Oracle Management Agent supports a versatile and secure collection of full-stack observability data from diverse sources. It is designed to support multiple platforms and can be installed with various installation packages on all operating systems, such as on Linux, Windows, AIX, Solaris, and MACOS. This blog explains the process of automating the bulk deployment of management agents with Ansible playbook script on multiple target hosts where monitoring is required. This automation eliminates the need for users to log into each host individually to install management agents. Instead, users can trigger installations from a single controller host to all target hosts.
This blog covers the prerequisites, configuration, and execution of the playbooks needed for this setup. It is applicable for installing agents on on-premises systems or cloud environments other than Oracle Cloud Agents (OCA).
Benefits of Oracle Management Agent bulk deployment using Ansible Playbooks:
- Resource optimization: Reduce the time and effort required to install management agents on multiple hosts.
- Single setup: Provide a single setup process for management agents across multiple hosts.
- Centralized management: Allow a centralized control of all hosts from a single controller host during installation.
- Auto creation of Install key: The install key is auto-created in the Ansible playbook script.
Management Agent deployment and lifecycle concepts:
The following terminology and concepts describe the management agent’s deployment and lifecycle.
- Management Agent (Agent): Collects data from the host where it is installed and connects and sends data to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure’s Observability and Management services.
- Management Agent Cloud Service (MACS): Manages Management Agents and their lifecycle, allowing Oracle Cloud services to interact and collect data.
- Agent Install Key: An install key is issued against your identity domain and validates the authenticity of the installation.
Prerequisites:
- Ansible installation: Ensure Ansible (version 2.9 or above) is installed on the controller host.
- Refer to Ansible Installation Guide
- Python installation: Ensure Python3 (version 3.6 or above) is installed on all target hosts and the controller host.
- Refer to Python Installation Guide
- SSH capability: Ensure SSH capability on all target hosts, with the user having the capability to become a root user.
- OCI CLI installation: Install OCI CLI and create OCI configuration on the controller host.
- Refer to OCI CLI Quickstart
- Refer user’s policy prerequisite for Management Agent installation
- Ansible collection: Ensure Ansible collection is configured with OCI CLI on the controller host.
Configuration steps:
- Clone the Git Repository: Login to the controller host, clone the Git repository:
git clone https://github.com/oracle-quickstart/oci-management-agent.git
-
Navigate to the Playbooks directory:
cd deployment/ansible-playbooks
- Edit the following hosts files:
-
target_hosts: Specifies where to install the agent
-
target_hosts:vars: Target host-specific variables
-
all:vars: Global variables applicable to all hosts, including the controller host
-
- Set environment variables: On the controller host, set the compartment OCID:
exportcompartment_ocid=ocid1.compartment.oc1.aaaaaa............xxxxxxx
Execution:
Execute the following command on the controller host to initiate the installation:
ansible-playbook -i hosts mgmt_agent_install.yaml -kK
-
Note: The -kK option is shorthand for –ask-pass and –ask-become-pass.
- SSH password: The SSH user password
- BECOME password: The password to become the root user (it defaults to SSH password)
Verify the Execution:
After executing the playbook, verify that the installation was successful. The output should be similar to:
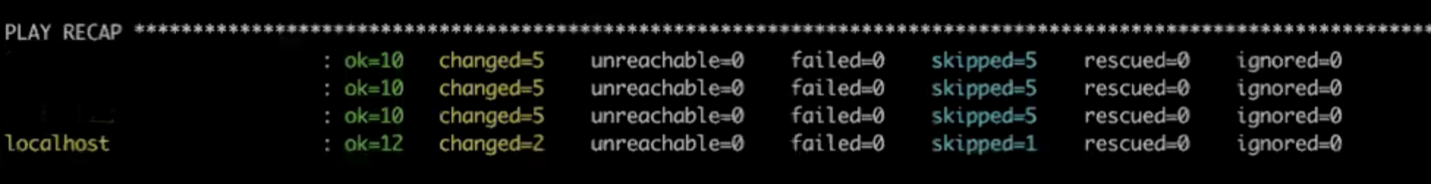
Login to Oracle Cloud:
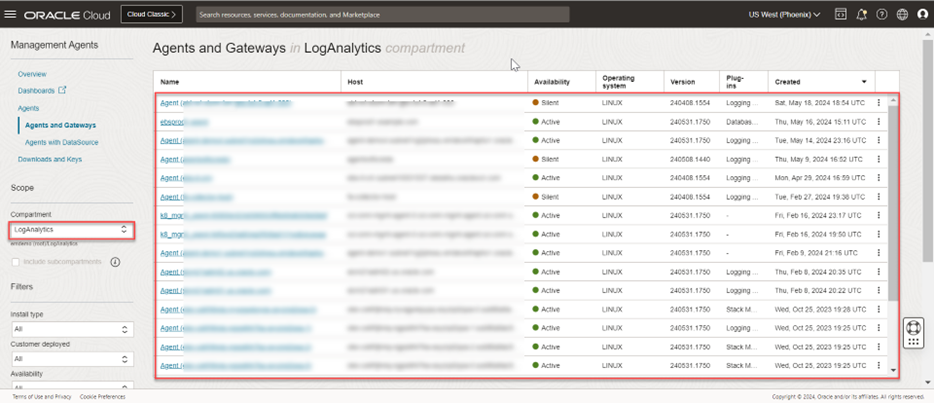
- Navigate to Observability & Management -> Management Agents -> Agents
- Select the compartment and check that the agents are installed on your hosts:
This blog provides a comprehensive guide in setting up the workbench and executing playbooks for installing management agents across multiple hosts from a single controller host, streamlining the installation process and eliminating redundant steps.
Resources:
- Learn more about Management Agent capabilities
- Read more on Management Gateway batching feature
- View the Management Agent documentation

