data scenarios:
- Use enterprise LLMs with zero-retention policies.
- Deploy local or OCI-hosted LLMs where possible.
- Work with aggregated or masked datasets.
- Align with organizational compliance standards.
Summary
OAC already empowers users with rich visualizations, governed data models, self-service analytics, and the AI Assistant for natural-language querying.
With the OAC MCP Server, analytics now extends beyond the OAC interface into a broader ecosystem of AI tools and intelligent automation platforms. You can query governed data in plain English through your preferred AI client, explore relationships conversationally, and integrate analytics into agentic workflows — all while OAC enforces full governance during query execution.
The AI Assistant and MCP Server are complementary:
- OAC AI Assistant: Conversational analytics inside OAC’s user interface for interactive data exploration.
- OAC MCP Server: External integration layer enabling AI clients and automation platforms to access governed OAC data from outside OAC.
By combining Oracle’s enterprise governance with AI-driven natural language understanding, the OAC MCP server transforms data interactions into intelligent dialogues, extending the reach of analytics to anyone who can ask a question — whether they’re using Claude Desktop, building agentic workflows in n8n, or creating AI-powered applications with LangChain.
Call to Action
Oracle Analytics Cloud MCP server is available now in the November 2025 update. For a quick introduction to the Oracle Analytics MCP Server, check out this YouTube video.
Get Started Today
✅ Connect to your OAC instance from AI clients.
✅ Explore the Discover → Describe → Execute workflow to find, understand, and analyze data conversationally.
✅ Build agentic workflows using n8n or LangChain to automate analytics-driven decision making.
Stay Tuned for Upcoming Blog Articles
📝 Understanding the OAC MCP interaction flow — A conceptual overview of how AI clients interact with governed analytics.
📝 Automating token refresh — Maintaining uninterrupted AI connections for production use.
📝 End-to-end conversational analytics demo — Real-world examples using the OAC MCP server.
📝 Inline machine learning with OAC — Combining analytics and AI/ML in conversational workflows.
📝 Building agentic workflows — Integrating OAC with n8n and LangChain.
Join the Community
Have questions or want to share your journey?
Join the conversation in the Oracle Analytics Community, connect with other practitioners, and get expert insights.
Learn More
To learn more about OAC:
- Visit the Oracle Analytics product page
- Follow twitter@OracleAnalytics
- Read the documentation on Oracle Help Center

