Schema annotations are key-value metadata you can use to document database objects. Introduced in Oracle AI Database 26ai, they have been backported to 19.28.
You can add annotations to objects with alter statements. The syntax to annotate tables and their columns is:
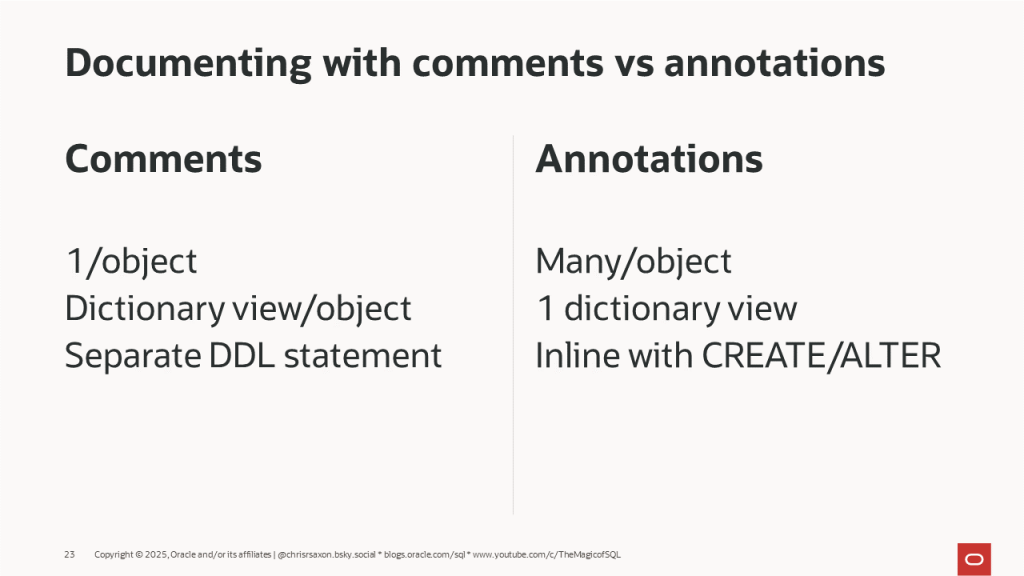
Annotations are a more powerful way to document objects than comments. You can add as many annotations to an object as you want, unlike comments, which are limited to one per object. You can view annotations for all objects in the user|all|dba_annotations_usage views.
These objects support both comments and annotations:
- Tables
- Views
- Materialized views
- Columns of these objects
If you’ve meticulously documented these objects with comments, you may want to migrate them to become annotations.
To do this:
- Read comments from the
user_*_commentsviews wherecomments is not null - Write these as annotations using the appropriate
altercommand
Here’s an example script to transfer comments into annotations named “comments”:
Notes:
- The
run_changesvariable controls whether this executes the commands to add annotations. When this is false, it only displays the commands. Setrun_changesto true to apply the annotations at the same time. - If the target objects already have an annotation named “comments”, the script will raise an
ORA-11552: Annotation name 'COMMENTS' already exists for the object '…'error. Either rename the annotation or use the syntaxannotations ( add or replace comments '...' ). This overwrites existing comments annotations. - To handle comments that contain single quotes, it uses the q quoting method. If a comment includes the sequence >’ (greater than, single quote), it will close the annotation value and raise an error. To overcome this, use different quote delimited characters. For example
q'!string>'value'!'orq'[string>'value']'.
To see this in action, here are a series of objects with comments:
Running the script with run_changes := true generates and executes these commands to turn them into annotations:
You can then view the annotations with this query:
Download Oracle AI Database Free and try annotations today.
