There are 3 database distribution types in TimesTen Scaleout. A sample SQL script below is provided for this post. Save the SQL Script with file name cr_tables.sql.
CREATE TABLE account_type
(
type CHAR(1) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
description VARCHAR2(100) NOT NULL
)
DUPLICATE;
CREATE TABLE account_status
(
status NUMBER(2) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
description VARCHAR2(100) NOT NULL
)
DUPLICATE;
CREATE TABLE customers
(
cust_id NUMBER(10,0) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR2(30) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR2(30) NOT NULL,
addr1 VARCHAR2(64),
addr2 VARCHAR2(64),
zipcode VARCHAR2(5),
member_since DATE NOT NULL
)
DISTRIBUTE BY HASH;
CREATE TABLE accounts
(
account_id NUMBER(10,0) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
phone VARCHAR2(15) NOT NULL,
account_type CHAR(1) NOT NULL,
status NUMBER(2) NOT NULL,
current_balance NUMBER(10,2) NOT NULL,
prev_balance NUMBER(10,2) NOT NULL,
date_created DATE NOT NULL,
cust_id NUMBER(10,0) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT fk_customer
FOREIGN KEY (cust_id)
REFERENCES customers(cust_id),
CONSTRAINT fk_acct_type
FOREIGN KEY (account_type)
REFERENCES account_type(type),
CONSTRAINT fk_acct_status
FOREIGN KEY (status)
REFERENCES account_status(status)
)
DISTRIBUTE BY REFERENCE (fk_customer);
CREATE TABLE transactions
(
transaction_id NUMBER(10,0) NOT NULL,
account_id NUMBER(10,0) NOT NULL ,
transaction_ts TIMESTAMP NOT NULL,
description VARCHAR2(60),
optype CHAR(1) NOT NULL,
amount NUMBER(6,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (account_id, transaction_id, transaction_ts),
CONSTRAINT fk_transactions
FOREIGN KEY (account_id)
REFERENCES accounts(account_id)
)
DISTRIBUTE BY REFERENCE (fk_transactions);
The SQL script utilizes all 3 distribution types: hash, duplicate and reference.
- Distributed by Hash is the default type if no distribution type is specified. The hash key can be the primary key (default) or user_defined columns. It uses the consistent hash algorithms. CUSTOMERS table is an example table of Distribution by Hash.
- Distributed by Duplicate tables is commonly used for reference tables because identical copies of the data are on all elements. Distributed by Duplicate tables are optimized for read and joins. The ACCOUNT_TYPE and ACCOUNT_STATUS are examples of such tables.
- Distributed by Reference tables allow related data to be co-locate together for join optimization. It is based on foreign key relationship. It supports multi-level hierachy. ACCOUNTS table is an example of a reference table.
Entity Relation(ER) diagram of the sample script is followed:
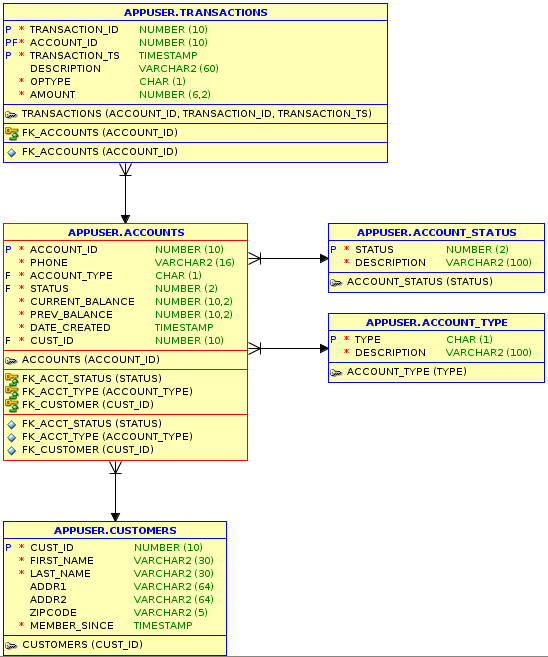
For more detail information on the distribution types, consult the TimesTen In-Memory Database Scaleout User’s Guide.
Create Schema using ttIsql
Follow the steps below to create the sample schema using cr_tables.sql script file.
| 1: |
On a data instance, source the TimesTen environment. For this example, the data instance used here is /home/oracle/TimesTen/instances/instance1. $ source /home/oracle/TimesTen/instances/instance1/bin/ttenv.sh |
| 2: |
Go to the directory where the sample scheme file is saved to. For this example, the sample schema file is saved to /home/timesten directory with the file name, cr_tables.sql. $ cd /home/timesten |
| 3.: |
Run the SQL cr_tables.sql script against the database using the ttIsql -f option.
$ ttisql -f cr_tables.sql “dsn=sampledb;uid=appuser” |
At this point, the tables in the cr_tables.sql are created in your TimesTen Scaleout Database. For more information about TimesTen Scaleout, please visit the TimesTen 18.1 documentation library.
Disclaimer: These are my personal thoughts and do not represent Oracle’s official viewpoint in any way, shape, or form.
