Introduction
Oracle Fusion Analytics allows joining between facts and dimensions in semantic model tables, which are usually defined as Normal Joins. These join conditions are simple comparisons using the “=” operator, for instance, Fact.columnA=Dimension.columnB. Sometimes you must perform more complex joining conditions.
Also, when using normal joins, you don’t specify the exact table that you’re joining. For instance, if you join a customer fact with Dim – Fiscal Calendar, the join is performed at the day level. It’s assumed that your fact table has a record by day. If, instead, your fact table is aggregated by month, you can’t specify it in a normal join. But you can specify it using a complex join. This can have an impact on data integrity if your custom fact is joined at the wrong level of the dimension.
This article shows how to leverage Complex Joins. It demonstrates how to build complex joins to join a condition to a required level (for example, the Period level) from the default day level using a custom fact table. Assume that a custom fact table by period already exists in the database.
Complete the following steps:
1. In Fusion Analytics, navigate to the Console and click the Semantic Model Extensions tile.

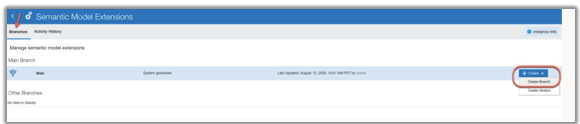
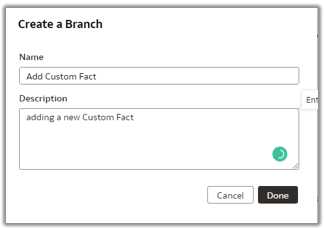
2. Create a branch of the main semantic model.
3. Add the Add a Fact step.
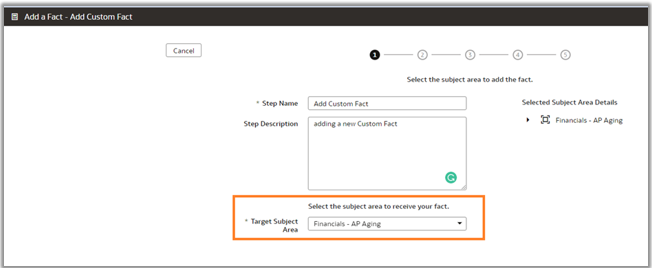
4. Select the custom fact table that’s being created, and select the target subject area (for example, Financials – AP Aging).
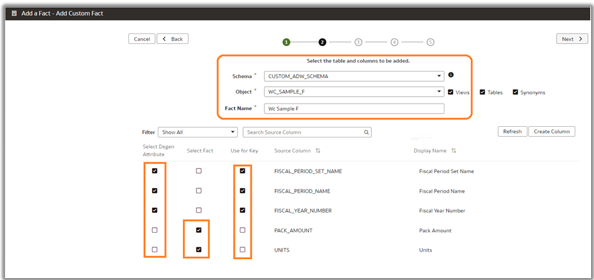
5. Select the custom schema and custom table from the custom schema of Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse (ADW).
The GRANT SELECT SQL statement executed on the CUSTOM_ADW_SCHEMA.WC_SAMPLE_F table to the OAX$OAC schema makes it appear in the drop-down list for the table. Select the attributes, key columns, and metrics or KPIs to add.
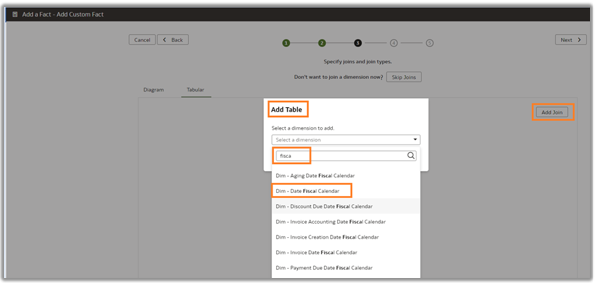
6. Add a join between the custom Fact – WC_SAMPLE_F and Dim – Fiscal Calendar. Click Add Join and select the required ready-to-use table as shown. Click OK.
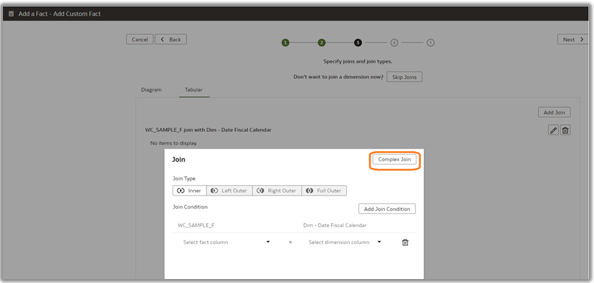
7. Select the join type Complex Join to join with the ready-to-use dimensions to achieve the joins such as expressions or ranges. Click Add Joins to form a complex join expression with the selected facts and dimension tables.
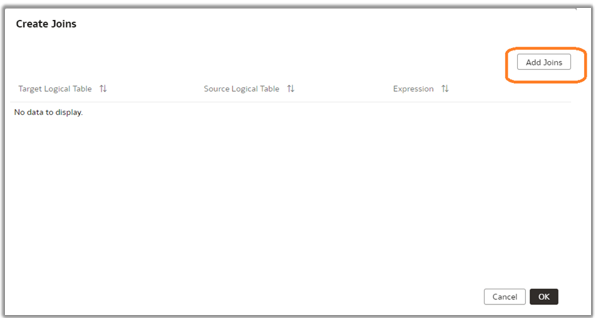
8. Select the Target Logical Table and the Source Logical Table and click the expression editor. Make sure to select the correct source logical table for the level (for example, Dim DW_FISCAL_PERIOD_D).
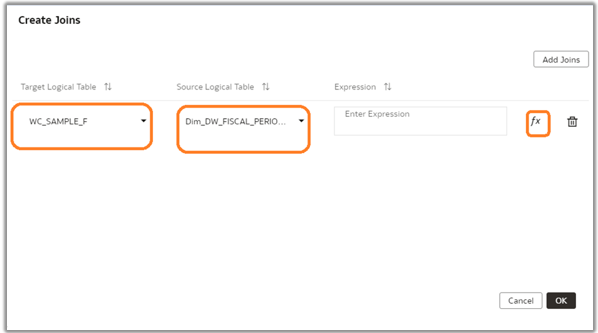
9. Create Complex Join expressions between the custom Fact – WC_SAMPLE_F and Dim – Fiscal Calendar, which is at the period level with combinations of columns.
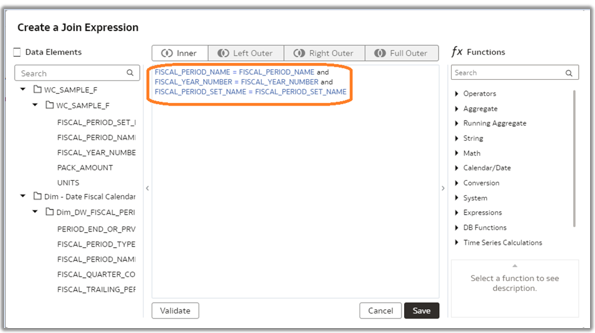
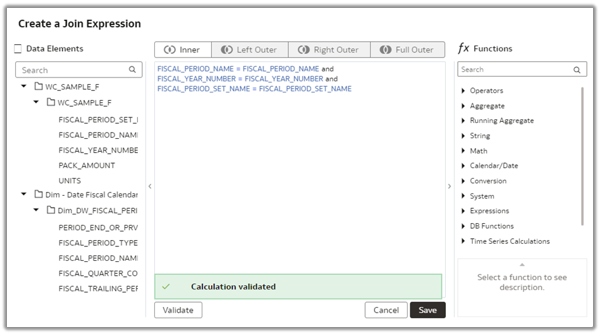
10. Click Validate and Save.
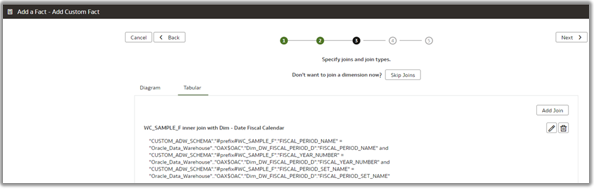
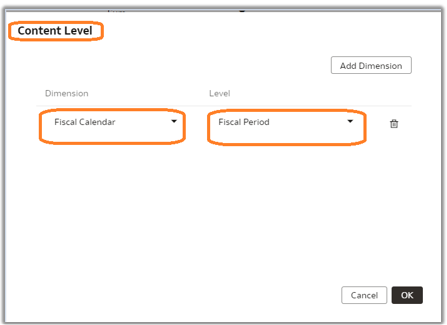
11. Set the aggregation rule for the metrics and select the LTS content level. In the example, the custom Fact – WC_SAMPLE_F is joined with Dim – Fiscal Calendar at the period level, which is higher than the default day level.
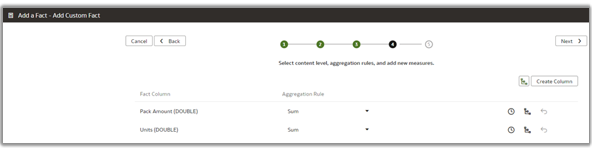
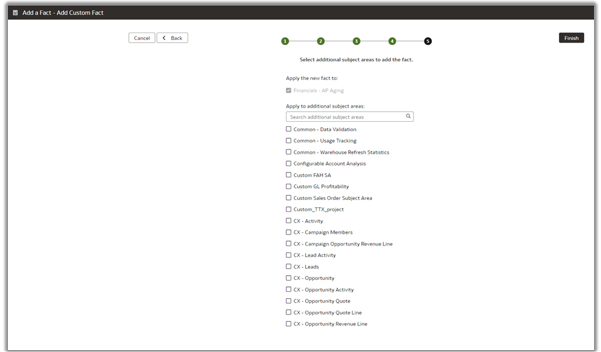
12. Select the subject areas to add to the custom fact columns and click Finish.
Call to Action
Implement the steps described in this blog to create complex joins if a fact table holds the data at a different level than the default grain level, which results in the correct data. Click here for more information.
Learn More about Oracle Fusion Analytics. Follow us on Twitter@OracleAnalytics and connect with us on LinkedIn. You can also post questions in our community.
