What is Essbase Aggregate Option (ASO)?
Thank you to Jane Story for the presentation on key concepts for understanding Essbase ASO.
The presentation covers the following topics in detail:
- What is the Magic of Essbase? Quick Review.
- What is ASO? The key features of ASO
- What are Dimensions, Members, and Hierarchies? The Basics for understanding ASO.
- What is a Hierarchy Type? Hierarchy Types: Stored, Dynamic, or Multiple
- How is Data Stored in ASO? Buffers, Slices, and Views!
- Other ASO Maintenance? Compact Outline.
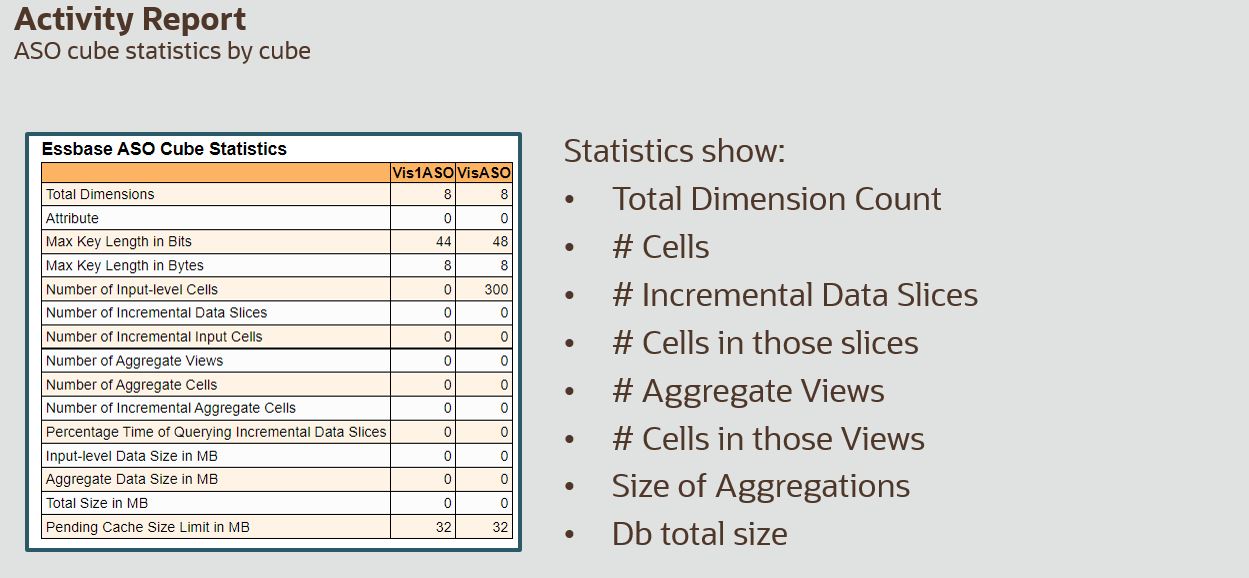
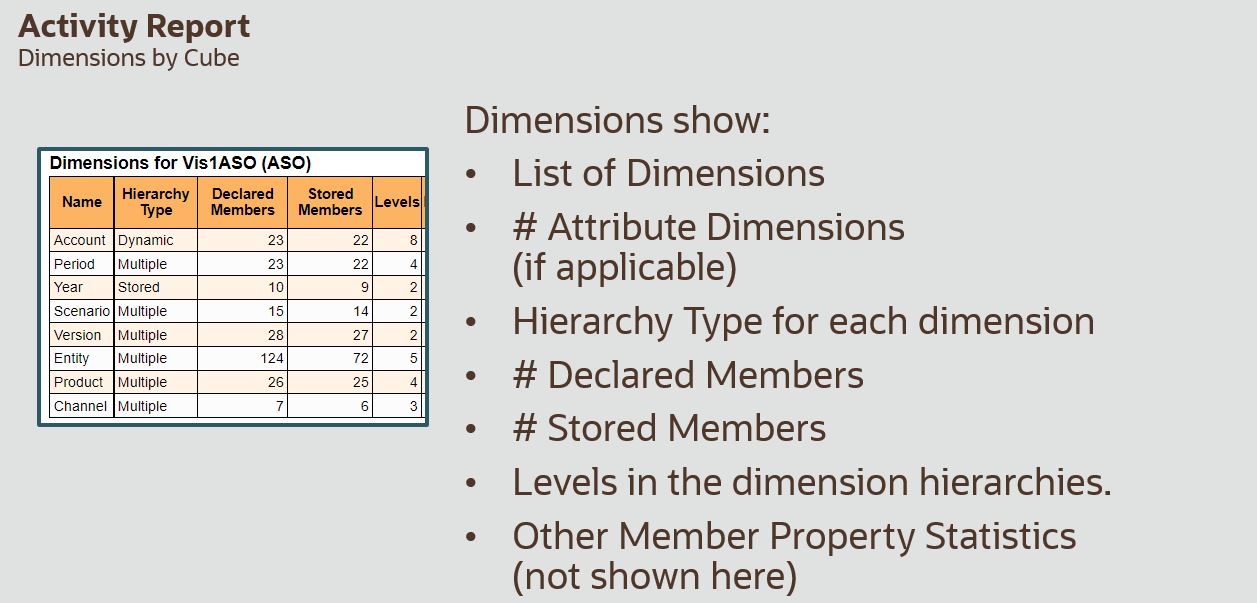
- Where to find ASO Cube Statistics? And how do they relate to what we know?
What is the Magic of Essbase? Quick Review:
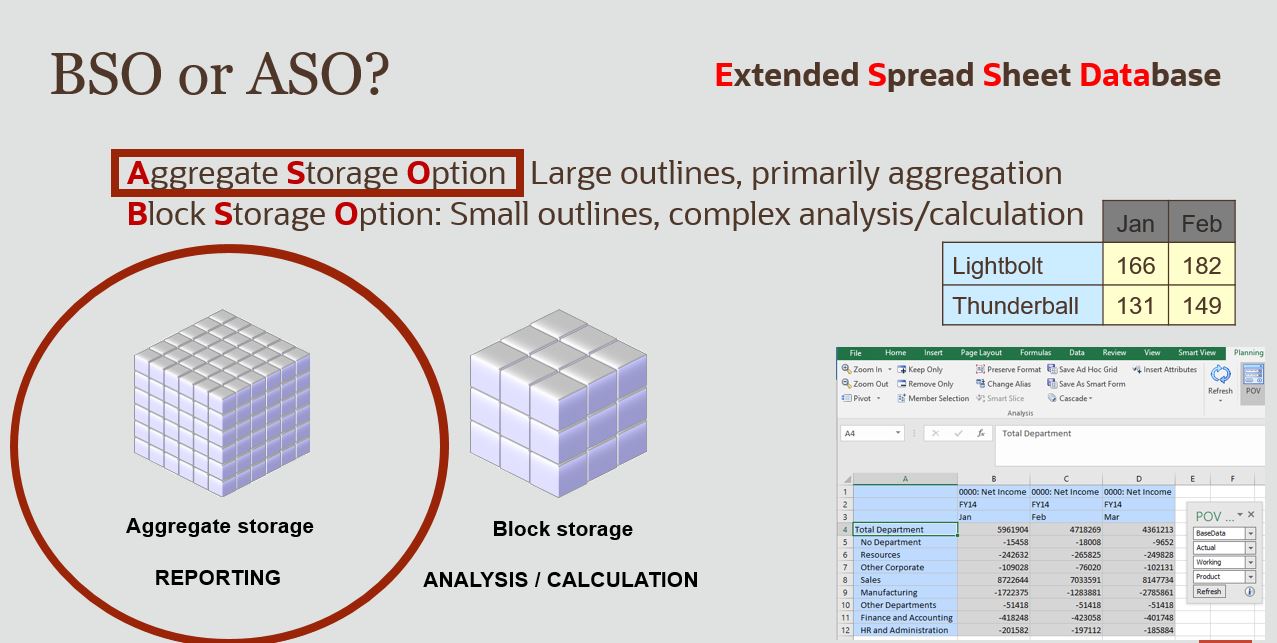
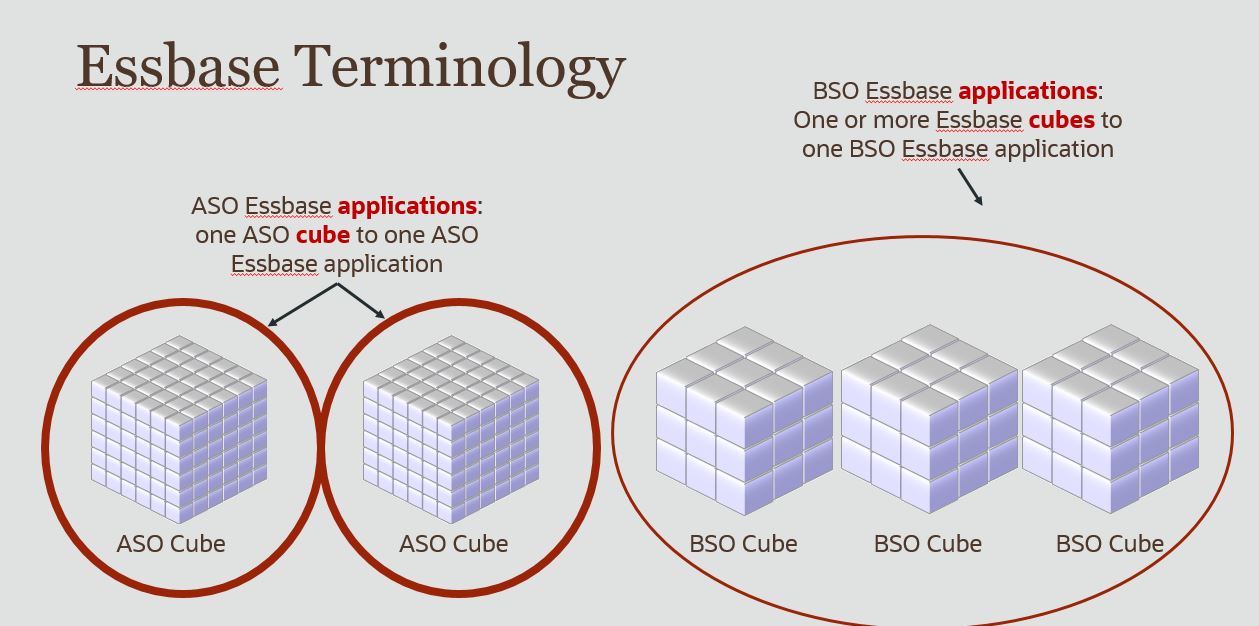
How is ASO different than BSO? Key features of ASO
- Aggregate-intensive cubes.
- Can handle larger numbers of dimensions and members.
- Optimized for sparser data sets for operational analytics.
- Use of ASO for aggregation can significantly reduce BSO size and calculation times.
- Designed to work seamlessly with existing interfaces and user skills i.e., same requirements for data in, same requirements for data out.
- Data can only be loaded at level0.
- Data is aggregated “on the fly”.
- Data “views” can be materialized, if required.
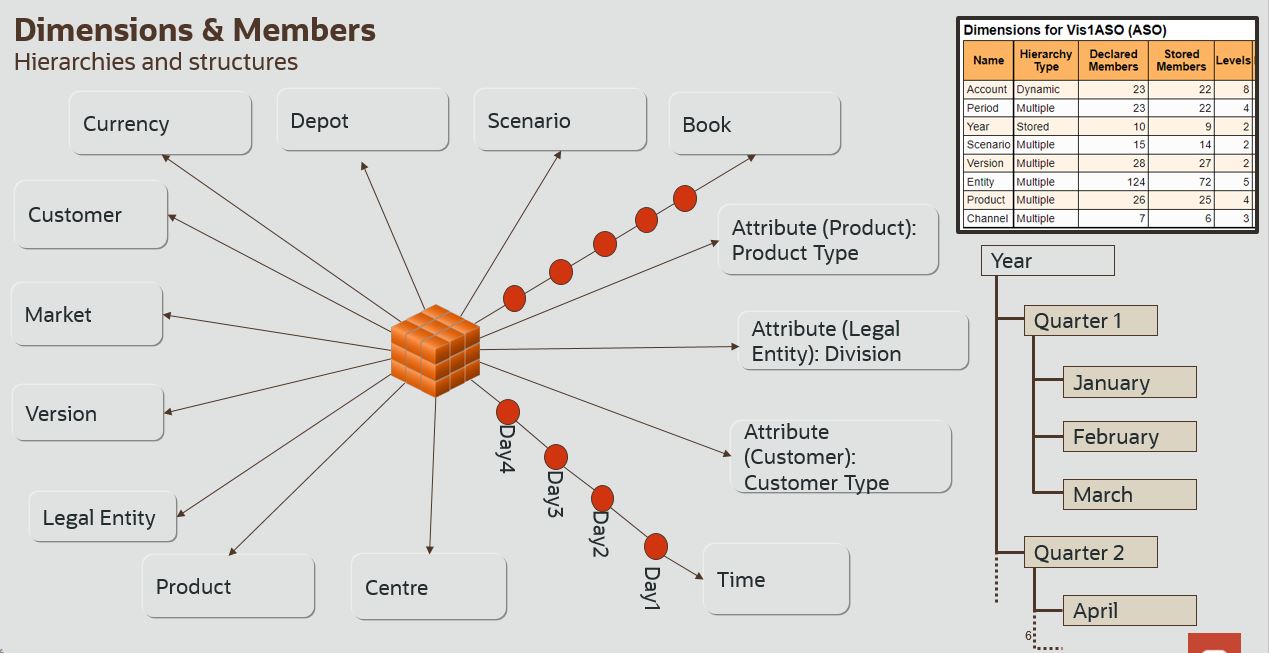
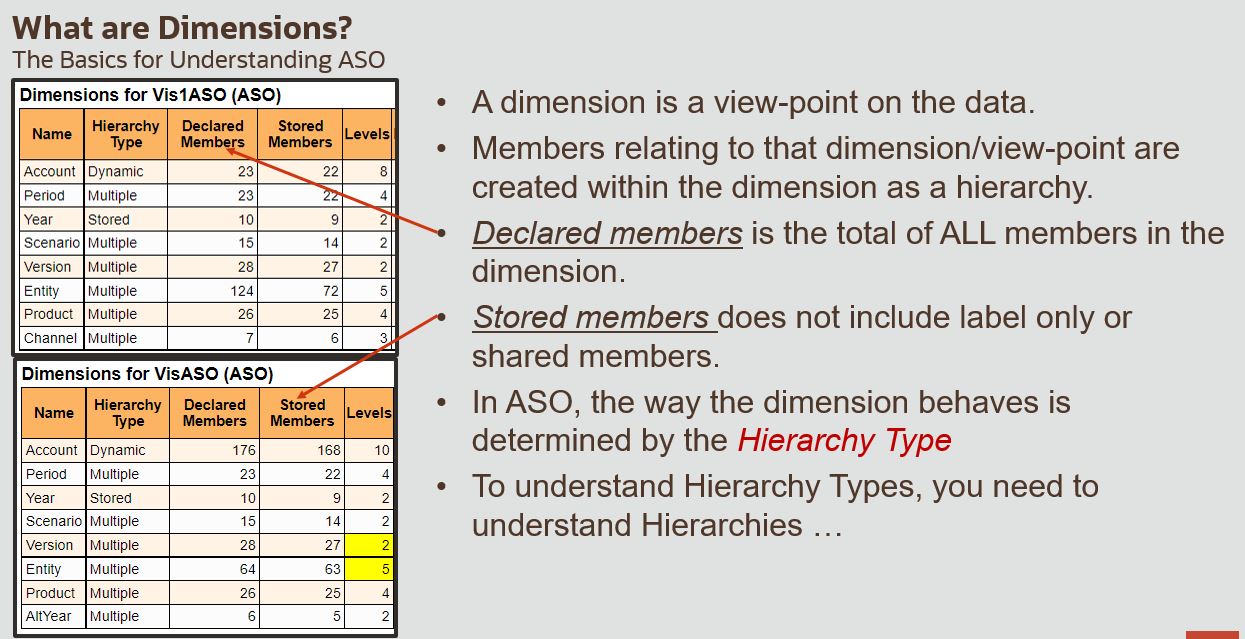
What are Dimensions, Members, and Hierarchies?
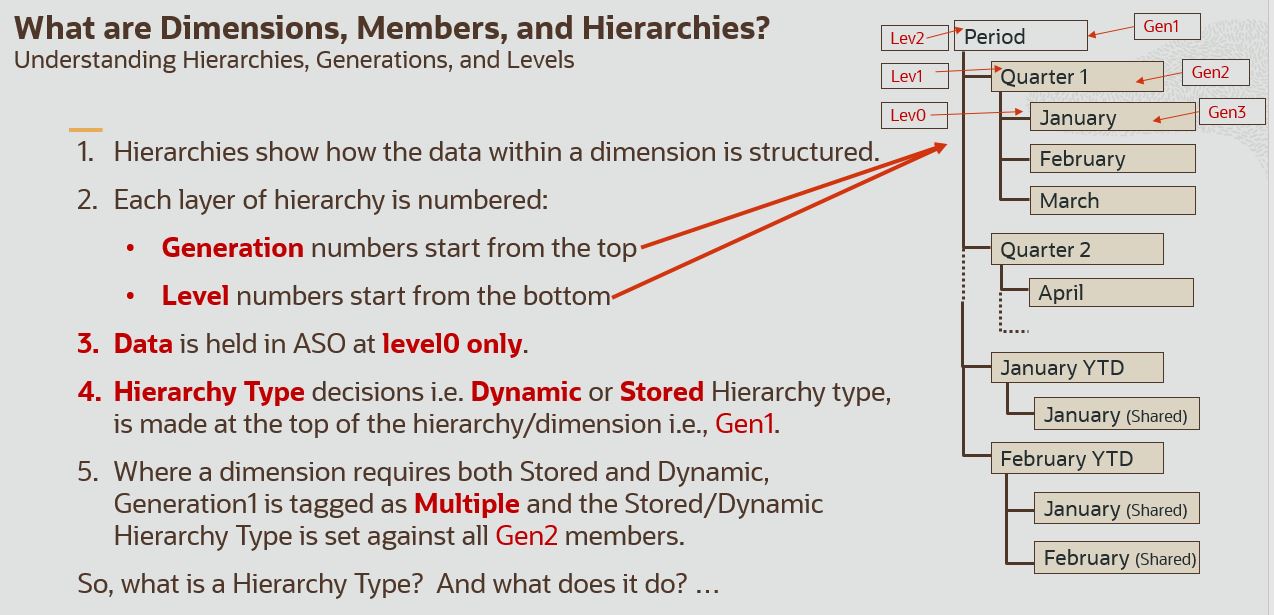
What is a Hierarchy Type?
ASO Hierarchy Types – Stored, Dynamic and Multiple
ASO has TWO main hierarchy types:
- Store
- Dynamic
Hierarchy type is inherited down from the point it is set.
There are, however, THREE settings at DIMENSION level (i.e. set against the Gen1 member):
- Store – the entire dimension is stored.
- Dynamic – the entire dimension is dynamic.
- Multiple – i.e. both Hierarchy Types are required within this dimension. In these cases, Store and Dynamic is made at Generation2 of that dimension rather than Genration1 (i.e., the DIMENSION can contain MULTIPLE hierarchy types).
ASO Hierarchy Types – How to Choose?
- The ideal is to have as much stored as possible. i.e., the dimension should be Store if possible, and if not, preference is Multiple.
- If the dimension cannot be Store (e.g., it contains formula), make only the hierarchy that has the formula dynamic (at Gen2 in a Multiple dimension) and make the rest of the dimension Store (at gen2).
- There are some considerations to use of Multiple (when converting from a Dynamic dimension) etc. with regards to Shared members, formula and aggregation of a dimension.
Refer to the presentation for detailed examples.

How is Data Stored in ASO? – Buffers, Slices, and Views
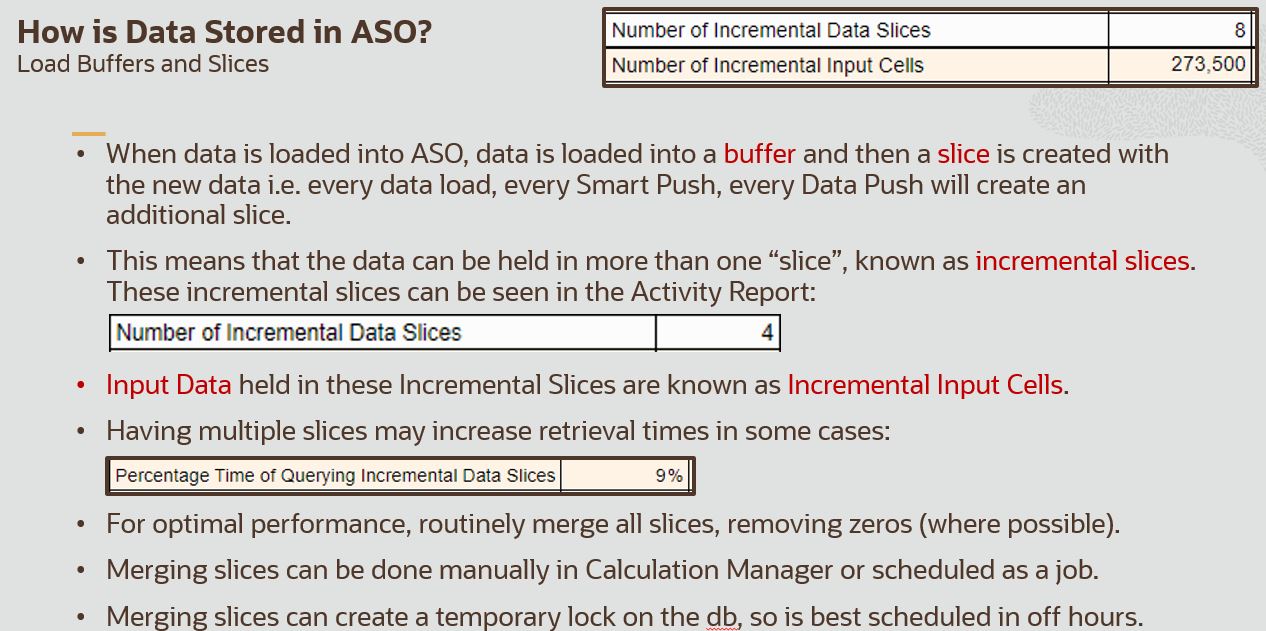
Merging Incremental Slices:
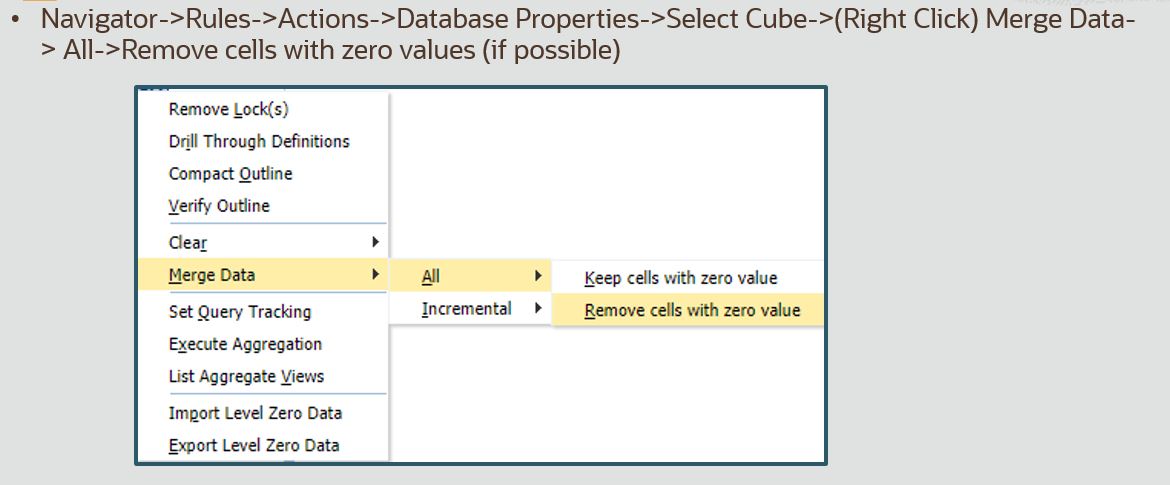

Other ASO Maintenance:
Compact Outline
- When dimension changes are made to an ASO cube, these are stored in an OUTLINE.
- It is recommended that the outline is regularly compacted (similar to a BSO outline restructure), especially after dimension changes.
- Navigator->Rules->Actions->Database Properties->Select Cube->(Right Click) Compact Outline.
- Always review the Details after the Compact Outline.
Where to find ASO information – Activity Report