MySQL HeatWave is the only fully managed MySQL database service that combines transactions, analytics, machine learning, and GenAI services, without ETL duplication. It also includes MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse, allowing users to query data stored in object storage, MySQL databases, or a combination of both. Users can deploy MySQL HeatWave–powered apps on a choice of public clouds: Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure.
Agentic AI improves on Generative AI and enables the development of automated systems where components, or software agents, can act independently or collaborate with other components to achieve a task. For example, a software agent can handle a customer inquiry by retrieving documents or gathering information from proprietary knowledge bases. This blog post shows how to use MySQL HeatWave’s vector store as a knowledge base when using OCI’s Generative AI Agent Service.
OCI’s Generative AI Agents (also known as the OCI AI Agent Platform) is a fully managed, cloud-native service that lets you build, deploy, and orchestrate intelligent AI agents using large language models (LLMs). These agents enable rich, multi-turn conversational experiences by retaining context, interacting with tools like RAG and SQL for data retrieval and execution, enforcing guardrails and content moderation, and integrating optional human-in-the-loop workflows for secure, scalable deployments. Let’s delve into the details of using the OCI AI Agent Platform and MySQL HeatWave’s vector store as a knowledge base.
Prerequisites
- A functional MySQL HeatWave instance with Lakehouse enabled.
- A configured OCI Database Tools Connection for accessing your HeatWave instance (see Step 5 here).
Getting Started
The steps to configure an AI Agent to talk to a HeatWave Knowledge Base are:
- Create an AI Agent.
- Create a HeatWave knowledge base. This includes:
- Creating a context retrieval procedure on your MySQL HeatWave instance.
- Creating the knowledge base and connecting it to your MySQL HeatWave instance.
- Configuring the AI Agent RAG Tool to use your new knowledge base.
- Ingest data into your knowledge base.
Now let’s look at each step in detail.
Step 1: Creating an AI Agent
If you already have an agent that you want to use with your new knowledge base, you can skip this step.
In the OCI Console, navigate to Analytics & AI, then select Generative AI Agents.
Then click on the “Create agent” button.
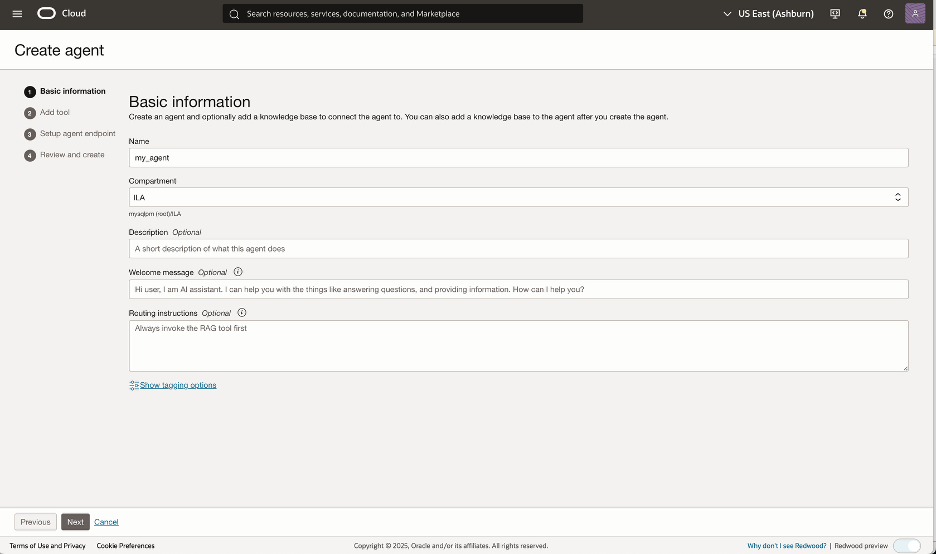
Select a name and a compartment for your agent.
Optionally enter a description, welcome message or routing instructions. Click next.
On the next page, you can skip adding tools for now. We will come back to this step.
Follow the wizard and complete creating your agent. Make sure you setup an agent endpoint as well.
Step 2: Create a HeatWave Knowledge Base for AI Agent
A HeatWave knowledge base utilizes the vector search capability of your MySQL HeatWave instance. You first need to create a context search stored procedure on your MySQL HeatWave instance, that an AI Agent will call into when retrieving context. Then you can create a knowledge base and configure it to connect to your MySQL HeatWave instance and use your context search procedure.
Step 2.1: Context search procedure creation
The stored procedure for context search must accept a query string (p_query) and a number of retrieved context items (top_k) as input parameters and return retrieved context as a specifically formatted JSON (context). This is the interface that AI Agent Platform expects. The goal of the retrieval procedure is to perform vector search on one or more vector tables and return contextually most similar results. It must embed the query using the same model used for vector store creation, as to perform the comparison of embeddings in the same vector space. While there are multiple ways to implement the retrieval procedure, perhaps the easiest is based on the sys.ML_RAG stored procedure, which will automatically discover all compatible vector store tables on your instance. As we are not explicitly specifying the embedding model, we will use the default one.
Below is an implementation that we will use. Note that we pass skip_generate = true parameter to ML_RAG. This parameter makes HeatWave GenAI skip generating a response, and only returns fetched context, formatted as JSON, and containing the fields such as SCORE, DOCID and BODY, as expected by AI Agent. This procedure is invoked by the AI Agent, which then performs reasoning and actions. Connect to your MySQL HeatWave instance using your favorite MySQL client, then execute the following code to create the context search stored procedure.
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS my_vector_store;
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS my_vector_store.context_search;
-- Create the search procedure
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE my_vector_store.context_search( IN p_query TEXT, IN top_k INT UNSIGNED, OUT context JSON )
SQL SECURITY INVOKER
BEGIN
CALL sys.ML_RAG(p_query, @ml_rag_out, JSON_OBJECT('skip_generate', true, 'n_citations', top_k));
SELECT JSON_ARRAYAGG(
JSON_OBJECT( 'SCORE', JSON_EXTRACT(obj, '$.distance'), 'DOCID', JSON_EXTRACT(obj, '$. document_name'), 'BODY',
JSON_EXTRACT (obj, '$. segment') ) ) INTO context
FROM JSON_TABLE(@ml_rag_out, '$.citations [*]' COLUMNS ( obj JSON PATH '$' )) as jt;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
Step 2.2: Knowledge Base Creation
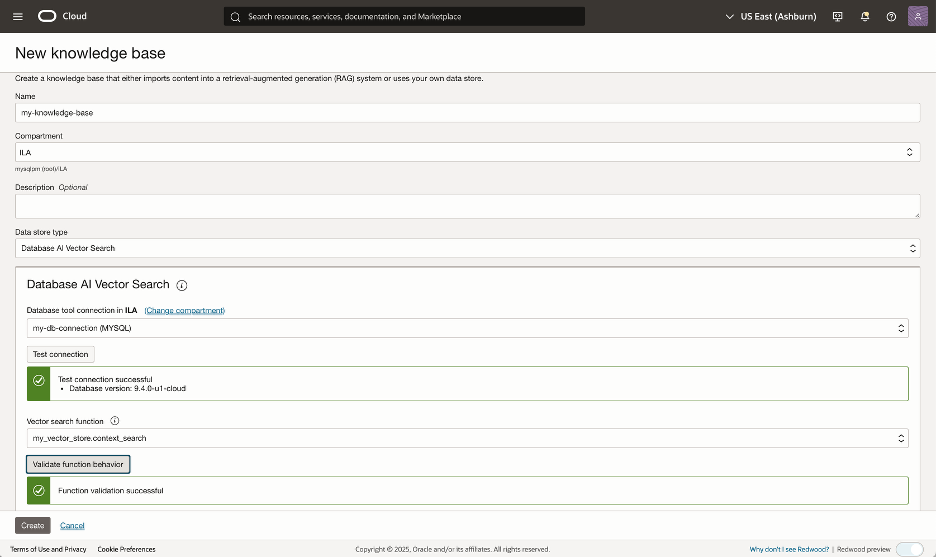
Navigate to Generative AI Agents page in OCI Cloud Console, and click on the Knowledge Bases link, then create a new knowledge base.
As the data store type, select “Database AI Vector Search”.
Then choose your Database tool connection that is configured for your MySQL HeatWave database. Test that the connection works.
Then, from the drop-down list, choose the context search procedure that you created in Step 2a. Finally, click on the “Create” button.
Step 2.3: Configure the RAG Tool
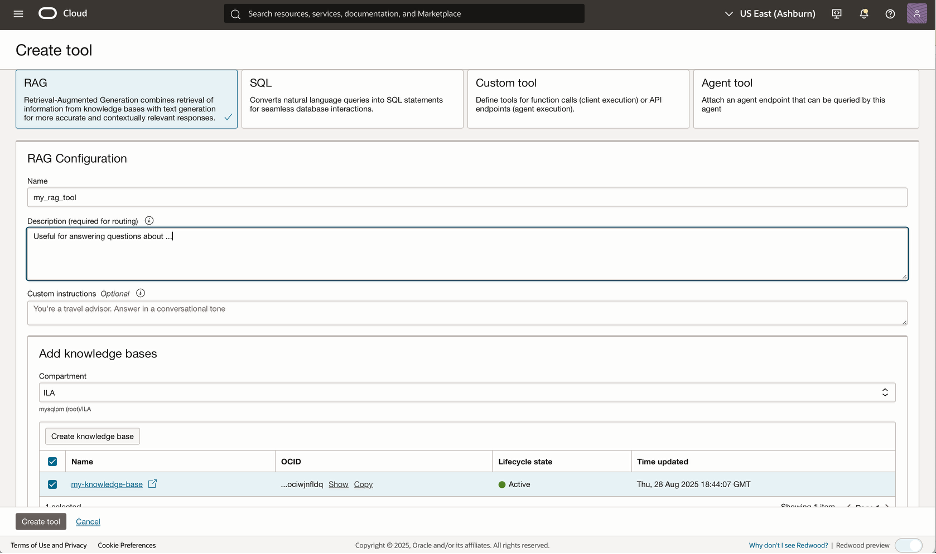
After successful knowledge base creation, navigate to your Agent in the OCI console, click on the Resources pane, then select Tools. The agent needs to be given a RAG tool for interacting with the knowledge base.
Create a new RAG tool, or if your agent already has a RAG tool, modify it. Associate your MySQL HeatWave knowledge base with your RAG tool.
Step 3: Ingesting your unstructured documents into HeatWave Vector Store
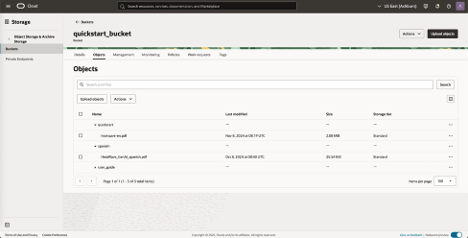
If you already have one or more vector store tables on your MySQL HeatWave instance, you can skip this step. Note: for the remainder of this step, you may need to add policies allowing your MySQL HeatWave instance to access your Object Storage buckets, see this blog for detailed instructions. Connect to your MySQL HeatWave Instance from a MySQL client. Ingestion of your unstructured documents from OCI Object Storage is as simple as invoking sys.vector_store_load stored procedure, which will automatically parse documents, split them into segments and embed segments into vectors. In the following example, we have a bucket named quickstart_bucket in namespace my_os_ns with some documents that we will ingest.
We will now create a database called my_vector_store to store our vector table, then we will invoke sys.vector_store_load.
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS my_vector_store;
USE my_vector_store;
CALL sys.vector_store_load(‘oci://quickstart_bucket@my_os_ns/’, NULL);
+————————————–+——————————————————————————-+
| task_id | task_status_query |
+————————————–+——————————————————————————-+
| 75812529-7ea2-11f0-b2a4-020017021030 | SELECT mysql_tasks.task_status_brief(“75812529-7ea2-11f0-b2a4-020017021030”); |
+————————————–+——————————————————————————-+
The loading task runs in the background, and its progress can be monitored using the returned task status query. Upon successful completion, the output should look similar to the following:
SELECT mysql_tasks.task_status_brief(“75812529-7ea2-11f0-b2a4-020017021030”);
+————————————————————————————–+
| mysql_tasks.task_status_brief(“75812529-7ea2-11f0-b2a4-020017021030”) |
+————————————————————————————–+
Use your Agent
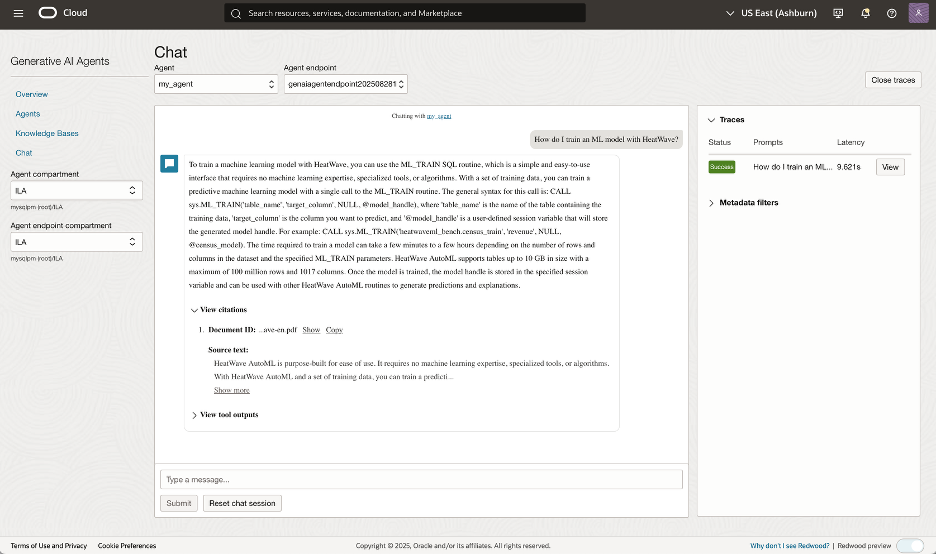
You are done! You can now use your Agent, which will automatically utilize your knowledge base to source information from it when needed. The easiest way to test your Agent is by navigating to the Chat section and selecting your agent from the drop-down menu. Feel free to play with it. A great way to start is by asking a question that requires information from your MySQL HeatWave knowledge base.
Learn More
New to OCI? Sign up for the Free Tier to get started.
For more details and technical information, see:
Start building with GenAI today using the OCI Free Tier. Discover the simplicity, speed, and power of MySQL HeatWave GenAI—on Always Free.


